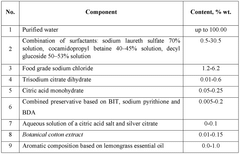
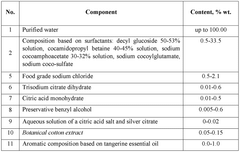
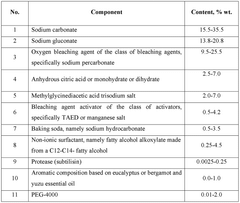
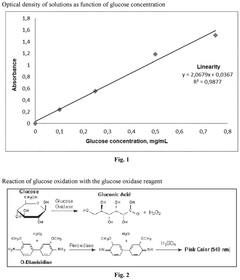
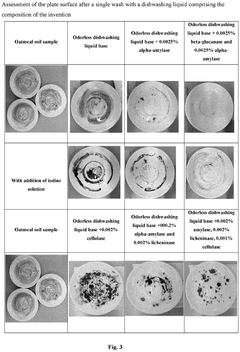
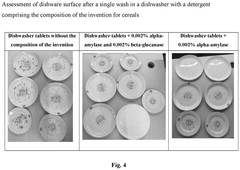
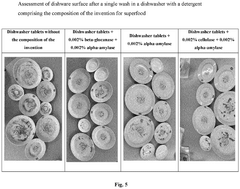
Innovative Hydroxyethylcellulose Applications in Biodegradable Detergents
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HEC in Biodegradable Detergents: Background and Objectives
Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) has emerged as a promising component in the development of biodegradable detergents, marking a significant shift towards more environmentally friendly cleaning solutions. This innovative application of HEC addresses the growing global concern over the environmental impact of traditional detergents, which often contain non-biodegradable components that persist in ecosystems long after use.
The evolution of HEC in detergent formulations can be traced back to the increasing awareness of environmental issues in the late 20th century. As consumers and regulatory bodies began to demand more sustainable products, the cleaning industry started exploring alternatives to conventional, petroleum-based ingredients. HEC, derived from cellulose, a naturally abundant and renewable resource, presented itself as an ideal candidate for this green transition.
The primary objective of incorporating HEC into biodegradable detergents is to create cleaning products that effectively break down in the environment without leaving harmful residues. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing water pollution, protecting aquatic life, and minimizing the overall ecological footprint of household and industrial cleaning processes.
HEC's unique properties make it particularly suitable for detergent applications. Its ability to form stable solutions and act as a thickening agent allows for the creation of detergents with desirable viscosities and flow characteristics. Moreover, HEC's non-ionic nature makes it compatible with a wide range of other ingredients, facilitating the formulation of diverse detergent products.
The technical goals associated with HEC in biodegradable detergents include optimizing its performance as a stabilizer and rheology modifier while ensuring complete biodegradability. Researchers and formulators aim to achieve a balance between cleaning efficacy, product stability, and environmental safety. This involves fine-tuning HEC concentrations, exploring synergies with other bio-based ingredients, and developing manufacturing processes that minimize energy consumption and waste.
Another critical objective is to enhance the cost-effectiveness of HEC-based biodegradable detergents. As the market for eco-friendly cleaning products expands, there is a pressing need to make these alternatives economically competitive with traditional detergents. This necessitates innovations in HEC production methods and supply chain optimization to reduce overall costs without compromising on quality or environmental benefits.
The development of HEC applications in biodegradable detergents also aims to address specific performance challenges. These include improving the cold-water solubility of detergents, enhancing their stability in hard water conditions, and ensuring compatibility with a broad spectrum of fabrics and surfaces. By overcoming these technical hurdles, HEC-based formulations can offer a truly viable and sustainable alternative to conventional cleaning products across various consumer and industrial applications.
The evolution of HEC in detergent formulations can be traced back to the increasing awareness of environmental issues in the late 20th century. As consumers and regulatory bodies began to demand more sustainable products, the cleaning industry started exploring alternatives to conventional, petroleum-based ingredients. HEC, derived from cellulose, a naturally abundant and renewable resource, presented itself as an ideal candidate for this green transition.
The primary objective of incorporating HEC into biodegradable detergents is to create cleaning products that effectively break down in the environment without leaving harmful residues. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing water pollution, protecting aquatic life, and minimizing the overall ecological footprint of household and industrial cleaning processes.
