How Thermochromic Additives Facilitate Polypropylene Applications
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Thermochromic PP Tech Evolution and Objectives
Thermochromic additives have revolutionized the applications of polypropylene (PP) over the past few decades. These innovative materials have enabled PP to change color in response to temperature variations, opening up new possibilities in various industries. The evolution of thermochromic PP technology can be traced back to the 1970s when the first thermochromic dyes were developed.
Initially, the primary focus was on creating basic color-changing effects in PP products. However, as research progressed, the technology evolved to offer more sophisticated and precise color transitions. The 1990s saw significant advancements in thermochromic PP, with improved stability and durability of the additives. This period marked the beginning of widespread commercial applications, particularly in packaging and consumer goods.
The early 2000s brought about a shift towards environmentally friendly thermochromic additives, addressing concerns about toxicity and sustainability. This led to the development of organic-based thermochromic compounds that were safer and more eco-friendly. Concurrently, efforts were made to enhance the temperature sensitivity and color intensity of these additives, resulting in more vibrant and responsive PP products.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating multi-functional thermochromic PP materials. These advanced composites not only change color but also exhibit additional properties such as improved mechanical strength, UV resistance, or antimicrobial activity. The integration of nanotechnology has played a crucial role in achieving these multi-functional characteristics.
The current objectives in thermochromic PP technology are multifaceted. One primary goal is to expand the temperature range at which color changes occur, allowing for broader applications in extreme environments. Another objective is to improve the longevity and consistency of color-changing effects, ensuring that products maintain their functionality over extended periods.
Researchers are also working on developing reversible thermochromic systems that can switch between multiple colors, offering more complex visual indicators. Additionally, there is a growing interest in combining thermochromic properties with other smart materials, such as shape-memory polymers or self-healing compounds, to create highly adaptive PP products.
The future of thermochromic PP technology aims to push the boundaries of what's possible in terms of precision, responsiveness, and functionality. This includes the development of thermochromic PP that can respond to minute temperature changes, potentially opening up applications in fields like medical diagnostics or advanced thermal management systems. As the technology continues to evolve, the goal is to create increasingly sophisticated, sustainable, and versatile thermochromic PP materials that can meet the diverse needs of various industries and contribute to innovative solutions for complex challenges.
Initially, the primary focus was on creating basic color-changing effects in PP products. However, as research progressed, the technology evolved to offer more sophisticated and precise color transitions. The 1990s saw significant advancements in thermochromic PP, with improved stability and durability of the additives. This period marked the beginning of widespread commercial applications, particularly in packaging and consumer goods.
The early 2000s brought about a shift towards environmentally friendly thermochromic additives, addressing concerns about toxicity and sustainability. This led to the development of organic-based thermochromic compounds that were safer and more eco-friendly. Concurrently, efforts were made to enhance the temperature sensitivity and color intensity of these additives, resulting in more vibrant and responsive PP products.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating multi-functional thermochromic PP materials. These advanced composites not only change color but also exhibit additional properties such as improved mechanical strength, UV resistance, or antimicrobial activity. The integration of nanotechnology has played a crucial role in achieving these multi-functional characteristics.
The current objectives in thermochromic PP technology are multifaceted. One primary goal is to expand the temperature range at which color changes occur, allowing for broader applications in extreme environments. Another objective is to improve the longevity and consistency of color-changing effects, ensuring that products maintain their functionality over extended periods.
Researchers are also working on developing reversible thermochromic systems that can switch between multiple colors, offering more complex visual indicators. Additionally, there is a growing interest in combining thermochromic properties with other smart materials, such as shape-memory polymers or self-healing compounds, to create highly adaptive PP products.
