ULED vs QLED: Evaluating Picture Quality Enhancements
JUN 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED and QLED Background and Objectives
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) and QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) represent two cutting-edge display technologies that have emerged as significant advancements in the pursuit of superior picture quality. These technologies have evolved from the foundation of LED displays, each offering unique approaches to enhance color reproduction, contrast, and overall visual performance.
The development of ULED technology can be traced back to Hisense's efforts to improve upon traditional LED-LCD displays. ULED incorporates a suite of proprietary technologies aimed at optimizing various aspects of picture quality, including local dimming, quantum dot color, and HDR processing. The primary objective of ULED is to deliver a more vibrant, high-contrast image while maintaining energy efficiency.
QLED, on the other hand, was pioneered by Samsung as a response to OLED technology. It utilizes quantum dots, which are nano-sized semiconductor particles that emit light of specific wavelengths when excited by electricity. The goal of QLED is to achieve OLED-like picture quality while overcoming some of OLED's limitations, such as potential burn-in issues and lower brightness levels.
Both technologies aim to push the boundaries of what's possible in display technology, with a focus on delivering wider color gamuts, higher peak brightness, deeper blacks, and improved energy efficiency. The ongoing development of these technologies is driven by the ever-increasing demand for more immersive viewing experiences in both consumer and professional markets.
The evolution of ULED and QLED is closely tied to advancements in materials science, particularly in the realm of quantum dot technology and LED manufacturing processes. As research progresses, we can expect to see further refinements in these technologies, potentially leading to even more significant improvements in picture quality and energy efficiency.
The primary technical objectives for both ULED and QLED include achieving 100% coverage of the DCI-P3 and Rec. 2020 color spaces, increasing peak brightness levels while maintaining deep blacks for improved HDR performance, and reducing power consumption. Additionally, there is a focus on improving viewing angles and reducing motion blur to create a more consistent and enjoyable viewing experience across various content types and viewing environments.
As these technologies continue to mature, we can anticipate a convergence of features and performance metrics, potentially blurring the lines between ULED and QLED. This convergence may lead to hybrid solutions that combine the strengths of both approaches, further advancing the state of display technology and pushing the boundaries of picture quality enhancements.
The development of ULED technology can be traced back to Hisense's efforts to improve upon traditional LED-LCD displays. ULED incorporates a suite of proprietary technologies aimed at optimizing various aspects of picture quality, including local dimming, quantum dot color, and HDR processing. The primary objective of ULED is to deliver a more vibrant, high-contrast image while maintaining energy efficiency.
QLED, on the other hand, was pioneered by Samsung as a response to OLED technology. It utilizes quantum dots, which are nano-sized semiconductor particles that emit light of specific wavelengths when excited by electricity. The goal of QLED is to achieve OLED-like picture quality while overcoming some of OLED's limitations, such as potential burn-in issues and lower brightness levels.
Both technologies aim to push the boundaries of what's possible in display technology, with a focus on delivering wider color gamuts, higher peak brightness, deeper blacks, and improved energy efficiency. The ongoing development of these technologies is driven by the ever-increasing demand for more immersive viewing experiences in both consumer and professional markets.
The evolution of ULED and QLED is closely tied to advancements in materials science, particularly in the realm of quantum dot technology and LED manufacturing processes. As research progresses, we can expect to see further refinements in these technologies, potentially leading to even more significant improvements in picture quality and energy efficiency.
The primary technical objectives for both ULED and QLED include achieving 100% coverage of the DCI-P3 and Rec. 2020 color spaces, increasing peak brightness levels while maintaining deep blacks for improved HDR performance, and reducing power consumption. Additionally, there is a focus on improving viewing angles and reducing motion blur to create a more consistent and enjoyable viewing experience across various content types and viewing environments.
As these technologies continue to mature, we can anticipate a convergence of features and performance metrics, potentially blurring the lines between ULED and QLED. This convergence may lead to hybrid solutions that combine the strengths of both approaches, further advancing the state of display technology and pushing the boundaries of picture quality enhancements.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Display Technologies
The market demand for advanced display technologies, particularly ULED (Ultra LED) and QLED (Quantum Dot LED), has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is driven by consumers' increasing desire for superior picture quality, enhanced color accuracy, and improved energy efficiency in their display devices.
