Isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isotonicity in PN: Background and Objectives
Parenteral nutrition (PN) has been a critical component of medical care for patients unable to receive adequate nutrition through oral or enteral routes. The concept of isotonicity in PN solutions plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and optimal nutrient delivery. Isotonicity refers to the osmotic pressure of a solution being equal to that of human blood, which is essential for maintaining cellular integrity and preventing adverse reactions.
The development of PN solutions has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s. Initially, the focus was primarily on providing sufficient calories and essential nutrients. However, as understanding of fluid and electrolyte balance improved, the importance of maintaining isotonicity became increasingly apparent. This shift in focus led to extensive research on isotonicity adjustments in PN formulations.
The primary objective of isotonicity research in PN is to develop solutions that closely mimic the osmolality of human plasma, which is approximately 290 mOsm/kg. Achieving this balance is challenging due to the complex nature of PN solutions, which contain a mixture of macronutrients, micronutrients, electrolytes, and other additives. Each component contributes to the overall osmolality, necessitating careful formulation to maintain isotonicity.
Historically, hypertonic PN solutions were common, often leading to complications such as phlebitis, thrombosis, and electrolyte imbalances. These issues highlighted the need for more physiologically compatible formulations. As a result, researchers began exploring various techniques to adjust the tonicity of PN solutions, including the use of different carbohydrate sources, amino acid profiles, and electrolyte concentrations.
The goals of isotonicity research in PN extend beyond simply matching plasma osmolality. They also include improving patient outcomes, reducing complications associated with PN administration, and enhancing the overall efficacy of nutritional support. This multifaceted approach requires a deep understanding of human physiology, pharmacology, and nutrition science.
Recent technological advancements have facilitated more precise control over PN formulations. Automated compounding systems and advanced analytical techniques have enabled the development of tailored solutions that can be adjusted to meet individual patient needs while maintaining isotonicity. This personalized approach represents a significant step forward in PN therapy, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing complications.
As research in this field progresses, the objectives continue to evolve. Current areas of focus include developing novel osmotic agents, improving the stability of isotonic formulations, and investigating the long-term effects of different isotonicity adjustment strategies on patient health. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the impact of isotonicity on nutrient absorption and utilization at the cellular level.
The development of PN solutions has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1960s. Initially, the focus was primarily on providing sufficient calories and essential nutrients. However, as understanding of fluid and electrolyte balance improved, the importance of maintaining isotonicity became increasingly apparent. This shift in focus led to extensive research on isotonicity adjustments in PN formulations.
The primary objective of isotonicity research in PN is to develop solutions that closely mimic the osmolality of human plasma, which is approximately 290 mOsm/kg. Achieving this balance is challenging due to the complex nature of PN solutions, which contain a mixture of macronutrients, micronutrients, electrolytes, and other additives. Each component contributes to the overall osmolality, necessitating careful formulation to maintain isotonicity.
Historically, hypertonic PN solutions were common, often leading to complications such as phlebitis, thrombosis, and electrolyte imbalances. These issues highlighted the need for more physiologically compatible formulations. As a result, researchers began exploring various techniques to adjust the tonicity of PN solutions, including the use of different carbohydrate sources, amino acid profiles, and electrolyte concentrations.
The goals of isotonicity research in PN extend beyond simply matching plasma osmolality. They also include improving patient outcomes, reducing complications associated with PN administration, and enhancing the overall efficacy of nutritional support. This multifaceted approach requires a deep understanding of human physiology, pharmacology, and nutrition science.
Recent technological advancements have facilitated more precise control over PN formulations. Automated compounding systems and advanced analytical techniques have enabled the development of tailored solutions that can be adjusted to meet individual patient needs while maintaining isotonicity. This personalized approach represents a significant step forward in PN therapy, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing complications.
As research in this field progresses, the objectives continue to evolve. Current areas of focus include developing novel osmotic agents, improving the stability of isotonic formulations, and investigating the long-term effects of different isotonicity adjustment strategies on patient health. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the impact of isotonicity on nutrient absorption and utilization at the cellular level.