The future of thermochromic PP technology aims to push the boundaries of what's possible in terms of precision, responsiveness, and functionality. This includes the development of thermochromic PP that can respond to minute temperature changes, potentially opening up applications in fields like medical diagnostics or advanced thermal management systems. As the technology continues to evolve, the goal is to create increasingly sophisticated, sustainable, and versatile thermochromic PP materials that can meet the diverse needs of various industries and contribute to innovative solutions for complex challenges.
Market Demand for Smart Packaging Solutions
The market demand for smart packaging solutions incorporating thermochromic additives in polypropylene applications has been steadily growing in recent years. This trend is driven by the increasing need for innovative packaging that can enhance product safety, quality assurance, and consumer engagement. Thermochromic additives, when integrated into polypropylene packaging, offer a visual indication of temperature changes, making them particularly valuable in various industries.
In the food and beverage sector, there is a significant demand for temperature-sensitive packaging that can indicate whether products have been exposed to potentially harmful temperatures during storage or transportation. This is crucial for maintaining food safety and quality, especially for perishable goods. The ability of thermochromic polypropylene packaging to change color when exposed to specific temperature thresholds provides consumers with an easy-to-understand visual cue about the product's condition.
The pharmaceutical industry also shows a strong interest in smart packaging solutions using thermochromic additives. With the increasing complexity of drug supply chains and the critical nature of temperature control for many medications, there is a growing need for packaging that can verify proper storage conditions. Thermochromic polypropylene packaging can help ensure the efficacy and safety of temperature-sensitive drugs, vaccines, and biological products.
In the cosmetics and personal care market, brands are looking for ways to differentiate their products and enhance user experience. Thermochromic packaging can add an element of interactivity and novelty to products, such as color-changing containers that respond to body heat or ambient temperature. This not only serves a functional purpose but also creates a unique selling point for brands in a highly competitive market.
The beverage industry, particularly for alcoholic and premium non-alcoholic drinks, has shown interest in thermochromic packaging to indicate optimal serving temperatures. This feature can enhance the consumer experience by ensuring that beverages are consumed at their best quality, potentially increasing brand loyalty and perceived value.
E-commerce and logistics companies are exploring the use of thermochromic polypropylene in shipping materials to monitor temperature exposure during transit. This is particularly important for temperature-sensitive products and can help reduce waste and improve supply chain efficiency by providing real-time temperature monitoring without the need for electronic devices.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in packaging decisions, the market is showing a preference for solutions that combine smart features with eco-friendly materials. Polypropylene, being recyclable and relatively lightweight, aligns well with these sustainability goals when combined with thermochromic additives.
The growing consumer awareness and demand for product authenticity and safety are also driving the adoption of smart packaging solutions. Thermochromic features can serve as a form of tamper-evidence or authenticity verification, addressing concerns about product integrity and counterfeiting.
In the food and beverage sector, there is a significant demand for temperature-sensitive packaging that can indicate whether products have been exposed to potentially harmful temperatures during storage or transportation. This is crucial for maintaining food safety and quality, especially for perishable goods. The ability of thermochromic polypropylene packaging to change color when exposed to specific temperature thresholds provides consumers with an easy-to-understand visual cue about the product's condition.
The pharmaceutical industry also shows a strong interest in smart packaging solutions using thermochromic additives. With the increasing complexity of drug supply chains and the critical nature of temperature control for many medications, there is a growing need for packaging that can verify proper storage conditions. Thermochromic polypropylene packaging can help ensure the efficacy and safety of temperature-sensitive drugs, vaccines, and biological products.
In the cosmetics and personal care market, brands are looking for ways to differentiate their products and enhance user experience. Thermochromic packaging can add an element of interactivity and novelty to products, such as color-changing containers that respond to body heat or ambient temperature. This not only serves a functional purpose but also creates a unique selling point for brands in a highly competitive market.
The beverage industry, particularly for alcoholic and premium non-alcoholic drinks, has shown interest in thermochromic packaging to indicate optimal serving temperatures. This feature can enhance the consumer experience by ensuring that beverages are consumed at their best quality, potentially increasing brand loyalty and perceived value.
