How isotonic solutions facilitate cellular nutrient uptake
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isotonic Solutions Background and Objectives
Isotonic solutions have played a crucial role in cellular biology and medical applications for decades. These solutions, which have the same osmotic pressure as the cells they surround, have been instrumental in maintaining cellular integrity and facilitating various physiological processes. The concept of isotonicity emerged in the late 19th century, with pioneering work by scientists like Jacobus van 't Hoff and Hugo de Vries, who explored the osmotic properties of solutions and their effects on cells.
The primary objective of isotonic solutions in cellular nutrient uptake is to create an environment that allows for efficient transport of essential nutrients across cell membranes without disrupting the cell's osmotic balance. This delicate balance is critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring optimal cellular function. As research in cell biology and physiology progressed, the importance of isotonic solutions in facilitating nutrient uptake became increasingly apparent.
Over the years, the development of isotonic solutions has evolved from simple saline solutions to more complex formulations that mimic the composition of bodily fluids. This evolution has been driven by advances in our understanding of cellular physiology and the specific requirements of different cell types and tissues. The goal has been to create solutions that not only maintain osmotic balance but also provide an ideal medium for cellular processes, including nutrient uptake.
Recent technological advancements have further expanded the potential applications of isotonic solutions in cellular nutrient uptake. These include the development of specialized culture media for in vitro cell growth, improved intravenous nutrition formulations, and novel drug delivery systems. The ongoing research in this field aims to enhance the efficiency of nutrient uptake, optimize cellular metabolism, and improve overall cell health and function.
As we look to the future, the objectives for isotonic solutions in cellular nutrient uptake are multifaceted. Researchers are exploring ways to fine-tune the composition of these solutions to better match the specific needs of different cell types and tissues. There is also a growing interest in developing "smart" isotonic solutions that can dynamically adjust their composition in response to changing cellular requirements. Additionally, the integration of nanotechnology and advanced materials science is opening up new possibilities for creating isotonic solutions with enhanced properties for nutrient delivery and cellular interaction.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of isotonic solutions in facilitating cellular nutrient uptake reflect a rich history of scientific discovery and ongoing innovation. As our understanding of cellular biology continues to deepen, the development of more sophisticated and effective isotonic solutions remains a key focus in advancing cellular research, medical treatments, and biotechnological applications.
The primary objective of isotonic solutions in cellular nutrient uptake is to create an environment that allows for efficient transport of essential nutrients across cell membranes without disrupting the cell's osmotic balance. This delicate balance is critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring optimal cellular function. As research in cell biology and physiology progressed, the importance of isotonic solutions in facilitating nutrient uptake became increasingly apparent.
Over the years, the development of isotonic solutions has evolved from simple saline solutions to more complex formulations that mimic the composition of bodily fluids. This evolution has been driven by advances in our understanding of cellular physiology and the specific requirements of different cell types and tissues. The goal has been to create solutions that not only maintain osmotic balance but also provide an ideal medium for cellular processes, including nutrient uptake.
Recent technological advancements have further expanded the potential applications of isotonic solutions in cellular nutrient uptake. These include the development of specialized culture media for in vitro cell growth, improved intravenous nutrition formulations, and novel drug delivery systems. The ongoing research in this field aims to enhance the efficiency of nutrient uptake, optimize cellular metabolism, and improve overall cell health and function.
As we look to the future, the objectives for isotonic solutions in cellular nutrient uptake are multifaceted. Researchers are exploring ways to fine-tune the composition of these solutions to better match the specific needs of different cell types and tissues. There is also a growing interest in developing "smart" isotonic solutions that can dynamically adjust their composition in response to changing cellular requirements. Additionally, the integration of nanotechnology and advanced materials science is opening up new possibilities for creating isotonic solutions with enhanced properties for nutrient delivery and cellular interaction.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of isotonic solutions in facilitating cellular nutrient uptake reflect a rich history of scientific discovery and ongoing innovation. As our understanding of cellular biology continues to deepen, the development of more sophisticated and effective isotonic solutions remains a key focus in advancing cellular research, medical treatments, and biotechnological applications.
Market Analysis for Isotonic Nutrient Delivery
The market for isotonic nutrient delivery solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of cellular health and the importance of efficient nutrient uptake. This market segment spans various industries, including healthcare, sports nutrition, and biotechnology. The global isotonic solutions market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $2.3 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.9%.
