Isotonic solutions in intravenous infusion: balancing therapeutic needs
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
IV Isotonic Solutions: Background and Objectives
Intravenous (IV) isotonic solutions have been a cornerstone of medical treatment for over a century, playing a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and delivering essential nutrients to patients. The concept of isotonicity, where the solution has the same osmotic pressure as blood, is fundamental to preventing cellular damage and ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes.
The development of IV isotonic solutions can be traced back to the late 19th century when physiologists began to understand the importance of maintaining electrolyte balance in the body. The first successful use of saline solution for fluid replacement was reported in 1831 by Thomas Latta during a cholera epidemic. However, it wasn't until the early 20th century that the formulation of truly isotonic solutions became standardized.
Over the years, the composition of IV isotonic solutions has evolved to meet diverse therapeutic needs. From simple saline solutions to more complex balanced electrolyte formulations, these fluids have been tailored to address specific clinical scenarios. The introduction of lactated Ringer's solution in the 1930s marked a significant advancement, offering a more physiologically balanced alternative to normal saline.
The primary objective of IV isotonic solutions is to restore and maintain fluid balance in the body without causing significant shifts in osmotic pressure. This is particularly critical in situations such as dehydration, blood loss, or electrolyte imbalances. Additionally, these solutions serve as vehicles for medication delivery, providing a means to administer drugs directly into the bloodstream.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving the safety and efficacy of IV isotonic solutions. This includes the development of buffered solutions to mitigate acid-base disturbances, the incorporation of glucose for energy provision, and the creation of specialized formulations for specific patient populations, such as those with renal or hepatic impairments.
The ongoing challenge in the field of IV isotonic solutions lies in striking the perfect balance between therapeutic efficacy and physiological compatibility. Researchers and clinicians continue to explore ways to optimize fluid composition, addressing concerns such as hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis associated with large-volume saline infusions and the potential benefits of balanced crystalloid solutions.
As we look to the future, the evolution of IV isotonic solutions is likely to be driven by personalized medicine approaches. This may involve tailoring fluid compositions based on individual patient characteristics, underlying conditions, and specific therapeutic goals. Additionally, the integration of smart infusion systems and real-time monitoring technologies promises to enhance the precision and safety of fluid therapy.
The development of IV isotonic solutions can be traced back to the late 19th century when physiologists began to understand the importance of maintaining electrolyte balance in the body. The first successful use of saline solution for fluid replacement was reported in 1831 by Thomas Latta during a cholera epidemic. However, it wasn't until the early 20th century that the formulation of truly isotonic solutions became standardized.
Over the years, the composition of IV isotonic solutions has evolved to meet diverse therapeutic needs. From simple saline solutions to more complex balanced electrolyte formulations, these fluids have been tailored to address specific clinical scenarios. The introduction of lactated Ringer's solution in the 1930s marked a significant advancement, offering a more physiologically balanced alternative to normal saline.
The primary objective of IV isotonic solutions is to restore and maintain fluid balance in the body without causing significant shifts in osmotic pressure. This is particularly critical in situations such as dehydration, blood loss, or electrolyte imbalances. Additionally, these solutions serve as vehicles for medication delivery, providing a means to administer drugs directly into the bloodstream.
Recent technological advancements have focused on improving the safety and efficacy of IV isotonic solutions. This includes the development of buffered solutions to mitigate acid-base disturbances, the incorporation of glucose for energy provision, and the creation of specialized formulations for specific patient populations, such as those with renal or hepatic impairments.
The ongoing challenge in the field of IV isotonic solutions lies in striking the perfect balance between therapeutic efficacy and physiological compatibility. Researchers and clinicians continue to explore ways to optimize fluid composition, addressing concerns such as hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis associated with large-volume saline infusions and the potential benefits of balanced crystalloid solutions.
As we look to the future, the evolution of IV isotonic solutions is likely to be driven by personalized medicine approaches. This may involve tailoring fluid compositions based on individual patient characteristics, underlying conditions, and specific therapeutic goals. Additionally, the integration of smart infusion systems and real-time monitoring technologies promises to enhance the precision and safety of fluid therapy.
Market Analysis of IV Fluid Therapies
The global intravenous (IV) fluid therapy market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, rising surgical procedures, and growing demand for emergency care. The market is segmented into various types of IV fluids, including isotonic solutions, which play a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and electrolyte concentrations in patients.
