QLED in Smart TVs: Enhancing User Interaction
JUN 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
QLED TV Evolution
The evolution of QLED TV technology has been a significant journey in the realm of display innovation, particularly in enhancing user interaction within smart TV ecosystems. QLED, or Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode, technology has undergone several key developmental stages since its inception, each marking a leap forward in picture quality, energy efficiency, and interactive capabilities.
In the early stages of QLED development, the focus was primarily on improving color accuracy and brightness. Quantum dots, nano-sized semiconductor particles, were integrated into LED-backlit LCD panels to produce more vibrant and precise colors. This initial phase laid the groundwork for future advancements in display technology, setting new standards for color reproduction in consumer televisions.
As QLED technology matured, manufacturers began to explore ways to enhance contrast ratios and black levels, addressing one of the primary criticisms of LCD-based displays. Advanced local dimming techniques and improved quantum dot formulations resulted in deeper blacks and more dynamic range, bringing QLED closer to the performance of OLED displays while maintaining advantages in brightness and longevity.
The integration of QLED technology with smart TV platforms marked a pivotal moment in its evolution. This convergence allowed for more sophisticated user interfaces, leveraging the superior color and brightness capabilities of QLED to create more engaging and intuitive menu systems. The enhanced visual fidelity also opened new possibilities for interactive content and applications, making the TV a more central hub for home entertainment and information.
Recent developments in QLED technology have focused on improving energy efficiency and expanding the color gamut. The latest generations of QLED TVs boast significantly reduced power consumption while offering an even wider color spectrum, approaching or exceeding 100% of the DCI-P3 color space. This advancement not only improves the viewing experience but also aligns with growing consumer demand for more environmentally friendly electronics.
The evolution of QLED has also seen advancements in panel design and form factor. Manufacturers have achieved thinner profiles and more uniform backlighting, allowing for sleeker designs that blend seamlessly into modern living spaces. This aesthetic improvement, coupled with enhanced picture quality, has contributed to the growing popularity of QLED TVs in the premium market segment.
Looking towards the future, the QLED TV evolution is poised to continue with a focus on further enhancing user interaction. Emerging trends include the integration of advanced voice recognition, gesture control, and AI-driven personalization. These features aim to create a more intuitive and responsive viewing experience, leveraging the superior visual capabilities of QLED technology to deliver more immersive and interactive smart TV functionalities.
In the early stages of QLED development, the focus was primarily on improving color accuracy and brightness. Quantum dots, nano-sized semiconductor particles, were integrated into LED-backlit LCD panels to produce more vibrant and precise colors. This initial phase laid the groundwork for future advancements in display technology, setting new standards for color reproduction in consumer televisions.
As QLED technology matured, manufacturers began to explore ways to enhance contrast ratios and black levels, addressing one of the primary criticisms of LCD-based displays. Advanced local dimming techniques and improved quantum dot formulations resulted in deeper blacks and more dynamic range, bringing QLED closer to the performance of OLED displays while maintaining advantages in brightness and longevity.
The integration of QLED technology with smart TV platforms marked a pivotal moment in its evolution. This convergence allowed for more sophisticated user interfaces, leveraging the superior color and brightness capabilities of QLED to create more engaging and intuitive menu systems. The enhanced visual fidelity also opened new possibilities for interactive content and applications, making the TV a more central hub for home entertainment and information.
Recent developments in QLED technology have focused on improving energy efficiency and expanding the color gamut. The latest generations of QLED TVs boast significantly reduced power consumption while offering an even wider color spectrum, approaching or exceeding 100% of the DCI-P3 color space. This advancement not only improves the viewing experience but also aligns with growing consumer demand for more environmentally friendly electronics.
The evolution of QLED has also seen advancements in panel design and form factor. Manufacturers have achieved thinner profiles and more uniform backlighting, allowing for sleeker designs that blend seamlessly into modern living spaces. This aesthetic improvement, coupled with enhanced picture quality, has contributed to the growing popularity of QLED TVs in the premium market segment.