HEC's unique properties make it particularly suitable for detergent applications. Its ability to form stable solutions and act as a thickening agent allows for the creation of detergents with desirable viscosities and flow characteristics. Moreover, HEC's non-ionic nature makes it compatible with a wide range of other ingredients, facilitating the formulation of diverse detergent products.
The technical goals associated with HEC in biodegradable detergents include optimizing its performance as a stabilizer and rheology modifier while ensuring complete biodegradability. Researchers and formulators aim to achieve a balance between cleaning efficacy, product stability, and environmental safety. This involves fine-tuning HEC concentrations, exploring synergies with other bio-based ingredients, and developing manufacturing processes that minimize energy consumption and waste.
Another critical objective is to enhance the cost-effectiveness of HEC-based biodegradable detergents. As the market for eco-friendly cleaning products expands, there is a pressing need to make these alternatives economically competitive with traditional detergents. This necessitates innovations in HEC production methods and supply chain optimization to reduce overall costs without compromising on quality or environmental benefits.
The development of HEC applications in biodegradable detergents also aims to address specific performance challenges. These include improving the cold-water solubility of detergents, enhancing their stability in hard water conditions, and ensuring compatibility with a broad spectrum of fabrics and surfaces. By overcoming these technical hurdles, HEC-based formulations can offer a truly viable and sustainable alternative to conventional cleaning products across various consumer and industrial applications.
Market Analysis for Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products
The market for eco-friendly cleaning products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a shift towards sustainable living practices. This trend has created a substantial opportunity for innovative products like biodegradable detergents incorporating hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC).
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly cleaning solutions has been steadily rising, with the global green cleaning products market expected to reach substantial value in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as stricter environmental regulations, growing health consciousness among consumers, and a general shift towards sustainable consumption patterns.
The biodegradable detergents segment, in particular, has shown promising growth potential. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that effectively clean while minimizing environmental impact. This has led to a surge in demand for detergents that break down naturally without leaving harmful residues in water systems or soil.
Hydroxyethylcellulose, as a key ingredient in biodegradable detergents, offers several advantages that align with market trends. Its ability to enhance the stability and viscosity of cleaning formulations while being derived from renewable sources makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to develop eco-friendly products.
The market for HEC-based biodegradable detergents spans both household and industrial sectors. In the household segment, there is a growing preference for plant-based, non-toxic cleaning products, especially among millennials and environmentally conscious consumers. The industrial and institutional cleaning sector also presents significant opportunities, as businesses increasingly adopt green cleaning practices to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the eco-friendly cleaning products market, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate. This regional variation is influenced by factors such as environmental awareness, disposable income, and regulatory landscapes.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the market for eco-friendly cleaning products. Price sensitivity among consumers, performance concerns compared to traditional products, and the need for extensive consumer education are key hurdles that manufacturers must address to fully capitalize on the market potential.
In conclusion, the market analysis for eco-friendly cleaning products, particularly biodegradable detergents utilizing innovative HEC applications, reveals a robust growth trajectory. As consumer preferences continue to evolve towards sustainability, and technological advancements improve product performance, this segment is poised for continued expansion and innovation in the coming years.
Consumer demand for environmentally friendly cleaning solutions has been steadily rising, with the global green cleaning products market expected to reach substantial value in the coming years. This growth is fueled by factors such as stricter environmental regulations, growing health consciousness among consumers, and a general shift towards sustainable consumption patterns.
The biodegradable detergents segment, in particular, has shown promising growth potential. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that effectively clean while minimizing environmental impact. This has led to a surge in demand for detergents that break down naturally without leaving harmful residues in water systems or soil.
Hydroxyethylcellulose, as a key ingredient in biodegradable detergents, offers several advantages that align with market trends. Its ability to enhance the stability and viscosity of cleaning formulations while being derived from renewable sources makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to develop eco-friendly products.