ULED and QLED technologies have emerged as key players in the high-end television and monitor markets, offering substantial improvements over traditional LED displays. These technologies cater to a growing segment of consumers who prioritize immersive viewing experiences and are willing to invest in premium display products.
The global market for advanced display technologies is projected to expand rapidly, with QLED and ULED playing crucial roles. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of 4K and 8K resolution displays, which require advanced technologies to fully showcase their capabilities. Additionally, the increasing popularity of large-screen televisions in home entertainment systems is driving demand for these cutting-edge display solutions.
In the commercial sector, there is a growing need for high-quality displays in various applications, including digital signage, control rooms, and professional video production. ULED and QLED technologies are well-positioned to meet these demands, offering superior color reproduction and brightness levels that are essential in these environments.
The gaming industry is another significant driver of market demand for advanced display technologies. Gamers are increasingly seeking displays that can deliver high refresh rates, low input lag, and vibrant colors, all of which are strengths of ULED and QLED technologies.
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the energy efficiency of display technologies has become a crucial factor in purchasing decisions. Both ULED and QLED offer improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays, aligning with the growing trend towards sustainable consumer electronics.
The market is also seeing increased demand for flexible and transparent displays, areas where QLED technology, in particular, shows promise for future development. This opens up new possibilities for innovative product designs and applications in various industries, from automotive to wearable technology.
While the market for ULED and QLED technologies is expanding, it faces competition from OLED technology, which has its own set of advantages. However, the continuous improvements in ULED and QLED technologies, coupled with their cost-effectiveness in larger screen sizes, position them favorably in the market.
ULED and QLED technologies have emerged as key players in the high-end television and monitor markets, offering substantial improvements over traditional LED displays. These technologies cater to a growing segment of consumers who prioritize immersive viewing experiences and are willing to invest in premium display products.
The global market for advanced display technologies is projected to expand rapidly, with QLED and ULED playing crucial roles. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of 4K and 8K resolution displays, which require advanced technologies to fully showcase their capabilities. Additionally, the increasing popularity of large-screen televisions in home entertainment systems is driving demand for these cutting-edge display solutions.
In the commercial sector, there is a growing need for high-quality displays in various applications, including digital signage, control rooms, and professional video production. ULED and QLED technologies are well-positioned to meet these demands, offering superior color reproduction and brightness levels that are essential in these environments.
The gaming industry is another significant driver of market demand for advanced display technologies. Gamers are increasingly seeking displays that can deliver high refresh rates, low input lag, and vibrant colors, all of which are strengths of ULED and QLED technologies.
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the energy efficiency of display technologies has become a crucial factor in purchasing decisions. Both ULED and QLED offer improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays, aligning with the growing trend towards sustainable consumer electronics.
The market is also seeing increased demand for flexible and transparent displays, areas where QLED technology, in particular, shows promise for future development. This opens up new possibilities for innovative product designs and applications in various industries, from automotive to wearable technology.
While the market for ULED and QLED technologies is expanding, it faces competition from OLED technology, which has its own set of advantages. However, the continuous improvements in ULED and QLED technologies, coupled with their cost-effectiveness in larger screen sizes, position them favorably in the market.
Current State and Challenges in ULED and QLED Technologies
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) and QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technologies represent the cutting edge in display technology, offering significant advancements in picture quality. Both technologies have made substantial progress in recent years, but they also face unique challenges in their development and implementation.
ULED, developed by Hisense, utilizes a combination of quantum dot technology and proprietary image processing algorithms to enhance picture quality. The current state of ULED technology boasts impressive color gamut coverage, reaching up to 110% of the NTSC color space. This allows for more vibrant and accurate color reproduction compared to traditional LED displays. ULED also incorporates local dimming technology, which enables better contrast ratios and deeper blacks by selectively dimming or brightening specific areas of the screen.
QLED, pioneered by Samsung, relies on quantum dot technology to enhance color reproduction and brightness. The latest QLED displays can achieve peak brightness levels of up to 2,000 nits, significantly surpassing OLED and traditional LED displays. QLED technology also offers excellent color volume, maintaining color accuracy even at high brightness levels. Additionally, QLED displays benefit from improved viewing angles and reduced screen burn-in compared to OLED technology.
