Antifreeze Sustains Breakthroughs in Environmental Solution Practices
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Antifreeze Evolution
The evolution of antifreeze technology has been driven by the need for more environmentally friendly and effective solutions to prevent freezing in various applications. Initially, antifreeze formulations primarily consisted of ethylene glycol, a highly effective but toxic substance. As environmental concerns grew, propylene glycol emerged as a less toxic alternative, marking a significant shift in the industry.
In the 1970s and 1980s, researchers began exploring the use of natural antifreeze proteins found in cold-adapted organisms such as fish and insects. These proteins, known as antifreeze glycoproteins (AFGPs) and antifreeze proteins (AFPs), demonstrated remarkable ice crystal growth inhibition properties. This discovery opened up new avenues for biomimetic approaches in antifreeze development.
The 1990s saw the introduction of synthetic antifreeze polymers, designed to mimic the ice-binding properties of natural antifreeze proteins. These polymers, including poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(ethylene glycol), offered improved performance and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional glycol-based solutions.
In the early 2000s, nanotechnology began to play a role in antifreeze development. Researchers explored the use of nanoparticles, such as silica and carbon nanotubes, to enhance the thermal properties and ice nucleation inhibition of antifreeze formulations. This approach led to more efficient heat transfer and improved freeze protection in various applications.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in bio-based antifreeze solutions, utilizing renewable resources such as corn, soybeans, and other plant-derived materials. These eco-friendly alternatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of antifreeze production while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
The development of smart antifreeze systems has also gained traction, incorporating sensors and responsive materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions. These advanced systems offer more precise control over freeze protection, optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the focus has shifted towards developing antifreeze solutions with minimal ecological impact. This has led to the exploration of biodegradable additives and the implementation of closed-loop recycling systems for antifreeze fluids.
The ongoing evolution of antifreeze technology continues to be driven by the dual goals of enhancing performance and reducing environmental impact. Future developments are likely to focus on further improving the efficiency of bio-based solutions, expanding the use of nanotechnology, and integrating smart systems for more sustainable freeze protection practices.
In the 1970s and 1980s, researchers began exploring the use of natural antifreeze proteins found in cold-adapted organisms such as fish and insects. These proteins, known as antifreeze glycoproteins (AFGPs) and antifreeze proteins (AFPs), demonstrated remarkable ice crystal growth inhibition properties. This discovery opened up new avenues for biomimetic approaches in antifreeze development.
The 1990s saw the introduction of synthetic antifreeze polymers, designed to mimic the ice-binding properties of natural antifreeze proteins. These polymers, including poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(ethylene glycol), offered improved performance and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional glycol-based solutions.
In the early 2000s, nanotechnology began to play a role in antifreeze development. Researchers explored the use of nanoparticles, such as silica and carbon nanotubes, to enhance the thermal properties and ice nucleation inhibition of antifreeze formulations. This approach led to more efficient heat transfer and improved freeze protection in various applications.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in bio-based antifreeze solutions, utilizing renewable resources such as corn, soybeans, and other plant-derived materials. These eco-friendly alternatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of antifreeze production while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
The development of smart antifreeze systems has also gained traction, incorporating sensors and responsive materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions. These advanced systems offer more precise control over freeze protection, optimizing energy consumption and reducing waste.
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the focus has shifted towards developing antifreeze solutions with minimal ecological impact. This has led to the exploration of biodegradable additives and the implementation of closed-loop recycling systems for antifreeze fluids.
The ongoing evolution of antifreeze technology continues to be driven by the dual goals of enhancing performance and reducing environmental impact. Future developments are likely to focus on further improving the efficiency of bio-based solutions, expanding the use of nanotechnology, and integrating smart systems for more sustainable freeze protection practices.
Market Analysis
The market for antifreeze solutions in environmental practices has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing awareness of environmental issues and the stringent regulations imposed by governments worldwide to combat climate change and reduce environmental impact.