The market for HEC-based biodegradable detergents spans both household and industrial sectors. In the household segment, there is a growing preference for plant-based, non-toxic cleaning products, especially among millennials and environmentally conscious consumers. The industrial and institutional cleaning sector also presents significant opportunities, as businesses increasingly adopt green cleaning practices to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the eco-friendly cleaning products market, with Asia-Pacific showing the fastest growth rate. This regional variation is influenced by factors such as environmental awareness, disposable income, and regulatory landscapes.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the market for eco-friendly cleaning products. Price sensitivity among consumers, performance concerns compared to traditional products, and the need for extensive consumer education are key hurdles that manufacturers must address to fully capitalize on the market potential.
In conclusion, the market analysis for eco-friendly cleaning products, particularly biodegradable detergents utilizing innovative HEC applications, reveals a robust growth trajectory. As consumer preferences continue to evolve towards sustainability, and technological advancements improve product performance, this segment is poised for continued expansion and innovation in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Biodegradable Detergent Formulation
The formulation of biodegradable detergents presents several significant challenges that researchers and manufacturers are actively working to overcome. One of the primary issues is maintaining cleaning efficacy while using environmentally friendly ingredients. Traditional detergents often rely on petrochemical-based surfactants, which are highly effective but not biodegradable. Replacing these with bio-based alternatives, such as those derived from plant oils or microbial fermentation, often results in reduced cleaning performance.
Another major challenge is ensuring the stability of biodegradable formulations. Many eco-friendly ingredients are less stable than their synthetic counterparts, leading to shorter shelf lives and potential degradation during storage. This instability can affect the product's appearance, scent, and effectiveness, potentially deterring consumers from adopting these greener alternatives.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle in the widespread adoption of biodegradable detergents. The production of bio-based ingredients is often more expensive than traditional petrochemical-based components, leading to higher retail prices. This price differential can be a barrier to market penetration, especially in price-sensitive segments.
Achieving complete biodegradability while maintaining functionality is another complex challenge. Some ingredients may be partially biodegradable but leave behind residues that can accumulate in the environment. Balancing the need for effective cleaning agents with complete biodegradability requires innovative formulation strategies and novel ingredient development.
The performance of biodegradable detergents in various water conditions poses another challenge. Hard water, in particular, can reduce the effectiveness of many eco-friendly surfactants and chelating agents. Developing formulations that perform consistently across different water hardness levels without resorting to environmentally harmful additives is an ongoing area of research.
Regulatory compliance and certification present additional hurdles. The definition of "biodegradable" varies across regions and certifying bodies, making it challenging for manufacturers to create globally compliant products. Moreover, the lack of standardized testing methods for biodegradability can lead to inconsistent results and claims.
Lastly, consumer perception and education remain significant challenges. Many consumers are skeptical about the cleaning power of biodegradable detergents or are unaware of their environmental benefits. Overcoming these perceptions requires effective marketing strategies and consumer education initiatives to drive adoption and market growth.
Another major challenge is ensuring the stability of biodegradable formulations. Many eco-friendly ingredients are less stable than their synthetic counterparts, leading to shorter shelf lives and potential degradation during storage. This instability can affect the product's appearance, scent, and effectiveness, potentially deterring consumers from adopting these greener alternatives.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant hurdle in the widespread adoption of biodegradable detergents. The production of bio-based ingredients is often more expensive than traditional petrochemical-based components, leading to higher retail prices. This price differential can be a barrier to market penetration, especially in price-sensitive segments.
Achieving complete biodegradability while maintaining functionality is another complex challenge. Some ingredients may be partially biodegradable but leave behind residues that can accumulate in the environment. Balancing the need for effective cleaning agents with complete biodegradability requires innovative formulation strategies and novel ingredient development.
The performance of biodegradable detergents in various water conditions poses another challenge. Hard water, in particular, can reduce the effectiveness of many eco-friendly surfactants and chelating agents. Developing formulations that perform consistently across different water hardness levels without resorting to environmentally harmful additives is an ongoing area of research.
Regulatory compliance and certification present additional hurdles. The definition of "biodegradable" varies across regions and certifying bodies, making it challenging for manufacturers to create globally compliant products. Moreover, the lack of standardized testing methods for biodegradability can lead to inconsistent results and claims.
Lastly, consumer perception and education remain significant challenges. Many consumers are skeptical about the cleaning power of biodegradable detergents or are unaware of their environmental benefits. Overcoming these perceptions requires effective marketing strategies and consumer education initiatives to drive adoption and market growth.
