How to Evaluate Suppliers — Test Evidence & Warranty
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Supplier Evaluation Background and Objectives
In the rapidly evolving global marketplace, supplier evaluation has become a critical component of organizational success. The historical approach to supplier selection often prioritized cost considerations above all else, but modern business environments demand a more comprehensive assessment framework. This technical research aims to explore advanced methodologies for evaluating suppliers with specific focus on test evidence and warranty provisions as key indicators of supplier reliability and product quality.
The evolution of supplier evaluation practices has undergone significant transformation over the past decades. Initially focused on simple metrics like price and delivery time, evaluation criteria have expanded to include quality management systems, technical capabilities, financial stability, and more recently, sustainability practices. This progression reflects the increasing complexity of supply chains and the growing recognition of suppliers as strategic partners rather than mere vendors.
Test evidence represents a crucial aspect of supplier evaluation, providing objective data regarding product performance, durability, and compliance with specifications. The standardization of testing protocols across industries has created opportunities for more consistent supplier comparisons, yet challenges remain in establishing universally accepted benchmarks that account for industry-specific requirements and technological advancements.
Warranty provisions serve as tangible manifestations of a supplier's confidence in their products and willingness to stand behind them. The structure, duration, and scope of warranties can provide valuable insights into a supplier's quality control processes and long-term commitment to customer satisfaction. Recent trends indicate a shift toward performance-based warranties that align supplier incentives with customer outcomes.
The primary objective of this technical research is to develop a systematic framework for evaluating suppliers that integrates test evidence and warranty provisions into a comprehensive assessment model. This framework aims to enable organizations to make more informed supplier selection decisions, reduce supply chain risks, and establish more productive supplier relationships based on transparent performance metrics.
Secondary objectives include identifying industry best practices for documenting and validating test evidence, analyzing the correlation between warranty terms and actual product performance, and exploring innovative approaches to supplier evaluation that leverage emerging technologies such as blockchain for verification and artificial intelligence for predictive quality analysis.
By establishing more rigorous and objective evaluation criteria, organizations can move beyond subjective assessments and build supplier relationships founded on demonstrable capabilities and commitments. This research seeks to contribute to this evolution by providing actionable insights and methodologies for effective supplier evaluation.
The evolution of supplier evaluation practices has undergone significant transformation over the past decades. Initially focused on simple metrics like price and delivery time, evaluation criteria have expanded to include quality management systems, technical capabilities, financial stability, and more recently, sustainability practices. This progression reflects the increasing complexity of supply chains and the growing recognition of suppliers as strategic partners rather than mere vendors.
Test evidence represents a crucial aspect of supplier evaluation, providing objective data regarding product performance, durability, and compliance with specifications. The standardization of testing protocols across industries has created opportunities for more consistent supplier comparisons, yet challenges remain in establishing universally accepted benchmarks that account for industry-specific requirements and technological advancements.
Warranty provisions serve as tangible manifestations of a supplier's confidence in their products and willingness to stand behind them. The structure, duration, and scope of warranties can provide valuable insights into a supplier's quality control processes and long-term commitment to customer satisfaction. Recent trends indicate a shift toward performance-based warranties that align supplier incentives with customer outcomes.
The primary objective of this technical research is to develop a systematic framework for evaluating suppliers that integrates test evidence and warranty provisions into a comprehensive assessment model. This framework aims to enable organizations to make more informed supplier selection decisions, reduce supply chain risks, and establish more productive supplier relationships based on transparent performance metrics.
Secondary objectives include identifying industry best practices for documenting and validating test evidence, analyzing the correlation between warranty terms and actual product performance, and exploring innovative approaches to supplier evaluation that leverage emerging technologies such as blockchain for verification and artificial intelligence for predictive quality analysis.
By establishing more rigorous and objective evaluation criteria, organizations can move beyond subjective assessments and build supplier relationships founded on demonstrable capabilities and commitments. This research seeks to contribute to this evolution by providing actionable insights and methodologies for effective supplier evaluation.
