Preventing Flow In Check Valves: A Technical Guide
Preventing Flow In Check Valves: Background And Goals
By establishing a solid foundation in the technological context and objectives, this section will facilitate a deeper understanding of the problem at hand and pave the way for more targeted discussions on market demands, current technological solutions, and potential innovative approaches.
Check Valve Market Demand Analysis
- Market Size and Growth
Analyze the current market size for check valve products and services, including the breakdown by industry sectors and geographical regions. Estimate the projected growth rate and future market potential based on factors like industrial expansion, infrastructure development, and regulatory changes. - Key Drivers and Restraints
Identify the primary drivers fueling the demand for check valves, such as increasing need for fluid control systems, emphasis on safety and reliability, and adoption of new technologies. Discuss the major restraints hindering market growth, like cost concerns, availability of alternatives, and technological limitations. - Application Trends
Examine the emerging application areas for check valves, including industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, water and wastewater treatment, and power generation. Highlight the specific requirements and challenges associated with each application, and how they influence the demand for advanced check valve solutions. - Regional Market Dynamics
Analyze the regional market dynamics for check valves, considering factors like industrial development, infrastructure investments, and regulatory environments. Identify the high-growth regions and potential opportunities for market expansion. - Competitive Landscape
Provide an overview of the competitive landscape in the check valve market, including the major players, their market shares, and product offerings. Discuss the key competitive strategies employed by leading companies, such as product innovation, pricing strategies, and geographical expansion.
Preventing Flow In Check Valves: Technology Status And Challenges
- Valve Clogging Issues
Check valves are prone to clogging due to debris, sediments, or scale buildup, leading to reduced flow or complete blockage. - Material Compatibility
Incompatibility between valve materials and the fluid medium can cause corrosion, erosion, or chemical reactions, affecting valve performance. - Wear and Tear
Continuous operation and exposure to harsh conditions can lead to wear and tear of valve components, compromising sealing and flow control. - Installation and Maintenance Challenges
Improper installation or lack of regular maintenance can contribute to valve malfunctions and reduced service life.
Preventing Flow In Check Valves: Technology Evolution Path

Preventing Flow In Check Valves: Current Technical Solutions
01 Structure and Components
Check valves are designed with specific structures and components, such as valve bodies, seats, discs/balls, springs, and guides, to control fluid flow direction. The arrangement and materials used influence performance and flow characteristics.- Valve Structure and Components: Check valves are designed with specific structural components and configurations to control fluid flow in a particular direction. These components include valve bodies, seats, discs/balls, springs, and guides, which interact to permit flow in one direction while preventing backflow.
- Applications and Industries: Check valves find applications in various industries, such as water/wastewater treatment, oil and gas, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. They are used to prevent backflow, maintain system pressure, and ensure proper flow direction of liquids, gases, or slurries.
- Materials and Coatings: Check valves can be manufactured from metals (stainless steel, brass, cast iron), plastics (PVC, CPVC, PVDF), or composites, depending on the application and operating conditions. Coatings or linings may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or fluid compatibility.
- Design and Performance Optimization: Optimizing check valve design involves considerations like minimizing pressure drop, reducing water hammer effects, improving sealing efficiency, and enhancing flow characteristics. This can be achieved through modifications in valve geometry, materials, or incorporating additional components like dampers or springs.
- Maintenance and Testing: Regular maintenance and testing of check valves are crucial to ensure proper functioning and prevent failures. This may involve inspections, cleaning, component replacement, and performance testing under various flow conditions. Proper maintenance practices can extend the service life and reliability of check valves.
02 Applications and Flow Control
Check valves are used in various applications to control the flow of fluids, gases, or liquids. They are employed in piping systems, pumps, compressors, and fluid handling equipment to prevent backflow or regulate flow direction. The design and configuration impact flow control capabilities.03 Materials and Construction
Check valves can be constructed from metals, plastics, or composites, depending on the application and operating conditions. The choice of materials affects durability, corrosion resistance, and fluid compatibility. Construction methods and quality control also influence performance and reliability.04 Design and Flow Optimization
Check valve design can be optimized to improve flow characteristics, reduce pressure drop, and minimize turbulence or cavitation. This may involve modifications to valve geometry, flow paths, or incorporating features like damping mechanisms or flow guides to enhance efficiency and performance.05 Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance practices are crucial for effective check valve operation. This involves considerations like valve orientation, piping configurations, accessibility for inspection and servicing, and adherence to recommended maintenance schedules to prevent issues like leakage, sticking, or premature failure.
Preventing Flow In Check Valves: Technology Main Player Analysis
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Neoperl GmbH
Preventing Flow In Check Valves: Key Technology Interpretation
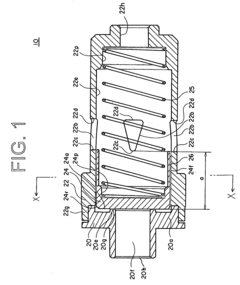
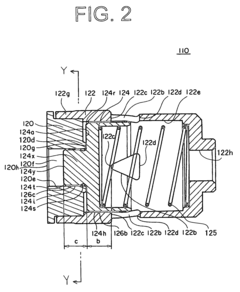
- The check valve includes a valve body that is movable to open and close a communication opening, allowing fluid flow in one direction and preventing backward flow.
- The valve body is urged against the valve seat by a spring, providing a sealing surface to prevent backward flow.
- The check valve is designed to inhibit valve hunting, reducing noise, vibration, and pressure loss in applications such as compressors and refrigeration circuits.