Isotonic solutions, such as normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride) and lactated Ringer's solution, represent a substantial portion of the IV fluid market. These solutions are widely used in hospitals, clinics, and emergency settings due to their ability to closely match the osmolarity of human blood, making them suitable for a wide range of therapeutic applications.
The market for isotonic solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing incidence of dehydration-related conditions, expanding geriatric population, and rising cases of trauma and burns requiring fluid resuscitation.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the IV fluid therapy market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing rapid market expansion due to improving healthcare access and rising awareness about the importance of fluid management in patient care.
Key players in the IV fluid market include Baxter International Inc., B. Braun Melsungen AG, Fresenius Kabi, and ICU Medical Inc. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to maintain their market positions and meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients.
The demand for isotonic solutions is also being influenced by the growing trend towards personalized medicine and the need for balanced fluid therapy. Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the importance of tailoring fluid administration to individual patient needs, considering factors such as underlying medical conditions, electrolyte imbalances, and specific therapeutic goals.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the critical role of IV fluid therapies in managing critically ill patients, leading to increased demand for isotonic solutions in intensive care settings. This has prompted manufacturers to ramp up production and ensure a stable supply chain to meet the surge in demand during health crises.
Isotonic solutions, such as normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride) and lactated Ringer's solution, represent a substantial portion of the IV fluid market. These solutions are widely used in hospitals, clinics, and emergency settings due to their ability to closely match the osmolarity of human blood, making them suitable for a wide range of therapeutic applications.
The market for isotonic solutions is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing incidence of dehydration-related conditions, expanding geriatric population, and rising cases of trauma and burns requiring fluid resuscitation.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the IV fluid therapy market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing rapid market expansion due to improving healthcare access and rising awareness about the importance of fluid management in patient care.
Key players in the IV fluid market include Baxter International Inc., B. Braun Melsungen AG, Fresenius Kabi, and ICU Medical Inc. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to maintain their market positions and meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients.
The demand for isotonic solutions is also being influenced by the growing trend towards personalized medicine and the need for balanced fluid therapy. Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the importance of tailoring fluid administration to individual patient needs, considering factors such as underlying medical conditions, electrolyte imbalances, and specific therapeutic goals.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the critical role of IV fluid therapies in managing critically ill patients, leading to increased demand for isotonic solutions in intensive care settings. This has prompted manufacturers to ramp up production and ensure a stable supply chain to meet the surge in demand during health crises.
Current Challenges in Isotonic Solution Formulation
The formulation of isotonic solutions for intravenous infusion presents several significant challenges in the current medical landscape. One of the primary difficulties lies in achieving and maintaining the delicate balance between osmolarity and tonicity. Isotonic solutions must closely match the osmolarity of blood plasma to prevent cellular damage or hemolysis. However, the addition of therapeutic agents or electrolytes can easily disrupt this balance, necessitating complex formulation strategies.
Another major challenge is ensuring the stability of isotonic solutions over extended periods. Many intravenous fluids are stored for prolonged durations before use, and maintaining their isotonicity throughout this time is crucial. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, light exposure, and container interactions can all potentially alter the solution's properties, compromising its therapeutic efficacy and safety.
The compatibility of isotonic solutions with a wide range of drugs and additives poses yet another significant hurdle. As intravenous therapy often involves the simultaneous administration of multiple medications, ensuring that the isotonic solution remains stable and effective when combined with various pharmaceutical agents is essential. This requires extensive testing and formulation adjustments to prevent precipitation, degradation, or altered drug efficacy.
Furthermore, the development of isotonic solutions that cater to specific patient populations or medical conditions presents unique challenges. For instance, formulating isotonic solutions for pediatric patients, geriatric individuals, or those with renal impairment requires careful consideration of fluid volumes, electrolyte concentrations, and potential metabolic impacts. Balancing these specific needs while maintaining isotonicity adds layers of complexity to the formulation process.
The selection of appropriate excipients and buffering agents also presents ongoing challenges in isotonic solution development. These components must not only contribute to maintaining isotonicity but also ensure pH stability, prevent microbial growth, and minimize potential adverse reactions. Finding the optimal combination of these elements that meets regulatory standards and ensures patient safety is a continual area of research and development.
Lastly, the manufacturing process itself poses challenges in consistently producing large volumes of isotonic solutions with precise osmolarity. Ensuring uniformity across batches, implementing stringent quality control measures, and developing robust sterilization techniques that do not affect the solution's properties are critical aspects that require ongoing attention and innovation in the field of intravenous fluid production.