Looking towards the future, the QLED TV evolution is poised to continue with a focus on further enhancing user interaction. Emerging trends include the integration of advanced voice recognition, gesture control, and AI-driven personalization. These features aim to create a more intuitive and responsive viewing experience, leveraging the superior visual capabilities of QLED technology to deliver more immersive and interactive smart TV functionalities.
Smart TV Market Trends
The Smart TV market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. As households increasingly seek immersive entertainment experiences, Smart TVs have become a central hub for digital content consumption and interactive experiences.
Market research indicates a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the Smart TV sector, with projections suggesting continued expansion through the next decade. This growth is fueled by factors such as increasing disposable income, rising demand for high-quality visual experiences, and the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and voice control.
Consumer behavior trends show a shift towards larger screen sizes and higher resolution displays, with 4K and 8K TVs gaining traction in premium market segments. The adoption of QLED technology has been particularly noteworthy, as it offers enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays.
Content streaming has become a primary driver of Smart TV adoption, with major platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ influencing consumer purchasing decisions. TVs with built-in streaming capabilities and user-friendly interfaces are increasingly preferred over traditional models.
The integration of smart home features has emerged as a key trend, with consumers seeking TVs that can seamlessly connect with other IoT devices. This has led to the development of TVs that serve as control centers for home automation systems, further enhancing their value proposition.
Personalization and user interaction have become focal points for manufacturers. Advanced recommendation algorithms, voice-activated controls, and gesture recognition are being incorporated to create more intuitive and engaging user experiences. QLED technology plays a crucial role in this trend by providing the visual fidelity necessary for these interactive features.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads in Smart TV market growth, driven by rapid urbanization and increasing tech-savvy populations in countries like China and India. North America and Europe maintain strong market positions, with consumers in these regions showing a preference for premium, feature-rich models.
The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry among major electronics manufacturers, with companies investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their offerings. Partnerships between TV manufacturers and content providers are becoming more common, aiming to create exclusive ecosystems that lock in consumer loyalty.
As the market evolves, sustainability has emerged as a growing concern. Consumers are increasingly considering energy efficiency and eco-friendly manufacturing processes in their purchasing decisions, prompting manufacturers to focus on developing more sustainable QLED and Smart TV technologies.
Market research indicates a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the Smart TV sector, with projections suggesting continued expansion through the next decade. This growth is fueled by factors such as increasing disposable income, rising demand for high-quality visual experiences, and the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and voice control.
Consumer behavior trends show a shift towards larger screen sizes and higher resolution displays, with 4K and 8K TVs gaining traction in premium market segments. The adoption of QLED technology has been particularly noteworthy, as it offers enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays.
Content streaming has become a primary driver of Smart TV adoption, with major platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ influencing consumer purchasing decisions. TVs with built-in streaming capabilities and user-friendly interfaces are increasingly preferred over traditional models.
The integration of smart home features has emerged as a key trend, with consumers seeking TVs that can seamlessly connect with other IoT devices. This has led to the development of TVs that serve as control centers for home automation systems, further enhancing their value proposition.
Personalization and user interaction have become focal points for manufacturers. Advanced recommendation algorithms, voice-activated controls, and gesture recognition are being incorporated to create more intuitive and engaging user experiences. QLED technology plays a crucial role in this trend by providing the visual fidelity necessary for these interactive features.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific leads in Smart TV market growth, driven by rapid urbanization and increasing tech-savvy populations in countries like China and India. North America and Europe maintain strong market positions, with consumers in these regions showing a preference for premium, feature-rich models.
The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry among major electronics manufacturers, with companies investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their offerings. Partnerships between TV manufacturers and content providers are becoming more common, aiming to create exclusive ecosystems that lock in consumer loyalty.
As the market evolves, sustainability has emerged as a growing concern. Consumers are increasingly considering energy efficiency and eco-friendly manufacturing processes in their purchasing decisions, prompting manufacturers to focus on developing more sustainable QLED and Smart TV technologies.
QLED Challenges
QLED technology in smart TVs faces several significant challenges that hinder its full potential in enhancing user interaction. One of the primary obstacles is the high production cost associated with QLED displays. The complex manufacturing process and the need for high-quality quantum dots contribute to elevated prices, making QLED TVs less accessible to a broader consumer base. This cost barrier limits widespread adoption and slows down the integration of advanced interactive features.