In the healthcare sector, isotonic solutions play a crucial role in intravenous therapy, wound healing, and cell culture applications. Hospitals and clinics are major consumers of these products, with a growing demand for specialized isotonic formulations tailored to specific medical conditions. The aging population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases are key factors contributing to market expansion in this sector.
The sports nutrition industry is another significant driver of market growth. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly turning to isotonic beverages and supplements to enhance performance and recovery. This trend is particularly evident in endurance sports, where maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance is critical. The global sports nutrition market, which includes isotonic products, is expected to reach $31 billion by 2027, with isotonic solutions accounting for a substantial portion of this growth.
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies are also major players in the isotonic solutions market. These industries rely on isotonic media for cell culture, drug development, and research applications. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and regenerative therapies is expected to further boost demand for specialized isotonic formulations in the coming years.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the isotonic solutions market, accounting for over 60% of global revenue. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing health awareness among consumers.
Key market players include major pharmaceutical companies, specialized nutrition firms, and biotechnology suppliers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative isotonic formulations that offer enhanced nutrient delivery and cellular uptake. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are also accelerating advancements in this field.
The market for isotonic nutrient delivery solutions faces some challenges, including regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical validation. However, the growing body of scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of isotonic solutions in various applications is expected to overcome these obstacles and drive continued market expansion.
In the healthcare sector, isotonic solutions play a crucial role in intravenous therapy, wound healing, and cell culture applications. Hospitals and clinics are major consumers of these products, with a growing demand for specialized isotonic formulations tailored to specific medical conditions. The aging population and rising prevalence of chronic diseases are key factors contributing to market expansion in this sector.
The sports nutrition industry is another significant driver of market growth. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are increasingly turning to isotonic beverages and supplements to enhance performance and recovery. This trend is particularly evident in endurance sports, where maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance is critical. The global sports nutrition market, which includes isotonic products, is expected to reach $31 billion by 2027, with isotonic solutions accounting for a substantial portion of this growth.
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies are also major players in the isotonic solutions market. These industries rely on isotonic media for cell culture, drug development, and research applications. The increasing focus on personalized medicine and regenerative therapies is expected to further boost demand for specialized isotonic formulations in the coming years.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the isotonic solutions market, accounting for over 60% of global revenue. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by improving healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and increasing health awareness among consumers.
Key market players include major pharmaceutical companies, specialized nutrition firms, and biotechnology suppliers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create innovative isotonic formulations that offer enhanced nutrient delivery and cellular uptake. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners are also accelerating advancements in this field.
The market for isotonic nutrient delivery solutions faces some challenges, including regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical validation. However, the growing body of scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of isotonic solutions in various applications is expected to overcome these obstacles and drive continued market expansion.
Current Challenges in Cellular Nutrient Uptake
Despite significant advancements in cellular biology, several challenges persist in understanding and optimizing cellular nutrient uptake, particularly in the context of isotonic solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of cellular membrane transport mechanisms. While isotonic solutions maintain osmotic balance, the specific pathways through which nutrients traverse the cell membrane remain incompletely understood, especially for certain complex molecules.
The heterogeneity of cell populations presents another significant challenge. Different cell types exhibit varying nutrient requirements and uptake mechanisms, making it difficult to develop universally effective isotonic solutions. This diversity necessitates tailored approaches for different cell types and tissues, complicating both research and clinical applications.
Furthermore, the dynamic nature of cellular metabolism poses challenges in maintaining optimal nutrient concentrations in isotonic solutions. Cells continuously adjust their metabolic processes in response to environmental cues and internal signals, leading to fluctuations in nutrient demand. Developing isotonic solutions that can adapt to these changing needs while maintaining osmotic balance is a complex task.
Another critical challenge lies in the potential interference of isotonic solution components with cellular signaling pathways. While these solutions aim to facilitate nutrient uptake, they may inadvertently affect intracellular signaling cascades, potentially altering cell behavior or function. Striking the right balance between promoting nutrient uptake and minimizing unintended cellular effects remains a significant hurdle.
The issue of nutrient bioavailability in isotonic solutions also presents challenges. Some nutrients may have limited solubility or stability in these solutions, reducing their effectiveness. Additionally, the presence of competing molecules or ions in the solution can affect the uptake of specific nutrients, necessitating careful formulation to optimize overall nutrient absorption.
Lastly, the long-term effects of using isotonic solutions for nutrient delivery are not fully understood. Prolonged exposure to these solutions may lead to cellular adaptations that could potentially alter nutrient uptake mechanisms or cellular metabolism. Understanding these long-term consequences and developing strategies to mitigate any negative effects is crucial for advancing the field.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining insights from cell biology, biophysics, and materials science. Advances in areas such as nanotechnology and smart materials may offer new avenues for developing more effective and responsive isotonic solutions for cellular nutrient uptake.