Market Requirements for Supplier Quality Assurance
The global market for supplier quality assurance is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing complexity in supply chains and heightened consumer expectations for product quality. Organizations across industries are recognizing that robust supplier evaluation mechanisms are essential for maintaining competitive advantage and brand reputation. Current market research indicates that companies with mature supplier quality assurance programs experience 50% fewer quality incidents and achieve approximately 30% lower total cost of poor quality compared to industry averages.
Key market requirements for supplier quality assurance focus on transparency, reliability, and standardization of evaluation processes. Procurement and quality assurance departments increasingly demand comprehensive test evidence documentation that demonstrates suppliers' adherence to industry standards and specifications. This documentation must be readily accessible, consistently formatted, and traceable throughout the product lifecycle.
Warranty terms have emerged as a critical evaluation criterion, with organizations seeking suppliers who offer robust warranty provisions that align with their risk management strategies. The market shows a clear preference for warranties that provide specific performance guarantees rather than generic coverage statements. Companies are willing to pay premium prices for suppliers who can demonstrate lower warranty claim rates through statistical evidence and historical performance data.
Industry-specific certification requirements continue to shape the supplier evaluation landscape. In regulated sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, compliance with standards like IATF 16949, AS9100, and ISO 13485 has become mandatory rather than optional. Market data shows that 87% of Fortune 500 companies now require suppliers to maintain at least one industry-specific quality certification.
Digital transformation is revolutionizing supplier quality assurance processes, with growing demand for integrated platforms that can automatically collect, analyze, and report supplier performance metrics. Real-time monitoring capabilities and predictive analytics for supplier quality issues represent the fastest-growing segment in quality management software, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15%.
Risk-based approaches to supplier evaluation are gaining prominence, with organizations prioritizing assessment resources based on the potential impact of supplier non-conformance. This trend is particularly evident in industries with complex products where component failures can lead to significant safety concerns or financial losses. Market leaders are implementing sophisticated risk scoring methodologies that incorporate both historical performance data and predictive indicators.
Key market requirements for supplier quality assurance focus on transparency, reliability, and standardization of evaluation processes. Procurement and quality assurance departments increasingly demand comprehensive test evidence documentation that demonstrates suppliers' adherence to industry standards and specifications. This documentation must be readily accessible, consistently formatted, and traceable throughout the product lifecycle.
Warranty terms have emerged as a critical evaluation criterion, with organizations seeking suppliers who offer robust warranty provisions that align with their risk management strategies. The market shows a clear preference for warranties that provide specific performance guarantees rather than generic coverage statements. Companies are willing to pay premium prices for suppliers who can demonstrate lower warranty claim rates through statistical evidence and historical performance data.
Industry-specific certification requirements continue to shape the supplier evaluation landscape. In regulated sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, compliance with standards like IATF 16949, AS9100, and ISO 13485 has become mandatory rather than optional. Market data shows that 87% of Fortune 500 companies now require suppliers to maintain at least one industry-specific quality certification.
Digital transformation is revolutionizing supplier quality assurance processes, with growing demand for integrated platforms that can automatically collect, analyze, and report supplier performance metrics. Real-time monitoring capabilities and predictive analytics for supplier quality issues represent the fastest-growing segment in quality management software, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15%.
Risk-based approaches to supplier evaluation are gaining prominence, with organizations prioritizing assessment resources based on the potential impact of supplier non-conformance. This trend is particularly evident in industries with complex products where component failures can lead to significant safety concerns or financial losses. Market leaders are implementing sophisticated risk scoring methodologies that incorporate both historical performance data and predictive indicators.
Current Challenges in Supplier Evaluation Methods
The current supplier evaluation landscape faces significant challenges that hinder effective assessment of test evidence and warranty offerings. Traditional evaluation methods often rely heavily on price comparisons and basic capability assessments, neglecting the critical analysis of test evidence validity and warranty substance. This creates a fundamental disconnect between procurement decisions and long-term product reliability.
Data inconsistency represents a major obstacle in supplier evaluation. Organizations frequently encounter disparate testing methodologies, non-standardized reporting formats, and varying certification standards across different suppliers. This heterogeneity makes direct comparisons exceedingly difficult and can obscure critical quality indicators that should inform decision-making processes.