Another challenge lies in the color accuracy and consistency of QLED displays. While QLED technology offers impressive color reproduction, maintaining uniform color performance across the entire screen and throughout the TV's lifespan remains a concern. Color shift and degradation over time can impact the user experience, particularly in interactive applications that rely on precise color representation.
Power consumption is a persistent issue for QLED displays. The technology requires significant energy to achieve high brightness levels, which is crucial for HDR content and visibility in well-lit environments. However, this increased power demand conflicts with growing consumer and regulatory pressures for more energy-efficient devices. Balancing performance with energy efficiency presents a complex challenge for manufacturers.
QLED technology also faces difficulties in achieving true black levels and infinite contrast ratios, which are critical for immersive viewing experiences. Unlike OLED, QLED relies on a backlight system, which can lead to light bleeding and reduced contrast in dark scenes. This limitation affects the overall picture quality and can detract from the user's interaction with content, especially in scenarios requiring fine detail perception.
The refresh rate and response time of QLED displays present another hurdle, particularly for interactive applications and gaming. While improvements have been made, QLED still lags behind some competing technologies in terms of motion handling and input lag. This can impact the smoothness and responsiveness of user interactions, potentially limiting the technology's application in fast-paced, interactive environments.
Lastly, the integration of touch functionality with QLED displays poses significant technical challenges. Implementing responsive and accurate touch interfaces on large-format QLED screens without compromising display quality or increasing thickness is a complex task. This limitation restricts the development of more intuitive and direct user interaction methods in smart TVs, which could otherwise revolutionize the way users engage with content and applications.
Another challenge lies in the color accuracy and consistency of QLED displays. While QLED technology offers impressive color reproduction, maintaining uniform color performance across the entire screen and throughout the TV's lifespan remains a concern. Color shift and degradation over time can impact the user experience, particularly in interactive applications that rely on precise color representation.
Power consumption is a persistent issue for QLED displays. The technology requires significant energy to achieve high brightness levels, which is crucial for HDR content and visibility in well-lit environments. However, this increased power demand conflicts with growing consumer and regulatory pressures for more energy-efficient devices. Balancing performance with energy efficiency presents a complex challenge for manufacturers.
QLED technology also faces difficulties in achieving true black levels and infinite contrast ratios, which are critical for immersive viewing experiences. Unlike OLED, QLED relies on a backlight system, which can lead to light bleeding and reduced contrast in dark scenes. This limitation affects the overall picture quality and can detract from the user's interaction with content, especially in scenarios requiring fine detail perception.
The refresh rate and response time of QLED displays present another hurdle, particularly for interactive applications and gaming. While improvements have been made, QLED still lags behind some competing technologies in terms of motion handling and input lag. This can impact the smoothness and responsiveness of user interactions, potentially limiting the technology's application in fast-paced, interactive environments.
Lastly, the integration of touch functionality with QLED displays poses significant technical challenges. Implementing responsive and accurate touch interfaces on large-format QLED screens without compromising display quality or increasing thickness is a complex task. This limitation restricts the development of more intuitive and direct user interaction methods in smart TVs, which could otherwise revolutionize the way users engage with content and applications.
Current QLED Solutions
01 Touch-based user interaction in QLED displays
QLED technology incorporates touch-based user interaction features, allowing users to directly interact with the display. This includes multi-touch capabilities, gesture recognition, and pressure-sensitive inputs, enhancing the overall user experience and providing intuitive control over the device's functions.- Touch-based user interaction in QLED displays: QLED displays are incorporating touch-based user interaction technologies to enhance user experience. These systems allow users to directly interact with the display through touch gestures, providing intuitive control and navigation. The integration of touch sensors with QLED technology enables responsive and accurate touch detection, making it suitable for various applications including smartphones, tablets, and interactive kiosks.
- Voice control and AI integration in QLED devices: QLED technology is being combined with voice recognition and artificial intelligence to create more advanced user interaction systems. These systems allow users to control QLED devices through voice commands, enabling hands-free operation and improved accessibility. AI algorithms are used to process and interpret voice inputs, enhancing the accuracy and responsiveness of the interaction.