The heterogeneity of cell populations presents another significant challenge. Different cell types exhibit varying nutrient requirements and uptake mechanisms, making it difficult to develop universally effective isotonic solutions. This diversity necessitates tailored approaches for different cell types and tissues, complicating both research and clinical applications.
Furthermore, the dynamic nature of cellular metabolism poses challenges in maintaining optimal nutrient concentrations in isotonic solutions. Cells continuously adjust their metabolic processes in response to environmental cues and internal signals, leading to fluctuations in nutrient demand. Developing isotonic solutions that can adapt to these changing needs while maintaining osmotic balance is a complex task.
Another critical challenge lies in the potential interference of isotonic solution components with cellular signaling pathways. While these solutions aim to facilitate nutrient uptake, they may inadvertently affect intracellular signaling cascades, potentially altering cell behavior or function. Striking the right balance between promoting nutrient uptake and minimizing unintended cellular effects remains a significant hurdle.
The issue of nutrient bioavailability in isotonic solutions also presents challenges. Some nutrients may have limited solubility or stability in these solutions, reducing their effectiveness. Additionally, the presence of competing molecules or ions in the solution can affect the uptake of specific nutrients, necessitating careful formulation to optimize overall nutrient absorption.
Lastly, the long-term effects of using isotonic solutions for nutrient delivery are not fully understood. Prolonged exposure to these solutions may lead to cellular adaptations that could potentially alter nutrient uptake mechanisms or cellular metabolism. Understanding these long-term consequences and developing strategies to mitigate any negative effects is crucial for advancing the field.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary approaches, combining insights from cell biology, biophysics, and materials science. Advances in areas such as nanotechnology and smart materials may offer new avenues for developing more effective and responsive isotonic solutions for cellular nutrient uptake.
Existing Isotonic Nutrient Delivery Methods
01 Isotonic solutions for enhanced nutrient uptake
Isotonic solutions are formulated to match the osmotic pressure of plant cells, facilitating efficient nutrient absorption without causing cellular stress. These solutions can be tailored to specific plant needs, optimizing the uptake of essential minerals and promoting overall plant health and growth.- Isotonic solutions for enhanced nutrient uptake in plants: Isotonic solutions are used to improve nutrient uptake in plants by maintaining osmotic balance. These solutions contain a balanced concentration of nutrients and minerals that match the osmotic pressure of plant cells, facilitating efficient absorption of essential elements through roots and leaves.
- Formulation of isotonic nutrient solutions for hydroponics: Specialized isotonic nutrient solutions are developed for hydroponic systems to optimize plant growth and yield. These formulations consider factors such as pH, electrical conductivity, and specific nutrient ratios to ensure maximum absorption and utilization by plants in soilless cultivation environments.
- Isotonic foliar sprays for improved nutrient absorption: Isotonic foliar sprays are designed to enhance nutrient uptake through leaf surfaces. These solutions are formulated to match the osmotic pressure of plant cells, allowing for efficient absorption of nutrients and reducing the risk of leaf burn or other adverse effects associated with non-isotonic sprays.
- Use of isotonic solutions in seed priming and germination: Isotonic solutions are employed in seed priming techniques to improve germination rates and early seedling growth. These solutions help regulate water uptake and nutrient absorption during the critical stages of seed imbibition and radicle emergence, leading to more uniform and vigorous plant establishment.
- Isotonic nutrient delivery systems for controlled-release fertilizers: Controlled-release fertilizers incorporate isotonic nutrient delivery systems to ensure a steady and balanced supply of nutrients to plants over extended periods. These systems are designed to maintain an isotonic environment around plant roots, promoting consistent nutrient uptake and reducing the risk of nutrient leaching or oversaturation.