Market Analysis of PN Solutions
The global parenteral nutrition (PN) solutions market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing prevalence of malnutrition, rising incidence of chronic diseases, and growing geriatric population. The market for PN solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory due to the rising demand for personalized nutrition therapies and advancements in healthcare infrastructure.
Isotonicity adjustments in PN solutions play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and efficacy of treatment. The market for isotonic PN solutions is particularly robust, as they are essential for maintaining proper fluid balance and preventing complications such as electrolyte imbalances and osmotic shifts. Hospitals and healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting ready-to-use PN solutions with pre-adjusted isotonicity, driving market growth in this segment.
The market for PN solutions is segmented based on type, including single-dose and multi-dose formulations. Multi-dose PN solutions are gaining traction due to their cost-effectiveness and reduced risk of contamination. However, single-dose formulations remain popular in certain clinical settings where patient-specific customization is required.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the PN solutions market, owing to well-established healthcare systems and high adoption rates of advanced nutritional therapies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising awareness about nutritional support, and increasing healthcare expenditure in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the PN solutions industry are focusing on product innovations, particularly in the area of isotonicity adjustments. These companies are investing in research and development to create novel formulations that offer improved stability, compatibility, and clinical outcomes. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards the development of lipid-based PN solutions, which provide better nutrient utilization and reduced complications.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the PN solutions market, with increased demand for nutritional support in critically ill patients. This has led to a surge in production and supply of PN solutions, particularly those with optimized isotonicity for COVID-19 patients with complex nutritional needs.
Looking ahead, the market for PN solutions is expected to witness further growth, driven by technological advancements in delivery systems, increasing focus on home parenteral nutrition, and growing demand for specialized formulations catering to specific patient populations. The emphasis on isotonicity adjustments will likely continue to be a key factor influencing market dynamics and product development strategies in the coming years.
Isotonicity adjustments in PN solutions play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and efficacy of treatment. The market for isotonic PN solutions is particularly robust, as they are essential for maintaining proper fluid balance and preventing complications such as electrolyte imbalances and osmotic shifts. Hospitals and healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting ready-to-use PN solutions with pre-adjusted isotonicity, driving market growth in this segment.
The market for PN solutions is segmented based on type, including single-dose and multi-dose formulations. Multi-dose PN solutions are gaining traction due to their cost-effectiveness and reduced risk of contamination. However, single-dose formulations remain popular in certain clinical settings where patient-specific customization is required.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the PN solutions market, owing to well-established healthcare systems and high adoption rates of advanced nutritional therapies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising awareness about nutritional support, and increasing healthcare expenditure in countries like China and India.
Key market players in the PN solutions industry are focusing on product innovations, particularly in the area of isotonicity adjustments. These companies are investing in research and development to create novel formulations that offer improved stability, compatibility, and clinical outcomes. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards the development of lipid-based PN solutions, which provide better nutrient utilization and reduced complications.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the PN solutions market, with increased demand for nutritional support in critically ill patients. This has led to a surge in production and supply of PN solutions, particularly those with optimized isotonicity for COVID-19 patients with complex nutritional needs.
Looking ahead, the market for PN solutions is expected to witness further growth, driven by technological advancements in delivery systems, increasing focus on home parenteral nutrition, and growing demand for specialized formulations catering to specific patient populations. The emphasis on isotonicity adjustments will likely continue to be a key factor influencing market dynamics and product development strategies in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Isotonicity Adjustment
Isotonicity adjustment in parenteral nutrition solutions presents several significant challenges that researchers and healthcare professionals must address. One of the primary difficulties lies in achieving and maintaining the correct osmolarity of the solution. Parenteral nutrition formulations often contain a complex mixture of nutrients, electrolytes, and other components, each contributing to the overall osmolarity. Balancing these elements to match the osmolarity of body fluids is crucial for patient safety and efficacy of the treatment.
The variability in patient needs further complicates the isotonicity adjustment process. Different medical conditions, metabolic states, and fluid balance requirements necessitate customized formulations. This individualization makes it challenging to develop standardized approaches to isotonicity adjustment, requiring careful consideration of each patient's specific needs and potential responses to the parenteral nutrition solution.
