Muriatic Acid's Role in the Production of Pharmaceuticals
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muriatic Acid in Pharma: Background and Objectives
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, has played a pivotal role in the pharmaceutical industry for decades. This strong mineral acid, with its unique chemical properties, has become an indispensable component in various stages of drug production. The evolution of muriatic acid's application in pharmaceuticals can be traced back to the early 20th century when industrial-scale production of medicines began to take shape.
Initially, muriatic acid was primarily used in basic chemical processes within pharmaceutical manufacturing. However, as the industry advanced, so did the understanding of this versatile compound's potential. The acid's ability to control pH levels, catalyze reactions, and act as a powerful cleaning agent has made it an essential tool in the pharmaceutical arsenal.
The objectives of utilizing muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production are multifaceted. Primarily, it serves as a crucial reagent in the synthesis of various drug compounds. Its strong acidic nature allows for the protonation of molecules, facilitating key reactions in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Additionally, muriatic acid plays a significant role in the purification and isolation of pharmaceutical compounds, helping to separate desired products from reaction mixtures.
Another critical objective is the use of muriatic acid in the cleaning and sterilization of pharmaceutical equipment. Its corrosive properties make it highly effective in removing mineral deposits, scale, and other contaminants from production machinery, ensuring the maintenance of sterile conditions essential for drug manufacturing.
Furthermore, muriatic acid is employed in the production of buffer solutions, which are vital for maintaining stable pH environments during various stages of drug formulation and testing. This application is particularly important in ensuring the stability and efficacy of pharmaceutical products throughout their shelf life.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of muriatic acid is expected to expand further. Emerging trends in drug discovery and production, such as continuous flow chemistry and green manufacturing processes, are likely to present new opportunities for the application of this versatile acid. The ongoing research into novel drug delivery systems and personalized medicine may also uncover additional uses for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of muriatic acid use in pharmaceuticals underscore its importance as a fundamental component in drug manufacturing. From synthesis to purification, cleaning to pH control, this acid continues to be a cornerstone in the production of safe and effective medicines. As the industry progresses, the adaptability and utility of muriatic acid ensure its continued relevance in addressing future challenges and innovations in pharmaceutical production.
Initially, muriatic acid was primarily used in basic chemical processes within pharmaceutical manufacturing. However, as the industry advanced, so did the understanding of this versatile compound's potential. The acid's ability to control pH levels, catalyze reactions, and act as a powerful cleaning agent has made it an essential tool in the pharmaceutical arsenal.
The objectives of utilizing muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production are multifaceted. Primarily, it serves as a crucial reagent in the synthesis of various drug compounds. Its strong acidic nature allows for the protonation of molecules, facilitating key reactions in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Additionally, muriatic acid plays a significant role in the purification and isolation of pharmaceutical compounds, helping to separate desired products from reaction mixtures.
Another critical objective is the use of muriatic acid in the cleaning and sterilization of pharmaceutical equipment. Its corrosive properties make it highly effective in removing mineral deposits, scale, and other contaminants from production machinery, ensuring the maintenance of sterile conditions essential for drug manufacturing.
Furthermore, muriatic acid is employed in the production of buffer solutions, which are vital for maintaining stable pH environments during various stages of drug formulation and testing. This application is particularly important in ensuring the stability and efficacy of pharmaceutical products throughout their shelf life.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of muriatic acid is expected to expand further. Emerging trends in drug discovery and production, such as continuous flow chemistry and green manufacturing processes, are likely to present new opportunities for the application of this versatile acid. The ongoing research into novel drug delivery systems and personalized medicine may also uncover additional uses for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of muriatic acid use in pharmaceuticals underscore its importance as a fundamental component in drug manufacturing. From synthesis to purification, cleaning to pH control, this acid continues to be a cornerstone in the production of safe and effective medicines. As the industry progresses, the adaptability and utility of muriatic acid ensure its continued relevance in addressing future challenges and innovations in pharmaceutical production.
Market Analysis: Pharmaceutical Demand for Muriatic Acid
The pharmaceutical industry's demand for muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, has been steadily increasing due to its crucial role in various stages of drug production. This versatile chemical is extensively used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), pH adjustment, and cleaning processes within pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities.