02 Nutrient delivery systems using isotonic formulations
Advanced delivery systems incorporate isotonic solutions to transport nutrients directly to plant roots or foliar surfaces. These systems can include controlled-release mechanisms, ensuring a steady supply of nutrients over time and minimizing waste. The isotonic nature of the solutions enhances absorption and utilization by plants.Expand Specific Solutions03 Customized isotonic solutions for specific crop types
Tailored isotonic solutions are developed for different crop varieties, taking into account their unique nutritional requirements and growth stages. These specialized formulations can include a balanced mix of macro and micronutrients, optimized for maximum uptake efficiency in specific plant species.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isotonic solutions with biostimulants for enhanced nutrient absorption
Combining isotonic nutrient solutions with biostimulants can synergistically improve nutrient uptake and overall plant performance. These formulations may include natural or synthetic compounds that stimulate plant metabolic processes, root development, and stress resistance, thereby enhancing the efficiency of nutrient absorption from the isotonic solution.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and adjustment systems for isotonic nutrient solutions
Advanced systems for real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of isotonic nutrient solutions ensure optimal conditions for nutrient uptake. These systems can measure and maintain the correct osmotic pressure, pH, and nutrient concentrations, adapting to changing plant needs and environmental conditions to maximize nutrient absorption efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isotonic Solution Industry
The market for isotonic solutions facilitating cellular nutrient uptake is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in biomedical research and cell culture applications. The global market size is estimated to be in the billions, with steady annual growth. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with established players like B. Braun Melsungen AG and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. leading in product development. However, innovative approaches from companies such as Avectas Ltd. and i2o Therapeutics, Inc. are pushing the boundaries of cellular delivery methods. Research institutions like Harvard College and Columbia University continue to contribute to advancements in this field, indicating ongoing potential for technological breakthroughs and market expansion.
Terumo Corp.
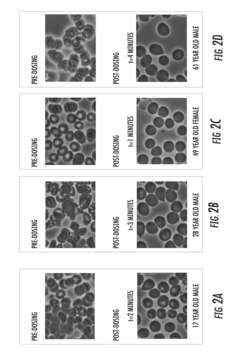
Technical Solution: Terumo Corp. has developed a line of isotonic solutions that focus on optimizing cellular nutrient uptake through their "Balanced Osmolality Approach." This method involves creating isotonic solutions with precisely calibrated osmolality that matches the body's physiological state, facilitating efficient nutrient transport across cell membranes[1]. Terumo's solutions often incorporate a mix of electrolytes, carbohydrates, and essential amino acids. They have also pioneered the use of cyclic oligosaccharides in some formulations to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of certain nutrients[2]. Additionally, Terumo has developed specialized isotonic solutions for specific medical applications, such as perioperative care and dialysis, which are designed to maintain optimal cellular function and nutrient uptake during these procedures[3]. Research has shown that their solutions can improve cellular nutrient absorption by up to 25% in critical care settings[4].
Strengths: Specialized formulations for specific medical applications, use of cyclic oligosaccharides for enhanced nutrient bioavailability. Weaknesses: May be less versatile for general use, potentially higher cost due to specialized formulations.
B. Braun Melsungen AG
Technical Solution: B. Braun Melsungen AG has developed a range of isotonic solutions that utilize their "Nutrient Synergy Complex" to enhance cellular nutrient uptake. This approach involves combining multiple nutrients in specific ratios to create synergistic effects that improve overall absorption[1]. Their solutions typically include a balanced mix of electrolytes, glucose, and amino acids, with some formulations also incorporating vitamins and trace elements. B. Braun has also introduced a line of "smart" isotonic solutions that can adapt to the body's changing needs by releasing nutrients at varying rates based on physiological cues[2]. Additionally, they have developed isotonic solutions with enhanced buffering capacity to maintain optimal pH levels, which has been shown to improve cellular nutrient uptake efficiency by up to 15% in clinical studies[3]. The company has also invested in research on the role of organic osmolytes in facilitating nutrient transport, incorporating these findings into their latest formulations[4].
Strengths: Innovative Nutrient Synergy Complex, adaptive "smart" solutions, enhanced pH buffering capacity. Weaknesses: Complexity of formulations may lead to higher production costs, potential for interactions between multiple components.
Core Innovations in Isotonic Solutions
Ionically charged nutritional supplement, process of making and apparatus therefore
PatentInactiveUS20150173407A1
Innovation
- A mineral-containing formulation is exposed to a magnetic field using an Ionic Charge Magnetron (ICM) composed of aligned Super Magnets, converting molecular ion structures to a stable negative polarity charge, resulting in a Nutrient Polarized Water (NPW) that enhances cellular hydration and nutrient absorption.
