How Polyglutamic Acid Assists in Prolonging Shelf-life of Poultry
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PGA in Poultry Preservation: Background and Objectives
Polyglutamic acid (PGA) has emerged as a promising solution in the food preservation industry, particularly in extending the shelf life of poultry products. This naturally occurring biopolymer, produced by various microbial species, has garnered significant attention due to its unique properties and potential applications in food science and technology.
The poultry industry faces substantial challenges in maintaining product freshness and quality during storage and distribution. Microbial growth, lipid oxidation, and moisture loss are primary factors contributing to the deterioration of poultry products, resulting in reduced shelf life and potential food safety risks. As consumer demand for fresh, minimally processed poultry continues to rise, the need for effective preservation methods becomes increasingly critical.
PGA's role in poultry preservation stems from its multifaceted properties. As a high-molecular-weight polymer of glutamic acid, PGA exhibits excellent water-retention capabilities, antimicrobial activity, and antioxidant properties. These characteristics make it an ideal candidate for addressing the key issues in poultry preservation.
The evolution of PGA technology in food preservation can be traced back to its initial discovery and characterization in the mid-20th century. However, it is only in recent decades that its potential in food applications, particularly in meat and poultry preservation, has been fully recognized and explored. This growing interest is driven by the increasing demand for natural, safe, and effective food preservatives that can replace synthetic alternatives.
The primary objective of utilizing PGA in poultry preservation is to develop a comprehensive solution that addresses multiple aspects of product deterioration simultaneously. By leveraging PGA's unique properties, researchers and industry professionals aim to create innovative preservation methods that can significantly extend the shelf life of poultry products while maintaining their quality, safety, and sensory attributes.
Key goals in this technological pursuit include enhancing PGA's efficacy in inhibiting microbial growth, optimizing its application methods for various poultry products, and investigating potential synergistic effects with other natural preservatives. Additionally, there is a focus on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying PGA's preservative action and exploring ways to enhance its stability and functionality in different processing and storage conditions.
As the food industry continues to evolve, with an increasing emphasis on sustainability and clean-label products, PGA presents a promising avenue for innovation in poultry preservation. Its natural origin and biodegradability align well with current consumer trends and regulatory requirements, positioning it as a potential game-changer in the quest for extended shelf life and improved food safety in the poultry sector.
The poultry industry faces substantial challenges in maintaining product freshness and quality during storage and distribution. Microbial growth, lipid oxidation, and moisture loss are primary factors contributing to the deterioration of poultry products, resulting in reduced shelf life and potential food safety risks. As consumer demand for fresh, minimally processed poultry continues to rise, the need for effective preservation methods becomes increasingly critical.
PGA's role in poultry preservation stems from its multifaceted properties. As a high-molecular-weight polymer of glutamic acid, PGA exhibits excellent water-retention capabilities, antimicrobial activity, and antioxidant properties. These characteristics make it an ideal candidate for addressing the key issues in poultry preservation.
The evolution of PGA technology in food preservation can be traced back to its initial discovery and characterization in the mid-20th century. However, it is only in recent decades that its potential in food applications, particularly in meat and poultry preservation, has been fully recognized and explored. This growing interest is driven by the increasing demand for natural, safe, and effective food preservatives that can replace synthetic alternatives.
The primary objective of utilizing PGA in poultry preservation is to develop a comprehensive solution that addresses multiple aspects of product deterioration simultaneously. By leveraging PGA's unique properties, researchers and industry professionals aim to create innovative preservation methods that can significantly extend the shelf life of poultry products while maintaining their quality, safety, and sensory attributes.
Key goals in this technological pursuit include enhancing PGA's efficacy in inhibiting microbial growth, optimizing its application methods for various poultry products, and investigating potential synergistic effects with other natural preservatives. Additionally, there is a focus on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying PGA's preservative action and exploring ways to enhance its stability and functionality in different processing and storage conditions.
As the food industry continues to evolve, with an increasing emphasis on sustainability and clean-label products, PGA presents a promising avenue for innovation in poultry preservation. Its natural origin and biodegradability align well with current consumer trends and regulatory requirements, positioning it as a potential game-changer in the quest for extended shelf life and improved food safety in the poultry sector.