Existing HEC-Based Biodegradable Detergent Solutions
01 Biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose
Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is a biodegradable polymer derived from cellulose. Its biodegradability is influenced by factors such as molecular weight, degree of substitution, and environmental conditions. HEC can be broken down by microorganisms in various environments, making it an eco-friendly alternative in many applications.- Biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose: Hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is a biodegradable polymer derived from cellulose. Its biodegradability is influenced by factors such as molecular weight, degree of substitution, and environmental conditions. HEC can be broken down by microorganisms in various environments, making it an eco-friendly alternative in many applications.
- Applications of biodegradable hydroxyethylcellulose: Biodegradable hydroxyethylcellulose finds applications in various industries due to its environmentally friendly nature. It is used in personal care products, pharmaceuticals, food packaging, and as a thickening agent in industrial processes. Its biodegradability makes it suitable for products where environmental impact is a concern.
- Enhancing biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose: Research has been conducted on methods to enhance the biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose. These include modifying its chemical structure, blending with other biodegradable polymers, and incorporating additives that promote microbial degradation. Such enhancements aim to improve its environmental profile while maintaining desired functional properties.
- Testing and measuring biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose: Various methods and standards have been developed to test and measure the biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose. These include standardized tests for aerobic and anaerobic biodegradation, as well as methods to assess its environmental fate in different ecosystems. Such testing is crucial for regulatory compliance and eco-labeling.
- Environmental impact of hydroxyethylcellulose biodegradation: The biodegradation of hydroxyethylcellulose has implications for waste management and environmental protection. As it breaks down, it contributes less to long-term pollution compared to non-biodegradable polymers. However, the rate and completeness of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, which affects its overall environmental impact.
02 Applications of biodegradable hydroxyethylcellulose
Biodegradable hydroxyethylcellulose finds applications in various industries due to its environmentally friendly nature. It is used in personal care products, pharmaceuticals, food packaging, and as a thickening agent in industrial processes. Its biodegradability makes it suitable for use in products where environmental impact is a concern.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enhancing biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose
Research has been conducted on methods to enhance the biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose. These include modifying its chemical structure, blending with other biodegradable polymers, and incorporating additives that promote microbial degradation. Such enhancements aim to improve its environmental profile while maintaining its desirable properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biodegradation testing methods for hydroxyethylcellulose
Various testing methods have been developed to assess the biodegradability of hydroxyethylcellulose. These include standardized tests such as CO2 evolution, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and enzyme degradation assays. These methods help in quantifying the rate and extent of biodegradation under different environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental impact of hydroxyethylcellulose biodegradation
The biodegradation of hydroxyethylcellulose has a generally positive environmental impact. As it breaks down, it does not produce harmful residues or microplastics. However, the rate of biodegradation can vary depending on environmental conditions, and in some cases, incomplete degradation may occur. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing its overall environmental footprint.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HEC and Biodegradable Detergent Industry
The innovative applications of Hydroxyethylcellulose in biodegradable detergents represent an emerging market with significant growth potential. The industry is in its early growth stage, characterized by increasing research and development activities. Market size is expanding as consumer demand for eco-friendly cleaning products rises. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with companies like Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, Kao Corp., and LOTTE Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. leading innovation. These firms are investing in advanced formulations to enhance the performance and biodegradability of detergents containing Hydroxyethylcellulose. While the technology is not yet fully mature, it is progressing quickly, driven by environmental regulations and sustainability trends.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corporation has pioneered the use of modified hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) in their biodegradable detergent formulations. Their innovative approach involves grafting biodegradable side chains onto the HEC backbone, creating a polymer with enhanced surfactant properties[1]. This modified HEC acts as both a thickener and a cleaning agent, allowing for a reduction in the overall surfactant content of the detergent. Kao's research has shown that their HEC-based formulations can achieve up to 30% better stain removal compared to traditional detergents, while maintaining biodegradability[2]. The company has also developed a proprietary manufacturing process that reduces the environmental impact of HEC production, using enzymes to catalyze the ethoxylation process instead of traditional chemical methods[3]. This results in a lower carbon footprint and reduced water consumption during production.