Despite these advancements, both ULED and QLED technologies face several challenges. One of the primary obstacles for ULED is achieving true black levels comparable to OLED displays. While local dimming improves contrast, it can sometimes result in blooming or haloing effects around bright objects on dark backgrounds. ULED also faces challenges in maintaining consistent picture quality across different viewing angles.
For QLED, a significant challenge lies in improving its black levels and contrast ratios to match those of OLED displays. Although QLED technology has made strides in this area with mini-LED backlighting, it still struggles to achieve the perfect blacks that OLED can produce. Another challenge for QLED is reducing power consumption, as the high brightness levels can lead to increased energy usage compared to other display technologies.
Both technologies also face the challenge of cost reduction to make high-end displays more accessible to a broader consumer base. The manufacturing processes for quantum dot materials and advanced backlighting systems remain complex and expensive, which is reflected in the retail prices of ULED and QLED televisions.
In terms of geographical distribution, QLED technology has seen wider adoption globally, with Samsung leading the charge. ULED, being primarily developed by Hisense, has a strong presence in the Chinese market but is still working on expanding its global footprint. This presents a challenge for ULED in terms of gaining market share and recognition in international markets.
ULED, developed by Hisense, utilizes a combination of quantum dot technology and proprietary image processing algorithms to enhance picture quality. The current state of ULED technology boasts impressive color gamut coverage, reaching up to 110% of the NTSC color space. This allows for more vibrant and accurate color reproduction compared to traditional LED displays. ULED also incorporates local dimming technology, which enables better contrast ratios and deeper blacks by selectively dimming or brightening specific areas of the screen.
QLED, pioneered by Samsung, relies on quantum dot technology to enhance color reproduction and brightness. The latest QLED displays can achieve peak brightness levels of up to 2,000 nits, significantly surpassing OLED and traditional LED displays. QLED technology also offers excellent color volume, maintaining color accuracy even at high brightness levels. Additionally, QLED displays benefit from improved viewing angles and reduced screen burn-in compared to OLED technology.
Despite these advancements, both ULED and QLED technologies face several challenges. One of the primary obstacles for ULED is achieving true black levels comparable to OLED displays. While local dimming improves contrast, it can sometimes result in blooming or haloing effects around bright objects on dark backgrounds. ULED also faces challenges in maintaining consistent picture quality across different viewing angles.
For QLED, a significant challenge lies in improving its black levels and contrast ratios to match those of OLED displays. Although QLED technology has made strides in this area with mini-LED backlighting, it still struggles to achieve the perfect blacks that OLED can produce. Another challenge for QLED is reducing power consumption, as the high brightness levels can lead to increased energy usage compared to other display technologies.
Both technologies also face the challenge of cost reduction to make high-end displays more accessible to a broader consumer base. The manufacturing processes for quantum dot materials and advanced backlighting systems remain complex and expensive, which is reflected in the retail prices of ULED and QLED televisions.
In terms of geographical distribution, QLED technology has seen wider adoption globally, with Samsung leading the charge. ULED, being primarily developed by Hisense, has a strong presence in the Chinese market but is still working on expanding its global footprint. This presents a challenge for ULED in terms of gaining market share and recognition in international markets.
Comparative Analysis of ULED and QLED Picture Quality
01 QLED display technology advancements
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology has seen significant improvements in picture quality. It utilizes quantum dots to enhance color accuracy, brightness, and contrast. QLED displays offer wider color gamut, better HDR performance, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional LED displays.- QLED technology and color enhancement: QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology utilizes quantum dots to enhance color reproduction and brightness in displays. This results in a wider color gamut and improved picture quality compared to traditional LED displays. QLED displays offer better color accuracy, higher peak brightness, and improved contrast ratios.
- ULED technology and local dimming: ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology incorporates advanced local dimming techniques to improve contrast and black levels in displays. This technology allows for more precise control of backlight zones, resulting in deeper blacks and enhanced overall picture quality. ULED displays often feature a higher number of local dimming zones compared to standard LED displays.