In recent years, the global pharmaceutical market has experienced significant growth, driven by factors such as an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and advancements in drug discovery technologies. This expansion has directly contributed to the rising demand for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical applications.
The API synthesis segment represents a substantial portion of muriatic acid consumption in the pharmaceutical industry. Many drug molecules require acidic conditions during their production, and muriatic acid serves as an essential reagent in these processes. Its ability to catalyze reactions, control pH levels, and facilitate the formation of salt compounds makes it indispensable in API manufacturing.
Furthermore, the growing trend towards personalized medicine and biopharmaceuticals has opened new avenues for muriatic acid usage. These specialized drugs often require precise pH control during production, which can be achieved through the careful application of muriatic acid.
The pharmaceutical industry's stringent quality standards have also influenced the demand for high-purity muriatic acid. Manufacturers are increasingly seeking pharmaceutical-grade hydrochloric acid to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and maintain product quality. This has led to the development of specialized production processes and purification techniques to meet the industry's exacting standards.
Geographically, the demand for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical applications is most pronounced in regions with established pharmaceutical manufacturing hubs. North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, particularly India and China, are key markets driving the consumption of muriatic acid in this sector.
Looking ahead, the pharmaceutical industry's demand for muriatic acid is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors such as the ongoing development of novel drug formulations, expansion of generic drug production, and increasing focus on quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing are likely to sustain this growth trend.
However, it is important to note that the industry is also exploring alternative technologies and greener chemistry approaches, which may impact the long-term demand for traditional chemicals like muriatic acid. Nonetheless, for the foreseeable future, muriatic acid remains an integral component in pharmaceutical production processes, with its market closely tied to the overall growth and innovation within the pharmaceutical sector.
In recent years, the global pharmaceutical market has experienced significant growth, driven by factors such as an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and advancements in drug discovery technologies. This expansion has directly contributed to the rising demand for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical applications.
The API synthesis segment represents a substantial portion of muriatic acid consumption in the pharmaceutical industry. Many drug molecules require acidic conditions during their production, and muriatic acid serves as an essential reagent in these processes. Its ability to catalyze reactions, control pH levels, and facilitate the formation of salt compounds makes it indispensable in API manufacturing.
Furthermore, the growing trend towards personalized medicine and biopharmaceuticals has opened new avenues for muriatic acid usage. These specialized drugs often require precise pH control during production, which can be achieved through the careful application of muriatic acid.
The pharmaceutical industry's stringent quality standards have also influenced the demand for high-purity muriatic acid. Manufacturers are increasingly seeking pharmaceutical-grade hydrochloric acid to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and maintain product quality. This has led to the development of specialized production processes and purification techniques to meet the industry's exacting standards.
Geographically, the demand for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical applications is most pronounced in regions with established pharmaceutical manufacturing hubs. North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, particularly India and China, are key markets driving the consumption of muriatic acid in this sector.
Looking ahead, the pharmaceutical industry's demand for muriatic acid is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors such as the ongoing development of novel drug formulations, expansion of generic drug production, and increasing focus on quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing are likely to sustain this growth trend.
However, it is important to note that the industry is also exploring alternative technologies and greener chemistry approaches, which may impact the long-term demand for traditional chemicals like muriatic acid. Nonetheless, for the foreseeable future, muriatic acid remains an integral component in pharmaceutical production processes, with its market closely tied to the overall growth and innovation within the pharmaceutical sector.
Current Applications and Challenges in Pharma Production
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, plays a crucial role in various stages of pharmaceutical production. Its primary applications include synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), pH adjustment, and equipment cleaning. In API synthesis, muriatic acid serves as a catalyst or reagent in numerous chemical reactions, facilitating the formation of complex molecular structures essential for drug efficacy.
One of the most significant uses of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical manufacturing is in the production of antibiotics. For instance, it is employed in the synthesis of cephalosporins, a widely used class of antibiotics. The acid catalyzes key reactions in the production process, enabling the formation of the β-lactam ring structure characteristic of these compounds. Additionally, muriatic acid is utilized in the manufacture of other antibiotics such as amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin.
pH adjustment is another critical application of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production. Many drug formulations require precise pH levels to ensure stability, solubility, and bioavailability. Muriatic acid's strong acidic properties make it an ideal agent for lowering pH in various pharmaceutical solutions and suspensions. This is particularly important in the production of injectable drugs, where pH control is crucial for patient safety and drug efficacy.