E-commerce and logistics companies are exploring the use of thermochromic polypropylene in shipping materials to monitor temperature exposure during transit. This is particularly important for temperature-sensitive products and can help reduce waste and improve supply chain efficiency by providing real-time temperature monitoring without the need for electronic devices.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in packaging decisions, the market is showing a preference for solutions that combine smart features with eco-friendly materials. Polypropylene, being recyclable and relatively lightweight, aligns well with these sustainability goals when combined with thermochromic additives.
The growing consumer awareness and demand for product authenticity and safety are also driving the adoption of smart packaging solutions. Thermochromic features can serve as a form of tamper-evidence or authenticity verification, addressing concerns about product integrity and counterfeiting.
Current Challenges in Thermochromic PP Applications
The integration of thermochromic additives into polypropylene (PP) applications presents several significant challenges that researchers and manufacturers are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is achieving consistent and reliable color-changing performance across various environmental conditions. The thermochromic effect in PP is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which can lead to inconsistent color transitions in real-world applications.
Another major challenge lies in maintaining the durability and longevity of thermochromic properties in PP products. Exposure to UV radiation, humidity, and repeated temperature cycles can cause degradation of the thermochromic additives over time, resulting in diminished color-changing capabilities or complete loss of functionality. This issue is particularly pronounced in outdoor applications or products subjected to frequent use and environmental stresses.
The compatibility between thermochromic additives and PP matrices poses another significant hurdle. Ensuring uniform dispersion of the additives throughout the polymer matrix without compromising the material's mechanical properties is crucial. Poor dispersion can lead to inconsistent color change, while excessive additive concentrations may negatively impact the strength, flexibility, or other physical characteristics of the PP product.
Cost-effectiveness remains a persistent challenge in thermochromic PP applications. The additives and processing techniques required to incorporate thermochromic properties into PP can significantly increase production costs, limiting widespread adoption in price-sensitive markets. Balancing the added functionality with economic viability is an ongoing concern for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the limited color palette available for thermochromic PP applications restricts design possibilities and potential use cases. Expanding the range of achievable colors and color-changing effects while maintaining performance and stability is a key area of focus for researchers in the field.
Regulatory compliance and safety considerations also present challenges, particularly in applications involving food contact or medical devices. Ensuring that thermochromic PP products meet stringent safety standards and do not leach harmful substances under various conditions is critical for market acceptance and consumer trust.
Lastly, the development of multi-functional thermochromic PP materials that combine color-changing properties with other desirable characteristics, such as antimicrobial properties or enhanced mechanical strength, remains a complex challenge. Integrating these diverse functionalities without compromising performance or increasing costs significantly is an area of active research and development in the field.
Another major challenge lies in maintaining the durability and longevity of thermochromic properties in PP products. Exposure to UV radiation, humidity, and repeated temperature cycles can cause degradation of the thermochromic additives over time, resulting in diminished color-changing capabilities or complete loss of functionality. This issue is particularly pronounced in outdoor applications or products subjected to frequent use and environmental stresses.
The compatibility between thermochromic additives and PP matrices poses another significant hurdle. Ensuring uniform dispersion of the additives throughout the polymer matrix without compromising the material's mechanical properties is crucial. Poor dispersion can lead to inconsistent color change, while excessive additive concentrations may negatively impact the strength, flexibility, or other physical characteristics of the PP product.
Cost-effectiveness remains a persistent challenge in thermochromic PP applications. The additives and processing techniques required to incorporate thermochromic properties into PP can significantly increase production costs, limiting widespread adoption in price-sensitive markets. Balancing the added functionality with economic viability is an ongoing concern for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the limited color palette available for thermochromic PP applications restricts design possibilities and potential use cases. Expanding the range of achievable colors and color-changing effects while maintaining performance and stability is a key area of focus for researchers in the field.