The verification gap presents another substantial challenge. Procurement teams typically lack specialized technical expertise to properly validate test claims and evidence provided by suppliers. Without robust verification mechanisms, organizations remain vulnerable to misleading or incomplete test data that may not accurately reflect product performance under real-world conditions or over extended timeframes.
Warranty evaluation suffers from similar complexity issues. The legal language in warranty documents often contains nuanced exclusions and limitations that require specialized knowledge to interpret correctly. Many organizations lack systematic approaches to analyze warranty terms beyond surface-level coverage periods, missing critical details about claim processes, response times, and exclusion clauses that significantly impact the actual value of warranty offerings.
Global supply chain dynamics further complicate evaluation efforts. With suppliers operating across different regulatory environments, organizations struggle to establish consistent evaluation frameworks that account for regional variations in testing standards, certification requirements, and warranty enforcement mechanisms. This geographic disparity creates additional layers of complexity in supplier assessment.
Digital transformation has introduced new evaluation challenges related to cybersecurity and data protection. Traditional supplier assessment methods rarely incorporate adequate evaluation of suppliers' digital security practices, creating potential vulnerabilities when integrating with suppliers' systems or utilizing their technology components.
Resource constraints compound these challenges, as thorough evaluation of test evidence and warranty terms requires significant time investment and specialized expertise. Many organizations, particularly smaller enterprises, lack dedicated resources for comprehensive supplier assessment, leading to abbreviated evaluation processes that prioritize convenience over thoroughness.
Data inconsistency represents a major obstacle in supplier evaluation. Organizations frequently encounter disparate testing methodologies, non-standardized reporting formats, and varying certification standards across different suppliers. This heterogeneity makes direct comparisons exceedingly difficult and can obscure critical quality indicators that should inform decision-making processes.
The verification gap presents another substantial challenge. Procurement teams typically lack specialized technical expertise to properly validate test claims and evidence provided by suppliers. Without robust verification mechanisms, organizations remain vulnerable to misleading or incomplete test data that may not accurately reflect product performance under real-world conditions or over extended timeframes.
Warranty evaluation suffers from similar complexity issues. The legal language in warranty documents often contains nuanced exclusions and limitations that require specialized knowledge to interpret correctly. Many organizations lack systematic approaches to analyze warranty terms beyond surface-level coverage periods, missing critical details about claim processes, response times, and exclusion clauses that significantly impact the actual value of warranty offerings.
Global supply chain dynamics further complicate evaluation efforts. With suppliers operating across different regulatory environments, organizations struggle to establish consistent evaluation frameworks that account for regional variations in testing standards, certification requirements, and warranty enforcement mechanisms. This geographic disparity creates additional layers of complexity in supplier assessment.
Digital transformation has introduced new evaluation challenges related to cybersecurity and data protection. Traditional supplier assessment methods rarely incorporate adequate evaluation of suppliers' digital security practices, creating potential vulnerabilities when integrating with suppliers' systems or utilizing their technology components.
Resource constraints compound these challenges, as thorough evaluation of test evidence and warranty terms requires significant time investment and specialized expertise. Many organizations, particularly smaller enterprises, lack dedicated resources for comprehensive supplier assessment, leading to abbreviated evaluation processes that prioritize convenience over thoroughness.