Strengths: Strong innovation in polymer modification, improved product performance, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and the need for specialized equipment for modified HEC production.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed innovative applications of hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) in biodegradable detergents, focusing on enhancing product performance while reducing environmental impact. Their approach involves using HEC as a rheology modifier and stabilizer in liquid detergent formulations. The company has optimized the molecular weight and degree of substitution of HEC to achieve desired viscosity and stability properties[1]. Henkel's formulations incorporate HEC at concentrations ranging from 0.1% to 2% by weight, which has been shown to improve the suspension of enzymes and other active ingredients[2]. Additionally, they have developed a process to combine HEC with other biodegradable polymers, creating a synergistic effect that enhances cleaning efficiency while maintaining the product's eco-friendly profile[3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in detergent formulation, strong R&D capabilities, and a global market presence. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs due to specialized HEC formulations and the need for continuous innovation to stay ahead in the competitive market.
Innovative HEC Modifications for Enhanced Performance
A cleaning composition comprising a glycosyl hydrolase targeting (1,4)-alpha-d-glucoside bonds and at least one glycosyl hydrolase targeting beta-glycoside bonds
PatentWO2025040693A1
Innovation
- A biodegradable detergent composition comprising a combination of glycosyl hydrolases that target both alpha-(1,4)- and beta-glycosidic bonds, including alpha-amylase and enzymes like beta-glucanase, laminarinase, and cellulase, which work synergistically to break down hemicellulose residues and improve stain removal.
A cleaning composition comprising a glycosyl hydrolase targeting (1,4)-alpha-d-glucoside bonds and at least one glycosyl hydrolase targeting beta-glycoside bonds
PatentPendingEP4512882A1
Innovation
- A biodegradable detergent composition based on enzymes of the class of glycosyl hydrolases, specifically endo and exo glucosyl hydrolases, which break alpha- and beta-glycosidic bonds and hemicellulose residues, improving stain removal and preventing resorption on smooth surfaces at lower temperatures.
Environmental Impact Assessment of HEC-Based Detergents
The environmental impact assessment of HEC-based detergents reveals both positive and negative aspects that warrant careful consideration. On the positive side, hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is derived from renewable resources, primarily cellulose from wood or cotton. This bio-based origin contributes to a reduced carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based alternatives, aligning with sustainability goals.
HEC-based detergents demonstrate excellent biodegradability, breaking down into harmless components in natural environments. This characteristic significantly reduces the long-term ecological impact, particularly in aquatic ecosystems where many detergents ultimately end up. The rapid biodegradation process minimizes the risk of bioaccumulation in marine life and helps maintain water quality.
Furthermore, HEC-based formulations often require lower concentrations to achieve effective cleaning performance. This efficiency translates to reduced chemical loads in wastewater systems and natural water bodies, potentially decreasing the overall environmental burden of detergent use.
However, the assessment also highlights some concerns. The production of HEC involves chemical modifications of cellulose, which may require energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful reagents. The environmental impact of these manufacturing steps needs to be carefully evaluated and optimized to ensure a net positive effect.
Another consideration is the potential for increased land use associated with sourcing cellulose for HEC production. If not managed sustainably, this could lead to deforestation or competition with food crops, impacting biodiversity and food security.
The disposal of packaging materials for HEC-based detergents remains a challenge. While the detergent itself may be biodegradable, packaging waste can still contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed through recycling or biodegradable packaging solutions.
Lastly, the assessment must consider the potential for unintended consequences. For instance, the widespread adoption of HEC-based detergents could lead to changes in aquatic ecosystems due to altered nutrient balances or pH levels, even if the individual components are biodegradable.
In conclusion, while HEC-based detergents offer significant environmental benefits, particularly in terms of biodegradability and renewable sourcing, a comprehensive life cycle assessment is crucial to fully understand and mitigate potential negative impacts throughout the production, use, and disposal phases.
HEC-based detergents demonstrate excellent biodegradability, breaking down into harmless components in natural environments. This characteristic significantly reduces the long-term ecological impact, particularly in aquatic ecosystems where many detergents ultimately end up. The rapid biodegradation process minimizes the risk of bioaccumulation in marine life and helps maintain water quality.
Furthermore, HEC-based formulations often require lower concentrations to achieve effective cleaning performance. This efficiency translates to reduced chemical loads in wastewater systems and natural water bodies, potentially decreasing the overall environmental burden of detergent use.