Regulatory compliance and safety considerations also present challenges, particularly in applications involving food contact or medical devices. Ensuring that thermochromic PP products meet stringent safety standards and do not leach harmful substances under various conditions is critical for market acceptance and consumer trust.
Lastly, the development of multi-functional thermochromic PP materials that combine color-changing properties with other desirable characteristics, such as antimicrobial properties or enhanced mechanical strength, remains a complex challenge. Integrating these diverse functionalities without compromising performance or increasing costs significantly is an area of active research and development in the field.
Existing Thermochromic PP Formulation Techniques
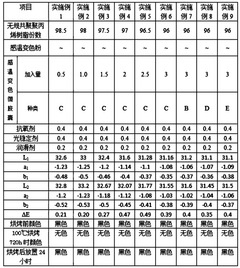
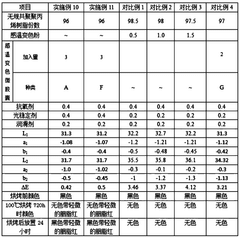
01 Thermochromic compositions and materials
Thermochromic additives are incorporated into various materials to create temperature-sensitive color-changing properties. These compositions can include leuco dyes, color developers, and solvents that respond to temperature changes, resulting in reversible color transitions. The thermochromic effect can be applied to a wide range of products, including textiles, plastics, and coatings.- Thermochromic compositions and materials: Thermochromic additives are incorporated into various materials to create compositions with temperature-dependent color-changing properties. These compositions can be used in inks, coatings, plastics, and other applications where visual temperature indication is desired. The thermochromic effect is typically achieved through the use of leuco dyes or liquid crystals that change their molecular structure in response to temperature variations.
- Temperature-sensitive color-changing textiles: Thermochromic additives are applied to textiles to create fabrics that change color in response to temperature changes. These smart textiles can be used in clothing, upholstery, and other fabric-based products to provide visual temperature feedback or aesthetic effects. The thermochromic properties are often achieved by incorporating microencapsulated thermochromic pigments into the fabric or coating.
- Thermochromic printing and packaging: Thermochromic additives are used in printing inks and packaging materials to create temperature-sensitive designs and labels. These applications can include security features, tamper-evident packaging, or interactive product labeling. The thermochromic properties allow for dynamic color changes that can indicate temperature exposure or provide visual engagement for consumers.
- Reversible and irreversible thermochromic systems: Thermochromic additives can be formulated to exhibit either reversible or irreversible color changes. Reversible systems return to their original color when the temperature is reversed, while irreversible systems undergo permanent color changes after exposure to specific temperatures. These different behaviors allow for diverse applications in temperature monitoring, safety indicators, and product authentication.
- Thermochromic liquid crystal technology: Liquid crystal-based thermochromic additives offer precise and tunable color-changing properties. These materials can display a range of colors across specific temperature intervals, making them suitable for high-resolution temperature mapping and visualization. Applications include thermal imaging, medical diagnostics, and scientific instruments that require accurate temperature indication.
02 Temperature-sensitive inks and printing methods
Thermochromic inks are developed for use in printing applications, allowing for the creation of temperature-sensitive designs and patterns. These inks can be formulated for various printing techniques, including inkjet, screen printing, and offset printing. The resulting prints exhibit color changes in response to temperature fluctuations, enabling interactive and dynamic visual effects.Expand Specific Solutions03 Smart textiles and wearable technology
Thermochromic additives are integrated into textile fibers and fabrics to create smart clothing and accessories. These materials can change color based on body temperature or environmental conditions, providing visual indicators of temperature changes. Applications include sportswear, safety gear, and fashion items with color-changing properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermochromic displays and indicators
Thermochromic materials are used to develop temperature-sensitive displays and indicators for various applications. These can include temperature gauges, safety indicators, and interactive displays that provide visual feedback based on temperature changes. The technology enables the creation of simple, low-power displays for temperature monitoring and user interaction.Expand Specific Solutions05 Encapsulation and stabilization of thermochromic additives
Techniques are developed to encapsulate and stabilize thermochromic additives, improving their durability and performance in various applications. This includes methods for microencapsulation, polymer matrix incorporation, and surface treatments to protect the thermochromic compounds from environmental factors and extend their functional lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Thermochromic Polymer Industry
The thermochromic additives market for polypropylene applications is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for smart packaging and temperature-sensitive products. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Milliken & Co., DuPont, and Chromatic Technologies leading innovation. These firms, along with others such as SABIC and Borealis AG, are developing more sophisticated and reliable thermochromic solutions, improving color change precision, durability, and compatibility with polypropylene. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring both established chemical giants and specialized additive manufacturers, indicating a maturing but still evolving market.