- Gesture recognition for QLED display control: Gesture recognition technology is being integrated into QLED displays to provide a novel form of user interaction. This allows users to control the display and navigate content using hand movements and gestures captured by sensors. The system interprets these gestures to perform various functions, offering a more immersive and intuitive user experience, particularly in large-screen applications and smart home environments.
- User interface design for QLED smart devices: Specialized user interface designs are being developed for QLED-based smart devices to optimize the user interaction experience. These interfaces take advantage of the high color accuracy and contrast ratios of QLED displays to create visually appealing and easy-to-navigate menus and controls. The design focuses on enhancing readability, reducing eye strain, and improving overall usability across various lighting conditions.
- Integration of haptic feedback in QLED user interfaces: Haptic feedback mechanisms are being incorporated into QLED display systems to provide tactile responses to user interactions. This technology enhances the user experience by offering physical feedback to touch inputs, creating a more engaging and responsive interface. The integration of haptic feedback with QLED displays is particularly useful in automotive displays, gaming devices, and professional equipment where tactile confirmation of inputs is crucial.
02 Voice control and AI integration in QLED systems
QLED devices are equipped with voice control capabilities and AI integration, enabling users to interact with the display using voice commands. This feature allows for hands-free operation, personalized content recommendations, and smart home integration, making the user interaction more convenient and efficient.Expand Specific Solutions03 Gesture-based control for QLED displays
Gesture recognition technology is implemented in QLED displays, allowing users to control the device through hand movements and gestures. This contactless interaction method provides a more immersive and hygienic user experience, particularly useful in public spaces or when hands are occupied.Expand Specific Solutions04 Customizable user interfaces for QLED technology
QLED systems offer customizable user interfaces that adapt to individual preferences and usage patterns. This includes personalized home screens, adjustable layouts, and user-specific content recommendations, enhancing the overall user experience and making interaction with the device more intuitive and efficient.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of external devices with QLED displays
QLED technology supports seamless integration with external devices such as smartphones, tablets, and smart home appliances. This allows for expanded functionality, including screen mirroring, content sharing, and remote control capabilities, creating a more connected and versatile user interaction experience.Expand Specific Solutions
QLED Industry Leaders
The QLED technology in Smart TVs is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market adoption and technological advancements. The global QLED TV market is expanding rapidly, driven by consumer demand for superior picture quality and enhanced user interaction. Technologically, QLED is maturing, with companies like Samsung Electronics, TCL, and Hisense leading the innovation. These firms, along with others such as Sony, LG, and Vizio, are continuously improving QLED's color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency. The competitive landscape is intense, with major players investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their products and capture market share in this high-potential segment of the Smart TV industry.
Hisense Visual Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hisense has developed ULED technology, a proprietary enhancement of QLED, which combines quantum dot technology with other proprietary technologies to improve picture quality. Their smart TVs feature AI-powered VIDAA U5 operating system for personalized content recommendations and voice control. Hisense has also implemented Far-Field Voice Control, allowing users to interact with the TV from across the room without a remote. Their TVs support various smart home platforms for enhanced connectivity and user interaction.
Strengths: Cost-effective QLED solution, AI-powered OS for personalization, far-field voice control. Weaknesses: Less brand recognition in some markets, potentially fewer high-end features compared to top-tier competitors.
Shenzhen Skyworth-RGB Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Skyworth has developed its AI Picture Quality Engine (AIpq) to enhance QLED display performance in smart TVs. Their Chameleon Extreme system uses AI to optimize picture settings based on ambient light and content. For user interaction, Skyworth has implemented far-field voice control and integrated with various AI assistants. Their COOCAA system provides a personalized content recommendation platform. Skyworth has also developed Swaiot, an AIoT ecosystem that allows seamless interaction between the TV and other smart home devices.
Strengths: Strong AI integration for picture quality and smart home features, competitive pricing in many markets. Weaknesses: Lesser-known brand in some regions, potentially fewer high-end features compared to top-tier global brands.