The global antifreeze market, which includes environmentally friendly solutions, was valued at approximately $5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $7.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period. This growth is largely attributed to the rising demand for sustainable and eco-friendly antifreeze products across various industries, including automotive, construction, and industrial manufacturing.
One of the key factors driving market demand is the automotive sector's shift towards more environmentally responsible practices. As electric vehicles gain popularity and traditional combustion engines become more efficient, there is a growing need for antifreeze solutions that not only provide excellent performance but also minimize environmental impact. This trend has led to increased research and development efforts in bio-based and recyclable antifreeze formulations.
The construction industry is another significant contributor to the market growth. With the expansion of infrastructure projects in developing countries and the emphasis on green building practices, there is a rising demand for antifreeze solutions that can withstand extreme temperatures while adhering to environmental standards. This has created opportunities for innovative products that offer both freeze protection and sustainability.
Industrial manufacturing sectors, particularly in regions with harsh climates, are also driving the demand for advanced antifreeze solutions. These industries require products that can maintain operational efficiency in extreme conditions while complying with increasingly strict environmental regulations. This has led to the development of specialized antifreeze formulations tailored to specific industrial applications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for environmentally friendly antifreeze solutions, owing to their stringent environmental regulations and high adoption rates of sustainable technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing environmental awareness, and government initiatives promoting sustainable practices.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, with companies investing heavily in research and development to gain a competitive edge. Major market players are focusing on developing bio-based antifreeze solutions, improving recycling processes, and enhancing product performance to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
In conclusion, the market for antifreeze solutions in environmental practices is poised for substantial growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and technological advancements. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the demand for innovative and eco-friendly antifreeze products is expected to rise, creating significant opportunities for market expansion and technological breakthroughs in the coming years.
The global antifreeze market, which includes environmentally friendly solutions, was valued at approximately $5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $7.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period. This growth is largely attributed to the rising demand for sustainable and eco-friendly antifreeze products across various industries, including automotive, construction, and industrial manufacturing.
One of the key factors driving market demand is the automotive sector's shift towards more environmentally responsible practices. As electric vehicles gain popularity and traditional combustion engines become more efficient, there is a growing need for antifreeze solutions that not only provide excellent performance but also minimize environmental impact. This trend has led to increased research and development efforts in bio-based and recyclable antifreeze formulations.
The construction industry is another significant contributor to the market growth. With the expansion of infrastructure projects in developing countries and the emphasis on green building practices, there is a rising demand for antifreeze solutions that can withstand extreme temperatures while adhering to environmental standards. This has created opportunities for innovative products that offer both freeze protection and sustainability.
Industrial manufacturing sectors, particularly in regions with harsh climates, are also driving the demand for advanced antifreeze solutions. These industries require products that can maintain operational efficiency in extreme conditions while complying with increasingly strict environmental regulations. This has led to the development of specialized antifreeze formulations tailored to specific industrial applications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for environmentally friendly antifreeze solutions, owing to their stringent environmental regulations and high adoption rates of sustainable technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing environmental awareness, and government initiatives promoting sustainable practices.
The market is characterized by intense competition among key players, with companies investing heavily in research and development to gain a competitive edge. Major market players are focusing on developing bio-based antifreeze solutions, improving recycling processes, and enhancing product performance to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
In conclusion, the market for antifreeze solutions in environmental practices is poised for substantial growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and technological advancements. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the demand for innovative and eco-friendly antifreeze products is expected to rise, creating significant opportunities for market expansion and technological breakthroughs in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The development of antifreeze solutions for environmental applications faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the need to balance effectiveness with environmental safety. Traditional antifreeze compounds, such as ethylene glycol, are highly effective but pose serious risks to ecosystems and human health if released into the environment. This necessitates the development of alternative solutions that maintain performance while minimizing ecological impact.