Milliken & Co. (South Carolina)
Technical Solution: Milliken & Co. has developed advanced thermochromic additives for polypropylene applications, focusing on reversible color-changing properties activated by temperature variations. Their technology incorporates microencapsulated thermochromic pigments into polypropylene matrices, allowing for precise control over color transition temperatures. The company's additives can be tailored to specific temperature ranges, typically between 15°C and 65°C, enabling a wide range of applications[1]. Milliken's thermochromic polypropylene compounds offer excellent dispersion and stability, maintaining color-changing performance even after multiple processing cycles. Their additives are compatible with various polypropylene grades and can be used in injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding processes[2].
Strengths: Highly customizable color transition temperatures, excellent dispersion in polypropylene, and stability during processing. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in extreme temperature environments and higher cost compared to conventional pigments.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed proprietary thermochromic additives for polypropylene applications, focusing on enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. Their technology incorporates advanced microencapsulation techniques to protect thermochromic pigments from degradation during processing and use. DuPont's additives offer a range of color-changing options, including multi-color transitions and reversible/irreversible changes. The company has also developed additives that combine thermochromic properties with other functional features such as UV resistance and antimicrobial properties[3]. DuPont's thermochromic polypropylene compounds have been successfully applied in packaging, consumer goods, and automotive applications, demonstrating excellent color stability and long-term performance[4].
Strengths: Multi-functional additives combining thermochromic properties with other features, wide range of color-changing options. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to advanced technology, may require specialized processing conditions.
Innovative Thermochromic Mechanisms for PP
Thermochromic polypropylene composite, preparation method for same, and applications thereof
PatentWO2018130120A1
Innovation
- A combination of polypropylene resin and thermochromic microcapsules is used. The core material of the microcapsules is triphenylmethane metal complex and the wall material is melamine formaldehyde resin. Microcapsules with a particle size of 10 to 50um are prepared through a specific preparation method. capsules, mixed with antioxidants, light stabilizers or lubricants, and melted and kneaded to prepare a thermochromic polypropylene composition.
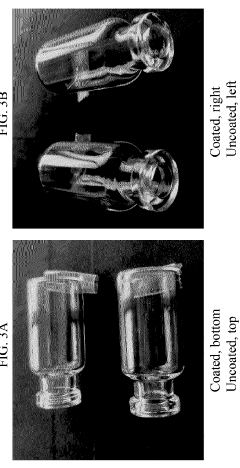
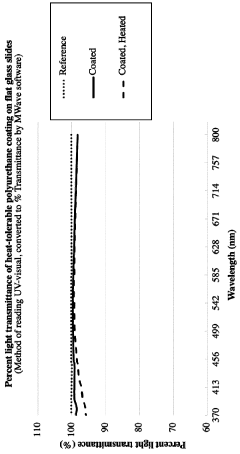
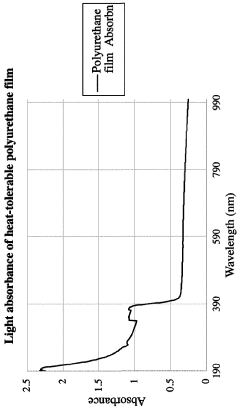
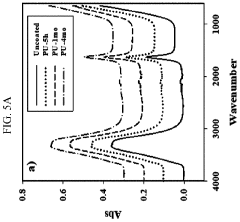
Polyurethane with high heat tolerance and other desirable properties including transparency, surface smoothness, desirable adhesiveness, resistance to impact damage, scratches and moisture, and method and use thereof
PatentInactiveCA3123892A1
Innovation
- A polyurethane composition comprising a polyfunctional isocyanate, a polyol with multiple hydroxyl groups, and optional additives such as antimicrobial agents, catalysts, and surface modification agents, formulated to achieve high heat tolerance, scratch resistance, and adhesion to glass and ceramic surfaces, with a specific molar ratio of isocyanate to hydroxyl groups to ensure proper crosslinking and reaction dynamics.