In the realm of quality control and equipment maintenance, muriatic acid is extensively used for cleaning and sanitizing pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. Its ability to dissolve mineral deposits and remove contaminants makes it an effective cleaning agent, ensuring that production equipment meets stringent hygiene standards required in the pharmaceutical industry.
Despite its widespread use, the application of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the corrosive nature of the acid, which necessitates the use of specialized handling equipment and storage facilities. This not only increases production costs but also poses potential safety risks to workers and the environment.
Another significant challenge is the need for precise control of acid concentration and purity. Pharmaceutical-grade muriatic acid must meet stringent quality standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of the final drug products. Achieving and maintaining these high purity levels can be technically demanding and costly.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices in the pharmaceutical industry presents a challenge to the traditional use of muriatic acid. There is growing pressure to develop alternative processes that reduce or eliminate the use of strong acids, driving research into more environmentally friendly production methods.
One of the most significant uses of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical manufacturing is in the production of antibiotics. For instance, it is employed in the synthesis of cephalosporins, a widely used class of antibiotics. The acid catalyzes key reactions in the production process, enabling the formation of the β-lactam ring structure characteristic of these compounds. Additionally, muriatic acid is utilized in the manufacture of other antibiotics such as amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin.
pH adjustment is another critical application of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production. Many drug formulations require precise pH levels to ensure stability, solubility, and bioavailability. Muriatic acid's strong acidic properties make it an ideal agent for lowering pH in various pharmaceutical solutions and suspensions. This is particularly important in the production of injectable drugs, where pH control is crucial for patient safety and drug efficacy.
In the realm of quality control and equipment maintenance, muriatic acid is extensively used for cleaning and sanitizing pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. Its ability to dissolve mineral deposits and remove contaminants makes it an effective cleaning agent, ensuring that production equipment meets stringent hygiene standards required in the pharmaceutical industry.
Despite its widespread use, the application of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the corrosive nature of the acid, which necessitates the use of specialized handling equipment and storage facilities. This not only increases production costs but also poses potential safety risks to workers and the environment.
Another significant challenge is the need for precise control of acid concentration and purity. Pharmaceutical-grade muriatic acid must meet stringent quality standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of the final drug products. Achieving and maintaining these high purity levels can be technically demanding and costly.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices in the pharmaceutical industry presents a challenge to the traditional use of muriatic acid. There is growing pressure to develop alternative processes that reduce or eliminate the use of strong acids, driving research into more environmentally friendly production methods.
Existing Methodologies for Muriatic Acid Utilization
01 Chemical properties and applications
Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, is a strong mineral acid with various industrial and commercial applications. It is used in metal cleaning, pH adjustment, and as a reagent in chemical processes. Its corrosive nature and ability to dissolve certain metals make it useful in surface preparation and etching.- Chemical properties and applications of muriatic acid: Muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, is a strong mineral acid with various industrial and commercial applications. It is used in metal cleaning, pH adjustment, and as a reagent in chemical processes. Its corrosive nature makes it effective for removing rust and scale from metals.
- Use of muriatic acid in construction and building materials: Muriatic acid is utilized in the construction industry for cleaning masonry, concrete, and other building materials. It can be used to etch concrete surfaces, remove efflorescence, and prepare surfaces for further treatment or coating. The acid is also employed in the production of certain building materials.
- Environmental and safety considerations for muriatic acid handling: Due to its corrosive nature, proper handling and storage of muriatic acid are crucial. Safety measures include using appropriate personal protective equipment, proper ventilation, and specialized containment systems. Environmental regulations govern its use and disposal to prevent pollution and protect ecosystems.
- Industrial processes involving muriatic acid: Muriatic acid plays a role in various industrial processes, including metal pickling, water treatment, and chemical manufacturing. It is used in the production of chlorides, in the extraction of certain minerals, and as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions. The acid's ability to dissolve metal oxides makes it valuable in metallurgical applications.