Another significant challenge is the stability of the solution over time. Even when initial isotonicity is achieved, maintaining it throughout the storage and administration period can be problematic. Chemical interactions between components, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to light can all affect the osmolarity of the solution, potentially leading to changes in its isotonic properties.
The precision required in measuring and adjusting osmolarity poses technical challenges. Current methods for osmolarity measurement may have limitations in accuracy or may not be suitable for real-time monitoring during the preparation and administration of parenteral nutrition solutions. This can lead to difficulties in making fine adjustments to ensure optimal isotonicity.
Furthermore, the presence of certain medications or additives in parenteral nutrition solutions can interfere with isotonicity adjustments. Some drugs or supplements may alter the osmotic properties of the solution, making it challenging to predict and control the final osmolarity. This is particularly problematic when multiple additives are required for a patient's treatment regimen.
The risk of adverse reactions due to improper isotonicity is a constant concern. Hypertonic or hypotonic solutions can lead to serious complications, including electrolyte imbalances, cellular damage, and hemolysis. The narrow therapeutic window for osmolarity in parenteral nutrition solutions leaves little room for error, adding pressure to the adjustment process.
Lastly, the cost and resource implications of precise isotonicity adjustment present economic challenges. Specialized equipment, trained personnel, and quality control measures necessary for accurate osmolarity management can be expensive, potentially limiting access to optimal parenteral nutrition in resource-constrained settings.
The variability in patient needs further complicates the isotonicity adjustment process. Different medical conditions, metabolic states, and fluid balance requirements necessitate customized formulations. This individualization makes it challenging to develop standardized approaches to isotonicity adjustment, requiring careful consideration of each patient's specific needs and potential responses to the parenteral nutrition solution.
Another significant challenge is the stability of the solution over time. Even when initial isotonicity is achieved, maintaining it throughout the storage and administration period can be problematic. Chemical interactions between components, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to light can all affect the osmolarity of the solution, potentially leading to changes in its isotonic properties.
The precision required in measuring and adjusting osmolarity poses technical challenges. Current methods for osmolarity measurement may have limitations in accuracy or may not be suitable for real-time monitoring during the preparation and administration of parenteral nutrition solutions. This can lead to difficulties in making fine adjustments to ensure optimal isotonicity.
Furthermore, the presence of certain medications or additives in parenteral nutrition solutions can interfere with isotonicity adjustments. Some drugs or supplements may alter the osmotic properties of the solution, making it challenging to predict and control the final osmolarity. This is particularly problematic when multiple additives are required for a patient's treatment regimen.
The risk of adverse reactions due to improper isotonicity is a constant concern. Hypertonic or hypotonic solutions can lead to serious complications, including electrolyte imbalances, cellular damage, and hemolysis. The narrow therapeutic window for osmolarity in parenteral nutrition solutions leaves little room for error, adding pressure to the adjustment process.
Lastly, the cost and resource implications of precise isotonicity adjustment present economic challenges. Specialized equipment, trained personnel, and quality control measures necessary for accurate osmolarity management can be expensive, potentially limiting access to optimal parenteral nutrition in resource-constrained settings.
Existing Isotonicity Adjustment Methods
01 Composition of isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions
Isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions are formulated to match the osmolarity of blood, typically around 280-300 mOsm/L. These solutions contain a balanced mixture of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) to provide complete nutrition. The composition is carefully adjusted to maintain isotonicity while meeting nutritional requirements.- Composition of isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions: Isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions are formulated to match the osmolarity of blood, typically around 280-300 mOsm/L. These solutions contain a balanced mixture of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) to provide complete nutritional support. The composition is carefully adjusted to maintain isotonicity while meeting the patient's nutritional requirements.
- Osmolarity adjustment techniques: Various techniques are employed to adjust the osmolarity of parenteral nutrition solutions to achieve isotonicity. These may include the use of electrolytes, sugar alcohols, or other osmotic agents. The concentration of these components is carefully controlled to ensure the final solution remains isotonic with blood, preventing complications associated with hyper- or hypo-osmolarity.