Another major challenge is ensuring the stability of isotonic solutions over extended periods. Many intravenous fluids are stored for prolonged durations before use, and maintaining their isotonicity throughout this time is crucial. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, light exposure, and container interactions can all potentially alter the solution's properties, compromising its therapeutic efficacy and safety.
The compatibility of isotonic solutions with a wide range of drugs and additives poses yet another significant hurdle. As intravenous therapy often involves the simultaneous administration of multiple medications, ensuring that the isotonic solution remains stable and effective when combined with various pharmaceutical agents is essential. This requires extensive testing and formulation adjustments to prevent precipitation, degradation, or altered drug efficacy.
Furthermore, the development of isotonic solutions that cater to specific patient populations or medical conditions presents unique challenges. For instance, formulating isotonic solutions for pediatric patients, geriatric individuals, or those with renal impairment requires careful consideration of fluid volumes, electrolyte concentrations, and potential metabolic impacts. Balancing these specific needs while maintaining isotonicity adds layers of complexity to the formulation process.
The selection of appropriate excipients and buffering agents also presents ongoing challenges in isotonic solution development. These components must not only contribute to maintaining isotonicity but also ensure pH stability, prevent microbial growth, and minimize potential adverse reactions. Finding the optimal combination of these elements that meets regulatory standards and ensures patient safety is a continual area of research and development.
Lastly, the manufacturing process itself poses challenges in consistently producing large volumes of isotonic solutions with precise osmolarity. Ensuring uniformity across batches, implementing stringent quality control measures, and developing robust sterilization techniques that do not affect the solution's properties are critical aspects that require ongoing attention and innovation in the field of intravenous fluid production.
Existing Isotonic Solution Formulations
01 Composition of isotonic solutions
Isotonic solutions are formulated to have the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, typically containing a balance of electrolytes and other solutes. These solutions are designed to maintain cellular hydration and prevent osmotic shock when administered to the body.- Composition of isotonic solutions: Isotonic solutions are formulated to have the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, typically containing a balance of electrolytes and other solutes. These solutions are designed to maintain cellular hydration and prevent osmotic stress. Common components include sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and glucose, with concentrations carefully adjusted to match physiological levels.
- Applications in medical treatments: Isotonic solutions are widely used in various medical treatments, including intravenous therapy, wound irrigation, and dialysis. They help maintain fluid balance, deliver medications, and support cellular functions without causing osmotic imbalances. These solutions are particularly crucial in critical care settings and during surgical procedures to prevent dehydration and electrolyte disturbances.
- Manufacturing processes for isotonic solutions: The production of isotonic solutions involves precise mixing and quality control processes to ensure consistent composition and sterility. Advanced manufacturing techniques may include automated mixing systems, filtration methods, and aseptic packaging. Strict adherence to pharmaceutical standards is essential to maintain the balance of solutes and prevent contamination.
- Specialized isotonic formulations: Researchers have developed specialized isotonic formulations for specific medical conditions or applications. These may include solutions tailored for ophthalmic use, sports rehydration, or specific types of dialysis. The composition of these solutions is optimized to address particular physiological needs while maintaining isotonicity with body fluids.
- Monitoring and maintaining isotonic balance: Maintaining the correct balance of isotonic solutions in medical settings requires careful monitoring and adjustment. This may involve the use of specialized equipment to measure osmolality, electrolyte concentrations, and pH levels. Advanced systems may incorporate real-time monitoring and automated adjustment mechanisms to ensure consistent isotonic balance during treatments.