- Innovations in muriatic acid formulations and alternatives: Research and development efforts focus on improving muriatic acid formulations for specific applications, as well as developing safer alternatives. This includes the creation of inhibited muriatic acid products to reduce corrosion, and the exploration of less hazardous substitutes that can perform similar functions in various industries.
02 Production and manufacturing methods
Various methods are employed to produce muriatic acid, including the reaction of sodium chloride with sulfuric acid, and as a byproduct in chlorine production. Innovations in manufacturing processes focus on improving yield, purity, and environmental impact of production.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety and handling considerations
Due to its corrosive nature, special precautions are necessary when handling muriatic acid. This includes proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods. Safety equipment and neutralization techniques are essential in managing potential hazards associated with its use.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact and waste management
The use and disposal of muriatic acid can have significant environmental implications. Research focuses on developing environmentally friendly alternatives, improving waste management practices, and implementing recycling methods to minimize its ecological footprint.Expand Specific Solutions05 Specialized applications in industry
Muriatic acid finds specialized applications in various industries, including water treatment, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. Innovations in these areas focus on optimizing its use for specific processes, such as scale removal in industrial equipment or as a catalyst in chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Muriatic Acid and Pharmaceutical Industries
The market for muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production is in a mature stage, with a stable global market size estimated in the billions of dollars. The technology is well-established, with key players like Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, and Janssen Pharmaceutica having extensive experience in its application. However, emerging companies such as Sunshine Lake Pharma and Guangzhou Nanxin Pharma are also making strides in this field. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized firms, with ongoing research focused on optimizing processes and exploring new applications in drug synthesis and purification.
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC
Technical Solution: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC utilizes muriatic acid (hydrochloric acid) in various pharmaceutical production processes. They employ it as a key reagent in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), particularly in the production of certain antibiotics and antiviral drugs. The company has developed advanced purification techniques that involve using muriatic acid for pH adjustment and as a catalyst in chemical reactions. Their approach includes a controlled-release system for muriatic acid application, ensuring precise dosing and minimizing waste[1]. Additionally, Merck has implemented a closed-loop recycling system for muriatic acid, significantly reducing environmental impact and improving cost-efficiency in pharmaceutical manufacturing[3].
Strengths: Advanced purification techniques, controlled-release system for precise application, and environmentally friendly recycling process. Weaknesses: Potential safety concerns due to the corrosive nature of muriatic acid, requiring stringent handling protocols.
Genentech, Inc.
Technical Solution: Genentech, Inc. employs muriatic acid in various aspects of biopharmaceutical production, particularly in the purification and modification of protein-based drugs. They have developed a proprietary process that uses controlled amounts of muriatic acid for selective pH adjustment during protein refolding and purification steps[9]. Genentech's approach includes a sophisticated buffer exchange system that precisely controls the introduction of muriatic acid to maintain optimal conditions for protein stability and activity. The company has also implemented an advanced inline dilution system that allows for real-time adjustment of muriatic acid concentrations, ensuring consistent and reproducible results in large-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing[10]. Additionally, Genentech has invested in developing novel chromatography resins that are highly resistant to muriatic acid, enabling more efficient and cost-effective purification processes for complex biological molecules.
Strengths: Precise pH control for protein processing, advanced inline dilution system, and acid-resistant chromatography resins. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up processes for certain sensitive biological products and the need for specialized training for handling biohazardous materials in conjunction with muriatic acid.
Innovative Uses of Muriatic Acid in Drug Synthesis
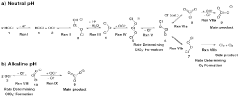
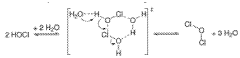
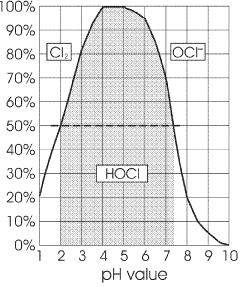
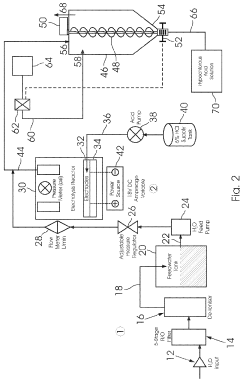
A method for manufacturing pharmaceutical grade hypochlorous acid
PatentWO2023152695A1
Innovation
- A method involving the electrolysis of platinum-grade hydrochloric acid in a single chamber with real-time pH adjustment using a buffering agent like disodium hydrogen orthophosphate to produce hypochlorous acid at a pH of 4.0 to 5.8, avoiding the formation of toxic by-products and ensuring a sodium-free solution.