- Specialized formulations for specific patient populations: Isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions are tailored for specific patient populations, such as neonates, pediatric patients, or those with particular medical conditions. These specialized formulations take into account the unique nutritional needs and physiological characteristics of these groups while maintaining isotonicity to ensure safe administration.
- Stability and compatibility considerations: Ensuring the stability and compatibility of components in isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions is crucial. This involves careful selection of ingredients, pH adjustment, and the use of stabilizers or emulsifiers. These considerations help maintain the isotonicity of the solution over time and prevent potential adverse reactions or precipitation during storage or administration.
- Delivery systems and administration methods: Various delivery systems and administration methods are developed to ensure the safe and effective delivery of isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions. These may include specialized infusion pumps, multi-chamber bags, or in-line filtration systems. The administration protocols are designed to maintain the isotonicity of the solution throughout the infusion process and minimize the risk of complications.
02 Osmolarity adjustment techniques
Various techniques are employed to adjust the osmolarity of parenteral nutrition solutions to achieve isotonicity. These may include the use of electrolytes, sugar alcohols, or other osmotic agents. The concentration of these components is carefully controlled to ensure the final solution remains isotonic with blood, preventing complications associated with hyper- or hypo-osmolarity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stability and compatibility considerations
Maintaining the stability and compatibility of components in isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions is crucial. Formulations are designed to prevent precipitation, degradation, or interactions between ingredients that could compromise the solution's isotonicity or efficacy. This may involve careful selection of ingredients, pH adjustment, or the use of stabilizing agents.Expand Specific Solutions04 Customization for specific patient needs
Isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions can be customized to meet the specific nutritional and metabolic needs of individual patients. This may involve adjusting the concentration of certain nutrients or adding specific components while maintaining isotonicity. Such customization allows for optimal nutritional support in various clinical scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions05 Delivery systems and administration methods
The development of specialized delivery systems and administration methods for isotonic parenteral nutrition solutions is important for ensuring safe and effective nutrition support. This includes innovations in infusion pumps, catheters, and monitoring systems that help maintain the integrity and isotonicity of the solution during administration.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PN Industry
The research on isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions is in a mature stage, with a competitive landscape dominated by established pharmaceutical and healthcare companies. The market size is substantial, driven by the growing demand for specialized nutritional solutions in clinical settings. Key players like Fresenius Kabi, B. Braun Melsungen, and Baxter International have developed advanced technologies and extensive product portfolios in this field. The technical maturity is high, with companies focusing on innovation in formulation, delivery systems, and patient-specific solutions to maintain their competitive edge in this critical healthcare segment.
Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH
Technical Solution: Fresenius Kabi has developed advanced parenteral nutrition solutions with optimized isotonicity adjustments. Their approach involves using a combination of electrolytes and amino acids to achieve physiological osmolarity levels. The company has implemented a proprietary mixing technology that ensures precise control over the final osmolarity of the solution, allowing for customization based on patient needs[1]. They have also introduced a multi-chamber bag system that separates incompatible components until the point of administration, maintaining solution stability and reducing the risk of precipitation[2]. This system allows for the inclusion of a wider range of nutrients while maintaining isotonicity.
Strengths: Customizable solutions, advanced mixing technology, and multi-chamber system for improved stability. Weaknesses: May require specialized training for healthcare providers to properly utilize the customization options.
B. Braun Melsungen AG
Technical Solution: B. Braun has focused on developing parenteral nutrition solutions with balanced electrolyte compositions to maintain isotonicity. Their research has led to the creation of a modular nutrition system that allows for the precise adjustment of individual components, including electrolytes, to achieve optimal osmolarity[3]. The company has also invested in developing lipid emulsions with improved stability and reduced particle size, which contribute to maintaining isotonicity while providing essential fatty acids[4]. B. Braun's solutions incorporate a buffering system that helps maintain pH balance and prevents shifts in osmolarity during storage and administration.
Strengths: Modular system for precise adjustments, stable lipid emulsions, and integrated buffering system. Weaknesses: May be more complex to prepare compared to pre-mixed solutions, potentially increasing the risk of errors in preparation.