Market Analysis for Extended Shelf-life Poultry Products
The market for extended shelf-life poultry products has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences and lifestyle trends. Consumers are increasingly seeking convenient, ready-to-eat options that maintain freshness and quality for longer periods. This demand has led to a surge in the development and adoption of technologies that can prolong the shelf life of poultry products.
The global market for extended shelf-life poultry products is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to factors such as urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and the growing popularity of protein-rich diets. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, but Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth due to changing dietary habits and increasing awareness of food safety.
One of the key drivers of this market is the reduction of food waste. Extended shelf-life technologies help minimize spoilage and decrease the amount of poultry products discarded due to expiration. This aligns with global sustainability initiatives and appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, retailers benefit from reduced inventory turnover and improved logistics efficiency.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for extended shelf-life poultry products. Consumers have shown a preference for less frequent shopping trips and stockpiling food items, making longer-lasting products more attractive. This trend is expected to continue even post-pandemic, as consumers have become accustomed to the convenience and safety aspects of these products.
In terms of product types, the market is segmented into whole birds, cuts, and processed products. Processed poultry products, such as ready-to-cook and ready-to-eat items, are witnessing the highest growth rate due to their convenience and longer shelf life. The foodservice industry, including restaurants and catering services, represents a significant market segment for extended shelf-life poultry products, as they help reduce operational costs and improve inventory management.
The use of polyglutamic acid in extending the shelf life of poultry products is gaining traction in the market. This technology offers several advantages, including natural preservation, improved texture retention, and enhanced food safety. As consumers increasingly prefer clean-label products with minimal artificial additives, polyglutamic acid-based solutions are well-positioned to capture market share from traditional preservatives.
However, the market also faces challenges, such as stringent regulations regarding food additives and preservation techniques. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance while meeting consumer demands for extended shelf life. Additionally, there is a growing need for education and transparency regarding the safety and benefits of shelf-life extension technologies to address consumer concerns and build trust.
The global market for extended shelf-life poultry products is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to factors such as urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and the growing popularity of protein-rich diets. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, but Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth due to changing dietary habits and increasing awareness of food safety.
One of the key drivers of this market is the reduction of food waste. Extended shelf-life technologies help minimize spoilage and decrease the amount of poultry products discarded due to expiration. This aligns with global sustainability initiatives and appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, retailers benefit from reduced inventory turnover and improved logistics efficiency.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for extended shelf-life poultry products. Consumers have shown a preference for less frequent shopping trips and stockpiling food items, making longer-lasting products more attractive. This trend is expected to continue even post-pandemic, as consumers have become accustomed to the convenience and safety aspects of these products.
In terms of product types, the market is segmented into whole birds, cuts, and processed products. Processed poultry products, such as ready-to-cook and ready-to-eat items, are witnessing the highest growth rate due to their convenience and longer shelf life. The foodservice industry, including restaurants and catering services, represents a significant market segment for extended shelf-life poultry products, as they help reduce operational costs and improve inventory management.
The use of polyglutamic acid in extending the shelf life of poultry products is gaining traction in the market. This technology offers several advantages, including natural preservation, improved texture retention, and enhanced food safety. As consumers increasingly prefer clean-label products with minimal artificial additives, polyglutamic acid-based solutions are well-positioned to capture market share from traditional preservatives.
However, the market also faces challenges, such as stringent regulations regarding food additives and preservation techniques. Manufacturers must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance while meeting consumer demands for extended shelf life. Additionally, there is a growing need for education and transparency regarding the safety and benefits of shelf-life extension technologies to address consumer concerns and build trust.
Current Challenges in Poultry Preservation Techniques
The poultry industry faces several significant challenges in preserving the quality and extending the shelf life of its products. One of the primary concerns is microbial contamination, which can lead to rapid spoilage and potential foodborne illnesses. Despite advancements in refrigeration and packaging technologies, controlling bacterial growth remains a persistent issue, particularly with pathogens like Salmonella and Campylobacter.