Environmental Impact of Thermochromic Additives
The environmental impact of thermochromic additives in polypropylene applications is a critical consideration as these materials gain popularity in various industries. These additives, which enable color changes in response to temperature fluctuations, introduce both benefits and potential concerns from an environmental perspective.
One of the primary environmental advantages of thermochromic polypropylene is its potential to reduce energy consumption. By providing visual cues about temperature changes, these materials can help optimize heating and cooling processes in various applications, leading to improved energy efficiency. For instance, in packaging applications, thermochromic indicators can signal when products have reached optimal temperatures, potentially reducing unnecessary refrigeration or heating.
However, the production and disposal of thermochromic additives raise important environmental questions. The synthesis of these compounds often involves complex chemical processes that may require significant energy inputs and potentially generate hazardous by-products. The environmental footprint of manufacturing these additives must be carefully assessed and balanced against their potential benefits in use.
The end-of-life management of thermochromic polypropylene products presents another environmental challenge. While polypropylene itself is recyclable, the presence of thermochromic additives may complicate recycling processes. These additives could potentially contaminate recycling streams or reduce the quality of recycled materials, necessitating the development of specialized recycling techniques or alternative disposal methods.
Leaching of thermochromic compounds from polypropylene products during use or disposal is another environmental concern. Depending on their chemical composition, these additives may pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if they enter water systems. Research into the long-term environmental fate and potential toxicity of these compounds is crucial to ensure their safe use and disposal.
On the positive side, the durability and reusability of thermochromic polypropylene products could contribute to waste reduction. By providing temperature-sensitive functionality, these materials may extend the useful life of certain products or enable their repurposing, potentially decreasing overall material consumption and waste generation.
The environmental impact of thermochromic additives in polypropylene applications also extends to their potential role in promoting sustainable behaviors. For example, in consumer products, visible temperature indicators could encourage more efficient energy use or proper food storage, indirectly contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
As the use of thermochromic polypropylene expands, ongoing research and life cycle assessments are essential to fully understand and mitigate its environmental impacts. This includes exploring bio-based or more environmentally friendly thermochromic additives, improving production processes to reduce environmental footprints, and developing effective recycling and disposal strategies for these materials.
One of the primary environmental advantages of thermochromic polypropylene is its potential to reduce energy consumption. By providing visual cues about temperature changes, these materials can help optimize heating and cooling processes in various applications, leading to improved energy efficiency. For instance, in packaging applications, thermochromic indicators can signal when products have reached optimal temperatures, potentially reducing unnecessary refrigeration or heating.
However, the production and disposal of thermochromic additives raise important environmental questions. The synthesis of these compounds often involves complex chemical processes that may require significant energy inputs and potentially generate hazardous by-products. The environmental footprint of manufacturing these additives must be carefully assessed and balanced against their potential benefits in use.
The end-of-life management of thermochromic polypropylene products presents another environmental challenge. While polypropylene itself is recyclable, the presence of thermochromic additives may complicate recycling processes. These additives could potentially contaminate recycling streams or reduce the quality of recycled materials, necessitating the development of specialized recycling techniques or alternative disposal methods.