Test Evidence Collection and Validation Approaches
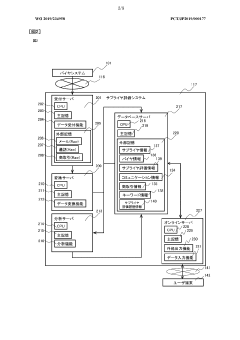
01 Supplier evaluation systems and methodologies
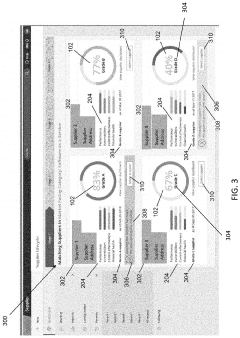
Various systems and methodologies for evaluating suppliers based on performance metrics, quality standards, and compliance requirements. These systems typically include frameworks for collecting, analyzing, and scoring supplier data to make informed decisions about supplier selection and management. The evaluation process may involve multiple criteria such as delivery performance, quality control measures, financial stability, and adherence to contractual obligations.- Supplier evaluation systems and methodologies: Various systems and methodologies are used to evaluate suppliers based on predefined criteria and metrics. These systems often include automated tools that collect, analyze, and score supplier performance data. The evaluation process typically involves assessing multiple factors such as quality, delivery, cost, and compliance. These systems help organizations make informed decisions about supplier selection and management, ultimately improving supply chain efficiency and reducing risks.
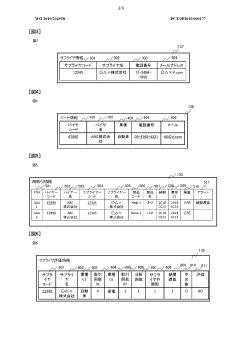
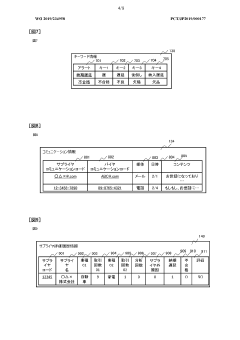
- Test evidence collection and verification: Systems and methods for collecting and verifying test evidence from suppliers ensure product quality and compliance. These approaches include digital platforms for documenting test results, automated verification processes, and secure storage of evidence. The collected test evidence may include quality control reports, compliance certifications, and performance test results. Verification mechanisms help validate the authenticity and accuracy of the submitted evidence, reducing the risk of non-compliant products entering the supply chain.
- Warranty management and tracking: Solutions for managing and tracking supplier warranties throughout the product lifecycle help organizations enforce warranty terms and process claims efficiently. These systems typically include warranty registration, claim processing, and performance analytics capabilities. They enable businesses to monitor warranty compliance, identify trends in product failures, and assess supplier reliability. Advanced warranty management systems may also incorporate predictive analytics to forecast potential warranty issues before they occur.
- Risk assessment and supplier compliance: Methods and systems for assessing supplier risks and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and company standards are essential for supply chain management. These approaches include risk scoring models, compliance monitoring tools, and audit management systems. They help organizations identify high-risk suppliers, track compliance status, and implement mitigation strategies. Continuous monitoring capabilities allow for real-time risk assessment and prompt response to compliance issues.
- Supplier performance analytics and reporting: Advanced analytics and reporting tools provide insights into supplier performance across multiple dimensions. These solutions collect data from various sources, apply analytical models, and generate comprehensive performance reports. They enable organizations to track key performance indicators, identify improvement opportunities, and make data-driven decisions about supplier relationships. Interactive dashboards and automated reporting features facilitate regular performance reviews and support continuous improvement initiatives.