Oxidation is another major challenge, causing rancidity and off-flavors in poultry products. This process is accelerated by the high content of unsaturated fatty acids in poultry meat, making it particularly susceptible to oxidative deterioration. The resulting changes in flavor, color, and nutritional value significantly impact consumer acceptance and product marketability.
Moisture loss during storage and distribution presents a dual problem. Excessive moisture loss leads to weight reduction, affecting profitability, while inadequate moisture control can create an environment conducive to microbial growth. Striking the right balance is crucial but often difficult to achieve consistently across various storage and transportation conditions.
The industry also grapples with the challenge of maintaining the texture and tenderness of poultry products over time. Protein degradation and muscle fiber changes during storage can result in toughening or loss of juiciness, negatively impacting consumer perception and satisfaction.
Furthermore, there is growing consumer demand for "clean label" products, pushing the industry to find natural preservation methods. This trend conflicts with the effectiveness of traditional chemical preservatives, creating a need for innovative, natural solutions that can match or exceed the performance of synthetic additives.
The global nature of the poultry supply chain introduces additional complexities. Varying regulations across different markets, extended transportation times, and diverse environmental conditions during distribution all contribute to the challenge of maintaining consistent quality and safety standards.
Lastly, the industry faces increasing pressure to reduce food waste while simultaneously extending shelf life. This necessitates the development of preservation techniques that not only prolong freshness but also maintain nutritional value and sensory qualities throughout the extended shelf life period. The search for such comprehensive solutions that address multiple preservation challenges simultaneously remains an ongoing endeavor in the poultry industry.
Oxidation is another major challenge, causing rancidity and off-flavors in poultry products. This process is accelerated by the high content of unsaturated fatty acids in poultry meat, making it particularly susceptible to oxidative deterioration. The resulting changes in flavor, color, and nutritional value significantly impact consumer acceptance and product marketability.
Moisture loss during storage and distribution presents a dual problem. Excessive moisture loss leads to weight reduction, affecting profitability, while inadequate moisture control can create an environment conducive to microbial growth. Striking the right balance is crucial but often difficult to achieve consistently across various storage and transportation conditions.
The industry also grapples with the challenge of maintaining the texture and tenderness of poultry products over time. Protein degradation and muscle fiber changes during storage can result in toughening or loss of juiciness, negatively impacting consumer perception and satisfaction.
Furthermore, there is growing consumer demand for "clean label" products, pushing the industry to find natural preservation methods. This trend conflicts with the effectiveness of traditional chemical preservatives, creating a need for innovative, natural solutions that can match or exceed the performance of synthetic additives.
The global nature of the poultry supply chain introduces additional complexities. Varying regulations across different markets, extended transportation times, and diverse environmental conditions during distribution all contribute to the challenge of maintaining consistent quality and safety standards.
Lastly, the industry faces increasing pressure to reduce food waste while simultaneously extending shelf life. This necessitates the development of preservation techniques that not only prolong freshness but also maintain nutritional value and sensory qualities throughout the extended shelf life period. The search for such comprehensive solutions that address multiple preservation challenges simultaneously remains an ongoing endeavor in the poultry industry.
Existing PGA Applications in Food Preservation
01 Stabilization methods for polyglutamic acid
Various stabilization methods are employed to extend the shelf-life of polyglutamic acid. These include the use of antioxidants, pH adjustments, and the addition of preservatives. Such techniques help prevent degradation and maintain the acid's efficacy over time.- Stabilization methods for polyglutamic acid: Various stabilization methods are employed to extend the shelf-life of polyglutamic acid. These include the use of preservatives, pH adjustment, and the addition of antioxidants. Such techniques help maintain the structural integrity and functional properties of polyglutamic acid over time, ensuring its efficacy in various applications.
- Formulation strategies for polyglutamic acid products: Specific formulation strategies are developed to enhance the shelf-life of polyglutamic acid-containing products. These may involve the use of compatible excipients, encapsulation techniques, or the development of anhydrous formulations. Such approaches aim to protect polyglutamic acid from degradation factors like moisture, light, and temperature.