Leaching of thermochromic compounds from polypropylene products during use or disposal is another environmental concern. Depending on their chemical composition, these additives may pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if they enter water systems. Research into the long-term environmental fate and potential toxicity of these compounds is crucial to ensure their safe use and disposal.
On the positive side, the durability and reusability of thermochromic polypropylene products could contribute to waste reduction. By providing temperature-sensitive functionality, these materials may extend the useful life of certain products or enable their repurposing, potentially decreasing overall material consumption and waste generation.
The environmental impact of thermochromic additives in polypropylene applications also extends to their potential role in promoting sustainable behaviors. For example, in consumer products, visible temperature indicators could encourage more efficient energy use or proper food storage, indirectly contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
As the use of thermochromic polypropylene expands, ongoing research and life cycle assessments are essential to fully understand and mitigate its environmental impacts. This includes exploring bio-based or more environmentally friendly thermochromic additives, improving production processes to reduce environmental footprints, and developing effective recycling and disposal strategies for these materials.
Regulatory Framework for Smart Packaging Materials
The regulatory framework for smart packaging materials, including those incorporating thermochromic additives in polypropylene applications, is a complex and evolving landscape. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the safety of food contact materials. The FDA's Food Contact Notification (FCN) program is the primary mechanism for reviewing and approving new food contact substances, including smart packaging components.
For thermochromic additives in polypropylene, manufacturers must demonstrate that these substances do not migrate into food at levels that could pose health risks. The FDA's Threshold of Regulation (TOR) exemption process may apply if the migration levels are extremely low. Additionally, the Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status may be applicable for certain additives with a history of safe use.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food contact materials. The EU's Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 sets out the general principles for all food contact materials, while specific measures exist for certain materials like plastics. Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food is particularly relevant for polypropylene applications with thermochromic additives.
The EU's approach includes a positive list of authorized substances, specific migration limits, and overall migration limits. Manufacturers must provide extensive safety data and migration studies to obtain approval for new additives. The concept of functional barriers is also important, as it may allow the use of non-listed substances behind an effective barrier layer.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) regulates food contact materials through the Food Sanitation Act. The Japanese regulatory system includes a positive list of substances and specifications for various materials, including plastics like polypropylene. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with these standards when incorporating thermochromic additives.
Globally, there is a trend towards more stringent regulations and increased scrutiny of novel packaging technologies. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the FAO and WHO, provides international food standards that influence national regulations. Many countries are developing or updating their regulatory frameworks to address emerging technologies in food packaging, including smart packaging materials.
For thermochromic additives in polypropylene, manufacturers must demonstrate that these substances do not migrate into food at levels that could pose health risks. The FDA's Threshold of Regulation (TOR) exemption process may apply if the migration levels are extremely low. Additionally, the Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status may be applicable for certain additives with a history of safe use.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is responsible for evaluating the safety of food contact materials. The EU's Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 sets out the general principles for all food contact materials, while specific measures exist for certain materials like plastics. Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food is particularly relevant for polypropylene applications with thermochromic additives.
The EU's approach includes a positive list of authorized substances, specific migration limits, and overall migration limits. Manufacturers must provide extensive safety data and migration studies to obtain approval for new additives. The concept of functional barriers is also important, as it may allow the use of non-listed substances behind an effective barrier layer.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) regulates food contact materials through the Food Sanitation Act. The Japanese regulatory system includes a positive list of substances and specifications for various materials, including plastics like polypropylene. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with these standards when incorporating thermochromic additives.
Globally, there is a trend towards more stringent regulations and increased scrutiny of novel packaging technologies. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the FAO and WHO, provides international food standards that influence national regulations. Many countries are developing or updating their regulatory frameworks to address emerging technologies in food packaging, including smart packaging materials.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!