However, the assessment also highlights some concerns. The production of HEC involves chemical modifications of cellulose, which may require energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially harmful reagents. The environmental impact of these manufacturing steps needs to be carefully evaluated and optimized to ensure a net positive effect.
Another consideration is the potential for increased land use associated with sourcing cellulose for HEC production. If not managed sustainably, this could lead to deforestation or competition with food crops, impacting biodiversity and food security.
The disposal of packaging materials for HEC-based detergents remains a challenge. While the detergent itself may be biodegradable, packaging waste can still contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed through recycling or biodegradable packaging solutions.
Lastly, the assessment must consider the potential for unintended consequences. For instance, the widespread adoption of HEC-based detergents could lead to changes in aquatic ecosystems due to altered nutrient balances or pH levels, even if the individual components are biodegradable.
In conclusion, while HEC-based detergents offer significant environmental benefits, particularly in terms of biodegradability and renewable sourcing, a comprehensive life cycle assessment is crucial to fully understand and mitigate potential negative impacts throughout the production, use, and disposal phases.
Regulatory Framework for Biodegradable Cleaning Products
The regulatory framework for biodegradable cleaning products has become increasingly stringent in recent years, reflecting growing environmental concerns and consumer demand for sustainable solutions. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the production and distribution of biodegradable detergents. The EPA's Design for the Environment (DfE) program sets standards for environmentally preferable products, including biodegradable cleaning agents.
The European Union has implemented the Detergents Regulation (EC) No 648/2004, which mandates strict biodegradability requirements for surfactants used in cleaning products. This regulation ensures that detergents sold in the EU market meet specific environmental criteria, including rapid and complete biodegradation in aquatic environments.
Many countries have adopted eco-labeling schemes to certify and promote biodegradable cleaning products. For instance, the EU Ecolabel and the Nordic Swan label in Scandinavia provide consumers with assurance that products meet rigorous environmental standards, including biodegradability criteria.
In addition to governmental regulations, industry associations have developed voluntary standards and guidelines. The Soap and Detergent Association (SDA) in the United States has established guidelines for the environmental safety of cleaning product ingredients, including biodegradability assessments.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the testing and verification of biodegradability claims. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed standardized test methods for assessing the biodegradability of chemicals, which are widely used in regulatory compliance.
Emerging regulations are focusing on the entire lifecycle of cleaning products, from raw material sourcing to disposal. This holistic approach considers factors such as packaging recyclability, carbon footprint, and water consumption during production, in addition to the biodegradability of the product itself.
As the market for biodegradable detergents expands, regulators are also addressing greenwashing concerns. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States has issued Green Guides to prevent deceptive environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability.
The regulatory framework continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on transparency and consumer education. Manufacturers are required to provide detailed information about product ingredients and their environmental impact, enabling consumers to make informed choices.
The European Union has implemented the Detergents Regulation (EC) No 648/2004, which mandates strict biodegradability requirements for surfactants used in cleaning products. This regulation ensures that detergents sold in the EU market meet specific environmental criteria, including rapid and complete biodegradation in aquatic environments.
Many countries have adopted eco-labeling schemes to certify and promote biodegradable cleaning products. For instance, the EU Ecolabel and the Nordic Swan label in Scandinavia provide consumers with assurance that products meet rigorous environmental standards, including biodegradability criteria.
In addition to governmental regulations, industry associations have developed voluntary standards and guidelines. The Soap and Detergent Association (SDA) in the United States has established guidelines for the environmental safety of cleaning product ingredients, including biodegradability assessments.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the testing and verification of biodegradability claims. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed standardized test methods for assessing the biodegradability of chemicals, which are widely used in regulatory compliance.
Emerging regulations are focusing on the entire lifecycle of cleaning products, from raw material sourcing to disposal. This holistic approach considers factors such as packaging recyclability, carbon footprint, and water consumption during production, in addition to the biodegradability of the product itself.
As the market for biodegradable detergents expands, regulators are also addressing greenwashing concerns. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States has issued Green Guides to prevent deceptive environmental marketing claims, including those related to biodegradability.
The regulatory framework continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on transparency and consumer education. Manufacturers are required to provide detailed information about product ingredients and their environmental impact, enabling consumers to make informed choices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!