Innovative Approaches to Isotonicity Control
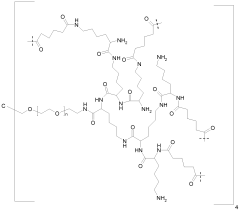
Use of dimethyl sulfone as isotonicity agent
PatentInactiveEP1539244A1
Innovation
- Dimethyl sulfone is used as an isotonicity agent in pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration, providing a stable and non-toxic environment for peptides, maintaining osmolarity and chemical stability without deteriorating the peptide, and is suitable for various administration routes including injection, infusion, and topical applications.
Subcutaneous paliperidone composition
PatentWO2011042453A1
Innovation
- A subcutaneous paliperidone composition with an immediate onset and extended release profile, formulated as a hydrogel prodrug, providing a continuous therapeutic plasma concentration for at least 3 weeks with minimal peak-to-trough variation, reducing the need for multiple injections and minimizing discomfort and absorption variability.
Regulatory Framework for PN Solutions
The regulatory framework for parenteral nutrition (PN) solutions is a complex and critical aspect of ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of PN solutions as pharmaceutical products. The FDA's guidance documents and regulations cover various aspects of PN formulation, including isotonicity adjustments.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides similar oversight in the European Union, with specific guidelines for the quality, safety, and efficacy of parenteral nutrition products. These guidelines address the importance of maintaining appropriate osmolarity and electrolyte balance in PN solutions.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) offers recommendations for the safe preparation and administration of parenteral nutrition, which include considerations for isotonicity adjustments. These guidelines serve as a reference for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Regulatory bodies require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their PN formulations through rigorous clinical trials and stability studies. This includes providing data on the osmolarity of the solutions and their impact on patient physiology.
Pharmacopoeias, such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia, provide standards for the quality and purity of ingredients used in PN solutions. These standards include specifications for electrolytes and other components that affect isotonicity.
Labeling requirements for PN solutions are stringent, with regulatory agencies mandating clear information on osmolarity, electrolyte content, and any necessary adjustments for specific patient populations. This ensures that healthcare providers can make informed decisions when administering these products.
Regulatory frameworks also address the compounding of PN solutions in hospital pharmacies. Guidelines for good compounding practices include protocols for ensuring proper isotonicity in custom-formulated PN solutions.
As research in isotonicity adjustments advances, regulatory bodies continuously update their guidelines to incorporate new scientific findings. This dynamic process ensures that regulations evolve alongside technological and medical advancements in parenteral nutrition.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides similar oversight in the European Union, with specific guidelines for the quality, safety, and efficacy of parenteral nutrition products. These guidelines address the importance of maintaining appropriate osmolarity and electrolyte balance in PN solutions.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) offers recommendations for the safe preparation and administration of parenteral nutrition, which include considerations for isotonicity adjustments. These guidelines serve as a reference for countries developing their own regulatory frameworks.
Regulatory bodies require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their PN formulations through rigorous clinical trials and stability studies. This includes providing data on the osmolarity of the solutions and their impact on patient physiology.
Pharmacopoeias, such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia, provide standards for the quality and purity of ingredients used in PN solutions. These standards include specifications for electrolytes and other components that affect isotonicity.
Labeling requirements for PN solutions are stringent, with regulatory agencies mandating clear information on osmolarity, electrolyte content, and any necessary adjustments for specific patient populations. This ensures that healthcare providers can make informed decisions when administering these products.
Regulatory frameworks also address the compounding of PN solutions in hospital pharmacies. Guidelines for good compounding practices include protocols for ensuring proper isotonicity in custom-formulated PN solutions.
As research in isotonicity adjustments advances, regulatory bodies continuously update their guidelines to incorporate new scientific findings. This dynamic process ensures that regulations evolve alongside technological and medical advancements in parenteral nutrition.
Patient Safety and Clinical Outcomes
Patient safety and clinical outcomes are paramount considerations in the research on isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions. The osmolarity of parenteral nutrition solutions plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and preventing adverse effects in patients receiving intravenous nutrition.
Isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions have been shown to significantly impact patient safety. Solutions that are not properly adjusted for isotonicity can lead to complications such as electrolyte imbalances, fluid shifts, and tissue damage. Research has demonstrated that hypotonic solutions may cause cellular swelling and potential lysis, while hypertonic solutions can result in cellular dehydration and shrinkage. These cellular-level changes can have systemic effects on patients, potentially leading to organ dysfunction and compromised clinical outcomes.
Studies have indicated that precise isotonicity adjustments can reduce the risk of adverse events associated with parenteral nutrition. For instance, research has shown that maintaining appropriate osmolarity in neonatal parenteral nutrition solutions can decrease the incidence of electrolyte disturbances and improve overall patient outcomes. Similarly, in adult patients, properly adjusted isotonic solutions have been linked to reduced rates of phlebitis and improved vascular access device longevity.
The impact of isotonicity adjustments on specific patient populations has been a focus of recent research. Critically ill patients, in particular, have shown improved clinical outcomes when receiving parenteral nutrition solutions with carefully tailored osmolarity. These adjustments have been associated with better glycemic control, reduced incidence of infections, and shorter lengths of hospital stay.
Furthermore, research has explored the relationship between isotonicity adjustments and the bioavailability of nutrients in parenteral nutrition solutions. Optimized isotonicity has been found to enhance the absorption and utilization of essential nutrients, contributing to improved nutritional status and faster recovery in patients requiring long-term parenteral support.
Advancements in monitoring techniques have allowed for more precise assessment of patient responses to isotonicity adjustments. Real-time osmolarity monitoring systems have enabled healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to parenteral nutrition formulations, further enhancing patient safety and clinical outcomes. These technological innovations have paved the way for personalized approaches to parenteral nutrition, taking into account individual patient factors such as underlying medical conditions, fluid status, and metabolic needs.
In conclusion, research on isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions has demonstrated significant implications for patient safety and clinical outcomes. The ongoing efforts to optimize these adjustments continue to drive improvements in the quality of care for patients receiving parenteral nutrition support.
Isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions have been shown to significantly impact patient safety. Solutions that are not properly adjusted for isotonicity can lead to complications such as electrolyte imbalances, fluid shifts, and tissue damage. Research has demonstrated that hypotonic solutions may cause cellular swelling and potential lysis, while hypertonic solutions can result in cellular dehydration and shrinkage. These cellular-level changes can have systemic effects on patients, potentially leading to organ dysfunction and compromised clinical outcomes.
Studies have indicated that precise isotonicity adjustments can reduce the risk of adverse events associated with parenteral nutrition. For instance, research has shown that maintaining appropriate osmolarity in neonatal parenteral nutrition solutions can decrease the incidence of electrolyte disturbances and improve overall patient outcomes. Similarly, in adult patients, properly adjusted isotonic solutions have been linked to reduced rates of phlebitis and improved vascular access device longevity.
The impact of isotonicity adjustments on specific patient populations has been a focus of recent research. Critically ill patients, in particular, have shown improved clinical outcomes when receiving parenteral nutrition solutions with carefully tailored osmolarity. These adjustments have been associated with better glycemic control, reduced incidence of infections, and shorter lengths of hospital stay.
Furthermore, research has explored the relationship between isotonicity adjustments and the bioavailability of nutrients in parenteral nutrition solutions. Optimized isotonicity has been found to enhance the absorption and utilization of essential nutrients, contributing to improved nutritional status and faster recovery in patients requiring long-term parenteral support.
Advancements in monitoring techniques have allowed for more precise assessment of patient responses to isotonicity adjustments. Real-time osmolarity monitoring systems have enabled healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to parenteral nutrition formulations, further enhancing patient safety and clinical outcomes. These technological innovations have paved the way for personalized approaches to parenteral nutrition, taking into account individual patient factors such as underlying medical conditions, fluid status, and metabolic needs.
In conclusion, research on isotonicity adjustments in parenteral nutrition solutions has demonstrated significant implications for patient safety and clinical outcomes. The ongoing efforts to optimize these adjustments continue to drive improvements in the quality of care for patients receiving parenteral nutrition support.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!