Pharmaceutical composition for topical use comprising at least one azolated local antifungal substance
PatentPendingUS20220193037A1
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical composition in the form of a water-in-oil emulsion containing 0.3-5% azole antifungal substances, a gelled aqueous phase, and a fatty phase with a specific emulsifying system comprising alkyl polyglycosides and polyglycerol esters, which maintains homogeneity at ambient and elevated temperatures for at least three months.
Environmental Impact and Regulatory Compliance
The use of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production raises significant environmental and regulatory concerns. The corrosive nature of this acid poses potential risks to ecosystems if not properly managed. Pharmaceutical companies must implement stringent waste management protocols to neutralize and safely dispose of acid residues, preventing contamination of water bodies and soil.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical manufacturing. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) to ensure proper hazardous waste management. Similarly, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of muriatic acid and other potentially harmful substances.
Compliance with these regulations requires pharmaceutical companies to invest in advanced treatment technologies and monitoring systems. Closed-loop systems and acid recovery units are increasingly being adopted to minimize environmental impact and improve resource efficiency. These systems not only reduce waste but also lower operational costs in the long run.
Air quality is another critical concern, as muriatic acid can release harmful fumes. Manufacturers must install effective ventilation systems and air scrubbers to capture and neutralize acid vapors, ensuring worker safety and compliance with air quality standards. Regular monitoring of air emissions is essential to meet regulatory requirements and maintain environmental permits.
The pharmaceutical industry is also exploring greener alternatives to muriatic acid where possible. This includes the development of less corrosive acids or entirely different chemical processes that achieve similar results with reduced environmental impact. Such innovations are driven by both regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability initiatives.
Water treatment is a crucial aspect of environmental compliance in muriatic acid usage. Effluent from pharmaceutical production must be carefully treated to neutralize acidity and remove any trace contaminants before release. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as membrane filtration and chemical precipitation, are employed to meet increasingly stringent discharge limits.
As global environmental regulations continue to evolve, pharmaceutical companies must stay proactive in their approach to muriatic acid management. This involves ongoing investment in research and development of cleaner technologies, regular environmental audits, and continuous improvement of waste management practices. By prioritizing environmental stewardship and regulatory compliance, the industry can ensure sustainable use of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical manufacturing. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) to ensure proper hazardous waste management. Similarly, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of muriatic acid and other potentially harmful substances.
Compliance with these regulations requires pharmaceutical companies to invest in advanced treatment technologies and monitoring systems. Closed-loop systems and acid recovery units are increasingly being adopted to minimize environmental impact and improve resource efficiency. These systems not only reduce waste but also lower operational costs in the long run.
Air quality is another critical concern, as muriatic acid can release harmful fumes. Manufacturers must install effective ventilation systems and air scrubbers to capture and neutralize acid vapors, ensuring worker safety and compliance with air quality standards. Regular monitoring of air emissions is essential to meet regulatory requirements and maintain environmental permits.
The pharmaceutical industry is also exploring greener alternatives to muriatic acid where possible. This includes the development of less corrosive acids or entirely different chemical processes that achieve similar results with reduced environmental impact. Such innovations are driven by both regulatory pressure and corporate sustainability initiatives.
Water treatment is a crucial aspect of environmental compliance in muriatic acid usage. Effluent from pharmaceutical production must be carefully treated to neutralize acidity and remove any trace contaminants before release. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies, such as membrane filtration and chemical precipitation, are employed to meet increasingly stringent discharge limits.