02 Test evidence collection and verification
Methods and systems for collecting, documenting, and verifying test evidence from suppliers. This includes platforms for suppliers to submit test results, certification documents, and quality assurance data. The systems enable standardized collection of evidence, verification of test methodologies, and validation of results against established requirements or specifications. These approaches help ensure that supplied products or services meet the necessary quality and performance standards.Expand Specific Solutions03 Warranty management and enforcement
Solutions for managing supplier warranties, including tracking warranty terms, documenting warranty claims, and enforcing warranty obligations. These systems facilitate the recording of warranty information, monitoring of warranty periods, processing of warranty claims, and resolution of warranty disputes. They help organizations ensure that suppliers honor their warranty commitments and provide appropriate remedies for defective products or services.Expand Specific Solutions04 Risk assessment and supplier compliance
Frameworks for assessing supplier-related risks and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and organizational policies. These systems help identify potential risks in the supply chain, evaluate supplier compliance with contractual obligations, and implement mitigation strategies. They typically include tools for conducting supplier audits, monitoring compliance metrics, and generating risk assessment reports to support decision-making.Expand Specific Solutions05 Supplier performance analytics and reporting
Tools and methods for analyzing supplier performance data and generating comprehensive reports to support decision-making. These systems collect and process data related to supplier performance metrics, test results, warranty claims, and compliance records. They provide analytical capabilities for identifying trends, comparing suppliers, and evaluating the effectiveness of supplier relationships. The resulting insights help organizations optimize their supplier management strategies and improve overall supply chain performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Supplier Certification
The supplier evaluation landscape for test evidence and warranty is currently in a growth phase, with an estimated market size of $5-7 billion and expanding at 12-15% annually. The technology maturity varies significantly across sectors, with financial institutions (Bank of America) and technology giants (IBM, SAP) demonstrating advanced capabilities through standardized evaluation frameworks. Manufacturing leaders like Hitachi, Hon Hai Precision, and Honda Motor have developed sophisticated supplier quality management systems incorporating automated test evidence verification. State Grid Corporation of China and its subsidiaries are pioneering blockchain-based warranty tracking systems, while companies like Lexmark and NTT are advancing AI-powered predictive warranty analytics. The competitive landscape is increasingly focused on integrating IoT sensors with warranty management for real-time performance monitoring.
Hitachi Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hitachi has developed an advanced supplier evaluation framework centered on their Total Quality Management philosophy. Their approach integrates IoT sensors and data analytics to create a continuous monitoring system for supplier quality and warranty performance. Hitachi's methodology includes a comprehensive supplier audit program that evaluates not just test results but the entire testing methodology and quality control processes. Their system incorporates blockchain technology to create immutable records of test evidence, material certifications, and quality assurance documentation throughout the supply chain. Hitachi has implemented a "Digital Quality Twin" concept that creates virtual models of supplier production processes to simulate potential quality issues and predict warranty performance. The company also employs AI-powered visual inspection systems that can be deployed at supplier facilities to standardize quality evaluation and reduce human error in test evidence collection.
Strengths: IoT integration provides real-time quality monitoring capabilities; blockchain implementation ensures test evidence integrity; simulation-based approach enables proactive warranty risk management. Weaknesses: Significant technological barriers for smaller suppliers; requires substantial investment in digital infrastructure; potential privacy concerns with deep integration into supplier operations.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM has developed a comprehensive Supplier Evaluation Framework that integrates both quantitative and qualitative assessment methodologies. Their approach includes a multi-tier supplier evaluation system that leverages AI and blockchain technology to verify test evidence authenticity and track warranty compliance. IBM's Supplier Quality Management System (SQMS) incorporates real-time performance monitoring with predictive analytics to forecast potential supplier issues before they impact the supply chain. The system evaluates suppliers based on a weighted scoring model that considers quality metrics, delivery performance, technical capabilities, and warranty fulfillment rates. IBM has also implemented a digital twin approach for critical suppliers, allowing for simulation-based testing of components and systems before physical implementation, significantly reducing warranty claims related to design flaws.
Strengths: Advanced AI integration enables predictive quality assurance; blockchain implementation ensures immutable test evidence records; global implementation scale provides extensive comparative data. Weaknesses: High implementation costs for smaller organizations; requires significant technical expertise; complex system may create barriers for smaller suppliers to engage with the evaluation process.
Critical Analysis of Warranty Documentation Systems
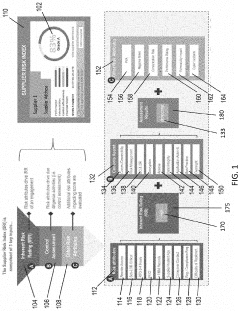
Supplier evaluation system and supplier evaluation method
PatentWO2019234958A1
Innovation
- A supplier evaluation system that analyzes communication and electronic commerce information to determine the cause of transaction results using a unified evaluation criteria, incorporating a reception device, conversion device, storage device, and analysis device to objectively evaluate suppliers based on transaction data between buyers and suppliers.