- Storage conditions for polyglutamic acid: Optimal storage conditions are crucial for maintaining the shelf-life of polyglutamic acid. This includes controlling temperature, humidity, and light exposure. Proper packaging materials and methods are also employed to protect the compound from environmental factors that could lead to degradation.
- Analytical methods for shelf-life determination: Various analytical techniques are used to assess and predict the shelf-life of polyglutamic acid. These may include chromatography, spectroscopy, and stability testing protocols. Such methods help in monitoring the quality and stability of polyglutamic acid over time, enabling accurate shelf-life predictions.
- Modification of polyglutamic acid for improved stability: Chemical or physical modifications of polyglutamic acid are explored to enhance its stability and extend shelf-life. This may involve cross-linking, conjugation with other molecules, or the development of novel derivatives. Such modifications aim to improve the resistance of polyglutamic acid to degradation factors, thereby prolonging its shelf-life.
02 Formulation techniques for improved stability
Specific formulation techniques are utilized to enhance the stability of polyglutamic acid products. These may involve encapsulation, the use of specific carriers or excipients, and optimized manufacturing processes to create more stable end products with extended shelf-life.Expand Specific Solutions03 Storage conditions for prolonged shelf-life
Proper storage conditions play a crucial role in maintaining the shelf-life of polyglutamic acid. Factors such as temperature control, protection from light and moisture, and appropriate packaging materials are considered to maximize product longevity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quality control and testing methods
Rigorous quality control measures and testing methods are implemented to ensure the stability and shelf-life of polyglutamic acid products. These include accelerated stability testing, microbial contamination checks, and periodic evaluations of physical and chemical properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications affecting shelf-life considerations
Emerging applications of polyglutamic acid in various industries, such as cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals, necessitate specific shelf-life considerations. These new uses may require tailored stabilization approaches and packaging solutions to meet industry-specific standards and regulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PGA Production and Poultry Processing
The market for polyglutamic acid in poultry shelf-life extension is in its growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the food industry's need for natural preservatives. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with potential for significant expansion. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Ajinomoto, Kao Corp., and CJ CheilJedang leading research and development efforts. These firms are exploring various applications of polyglutamic acid in food preservation, leveraging their expertise in biotechnology and food science. Academic institutions such as China Agricultural University and Huazhong Agricultural University are also contributing to the knowledge base, indicating a collaborative ecosystem between industry and academia in this emerging field.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto Co., Inc. has developed a polyglutamic acid (PGA) based solution for extending the shelf life of poultry products. Their approach involves applying a PGA coating to the surface of poultry, creating a protective barrier against microbial growth. The PGA coating is produced through fermentation of Bacillus subtilis, resulting in a high molecular weight polymer[1]. This natural, biodegradable coating helps maintain moisture content while inhibiting bacterial proliferation. Ajinomoto's research has shown that PGA-treated poultry can maintain freshness for up to 2-3 days longer than untreated samples under refrigerated conditions[2]. The company has also explored combining PGA with other natural preservatives like rosemary extract to enhance its antimicrobial properties[3].
Strengths: Natural and biodegradable solution, effective moisture retention, and proven shelf-life extension. Weaknesses: May alter the texture of poultry skin, potential cost implications for large-scale implementation.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corp. has developed a novel approach using polyglutamic acid (PGA) to extend the shelf life of poultry products. Their method involves incorporating PGA into a spray-on solution that forms a protective film on the surface of poultry meat. This PGA-based film acts as a barrier against oxygen and moisture, effectively slowing down oxidation processes and microbial growth. Kao's research has demonstrated that their PGA solution can reduce moisture loss by up to 30% compared to untreated samples[1]. Additionally, the company has engineered their PGA to have enhanced antimicrobial properties, showing a significant reduction in bacterial counts on treated poultry surfaces over a 7-day period[2]. The PGA film is also designed to be tasteless and odorless, ensuring it doesn't affect the sensory qualities of the poultry[3].
Strengths: Effective moisture retention, enhanced antimicrobial properties, and preservation of sensory qualities. Weaknesses: May require specialized application equipment, potential regulatory hurdles for food-contact substances.