- HDR (High Dynamic Range) implementation: Both QLED and ULED technologies can incorporate HDR capabilities to enhance picture quality. HDR allows for a wider range of brightness and color, resulting in more lifelike and vibrant images. Implementation of HDR in these display technologies can significantly improve contrast, color accuracy, and overall visual experience.
- Backlight and panel technologies: QLED and ULED displays utilize different backlight and panel technologies to achieve their respective picture quality improvements. These may include advanced LED arrangements, optical films, and panel structures that contribute to enhanced brightness, color reproduction, and viewing angles. The specific implementations can vary between manufacturers and models.
- Image processing and upscaling: Both QLED and ULED display technologies often incorporate advanced image processing algorithms and upscaling techniques to enhance picture quality. These may include AI-powered upscaling, motion smoothing, and noise reduction technologies. Such processing can improve the appearance of lower resolution content and enhance overall image clarity and detail.
02 ULED display technology features
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology focuses on enhancing picture quality through advanced local dimming, high dynamic range, and wide color gamut. ULED displays offer improved contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and more vibrant colors, resulting in a more immersive viewing experience.Expand Specific Solutions03 Comparison of QLED and ULED picture quality
Both QLED and ULED technologies aim to improve picture quality, but they use different approaches. QLED focuses on quantum dot technology for enhanced color reproduction, while ULED emphasizes local dimming and contrast enhancement. The choice between the two often depends on specific viewing preferences and environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Color gamut and brightness improvements
Both QLED and ULED technologies have made significant strides in expanding color gamut and increasing brightness levels. These improvements result in more vivid and lifelike images, with better representation of HDR content. Advanced color management systems and backlight technologies contribute to these enhancements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy efficiency and display longevity
QLED and ULED technologies have also focused on improving energy efficiency without compromising picture quality. These advancements lead to reduced power consumption and increased display longevity. Improved thermal management and optimized light output contribute to better overall performance and durability of the displays.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ULED and QLED Display Industry
The competition between ULED and QLED technologies is intensifying as the display industry matures. The market for advanced display technologies is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences. Companies like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology Group, and TCL are at the forefront of this technological race, investing heavily in research and development. The technology maturity varies, with QLED being more established and ULED emerging as a promising alternative. Both technologies are continuously evolving, with manufacturers like Sharp, Hisense, and Philips also contributing to advancements. The competition is likely to drive further innovations in picture quality enhancements, benefiting consumers with improved display options across various devices and applications.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed its own ULED (Ultra LED) technology, which combines quantum dot technology with mini-LED backlighting. Their ULED XDR (Extreme Dynamic Range) displays feature thousands of local dimming zones for enhanced contrast. BOE's AI-driven image processing algorithms optimize picture quality in real-time, adjusting parameters based on content and ambient light conditions. The company also implements advanced color management systems to ensure accurate and vibrant color reproduction.
Strengths: High brightness capabilities, good for HDR content. Weaknesses: May not achieve the same level of black levels as OLED technology.
Sharp Corp.
Technical Solution: Sharp's AQUOS LED TVs incorporate their proprietary UV2A II LCD panel technology for improved light control and contrast. While not specifically QLED or ULED, Sharp's latest models feature local dimming and quantum dot color enhancement. The company's AI-enabled picture processing adjusts image parameters in real-time based on content and ambient conditions. Sharp also implements motion enhancement technologies to reduce blur in fast-moving scenes.
Strengths: Good color accuracy and motion handling. Weaknesses: May not achieve the peak brightness levels of some QLED competitors.
Core Innovations in ULED and QLED Technologies
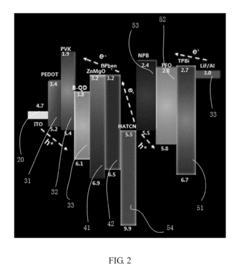
Series connected quantum dot light-emitting device, panel and display device
PatentActiveUS20180286927A1
Innovation
- A series connected quantum dot light-emitting device structure is introduced, comprising a first electrode, a first light-emitting unit with a quantum dot layer, a charge generation layer, and a second light-emitting unit with an organic layer, where the charge generation layer facilitates the series connection of both units, utilizing N-type and P-type layers formed by different materials to optimize electron and hole injection, thereby increasing luminous efficiency.