02 Applications in medical and pharmaceutical fields
Isotonic solutions are widely used in various medical and pharmaceutical applications, including intravenous fluids, eye drops, nasal sprays, and cell culture media. They help maintain proper fluid balance and cellular function in different physiological contexts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Methods for achieving isotonicity
Various methods are employed to achieve isotonicity in solutions, such as adjusting salt concentrations, adding non-electrolyte solutes like glucose, or using buffer systems. These methods ensure that the final solution has an osmotic pressure similar to that of body fluids.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isotonic solution stability and preservation
Maintaining the stability and preserving the isotonic balance of solutions is crucial for their effectiveness and safety. This involves careful formulation, appropriate packaging, and storage conditions to prevent contamination and maintain the desired osmotic properties over time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isotonic solutions in specialized applications
Isotonic solutions are tailored for specific applications, such as in sports nutrition, wound care, and dialysis. These specialized formulations take into account the unique requirements of different physiological systems and medical procedures to optimize their effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in IV Solution Manufacturing
The field of isotonic solutions for intravenous infusion is in a mature stage of development, with a well-established market and proven therapeutic applications. The global market size for IV solutions is substantial, driven by increasing healthcare needs and surgical procedures worldwide. Technologically, the focus is on refining formulations and delivery systems to enhance patient outcomes. Key players like Novartis AG, Becton, Dickinson & Co., and Baxter International are at the forefront, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global presence. Emerging companies such as Omeros Corp. and Zealand Pharma A/S are also contributing to innovation in this space, particularly in developing specialized formulations for specific therapeutic needs.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has made significant contributions to the field of isotonic solutions for intravenous infusion. Their research has focused on developing balanced electrolyte solutions that closely mimic the composition of human plasma[9]. Novartis has introduced innovative formulations that incorporate glucose and electrolytes in precise ratios to maintain osmotic balance and support cellular function[10]. The company has also invested in the development of multi-chamber bag systems that allow for the separate storage of incompatible components, which are mixed just before administration, ensuring stability and efficacy[11]. Novartis' isotonic solutions often include trace elements and vitamins to support overall patient health during intravenous therapy[12]. Their research extends to the use of novel preservatives that extend shelf life without compromising solution integrity or patient safety[13].
Strengths: Comprehensive research in electrolyte balance, innovative packaging solutions, and inclusion of micronutrients. Weaknesses: High development costs may lead to premium pricing, potentially limiting accessibility in some markets.
Becton, Dickinson & Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Becton, Dickinson & Co., Ltd. (BD) has made significant advancements in isotonic solution delivery systems for intravenous infusion. Their BD PhaSeal™ system provides a closed-system transfer device that maintains the sterility and stability of isotonic solutions during preparation and administration[5]. BD has also developed the BD Intelliport™ Medication Management System, which uses RFID technology to ensure accurate dosing and tracking of intravenous medications, including isotonic solutions[6]. The company's BD Alaris™ System integrates smart pump technology with medication safety software, allowing for precise control of infusion rates and volumes for isotonic solutions[7]. Additionally, BD has invested in research to optimize the composition of isotonic solutions, focusing on reducing the risk of electrolyte imbalances and improving patient outcomes[8].
Strengths: Advanced delivery systems, integration of smart technology for improved safety and accuracy. Weaknesses: High cost of implementation may limit adoption in resource-constrained healthcare settings.
Innovations in Electrolyte Balance Research
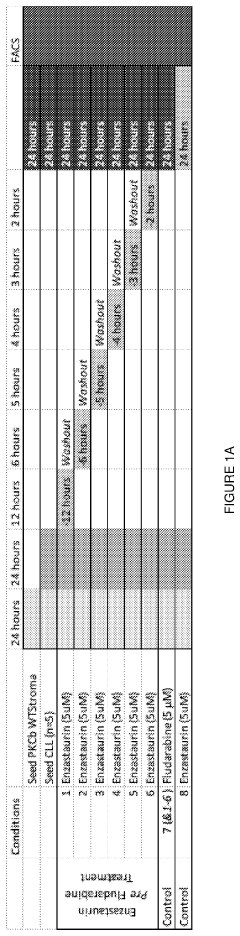
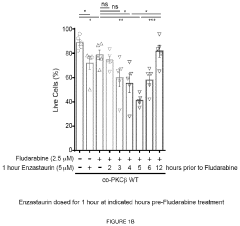
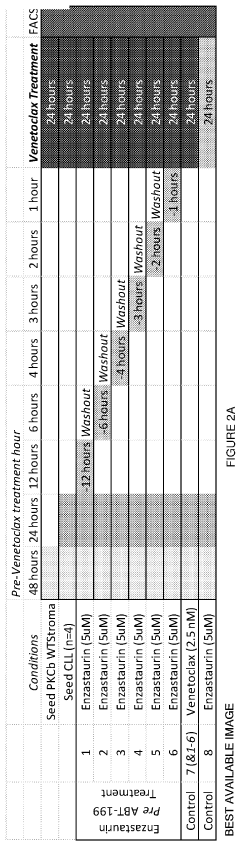
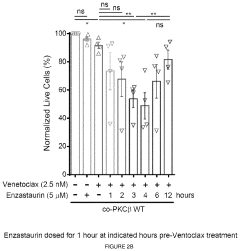
Therapeutic treatment using protein kinase c (PKC) inhibitors and cytotoxic agents
PatentPendingUS20230330080A1
Innovation
- The use of Protein Kinase C (PKC) inhibitors in combination with cytotoxic agents, where the PKC inhibitor reaches a peak concentration before the cytotoxic agent, to increase the sensitivity of disease cells to the cytotoxic agent, thereby enhancing treatment efficacy and reducing side effects.