System and method for a supplier risk index
PatentActiveUS20200065727A1
Innovation
- A system and method that calculate a Supplier Risk Index (SRI) using inherent risk ratings, control assessments, and other risk attributes, providing a holistic view of supplier risk and enabling real-time updates and dynamic scoring.
Risk Management in Supplier Selection
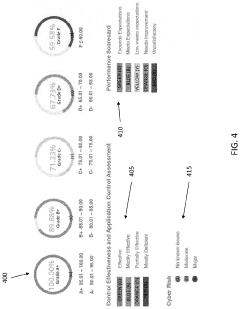
Risk management in supplier selection is a critical component of the procurement process that directly impacts an organization's operational resilience and financial health. When evaluating suppliers through test evidence and warranty provisions, companies must implement a structured risk assessment framework that identifies, analyzes, and mitigates potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain.
The primary categories of risk that require evaluation include financial stability, operational capability, quality consistency, and compliance adherence. Financial risk assessment involves analyzing suppliers' financial statements, credit ratings, and market position to determine their long-term viability. Organizations should establish financial thresholds that suppliers must meet to qualify for consideration, particularly for critical components or services.
Operational risks can be evaluated through production capacity assessments, business continuity plans, and geographical distribution of manufacturing facilities. Test evidence plays a crucial role here, as documented performance in stress tests, disaster recovery simulations, and capacity surge exercises provides tangible proof of a supplier's resilience under adverse conditions.
Quality risks demand particular attention through comprehensive evaluation of a supplier's quality management systems, certification status (ISO, industry-specific standards), and historical performance metrics. Test evidence should include statistical process control data, defect rates, and third-party validation reports. The warranty terms offered by suppliers serve as a financial proxy for their confidence in product quality and durability.
Compliance risk management requires thorough verification of regulatory adherence, ethical business practices, and environmental sustainability. This includes reviewing audit reports, certification documentation, and conducting site visits when feasible. Warranty provisions should explicitly address liability allocation for compliance failures and recall scenarios.
Effective risk management strategies incorporate diversification of the supplier base, implementation of early warning systems for supplier distress, and development of contingency plans for critical components. Organizations should establish a risk scoring matrix that weighs the relative importance of different risk factors based on the strategic significance of the procurement category.
The warranty evaluation process should assess coverage scope, duration, response time commitments, and remedy provisions. Advanced procurement organizations are increasingly implementing performance-based warranty structures that align supplier incentives with organizational objectives through gain-sharing and penalty mechanisms.
The primary categories of risk that require evaluation include financial stability, operational capability, quality consistency, and compliance adherence. Financial risk assessment involves analyzing suppliers' financial statements, credit ratings, and market position to determine their long-term viability. Organizations should establish financial thresholds that suppliers must meet to qualify for consideration, particularly for critical components or services.
Operational risks can be evaluated through production capacity assessments, business continuity plans, and geographical distribution of manufacturing facilities. Test evidence plays a crucial role here, as documented performance in stress tests, disaster recovery simulations, and capacity surge exercises provides tangible proof of a supplier's resilience under adverse conditions.
Quality risks demand particular attention through comprehensive evaluation of a supplier's quality management systems, certification status (ISO, industry-specific standards), and historical performance metrics. Test evidence should include statistical process control data, defect rates, and third-party validation reports. The warranty terms offered by suppliers serve as a financial proxy for their confidence in product quality and durability.
Compliance risk management requires thorough verification of regulatory adherence, ethical business practices, and environmental sustainability. This includes reviewing audit reports, certification documentation, and conducting site visits when feasible. Warranty provisions should explicitly address liability allocation for compliance failures and recall scenarios.
Effective risk management strategies incorporate diversification of the supplier base, implementation of early warning systems for supplier distress, and development of contingency plans for critical components. Organizations should establish a risk scoring matrix that weighs the relative importance of different risk factors based on the strategic significance of the procurement category.
The warranty evaluation process should assess coverage scope, duration, response time commitments, and remedy provisions. Advanced procurement organizations are increasingly implementing performance-based warranty structures that align supplier incentives with organizational objectives through gain-sharing and penalty mechanisms.
