Optimizing Flow Geometries And Designs For Check Valves To Improve Flow Efficiency
Technology Background And Goals
Key areas of focus include evaluating various valve body shapes, inlet/outlet configurations, and internal flow path designs to minimize turbulence, pressure drops, and flow restrictions. Additionally, investigating advanced materials, surface treatments, and manufacturing techniques that could improve flow characteristics and durability will be crucial. The goal is to develop innovative check valve solutions that offer superior flow efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness across diverse applications.
Check Valve Market Demand Analysis
- Market Size and Growth
Analyze the current and projected market size for check valves across various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, and power generation. Highlight key growth drivers and potential restraints. - Application Segmentation
Segment the market demand based on different applications, such as pipeline systems, pumping stations, and industrial machinery. Identify the specific requirements and challenges associated with each application. - Regional Demand Analysis
Evaluate the regional demand patterns for check valves, considering factors like infrastructure development, industrialization, and regulatory environments. Highlight regions with significant growth potential. - End-User Analysis
Analyze the demand from different end-user segments, such as oil and gas companies, water utilities, chemical manufacturers, and power plants. Understand their specific needs and preferences. - Competitive Landscape
Assess the competitive landscape, including major players, their market shares, and product offerings. Identify key differentiators and competitive advantages.
Technology Status And Challenges
- Valve Design Evolution
Tracing the development of check valve designs, from traditional swing and lift check valves to advanced designs like tilting disc, double door, and nozzle check valves. - Flow Efficiency Challenges
Identifying key challenges in optimizing flow efficiency, such as minimizing pressure drop, preventing backflow, reducing turbulence, and mitigating wear and tear. - Material and Manufacturing Constraints
Discussing material selection considerations, like corrosion resistance and durability, as well as manufacturing limitations that impact valve geometry and design. - Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling
Highlighting the role of CFD simulations in analyzing flow patterns, optimizing valve geometries, and evaluating design modifications before physical prototyping.
Current Technical Solutions
01 Streamlined Design
Optimize check valve design features like valve body shapes, seat geometries, and reduced obstructions to minimize pressure drops and turbulence, enhancing flow efficiency.- Optimized Valve Design: Enhance flow efficiency by optimizing valve geometry, seat configuration, disc shape, lightweight materials, and streamlined designs to minimize flow resistance and turbulence.
- Low-Friction Materials: Utilize low-friction materials, such as certain polymers or coatings, for valve components to reduce friction between moving parts and minimize flow resistance, while also considering corrosion resistance.
- Improved Valve Configurations: Employ configurations like dual-plate or swing check valves with specific hinge designs to reduce turbulence and pressure drop, or explore using multiple valves in parallel or series.
- Optimal Sizing and Placement: Select appropriate valve sizes based on flow rates and pressure conditions, and strategically place valves near bends or transitions to minimize flow restrictions and turbulence.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Conduct regular inspections, cleaning, and monitoring to prevent buildup or wear that could impede flow, enabling timely maintenance or replacement for sustained flow efficiency.
02 Low-Friction Materials
Use low-friction materials, such as certain polymers or coatings, for valve components to reduce surface roughness and minimize flow resistance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optimized Configurations
Choose appropriate check valve configurations, like swing, lift, or ball types, based on application requirements to optimize flow characteristics and efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Flow Control Mechanisms
Incorporate adjustable orifices or variable flow areas in check valves to regulate flow rates and improve efficiency under different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Maintenance and Monitoring
Conduct regular maintenance, inspections, cleaning, and replacement of worn components to maintain optimal flow efficiency and minimize increased flow resistance.Expand Specific Solutions
Technology Main Player Analysis
Robert Bosch GmbH
ZF Friedrichshafen AG
Key Technology Interpretation
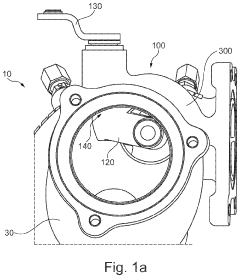
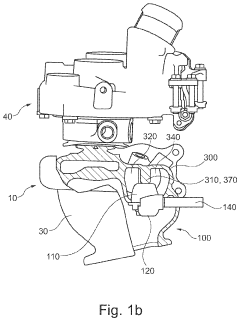
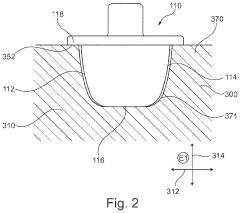
- An optimized valve arrangement that improves the flow transfer function of the multi-channel turbine. this helps to increase the rate of flow transfer between the volutes and enhances the overall performance of the turbine. the valve arrangement includes a housing section with a first volute, a second volute, and a connecting region between the two volutes. a wall region of the housing section, located in the connecting region and facing the valve body in a closed position, is configured to be optimized in terms of flow. this helps to prevent flow separation and increase the rate of flow transfer between the volutes. the optimization of the flow in the connecting region can also lead to a reduction in pressure between the loaded volute and the unloaded volute, as well as a decrease in the (static) pressure in the in each case loaded volute.
Check Valve Flow Efficiency Optimization Economic Analysis
Check Valve Flow Efficiency Optimization Policy And Regulatory Impact
Check valves with optimized flow geometries and designs are subject to various regulatory impacts. These impacts can influence their development, manufacturing, and application. Relevant regulations may cover aspects like material safety, design standards, performance requirements, and environmental considerations. Regulatory bodies at national and international levels establish guidelines to ensure product quality, reliability, and compliance. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for market acceptance and legal operation. Failure to adhere to regulations can result in fines, product recalls, or restrictions on distribution and use. Manufacturers and designers must thoroughly understand and navigate the regulatory landscape to mitigate risks and ensure successful commercialization of their optimized check valve solutions.