QLED Innovations
Systems and methods for enhancing television display for video conferencing and video watch party applications
PatentPendingUS20220270556A1
Innovation
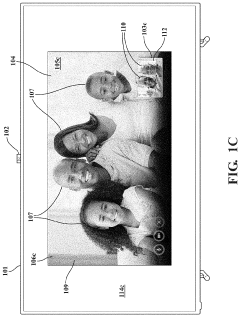
- Utilizing the pixels of a television display, such as LCD or OLED TVs, to selectively illuminate subjects by adjusting pixel parameters like luminance and RGB values, and creating a border of white pixels to provide additional lighting, allowing for improved illumination without the need for external lighting systems.
Interactive media system
PatentActiveUS7716715B2
Innovation
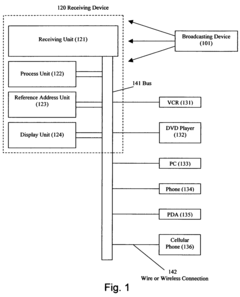
- An interactive media system that uses screen-related action codes embedded in content signals, allowing users to interact with various devices using a small remote control by pressing keys or buttons, without altering existing broadcasting protocols or requiring a mouse, by including a receiving device with a scanning unit, memory, and controller to process and execute commands based on action codes.
UI/UX in Smart TVs
The integration of QLED technology in Smart TVs has significantly transformed the user interface and experience. QLED displays offer enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and contrast, which directly impacts the visual quality of UI elements. This improvement allows for more vibrant and dynamic user interfaces, enabling designers to create more engaging and visually appealing layouts.
The increased color gamut and HDR capabilities of QLED screens enable the implementation of more sophisticated color schemes and gradients in UI design. This enhanced color reproduction allows for better differentiation between UI elements, improving overall usability and reducing eye strain during extended viewing sessions.
QLED's superior brightness and contrast ratios contribute to improved readability of on-screen text and icons, even in well-lit environments. This feature is particularly beneficial for Smart TV interfaces, where users often interact with menus and content descriptions from a distance. The enhanced visibility ensures that users can easily navigate through complex menu structures and read content details without straining their eyes.
The technology's ability to display deep blacks and bright whites simultaneously allows for more creative use of negative space in UI design. This contrast capability enables designers to create sleek, modern interfaces that effectively guide user attention and improve overall navigation efficiency.
QLED's wide viewing angles maintain color accuracy and contrast across different viewing positions, ensuring a consistent UI experience for multiple viewers. This feature is especially valuable in Smart TVs, where multiple users may be interacting with the interface from various angles in a living room setting.
The technology's fast response times and reduced motion blur contribute to smoother animations and transitions within the UI. This responsiveness enhances the overall feel of interactivity, making the interface more engaging and intuitive for users. Smooth scrolling and fluid menu transitions create a more premium and polished user experience.
QLED's energy efficiency allows for the implementation of always-on display features without significant power consumption. This capability enables the design of ambient modes and information displays that can show useful information or decorative elements even when the TV is not actively being watched, further enhancing the overall user experience.
The technology's longevity and resistance to burn-in make it ideal for displaying static UI elements for extended periods. This durability allows designers to implement persistent navigation bars, logos, and other static elements without concerns about screen degradation, ensuring a consistent UI experience throughout the TV's lifespan.
The increased color gamut and HDR capabilities of QLED screens enable the implementation of more sophisticated color schemes and gradients in UI design. This enhanced color reproduction allows for better differentiation between UI elements, improving overall usability and reducing eye strain during extended viewing sessions.
QLED's superior brightness and contrast ratios contribute to improved readability of on-screen text and icons, even in well-lit environments. This feature is particularly beneficial for Smart TV interfaces, where users often interact with menus and content descriptions from a distance. The enhanced visibility ensures that users can easily navigate through complex menu structures and read content details without straining their eyes.
The technology's ability to display deep blacks and bright whites simultaneously allows for more creative use of negative space in UI design. This contrast capability enables designers to create sleek, modern interfaces that effectively guide user attention and improve overall navigation efficiency.
QLED's wide viewing angles maintain color accuracy and contrast across different viewing positions, ensuring a consistent UI experience for multiple viewers. This feature is especially valuable in Smart TVs, where multiple users may be interacting with the interface from various angles in a living room setting.