Use of TNF and LT for preparation of medicaments
PatentInactiveEP0324464A2
Innovation
- The use of TNF, LT, and their muteins, administered parenterally through sterile isotonic solutions, specifically intravenously, intraperitoneally, intrapleurally, or intraarticularly, to address effusions by dissolving the proteins in a blood-isotonic buffer, filtering, and filling them into ampoules for injection, with doses ranging from 10 to 1000 μg per m² body surface area, repeated as necessary.
Regulatory Framework for IV Solutions
The regulatory framework for intravenous (IV) solutions plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of these essential medical products. In the context of isotonic solutions for intravenous infusion, regulatory bodies worldwide have established comprehensive guidelines and standards to govern their development, manufacturing, and distribution.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a key regulatory authority in this domain. The FDA classifies IV solutions as drug products and regulates them under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Manufacturers must comply with Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations, which outline requirements for quality control, production processes, and facility standards.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of IV solutions. The EMA's guidelines on parenteral preparations provide detailed requirements for the composition, manufacturing, and quality control of these products. Additionally, the European Pharmacopoeia sets specific standards for the quality and purity of IV solutions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) also plays a significant role in establishing global standards for IV solutions. The WHO's guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practices for sterile pharmaceutical products provide a framework for ensuring the quality and safety of IV solutions, particularly in developing countries.
Regulatory requirements for isotonic IV solutions typically include specifications for osmolality, pH, electrolyte composition, and sterility. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products meet these specifications through rigorous testing and documentation. Stability studies are also mandatory to ensure that the solutions maintain their quality throughout their shelf life.
Pharmacovigilance is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to monitor and report adverse events associated with their IV solutions, enabling regulatory agencies to identify and address potential safety concerns promptly.
The regulatory landscape for IV solutions is continually evolving to address emerging challenges and incorporate new scientific knowledge. Recent trends include increased focus on environmental sustainability in packaging and manufacturing processes, as well as the development of guidelines for novel formulations and delivery systems.
Compliance with these regulatory requirements is essential for manufacturers to obtain and maintain marketing authorization for their IV solutions. The stringent regulatory framework serves to protect patient safety, ensure product quality, and maintain public trust in these critical medical products.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a key regulatory authority in this domain. The FDA classifies IV solutions as drug products and regulates them under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Manufacturers must comply with Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations, which outline requirements for quality control, production processes, and facility standards.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of IV solutions. The EMA's guidelines on parenteral preparations provide detailed requirements for the composition, manufacturing, and quality control of these products. Additionally, the European Pharmacopoeia sets specific standards for the quality and purity of IV solutions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) also plays a significant role in establishing global standards for IV solutions. The WHO's guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practices for sterile pharmaceutical products provide a framework for ensuring the quality and safety of IV solutions, particularly in developing countries.
Regulatory requirements for isotonic IV solutions typically include specifications for osmolality, pH, electrolyte composition, and sterility. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products meet these specifications through rigorous testing and documentation. Stability studies are also mandatory to ensure that the solutions maintain their quality throughout their shelf life.
Pharmacovigilance is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Manufacturers are required to monitor and report adverse events associated with their IV solutions, enabling regulatory agencies to identify and address potential safety concerns promptly.
The regulatory landscape for IV solutions is continually evolving to address emerging challenges and incorporate new scientific knowledge. Recent trends include increased focus on environmental sustainability in packaging and manufacturing processes, as well as the development of guidelines for novel formulations and delivery systems.
Compliance with these regulatory requirements is essential for manufacturers to obtain and maintain marketing authorization for their IV solutions. The stringent regulatory framework serves to protect patient safety, ensure product quality, and maintain public trust in these critical medical products.