Another major challenge lies in the formulation of antifreeze solutions that can withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without losing efficacy. As climate change leads to more unpredictable weather patterns, antifreeze products must be able to perform consistently across a wider range of temperatures. This requires advanced research into molecular structures and additives that can maintain stability and functionality under diverse conditions.
The longevity and degradation of antifreeze solutions in environmental applications also present significant hurdles. Many current formulations break down over time, reducing their effectiveness and potentially releasing harmful byproducts. Developing solutions with extended lifespans and benign degradation pathways is crucial for sustainable environmental practices.
Compatibility with various materials and systems is another technical challenge. Antifreeze solutions must be non-corrosive and compatible with a wide range of materials used in environmental infrastructure, including metals, plastics, and rubber seals. Achieving this compatibility without compromising the solution's antifreeze properties requires careful chemical engineering and extensive testing.
The scalability of production for environmentally friendly antifreeze solutions is also a significant technical obstacle. Many promising formulations developed in laboratories face difficulties when scaled up for industrial production. Overcoming these scaling issues while maintaining cost-effectiveness is essential for widespread adoption of new antifreeze technologies in environmental applications.
Additionally, the development of multi-functional antifreeze solutions that can address multiple environmental concerns simultaneously is a complex challenge. Researchers are striving to create formulations that not only prevent freezing but also offer additional benefits such as corrosion inhibition, microbial resistance, or even carbon sequestration capabilities. Integrating these diverse functionalities into a single, effective solution requires interdisciplinary research and innovative approaches.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape poses a technical challenge in the development of new antifreeze solutions. Stringent environmental regulations and safety standards necessitate rigorous testing and validation processes. Meeting these regulatory requirements while pushing the boundaries of antifreeze technology demands a delicate balance between innovation and compliance.
Another major challenge lies in the formulation of antifreeze solutions that can withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without losing efficacy. As climate change leads to more unpredictable weather patterns, antifreeze products must be able to perform consistently across a wider range of temperatures. This requires advanced research into molecular structures and additives that can maintain stability and functionality under diverse conditions.
The longevity and degradation of antifreeze solutions in environmental applications also present significant hurdles. Many current formulations break down over time, reducing their effectiveness and potentially releasing harmful byproducts. Developing solutions with extended lifespans and benign degradation pathways is crucial for sustainable environmental practices.
Compatibility with various materials and systems is another technical challenge. Antifreeze solutions must be non-corrosive and compatible with a wide range of materials used in environmental infrastructure, including metals, plastics, and rubber seals. Achieving this compatibility without compromising the solution's antifreeze properties requires careful chemical engineering and extensive testing.
The scalability of production for environmentally friendly antifreeze solutions is also a significant technical obstacle. Many promising formulations developed in laboratories face difficulties when scaled up for industrial production. Overcoming these scaling issues while maintaining cost-effectiveness is essential for widespread adoption of new antifreeze technologies in environmental applications.
Additionally, the development of multi-functional antifreeze solutions that can address multiple environmental concerns simultaneously is a complex challenge. Researchers are striving to create formulations that not only prevent freezing but also offer additional benefits such as corrosion inhibition, microbial resistance, or even carbon sequestration capabilities. Integrating these diverse functionalities into a single, effective solution requires interdisciplinary research and innovative approaches.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape poses a technical challenge in the development of new antifreeze solutions. Stringent environmental regulations and safety standards necessitate rigorous testing and validation processes. Meeting these regulatory requirements while pushing the boundaries of antifreeze technology demands a delicate balance between innovation and compliance.
Current Solutions
01 Use of environmentally friendly antifreeze compositions
Development of antifreeze formulations using biodegradable and non-toxic ingredients to minimize environmental impact. These compositions often include natural or plant-derived components that are less harmful to ecosystems while maintaining effective antifreeze properties.- Use of environmentally friendly antifreeze compositions: Development of antifreeze formulations using biodegradable and non-toxic ingredients to minimize environmental impact. These compositions often include natural or plant-derived components that are less harmful to ecosystems when released into the environment.