The technology's fast response times and reduced motion blur contribute to smoother animations and transitions within the UI. This responsiveness enhances the overall feel of interactivity, making the interface more engaging and intuitive for users. Smooth scrolling and fluid menu transitions create a more premium and polished user experience.
QLED's energy efficiency allows for the implementation of always-on display features without significant power consumption. This capability enables the design of ambient modes and information displays that can show useful information or decorative elements even when the TV is not actively being watched, further enhancing the overall user experience.
The technology's longevity and resistance to burn-in make it ideal for displaying static UI elements for extended periods. This durability allows designers to implement persistent navigation bars, logos, and other static elements without concerns about screen degradation, ensuring a consistent UI experience throughout the TV's lifespan.
QLED Energy Efficiency
QLED technology in smart TVs has made significant strides in energy efficiency, addressing one of the key concerns in consumer electronics. The latest QLED displays have demonstrated remarkable improvements in power consumption without compromising on picture quality or performance.
One of the primary factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency is the use of quantum dots. These nanocrystals are highly efficient at converting light, resulting in less energy waste compared to traditional LED-LCD technologies. The quantum dots' ability to produce precise colors with minimal light leakage means that less backlight power is required to achieve the same brightness levels as conventional displays.
Advanced local dimming techniques have further enhanced QLED's energy efficiency. By selectively dimming or turning off LEDs in darker areas of the screen, these TVs can significantly reduce power consumption while maintaining excellent contrast ratios. This dynamic control of backlighting not only improves picture quality but also contributes to overall energy savings.
QLED TVs also benefit from optimized power management systems. These systems intelligently adjust the TV's power consumption based on ambient light conditions and content being displayed. For instance, in low-light environments or when displaying darker scenes, the TV can automatically reduce its brightness and power usage without noticeably affecting the viewing experience.
The incorporation of energy-efficient processors and improved heat management systems in QLED TVs has also played a crucial role in reducing power consumption. These processors are designed to handle complex image processing tasks with minimal energy use, while efficient heat dissipation allows the TV to operate at lower temperatures, further reducing power requirements.
Manufacturers have made significant progress in optimizing the optical stack of QLED displays. By improving light transmission and reducing reflections within the display layers, less backlight power is needed to achieve the desired brightness levels. This optimization not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to improved color accuracy and viewing angles.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in energy efficiency. Research is ongoing into more efficient quantum dot materials, improved backlight designs, and even more sophisticated power management algorithms. These developments promise to make future QLED TVs even more energy-efficient, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption in consumer electronics.
One of the primary factors contributing to QLED's energy efficiency is the use of quantum dots. These nanocrystals are highly efficient at converting light, resulting in less energy waste compared to traditional LED-LCD technologies. The quantum dots' ability to produce precise colors with minimal light leakage means that less backlight power is required to achieve the same brightness levels as conventional displays.
Advanced local dimming techniques have further enhanced QLED's energy efficiency. By selectively dimming or turning off LEDs in darker areas of the screen, these TVs can significantly reduce power consumption while maintaining excellent contrast ratios. This dynamic control of backlighting not only improves picture quality but also contributes to overall energy savings.
QLED TVs also benefit from optimized power management systems. These systems intelligently adjust the TV's power consumption based on ambient light conditions and content being displayed. For instance, in low-light environments or when displaying darker scenes, the TV can automatically reduce its brightness and power usage without noticeably affecting the viewing experience.
The incorporation of energy-efficient processors and improved heat management systems in QLED TVs has also played a crucial role in reducing power consumption. These processors are designed to handle complex image processing tasks with minimal energy use, while efficient heat dissipation allows the TV to operate at lower temperatures, further reducing power requirements.
Manufacturers have made significant progress in optimizing the optical stack of QLED displays. By improving light transmission and reducing reflections within the display layers, less backlight power is needed to achieve the desired brightness levels. This optimization not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to improved color accuracy and viewing angles.
As QLED technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in energy efficiency. Research is ongoing into more efficient quantum dot materials, improved backlight designs, and even more sophisticated power management algorithms. These developments promise to make future QLED TVs even more energy-efficient, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption in consumer electronics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!