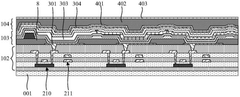
Display substrate and display device
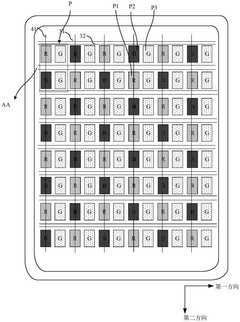
PatentActiveCN113707704B
Innovation
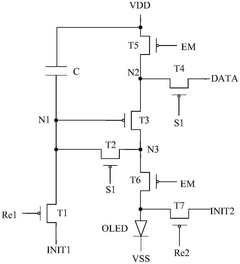
- A pixel driving circuit using multiple transistors and a specific conductive layer structure, including a third conductive layer and a fourth conductive layer, provides a constant potential signal to the pixel driving circuit through a parallel connection of the first power supply line and the second power supply line, and A flat portion is provided near the first electrode of the light-emitting device to reduce resistance and signal transmission loss.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of ULED and QLED
The environmental impact and sustainability of ULED and QLED technologies are crucial considerations in the ongoing debate about display technologies. Both ULED and QLED offer significant improvements in picture quality, but their ecological footprints differ in several key aspects.
ULED, or Ultra LED, is an advanced LED technology that enhances brightness and contrast while potentially reducing energy consumption. This technology typically uses less power than traditional LED displays, which can lead to lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of the device. Additionally, ULED panels often incorporate more efficient backlighting systems, further contributing to energy savings.
QLED, or Quantum Dot LED, relies on quantum dot technology to produce vibrant colors and high contrast ratios. While QLED displays can offer excellent picture quality, they may consume more power than ULED displays, particularly when producing bright, colorful images. However, recent advancements in QLED technology have focused on improving energy efficiency, narrowing the gap with ULED in terms of power consumption.
In terms of manufacturing, both technologies have environmental implications. ULED production generally involves fewer toxic materials compared to QLED, which requires the use of cadmium-based quantum dots in some cases. However, cadmium-free quantum dots are becoming more prevalent, addressing this concern. The production of both technologies involves the use of rare earth elements, which can have significant environmental impacts during mining and processing.
Lifespan is another critical factor in assessing environmental impact. ULED displays typically have a longer lifespan than QLED, potentially reducing electronic waste over time. However, the modular nature of some QLED displays allows for easier repair and component replacement, which can extend the overall life of the device and reduce waste.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations also differ between the two technologies. ULED displays are generally easier to recycle due to their simpler construction and fewer toxic materials. QLED displays, particularly those using cadmium-based quantum dots, may require more specialized recycling processes to prevent environmental contamination.
As the display industry continues to evolve, both ULED and QLED manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve the sustainability of their technologies. This includes efforts to reduce power consumption, minimize the use of harmful materials, and enhance recyclability. The ongoing competition between these technologies is likely to drive further innovations in eco-friendly display solutions, benefiting both consumers and the environment in the long run.
ULED, or Ultra LED, is an advanced LED technology that enhances brightness and contrast while potentially reducing energy consumption. This technology typically uses less power than traditional LED displays, which can lead to lower carbon emissions over the lifetime of the device. Additionally, ULED panels often incorporate more efficient backlighting systems, further contributing to energy savings.
QLED, or Quantum Dot LED, relies on quantum dot technology to produce vibrant colors and high contrast ratios. While QLED displays can offer excellent picture quality, they may consume more power than ULED displays, particularly when producing bright, colorful images. However, recent advancements in QLED technology have focused on improving energy efficiency, narrowing the gap with ULED in terms of power consumption.
In terms of manufacturing, both technologies have environmental implications. ULED production generally involves fewer toxic materials compared to QLED, which requires the use of cadmium-based quantum dots in some cases. However, cadmium-free quantum dots are becoming more prevalent, addressing this concern. The production of both technologies involves the use of rare earth elements, which can have significant environmental impacts during mining and processing.
Lifespan is another critical factor in assessing environmental impact. ULED displays typically have a longer lifespan than QLED, potentially reducing electronic waste over time. However, the modular nature of some QLED displays allows for easier repair and component replacement, which can extend the overall life of the device and reduce waste.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations also differ between the two technologies. ULED displays are generally easier to recycle due to their simpler construction and fewer toxic materials. QLED displays, particularly those using cadmium-based quantum dots, may require more specialized recycling processes to prevent environmental contamination.