- Recycling and reclamation of antifreeze solutions: Implementation of systems and methods for collecting, purifying, and reusing antifreeze solutions to reduce waste and environmental contamination. This includes on-site recycling processes and centralized reclamation facilities that can process large volumes of used antifreeze.
- Antifreeze additives for improved environmental performance: Incorporation of specific additives in antifreeze formulations to enhance biodegradability, reduce toxicity, or improve overall environmental performance. These additives may include corrosion inhibitors, stabilizers, or compounds that facilitate natural breakdown of the antifreeze in the environment.
- Alternative heat transfer fluids with reduced environmental impact: Development of alternative heat transfer fluids that can replace traditional antifreeze solutions while offering improved environmental characteristics. These may include novel compounds or mixtures designed to have lower toxicity and higher biodegradability.
- Containment and disposal practices for antifreeze solutions: Implementation of best practices for handling, storing, and disposing of antifreeze solutions to prevent environmental contamination. This includes the use of specialized containers, spill prevention measures, and proper disposal methods that comply with environmental regulations.
02 Recycling and reclamation of antifreeze solutions
Implementation of systems and methods for collecting, purifying, and reusing antifreeze solutions. This practice reduces waste and conserves resources by extending the life cycle of antifreeze products, minimizing the need for new production and disposal.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced filtration and treatment technologies
Utilization of innovative filtration and treatment technologies to remove contaminants from used antifreeze solutions. These methods allow for the safe disposal or reuse of treated antifreeze, reducing environmental pollution and improving overall sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of antifreeze systems with renewable energy sources
Design of antifreeze systems that incorporate renewable energy sources for heating and cooling. This approach reduces reliance on fossil fuels and decreases the overall carbon footprint of antifreeze applications in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Development of multi-functional antifreeze additives
Creation of antifreeze additives that serve multiple purposes, such as corrosion inhibition, pH stabilization, and microbial growth prevention. These multi-functional additives reduce the need for multiple chemical components, simplifying formulations and potentially decreasing environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The research on antifreeze sustaining breakthroughs in environmental solution practices is in a developing stage, with a growing market driven by increasing environmental concerns. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring academic institutions, multinational corporations, and specialized companies. Key players like Zhejiang University of Technology, Honeywell International, and BASF Corp. are advancing the field through research and product development. The technology's maturity varies, with established companies like Honda Motor Co. and L'Oréal SA potentially adapting antifreeze innovations to their existing product lines. Emerging players such as ProtoKinetix and AgriGenesis Biosciences are likely focusing on novel, eco-friendly antifreeze solutions, indicating a dynamic and evolving market with opportunities for innovation and growth.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative antifreeze solutions focusing on environmental sustainability. Their approach includes the use of bio-based raw materials and advanced formulation techniques to create more eco-friendly antifreeze products. BASF's latest antifreeze formulations incorporate renewable glycols derived from biomass, reducing reliance on petroleum-based ingredients[1]. They have also implemented a closed-loop recycling system for antifreeze, allowing for the recovery and reuse of glycol components, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact[2]. Additionally, BASF has introduced corrosion inhibitors that are biodegradable and less toxic to aquatic life, addressing concerns about the environmental effects of antifreeze leakage[3].
Strengths: Utilization of renewable resources, closed-loop recycling system, and biodegradable additives. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and the need for specialized recycling infrastructure.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT researchers have made significant strides in antifreeze technology with environmental considerations. They have developed a novel antifreeze solution using nanoparticles that can lower the freezing point of water more effectively than traditional methods[4]. This approach allows for a reduction in the concentration of antifreeze chemicals needed, thereby decreasing environmental impact. MIT's team has also explored the use of protein-based antifreeze agents inspired by Arctic fish, which are non-toxic and biodegradable[5]. Furthermore, they have investigated the application of graphene oxide in antifreeze solutions, which has shown promising results in enhancing heat transfer efficiency and reducing the overall volume of antifreeze required in systems[6].