Compliance Standards for Supplier Partnerships
Compliance Standards for Supplier Partnerships represent a critical framework for establishing and maintaining reliable business relationships in today's complex supply chain environment. These standards serve as benchmarks against which potential and existing suppliers can be measured to ensure they meet organizational requirements and industry regulations.
International standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental management provide foundational compliance frameworks that responsible suppliers should adhere to. When evaluating suppliers through test evidence and warranty provisions, organizations must verify certification to these standards as a baseline qualification. Documentation of compliance should be regularly updated and accessible during audit processes.
Industry-specific compliance requirements add another layer of necessary verification. For electronics suppliers, RoHS and WEEE directives regarding hazardous substances must be demonstrated through comprehensive test reports. Medical device suppliers must show FDA or equivalent regulatory body compliance, while automotive parts suppliers need IATF 16949 certification. These specialized standards ensure suppliers meet the unique requirements of particular sectors.
Contractual compliance frameworks should be established to formalize warranty obligations and testing protocols. Standard supplier agreements must clearly define warranty periods, coverage limitations, and claim procedures. Additionally, these agreements should specify required test evidence formats, testing frequency, and validation methodologies. Properly structured contracts create accountability and provide legal recourse when compliance issues arise.
Third-party verification mechanisms strengthen compliance assurance beyond self-reporting. Independent laboratory testing of supplier components provides objective evidence of quality and performance claims. Supplier audits conducted by qualified third parties can verify manufacturing processes and quality control systems. These external validations reduce risk and enhance confidence in supplier partnerships.
Data management systems for compliance documentation ensure efficient tracking and retrieval of critical information. Centralized digital repositories for supplier certifications, test reports, and warranty documentation facilitate quick access during evaluations. Automated notification systems for expiring certifications or required retesting help maintain continuous compliance. These technological solutions streamline the management of complex compliance requirements across multiple supplier relationships.
Continuous improvement protocols should be integrated into compliance standards. Regular review cycles for supplier performance against established metrics identify areas for enhancement. Collaborative improvement initiatives between organizations and their suppliers foster innovation and problem-solving. This dynamic approach to compliance ensures standards evolve with changing industry requirements and technological advancements.
International standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental management provide foundational compliance frameworks that responsible suppliers should adhere to. When evaluating suppliers through test evidence and warranty provisions, organizations must verify certification to these standards as a baseline qualification. Documentation of compliance should be regularly updated and accessible during audit processes.
Industry-specific compliance requirements add another layer of necessary verification. For electronics suppliers, RoHS and WEEE directives regarding hazardous substances must be demonstrated through comprehensive test reports. Medical device suppliers must show FDA or equivalent regulatory body compliance, while automotive parts suppliers need IATF 16949 certification. These specialized standards ensure suppliers meet the unique requirements of particular sectors.
Contractual compliance frameworks should be established to formalize warranty obligations and testing protocols. Standard supplier agreements must clearly define warranty periods, coverage limitations, and claim procedures. Additionally, these agreements should specify required test evidence formats, testing frequency, and validation methodologies. Properly structured contracts create accountability and provide legal recourse when compliance issues arise.
Third-party verification mechanisms strengthen compliance assurance beyond self-reporting. Independent laboratory testing of supplier components provides objective evidence of quality and performance claims. Supplier audits conducted by qualified third parties can verify manufacturing processes and quality control systems. These external validations reduce risk and enhance confidence in supplier partnerships.
Data management systems for compliance documentation ensure efficient tracking and retrieval of critical information. Centralized digital repositories for supplier certifications, test reports, and warranty documentation facilitate quick access during evaluations. Automated notification systems for expiring certifications or required retesting help maintain continuous compliance. These technological solutions streamline the management of complex compliance requirements across multiple supplier relationships.
Continuous improvement protocols should be integrated into compliance standards. Regular review cycles for supplier performance against established metrics identify areas for enhancement. Collaborative improvement initiatives between organizations and their suppliers foster innovation and problem-solving. This dynamic approach to compliance ensures standards evolve with changing industry requirements and technological advancements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!