As global environmental regulations continue to evolve, pharmaceutical companies must stay proactive in their approach to muriatic acid management. This involves ongoing investment in research and development of cleaner technologies, regular environmental audits, and continuous improvement of waste management practices. By prioritizing environmental stewardship and regulatory compliance, the industry can ensure sustainable use of muriatic acid in pharmaceutical production while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Safety Protocols and Handling Procedures
The handling of muriatic acid, also known as hydrochloric acid, in pharmaceutical production requires stringent safety protocols and handling procedures to ensure the protection of personnel and the integrity of the manufacturing process. These protocols are designed to mitigate the risks associated with the corrosive and potentially hazardous nature of the acid.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with muriatic acid. Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, protective eyewear, face shields, and acid-resistant aprons or suits. Respiratory protection may also be necessary, depending on the concentration and potential for vapor exposure. All PPE must be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure its effectiveness.
Proper storage of muriatic acid is critical to prevent accidents and maintain its quality. The acid should be stored in corrosion-resistant containers, typically made of polyethylene or other suitable materials, in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Storage areas must be equipped with appropriate spill containment systems and clearly labeled with hazard warnings.
Handling procedures for muriatic acid involve careful transfer techniques to minimize the risk of spills or splashes. The use of closed systems, such as pumps and pipelines, is preferred over manual pouring. When dilution is necessary, the acid should always be added to water, never the reverse, to prevent violent reactions and splattering.
Emergency response protocols must be in place and regularly practiced. This includes the installation of easily accessible emergency showers and eyewash stations in areas where muriatic acid is used or stored. Spill kits containing neutralizing agents, absorbents, and appropriate cleanup materials should be readily available.
Training is a crucial component of safety protocols. All personnel involved in handling muriatic acid must receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. This training should be regularly updated and reinforced through drills and refresher courses.
Environmental considerations are also integral to the safety protocols. Proper disposal methods for muriatic acid and its waste products must be implemented, adhering to local regulations and environmental standards. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized waste management services.
Monitoring and documentation play a vital role in maintaining safety standards. Regular inspections of storage areas, handling equipment, and safety systems should be conducted and documented. Incident reporting and analysis procedures should be established to learn from any accidents or near-misses and continuously improve safety measures.
By implementing and strictly adhering to these comprehensive safety protocols and handling procedures, pharmaceutical manufacturers can effectively manage the risks associated with muriatic acid use, ensuring the safety of their personnel and the quality of their products.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount when working with muriatic acid. Workers must wear chemical-resistant gloves, protective eyewear, face shields, and acid-resistant aprons or suits. Respiratory protection may also be necessary, depending on the concentration and potential for vapor exposure. All PPE must be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure its effectiveness.
Proper storage of muriatic acid is critical to prevent accidents and maintain its quality. The acid should be stored in corrosion-resistant containers, typically made of polyethylene or other suitable materials, in a well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Storage areas must be equipped with appropriate spill containment systems and clearly labeled with hazard warnings.
Handling procedures for muriatic acid involve careful transfer techniques to minimize the risk of spills or splashes. The use of closed systems, such as pumps and pipelines, is preferred over manual pouring. When dilution is necessary, the acid should always be added to water, never the reverse, to prevent violent reactions and splattering.
Emergency response protocols must be in place and regularly practiced. This includes the installation of easily accessible emergency showers and eyewash stations in areas where muriatic acid is used or stored. Spill kits containing neutralizing agents, absorbents, and appropriate cleanup materials should be readily available.
Training is a crucial component of safety protocols. All personnel involved in handling muriatic acid must receive comprehensive training on its properties, hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. This training should be regularly updated and reinforced through drills and refresher courses.
Environmental considerations are also integral to the safety protocols. Proper disposal methods for muriatic acid and its waste products must be implemented, adhering to local regulations and environmental standards. This may involve neutralization processes or specialized waste management services.
Monitoring and documentation play a vital role in maintaining safety standards. Regular inspections of storage areas, handling equipment, and safety systems should be conducted and documented. Incident reporting and analysis procedures should be established to learn from any accidents or near-misses and continuously improve safety measures.
By implementing and strictly adhering to these comprehensive safety protocols and handling procedures, pharmaceutical manufacturers can effectively manage the risks associated with muriatic acid use, ensuring the safety of their personnel and the quality of their products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!