Strengths: Cutting-edge nanotechnology and bio-inspired solutions, potential for significant reduction in antifreeze chemical usage. Weaknesses: Some technologies may be in early stages of development and face challenges in scaling up for commercial applications.
Key Patents
Antifreeze
PatentInactiveEP3476903A1
Innovation
- A combination of succinic acid, benzotriazole, and potassium hydroxide (KOH) with a pH range of 10.4 to 10.8, or succinic acid, cinnamic acid, benzotriazole, and KOH with a pH range of 8.5 to 10.8, which synergistically provides excellent frost protection and corrosion protection for all common metals, including solder, while reducing the need for high benzotriazole concentrations.
A bio-based antifreeze composition for potable water systems and method for its preparation
PatentPendingIN202431037668A
Innovation
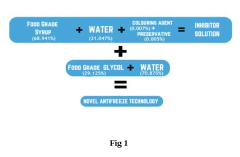
- A novel bio-based antifreeze composition comprising propanediol, water, a coloring agent, formaldehyde, and corn syrup, which is biodegradable and non-toxic, offering effective protection against freezing temperatures while minimizing environmental impact and health risks.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of antifreeze solutions has been a significant concern in various industries, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. Traditional antifreeze formulations, often based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, have posed substantial risks to ecosystems and human health when improperly disposed of or accidentally released into the environment.
Recent breakthroughs in environmental solution practices for antifreeze have focused on developing more eco-friendly alternatives and improving disposal methods. One notable advancement is the creation of bio-based antifreeze solutions derived from renewable resources such as corn, soybeans, or other plant materials. These biodegradable options significantly reduce the environmental footprint of antifreeze products while maintaining their effectiveness in preventing freezing and corrosion.
Another area of progress is the development of closed-loop recycling systems for antifreeze solutions. These systems allow for the collection, purification, and reuse of antifreeze, minimizing waste and reducing the need for new production. This approach not only conserves resources but also prevents the release of harmful chemicals into the environment.
Advancements in wastewater treatment technologies have also contributed to mitigating the environmental impact of antifreeze. Improved filtration and chemical treatment processes can effectively remove antifreeze compounds from industrial and municipal wastewater, preventing their release into natural water bodies and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
The implementation of stricter regulations and guidelines for antifreeze handling and disposal has played a crucial role in reducing environmental contamination. Many jurisdictions now require proper collection and treatment of used antifreeze, promoting responsible practices among businesses and consumers alike.
Research into the long-term effects of antifreeze on soil and groundwater has led to the development of more targeted remediation techniques. These methods focus on breaking down antifreeze compounds in contaminated sites, restoring ecosystem health, and preventing further spread of pollutants.
As awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, there is an increasing emphasis on developing antifreeze solutions with reduced toxicity. This includes exploring alternative chemical compositions that maintain performance while minimizing harm to wildlife and vegetation in case of accidental spills or leaks.
The ongoing research and innovation in antifreeze environmental solutions demonstrate a commitment to balancing technological needs with ecological responsibility. These advancements not only address immediate environmental concerns but also pave the way for more sustainable practices in industries reliant on antifreeze products.
Recent breakthroughs in environmental solution practices for antifreeze have focused on developing more eco-friendly alternatives and improving disposal methods. One notable advancement is the creation of bio-based antifreeze solutions derived from renewable resources such as corn, soybeans, or other plant materials. These biodegradable options significantly reduce the environmental footprint of antifreeze products while maintaining their effectiveness in preventing freezing and corrosion.
Another area of progress is the development of closed-loop recycling systems for antifreeze solutions. These systems allow for the collection, purification, and reuse of antifreeze, minimizing waste and reducing the need for new production. This approach not only conserves resources but also prevents the release of harmful chemicals into the environment.