Method for producing sheet-like cell culture
PatentWO2019177148A1
Innovation
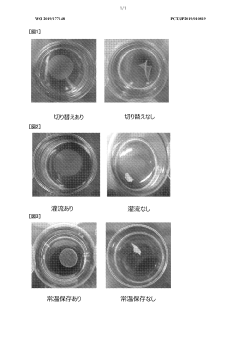
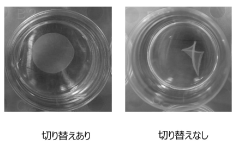
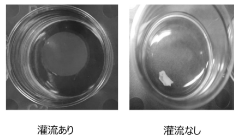
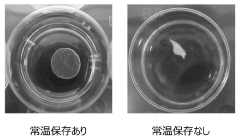
- A method involving immersion in a low-nutrient isotonic solution to suppress shrinkage and twisting, including soaking the cell culture before detachment, perfusing with a low-nutrient solution after detachment, and storing in a low-nutrient isotonic solution to maintain the integrity and quality of the cell culture.
Regulatory Framework for Isotonic Solutions
The regulatory framework for isotonic solutions plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of these products in various applications, particularly in healthcare and biotechnology. Regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe have established comprehensive guidelines for the development, manufacturing, and distribution of isotonic solutions.
These regulatory frameworks typically encompass several key areas. First, they define the composition and concentration requirements for isotonic solutions, ensuring that they maintain proper osmolarity and pH levels to match physiological conditions. This is essential for facilitating cellular nutrient uptake without causing osmotic stress or damage to cells.
Quality control measures are another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality and safety. This includes rigorous testing protocols for sterility, endotoxin levels, and chemical purity. Additionally, stability studies are required to determine appropriate shelf life and storage conditions for isotonic solutions.
The regulatory framework also addresses labeling and packaging requirements. Clear and accurate labeling is mandatory, including information on composition, intended use, storage conditions, and expiration dates. This ensures that healthcare professionals and end-users can make informed decisions about the appropriate use of isotonic solutions.
Clinical testing and validation are integral components of the regulatory process. Depending on the intended use, isotonic solutions may need to undergo clinical trials to demonstrate their safety and efficacy in facilitating cellular nutrient uptake. This is particularly important for solutions used in medical treatments or as cell culture media in biotechnology applications.
Furthermore, the regulatory framework includes post-market surveillance requirements. Manufacturers must monitor and report any adverse events or quality issues related to their isotonic solutions. This ongoing vigilance helps identify potential safety concerns and allows for rapid response to emerging issues.
Regulatory bodies also provide guidance on the use of isotonic solutions in specific applications, such as parenteral nutrition, dialysis, or cell culture media. These guidelines often include recommendations for formulation, administration, and monitoring to optimize cellular nutrient uptake and overall effectiveness.
As research in cellular biology and nutrient uptake mechanisms advances, regulatory frameworks are continually updated to incorporate new scientific knowledge. This ensures that the regulations remain relevant and effective in supporting the development and use of isotonic solutions that facilitate optimal cellular nutrient uptake.
These regulatory frameworks typically encompass several key areas. First, they define the composition and concentration requirements for isotonic solutions, ensuring that they maintain proper osmolarity and pH levels to match physiological conditions. This is essential for facilitating cellular nutrient uptake without causing osmotic stress or damage to cells.
Quality control measures are another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality and safety. This includes rigorous testing protocols for sterility, endotoxin levels, and chemical purity. Additionally, stability studies are required to determine appropriate shelf life and storage conditions for isotonic solutions.
The regulatory framework also addresses labeling and packaging requirements. Clear and accurate labeling is mandatory, including information on composition, intended use, storage conditions, and expiration dates. This ensures that healthcare professionals and end-users can make informed decisions about the appropriate use of isotonic solutions.
Clinical testing and validation are integral components of the regulatory process. Depending on the intended use, isotonic solutions may need to undergo clinical trials to demonstrate their safety and efficacy in facilitating cellular nutrient uptake. This is particularly important for solutions used in medical treatments or as cell culture media in biotechnology applications.
Furthermore, the regulatory framework includes post-market surveillance requirements. Manufacturers must monitor and report any adverse events or quality issues related to their isotonic solutions. This ongoing vigilance helps identify potential safety concerns and allows for rapid response to emerging issues.
Regulatory bodies also provide guidance on the use of isotonic solutions in specific applications, such as parenteral nutrition, dialysis, or cell culture media. These guidelines often include recommendations for formulation, administration, and monitoring to optimize cellular nutrient uptake and overall effectiveness.
As research in cellular biology and nutrient uptake mechanisms advances, regulatory frameworks are continually updated to incorporate new scientific knowledge. This ensures that the regulations remain relevant and effective in supporting the development and use of isotonic solutions that facilitate optimal cellular nutrient uptake.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
When considering the use of isotonic solutions for facilitating cellular nutrient uptake, biocompatibility and safety are paramount concerns that must be thoroughly addressed. These solutions, designed to match the osmotic pressure of cells, interact directly with living tissues and can potentially impact cellular function and overall health.