As the display industry continues to evolve, both ULED and QLED manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve the sustainability of their technologies. This includes efforts to reduce power consumption, minimize the use of harmful materials, and enhance recyclability. The ongoing competition between these technologies is likely to drive further innovations in eco-friendly display solutions, benefiting both consumers and the environment in the long run.
Consumer Perception and Adoption Trends
Consumer perception and adoption trends of ULED and QLED technologies play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics of high-end television displays. As these advanced display technologies continue to evolve, understanding consumer attitudes and behaviors becomes increasingly important for manufacturers and retailers alike.
Recent market research indicates that consumer awareness of ULED and QLED technologies has been steadily growing over the past few years. However, there remains a significant knowledge gap among the general public regarding the specific benefits and differences between these display technologies. This presents both challenges and opportunities for industry players in terms of consumer education and marketing strategies.
Early adopters and tech enthusiasts have shown a keen interest in both ULED and QLED displays, primarily driven by the promise of superior picture quality and enhanced viewing experiences. These consumers tend to be more informed about the technical aspects and are willing to invest in premium television sets featuring the latest display technologies.
However, the broader consumer market has exhibited a more cautious approach to adoption. Price sensitivity remains a significant factor, with many consumers weighing the perceived benefits against the higher cost of ULED and QLED televisions compared to traditional LED displays. This price-to-performance evaluation is a critical consideration in consumer decision-making processes.
Brand loyalty and reputation also play a substantial role in shaping consumer perceptions and adoption trends. Established manufacturers with strong brand recognition in the television market have an advantage in promoting their ULED or QLED offerings. Consumers often rely on brand trust as a proxy for quality and reliability when navigating the complex landscape of display technologies.
The impact of in-store demonstrations and word-of-mouth recommendations cannot be underestimated. Consumers who have the opportunity to experience ULED and QLED displays firsthand are more likely to appreciate the visual enhancements and consider purchasing. This highlights the importance of retail strategies and experiential marketing in driving adoption.
As the technology matures and production costs decrease, a gradual shift in consumer adoption patterns is expected. The mid-range market segment is likely to see increased penetration of ULED and QLED technologies, making these advanced displays more accessible to a broader consumer base. This trend is anticipated to accelerate as manufacturers continue to refine their product offerings and optimize production processes.
Recent market research indicates that consumer awareness of ULED and QLED technologies has been steadily growing over the past few years. However, there remains a significant knowledge gap among the general public regarding the specific benefits and differences between these display technologies. This presents both challenges and opportunities for industry players in terms of consumer education and marketing strategies.
Early adopters and tech enthusiasts have shown a keen interest in both ULED and QLED displays, primarily driven by the promise of superior picture quality and enhanced viewing experiences. These consumers tend to be more informed about the technical aspects and are willing to invest in premium television sets featuring the latest display technologies.
However, the broader consumer market has exhibited a more cautious approach to adoption. Price sensitivity remains a significant factor, with many consumers weighing the perceived benefits against the higher cost of ULED and QLED televisions compared to traditional LED displays. This price-to-performance evaluation is a critical consideration in consumer decision-making processes.
Brand loyalty and reputation also play a substantial role in shaping consumer perceptions and adoption trends. Established manufacturers with strong brand recognition in the television market have an advantage in promoting their ULED or QLED offerings. Consumers often rely on brand trust as a proxy for quality and reliability when navigating the complex landscape of display technologies.
The impact of in-store demonstrations and word-of-mouth recommendations cannot be underestimated. Consumers who have the opportunity to experience ULED and QLED displays firsthand are more likely to appreciate the visual enhancements and consider purchasing. This highlights the importance of retail strategies and experiential marketing in driving adoption.
As the technology matures and production costs decrease, a gradual shift in consumer adoption patterns is expected. The mid-range market segment is likely to see increased penetration of ULED and QLED technologies, making these advanced displays more accessible to a broader consumer base. This trend is anticipated to accelerate as manufacturers continue to refine their product offerings and optimize production processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!