Mechanisms of PGA in Prolonging Poultry Shelf-life
FEED COMPOSITION CONTAINING POLY-'gamma'-GLUTAMIC ACID
PatentWO1996035339A1
Innovation
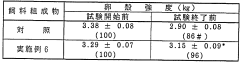
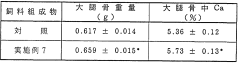
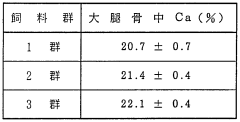
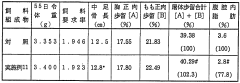
- Incorporating poly-γ-glutamic acid into animal feeds to enhance mineral absorption and reduce body fat, as it solubilizes minerals in the intestinal tract and is resistant to digestive enzymes, promoting bone formation and eggshell strength without degrading.
Apparatus for extending shelf-life of meat and poultry and method of using the same
PatentPendingUS20240108035A1
Innovation
- An integrated packaging system using self-activated oxygen scavengers and modified horizontal form, fill, and seal equipment to create a zero-oxygen environment within master-bags, reducing oxygen concentration to 0 ppm rapidly, thereby preserving the metmyoglobin reducing activity and extending the shelf-life of retail-ready meat cuts.
Food Safety Regulations for PGA Use in Poultry
The use of polyglutamic acid (PGA) in poultry preservation is subject to stringent food safety regulations to ensure consumer protection and maintain product quality. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of food additives, including PGA, under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
PGA is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food products, including poultry. However, manufacturers must adhere to specific guidelines regarding its application and concentration levels. The FDA stipulates that PGA should be used in accordance with good manufacturing practices (GMP) and at levels not exceeding those necessary to achieve the intended technical effect.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated PGA and deemed it safe for use in food products, including poultry. In the European Union, PGA is regulated under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives, which sets out the conditions for its use and maximum permitted levels.
Regulatory bodies require manufacturers to conduct thorough safety assessments and provide scientific evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of PGA in poultry preservation. This includes toxicological studies, stability tests, and shelf-life evaluations to demonstrate that PGA does not pose any health risks to consumers when used as intended.
Labeling requirements for poultry products containing PGA vary by jurisdiction. In general, manufacturers must clearly indicate the presence of PGA on product labels, either by its full name or appropriate E-number (E-411 in the EU). This ensures transparency and allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase.
Food safety regulations also mandate strict hygiene and quality control measures throughout the poultry processing and packaging stages where PGA is applied. Manufacturers must implement Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems to identify and mitigate potential food safety risks associated with PGA use.
Regular inspections and audits are conducted by regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with food safety regulations. These inspections may include on-site visits, product sampling, and laboratory testing to verify that PGA is being used in accordance with established guidelines and that poultry products meet all safety and quality standards.
As research on PGA continues to evolve, regulatory bodies periodically review and update their guidelines. Manufacturers and food processors must stay informed about any changes in regulations and adjust their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of poultry products treated with PGA.
PGA is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food products, including poultry. However, manufacturers must adhere to specific guidelines regarding its application and concentration levels. The FDA stipulates that PGA should be used in accordance with good manufacturing practices (GMP) and at levels not exceeding those necessary to achieve the intended technical effect.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated PGA and deemed it safe for use in food products, including poultry. In the European Union, PGA is regulated under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives, which sets out the conditions for its use and maximum permitted levels.
Regulatory bodies require manufacturers to conduct thorough safety assessments and provide scientific evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of PGA in poultry preservation. This includes toxicological studies, stability tests, and shelf-life evaluations to demonstrate that PGA does not pose any health risks to consumers when used as intended.
Labeling requirements for poultry products containing PGA vary by jurisdiction. In general, manufacturers must clearly indicate the presence of PGA on product labels, either by its full name or appropriate E-number (E-411 in the EU). This ensures transparency and allows consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase.
Food safety regulations also mandate strict hygiene and quality control measures throughout the poultry processing and packaging stages where PGA is applied. Manufacturers must implement Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) systems to identify and mitigate potential food safety risks associated with PGA use.