Patient Safety and Quality Control Measures
Patient safety and quality control measures are paramount in the administration of isotonic solutions for intravenous infusion. These measures ensure that the therapeutic needs of patients are met while minimizing the risk of adverse events. A comprehensive approach to safety and quality control encompasses several key areas.
Firstly, the production and preparation of isotonic solutions must adhere to strict pharmaceutical manufacturing standards. This includes maintaining sterile conditions throughout the production process, implementing rigorous quality assurance protocols, and conducting regular batch testing to ensure consistency and purity. The use of high-grade materials and state-of-the-art equipment is essential to minimize contamination risks and maintain the integrity of the solutions.
Secondly, proper storage and handling of isotonic solutions are critical to maintaining their efficacy and safety. Healthcare facilities must implement robust inventory management systems to track expiration dates, lot numbers, and storage conditions. Temperature-controlled environments are necessary to prevent degradation of the solutions, and regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of contamination or compromise.
Thirdly, the administration of isotonic solutions requires careful monitoring and documentation. Healthcare providers must be trained in proper infusion techniques, including the use of sterile equipment and aseptic procedures. The implementation of electronic health records and barcode scanning systems can help reduce medication errors and ensure accurate documentation of infusion rates, volumes, and patient responses.
Furthermore, continuous patient monitoring during intravenous therapy is essential. This includes regular assessment of vital signs, fluid balance, and electrolyte levels to detect any adverse reactions or imbalances promptly. The use of smart infusion pumps with built-in safety features, such as dose error reduction systems and flow rate limits, can significantly enhance patient safety.
Quality control measures should also extend to the evaluation of clinical outcomes and the reporting of adverse events. Establishing a robust pharmacovigilance system allows for the early detection of any safety concerns related to specific batches or formulations of isotonic solutions. Regular audits and reviews of infusion practices can help identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with best practices and regulatory requirements.
Lastly, ongoing education and training for healthcare professionals are crucial components of patient safety and quality control. This includes staying updated on the latest guidelines for intravenous therapy, understanding the specific properties and indications of different isotonic solutions, and being proficient in recognizing and managing potential complications.
By implementing these comprehensive patient safety and quality control measures, healthcare providers can optimize the therapeutic benefits of isotonic solutions while minimizing risks to patient well-being. This holistic approach ensures that intravenous infusion therapy remains a safe and effective treatment modality across various clinical settings.
Firstly, the production and preparation of isotonic solutions must adhere to strict pharmaceutical manufacturing standards. This includes maintaining sterile conditions throughout the production process, implementing rigorous quality assurance protocols, and conducting regular batch testing to ensure consistency and purity. The use of high-grade materials and state-of-the-art equipment is essential to minimize contamination risks and maintain the integrity of the solutions.
Secondly, proper storage and handling of isotonic solutions are critical to maintaining their efficacy and safety. Healthcare facilities must implement robust inventory management systems to track expiration dates, lot numbers, and storage conditions. Temperature-controlled environments are necessary to prevent degradation of the solutions, and regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of contamination or compromise.
Thirdly, the administration of isotonic solutions requires careful monitoring and documentation. Healthcare providers must be trained in proper infusion techniques, including the use of sterile equipment and aseptic procedures. The implementation of electronic health records and barcode scanning systems can help reduce medication errors and ensure accurate documentation of infusion rates, volumes, and patient responses.
Furthermore, continuous patient monitoring during intravenous therapy is essential. This includes regular assessment of vital signs, fluid balance, and electrolyte levels to detect any adverse reactions or imbalances promptly. The use of smart infusion pumps with built-in safety features, such as dose error reduction systems and flow rate limits, can significantly enhance patient safety.
Quality control measures should also extend to the evaluation of clinical outcomes and the reporting of adverse events. Establishing a robust pharmacovigilance system allows for the early detection of any safety concerns related to specific batches or formulations of isotonic solutions. Regular audits and reviews of infusion practices can help identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with best practices and regulatory requirements.
Lastly, ongoing education and training for healthcare professionals are crucial components of patient safety and quality control. This includes staying updated on the latest guidelines for intravenous therapy, understanding the specific properties and indications of different isotonic solutions, and being proficient in recognizing and managing potential complications.
By implementing these comprehensive patient safety and quality control measures, healthcare providers can optimize the therapeutic benefits of isotonic solutions while minimizing risks to patient well-being. This holistic approach ensures that intravenous infusion therapy remains a safe and effective treatment modality across various clinical settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!