Advancements in wastewater treatment technologies have also contributed to mitigating the environmental impact of antifreeze. Improved filtration and chemical treatment processes can effectively remove antifreeze compounds from industrial and municipal wastewater, preventing their release into natural water bodies and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
The implementation of stricter regulations and guidelines for antifreeze handling and disposal has played a crucial role in reducing environmental contamination. Many jurisdictions now require proper collection and treatment of used antifreeze, promoting responsible practices among businesses and consumers alike.
Research into the long-term effects of antifreeze on soil and groundwater has led to the development of more targeted remediation techniques. These methods focus on breaking down antifreeze compounds in contaminated sites, restoring ecosystem health, and preventing further spread of pollutants.
As awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, there is an increasing emphasis on developing antifreeze solutions with reduced toxicity. This includes exploring alternative chemical compositions that maintain performance while minimizing harm to wildlife and vegetation in case of accidental spills or leaks.
The ongoing research and innovation in antifreeze environmental solutions demonstrate a commitment to balancing technological needs with ecological responsibility. These advancements not only address immediate environmental concerns but also pave the way for more sustainable practices in industries reliant on antifreeze products.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding antifreeze and environmental solutions has evolved significantly in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of environmental impacts and the need for sustainable practices. At the international level, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has established guidelines for the management of hazardous substances, including antifreeze compounds. These guidelines emphasize the importance of proper disposal and recycling of antifreeze to prevent contamination of water sources and soil.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented strict regulations on the use and disposal of antifreeze under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). The EPA classifies used antifreeze as a hazardous waste due to its potential toxicity and mandates specific handling and disposal procedures. Many states have also enacted their own regulations, often more stringent than federal standards, to address local environmental concerns.
The European Union has taken a proactive approach through the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with chemicals, including those used in antifreeze formulations. This has led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives and improved recycling processes.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have implemented their own regulatory frameworks to address environmental concerns related to antifreeze. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has introduced stricter controls on chemical production and waste management, while Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law regulates the manufacture and import of chemical substances, including those used in antifreeze.
The regulatory landscape also extends to product labeling and consumer information. Many jurisdictions now require clear labeling of antifreeze products, including information on proper use, storage, and disposal. This has contributed to increased consumer awareness and more responsible usage patterns.
Industry self-regulation has played a significant role in complementing government regulations. Organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) have developed voluntary standards for antifreeze formulations and testing methods, which are widely adopted by manufacturers.
As research continues to advance in environmental solution practices, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on promoting innovation in sustainable antifreeze technologies. Incentives for the development of bio-based and recyclable antifreeze formulations are being introduced in various jurisdictions, encouraging industry players to invest in research and development of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented strict regulations on the use and disposal of antifreeze under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). The EPA classifies used antifreeze as a hazardous waste due to its potential toxicity and mandates specific handling and disposal procedures. Many states have also enacted their own regulations, often more stringent than federal standards, to address local environmental concerns.
The European Union has taken a proactive approach through the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with chemicals, including those used in antifreeze formulations. This has led to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives and improved recycling processes.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have implemented their own regulatory frameworks to address environmental concerns related to antifreeze. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has introduced stricter controls on chemical production and waste management, while Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law regulates the manufacture and import of chemical substances, including those used in antifreeze.
The regulatory landscape also extends to product labeling and consumer information. Many jurisdictions now require clear labeling of antifreeze products, including information on proper use, storage, and disposal. This has contributed to increased consumer awareness and more responsible usage patterns.
Industry self-regulation has played a significant role in complementing government regulations. Organizations such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) have developed voluntary standards for antifreeze formulations and testing methods, which are widely adopted by manufacturers.
As research continues to advance in environmental solution practices, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on promoting innovation in sustainable antifreeze technologies. Incentives for the development of bio-based and recyclable antifreeze formulations are being introduced in various jurisdictions, encouraging industry players to invest in research and development of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!