Regular inspections and audits are conducted by regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with food safety regulations. These inspections may include on-site visits, product sampling, and laboratory testing to verify that PGA is being used in accordance with established guidelines and that poultry products meet all safety and quality standards.
As research on PGA continues to evolve, regulatory bodies periodically review and update their guidelines. Manufacturers and food processors must stay informed about any changes in regulations and adjust their practices accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of poultry products treated with PGA.
Environmental Impact of PGA in Food Packaging
The use of polyglutamic acid (PGA) in food packaging for poultry products presents a significant opportunity to reduce environmental impact while extending shelf life. PGA, a biodegradable and non-toxic polymer, offers a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic packaging materials.
When used in food packaging, PGA forms a protective barrier that helps maintain the freshness of poultry products. This extended shelf life directly contributes to reducing food waste, a major environmental concern. By keeping poultry products fresh for longer periods, fewer products are discarded due to spoilage, thereby decreasing the overall waste generated in the food supply chain.
The biodegradability of PGA is a key factor in its positive environmental impact. Unlike traditional plastic packaging, which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, PGA-based packaging materials break down naturally in a relatively short time. This characteristic significantly reduces the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, mitigating long-term environmental damage.
Furthermore, the production of PGA involves less energy-intensive processes compared to the manufacture of petroleum-based plastics. This results in a lower carbon footprint associated with packaging production. The renewable nature of PGA's raw materials, often derived from bacterial fermentation of agricultural by-products, also contributes to its sustainability profile.
PGA's ability to be produced from various renewable resources adds to its environmental benefits. It can be synthesized using agricultural waste products, turning potential waste into valuable packaging material. This not only reduces the demand for virgin resources but also provides a solution for agricultural waste management.
The use of PGA in food packaging also aligns with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the adoption of PGA-based packaging can enhance brand image and market competitiveness for poultry producers.
However, it's important to consider the full lifecycle impact of PGA packaging. While it offers significant advantages in terms of biodegradability and waste reduction, factors such as the energy and resources required for its production and distribution must be carefully evaluated to ensure a net positive environmental impact.
In conclusion, the incorporation of PGA in food packaging for poultry represents a promising approach to reducing environmental impact. Its ability to extend shelf life while offering a biodegradable alternative to conventional plastics addresses multiple environmental concerns simultaneously. As research and development in this area continue, PGA-based packaging solutions are likely to play an increasingly important role in sustainable food packaging strategies.
When used in food packaging, PGA forms a protective barrier that helps maintain the freshness of poultry products. This extended shelf life directly contributes to reducing food waste, a major environmental concern. By keeping poultry products fresh for longer periods, fewer products are discarded due to spoilage, thereby decreasing the overall waste generated in the food supply chain.
The biodegradability of PGA is a key factor in its positive environmental impact. Unlike traditional plastic packaging, which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, PGA-based packaging materials break down naturally in a relatively short time. This characteristic significantly reduces the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, mitigating long-term environmental damage.
Furthermore, the production of PGA involves less energy-intensive processes compared to the manufacture of petroleum-based plastics. This results in a lower carbon footprint associated with packaging production. The renewable nature of PGA's raw materials, often derived from bacterial fermentation of agricultural by-products, also contributes to its sustainability profile.
PGA's ability to be produced from various renewable resources adds to its environmental benefits. It can be synthesized using agricultural waste products, turning potential waste into valuable packaging material. This not only reduces the demand for virgin resources but also provides a solution for agricultural waste management.
The use of PGA in food packaging also aligns with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the adoption of PGA-based packaging can enhance brand image and market competitiveness for poultry producers.
However, it's important to consider the full lifecycle impact of PGA packaging. While it offers significant advantages in terms of biodegradability and waste reduction, factors such as the energy and resources required for its production and distribution must be carefully evaluated to ensure a net positive environmental impact.
In conclusion, the incorporation of PGA in food packaging for poultry represents a promising approach to reducing environmental impact. Its ability to extend shelf life while offering a biodegradable alternative to conventional plastics addresses multiple environmental concerns simultaneously. As research and development in this area continue, PGA-based packaging solutions are likely to play an increasingly important role in sustainable food packaging strategies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!