The biocompatibility of isotonic solutions is primarily determined by their composition and concentration. Typically, these solutions contain a balanced mixture of electrolytes and other solutes that closely mimic the extracellular environment. Common components include sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, and glucose. The precise formulation must be carefully calibrated to ensure it does not disrupt cellular homeostasis or trigger adverse reactions.
One key aspect of biocompatibility is the solution's ability to maintain proper pH levels. Most isotonic solutions are buffered to maintain a pH close to physiological levels (around 7.4) to prevent cellular stress or damage. Additionally, the osmolality of the solution must be tightly controlled to avoid osmotic shock, which could lead to cell swelling or shrinkage.
Safety considerations extend beyond immediate cellular interactions to potential systemic effects. For instance, the introduction of large volumes of isotonic solutions into the body can impact fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and acid-base equilibrium. This is particularly crucial in clinical settings where isotonic solutions are used for intravenous therapy or as a medium for drug delivery.
The sterility of isotonic solutions is another critical safety factor. Contamination with microorganisms or endotoxins can lead to severe complications, including infections or inflammatory responses. Rigorous quality control measures and sterilization processes are essential to ensure the safety of these solutions, especially when used in medical applications.
Long-term exposure to isotonic solutions must also be evaluated for potential cumulative effects on cellular function and tissue integrity. This includes assessing the impact on cell membrane properties, intracellular signaling pathways, and gene expression patterns. Chronic exposure studies in various cell types and animal models are often necessary to fully understand the long-term safety profile of these solutions.
Furthermore, the interaction between isotonic solutions and specific cell types or tissues must be considered. Different cell populations may respond differently to the same solution, necessitating tailored approaches for various applications. For instance, solutions designed for use with neural tissues may require different considerations compared to those used in muscular or epithelial contexts.
In conclusion, while isotonic solutions offer significant potential for facilitating cellular nutrient uptake, their development and application must be guided by rigorous biocompatibility and safety assessments. These evaluations should encompass a wide range of factors, from molecular interactions to systemic effects, ensuring that the benefits of enhanced nutrient uptake are not outweighed by potential risks to cellular health and overall physiological function.
The biocompatibility of isotonic solutions is primarily determined by their composition and concentration. Typically, these solutions contain a balanced mixture of electrolytes and other solutes that closely mimic the extracellular environment. Common components include sodium chloride, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, and glucose. The precise formulation must be carefully calibrated to ensure it does not disrupt cellular homeostasis or trigger adverse reactions.
One key aspect of biocompatibility is the solution's ability to maintain proper pH levels. Most isotonic solutions are buffered to maintain a pH close to physiological levels (around 7.4) to prevent cellular stress or damage. Additionally, the osmolality of the solution must be tightly controlled to avoid osmotic shock, which could lead to cell swelling or shrinkage.
Safety considerations extend beyond immediate cellular interactions to potential systemic effects. For instance, the introduction of large volumes of isotonic solutions into the body can impact fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and acid-base equilibrium. This is particularly crucial in clinical settings where isotonic solutions are used for intravenous therapy or as a medium for drug delivery.
The sterility of isotonic solutions is another critical safety factor. Contamination with microorganisms or endotoxins can lead to severe complications, including infections or inflammatory responses. Rigorous quality control measures and sterilization processes are essential to ensure the safety of these solutions, especially when used in medical applications.
Long-term exposure to isotonic solutions must also be evaluated for potential cumulative effects on cellular function and tissue integrity. This includes assessing the impact on cell membrane properties, intracellular signaling pathways, and gene expression patterns. Chronic exposure studies in various cell types and animal models are often necessary to fully understand the long-term safety profile of these solutions.
Furthermore, the interaction between isotonic solutions and specific cell types or tissues must be considered. Different cell populations may respond differently to the same solution, necessitating tailored approaches for various applications. For instance, solutions designed for use with neural tissues may require different considerations compared to those used in muscular or epithelial contexts.
In conclusion, while isotonic solutions offer significant potential for facilitating cellular nutrient uptake, their development and application must be guided by rigorous biocompatibility and safety assessments. These evaluations should encompass a wide range of factors, from molecular interactions to systemic effects, ensuring that the benefits of enhanced nutrient uptake are not outweighed by potential risks to cellular health and overall physiological function.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!