Advancements in Carboxylic Acid-Derived Agrochemicals
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carboxylic Acid Agrochemicals: Background and Objectives
Carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals have emerged as a significant area of research and development in the agricultural industry over the past few decades. These compounds, characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH), have shown remarkable potential in addressing various agricultural challenges, including pest control, plant growth regulation, and crop protection.
The evolution of carboxylic acid agrochemicals can be traced back to the mid-20th century when scientists began exploring the potential of organic compounds in agriculture. Initially, the focus was primarily on synthetic pesticides, but as environmental concerns grew, researchers shifted their attention to more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. Carboxylic acids, with their natural occurrence in many plants and relatively low toxicity, emerged as promising candidates for agrochemical development.
Throughout the years, the field has witnessed significant advancements in the synthesis, formulation, and application of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. These developments have been driven by the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices, stricter regulations on chemical use in farming, and the need for more targeted and efficient crop protection solutions.
The current landscape of carboxylic acid agrochemicals encompasses a wide range of compounds, including herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and plant growth regulators. Some notable examples include 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), a widely used herbicide, and gibberellic acid, a plant hormone that promotes growth and development.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for advancing carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals are multifaceted. One primary goal is to enhance the efficacy and specificity of these compounds, allowing for more targeted pest control and reduced environmental impact. This involves developing novel molecular structures and formulations that can improve the compounds' stability, bioavailability, and mode of action.
Another critical objective is to expand the application range of carboxylic acid agrochemicals. Researchers are exploring new uses for these compounds, such as in precision agriculture, seed treatments, and post-harvest preservation. Additionally, there is a growing interest in leveraging the synergistic effects of combining carboxylic acids with other bioactive compounds to create more comprehensive and sustainable crop protection solutions.
Sustainability remains a key focus in the advancement of carboxylic acid agrochemicals. Scientists are working on developing bio-based production methods, utilizing renewable resources, and improving the biodegradability of these compounds. This aligns with the global trend towards more environmentally friendly agricultural practices and the reduction of chemical residues in food products.
In conclusion, the field of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals continues to evolve, driven by the need for innovative, sustainable, and effective solutions in agriculture. The ongoing research and development in this area hold promise for addressing current and future challenges in crop protection and management, contributing to global food security and sustainable farming practices.
The evolution of carboxylic acid agrochemicals can be traced back to the mid-20th century when scientists began exploring the potential of organic compounds in agriculture. Initially, the focus was primarily on synthetic pesticides, but as environmental concerns grew, researchers shifted their attention to more sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. Carboxylic acids, with their natural occurrence in many plants and relatively low toxicity, emerged as promising candidates for agrochemical development.
Throughout the years, the field has witnessed significant advancements in the synthesis, formulation, and application of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. These developments have been driven by the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices, stricter regulations on chemical use in farming, and the need for more targeted and efficient crop protection solutions.
The current landscape of carboxylic acid agrochemicals encompasses a wide range of compounds, including herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and plant growth regulators. Some notable examples include 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), a widely used herbicide, and gibberellic acid, a plant hormone that promotes growth and development.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for advancing carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals are multifaceted. One primary goal is to enhance the efficacy and specificity of these compounds, allowing for more targeted pest control and reduced environmental impact. This involves developing novel molecular structures and formulations that can improve the compounds' stability, bioavailability, and mode of action.
Another critical objective is to expand the application range of carboxylic acid agrochemicals. Researchers are exploring new uses for these compounds, such as in precision agriculture, seed treatments, and post-harvest preservation. Additionally, there is a growing interest in leveraging the synergistic effects of combining carboxylic acids with other bioactive compounds to create more comprehensive and sustainable crop protection solutions.
Sustainability remains a key focus in the advancement of carboxylic acid agrochemicals. Scientists are working on developing bio-based production methods, utilizing renewable resources, and improving the biodegradability of these compounds. This aligns with the global trend towards more environmentally friendly agricultural practices and the reduction of chemical residues in food products.
In conclusion, the field of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals continues to evolve, driven by the need for innovative, sustainable, and effective solutions in agriculture. The ongoing research and development in this area hold promise for addressing current and future challenges in crop protection and management, contributing to global food security and sustainable farming practices.
Market Analysis for Carboxylic Acid-Based Crop Protection
The global market for carboxylic acid-based crop protection products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural solutions. This segment of the agrochemical industry has shown robust expansion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding the overall crop protection market average.
The primary factors fueling this market growth include the rising global population, shrinking arable land, and the need for enhanced crop yields. Carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals offer advantages such as lower toxicity, improved biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional synthetic pesticides. These characteristics align well with the growing consumer preference for organic and eco-friendly food products.
Regionally, North America and Europe have been at the forefront of adopting carboxylic acid-based crop protection solutions, driven by stringent regulations on conventional pesticides and a strong emphasis on sustainable agriculture. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, propelled by rapid agricultural modernization and increasing awareness of environmental issues among farmers.
The market is segmented by crop type, with cereals and grains representing the largest share due to their widespread cultivation and economic importance. Fruits and vegetables follow closely, as producers seek to meet the rising demand for high-quality, residue-free produce. The ornamental plants segment, though smaller, is showing promising growth potential, particularly in developed economies.
In terms of product types, herbicides dominate the carboxylic acid-based crop protection market, followed by fungicides and insecticides. The herbicide segment's prominence is attributed to the growing problem of herbicide-resistant weeds and the need for more sustainable weed management solutions.
Key market players are investing heavily in research and development to expand their product portfolios and improve the efficacy of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. Collaborations between agrochemical companies and biotechnology firms are becoming more common, aiming to develop innovative formulations that combine the benefits of carboxylic acids with other advanced crop protection technologies.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain. The higher production costs of carboxylic acid-based products compared to conventional agrochemicals can limit their adoption, especially in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for these products varies significantly across regions, potentially impacting market growth and product development strategies.
The primary factors fueling this market growth include the rising global population, shrinking arable land, and the need for enhanced crop yields. Carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals offer advantages such as lower toxicity, improved biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional synthetic pesticides. These characteristics align well with the growing consumer preference for organic and eco-friendly food products.
Regionally, North America and Europe have been at the forefront of adopting carboxylic acid-based crop protection solutions, driven by stringent regulations on conventional pesticides and a strong emphasis on sustainable agriculture. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, propelled by rapid agricultural modernization and increasing awareness of environmental issues among farmers.
The market is segmented by crop type, with cereals and grains representing the largest share due to their widespread cultivation and economic importance. Fruits and vegetables follow closely, as producers seek to meet the rising demand for high-quality, residue-free produce. The ornamental plants segment, though smaller, is showing promising growth potential, particularly in developed economies.
In terms of product types, herbicides dominate the carboxylic acid-based crop protection market, followed by fungicides and insecticides. The herbicide segment's prominence is attributed to the growing problem of herbicide-resistant weeds and the need for more sustainable weed management solutions.
Key market players are investing heavily in research and development to expand their product portfolios and improve the efficacy of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. Collaborations between agrochemical companies and biotechnology firms are becoming more common, aiming to develop innovative formulations that combine the benefits of carboxylic acids with other advanced crop protection technologies.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain. The higher production costs of carboxylic acid-based products compared to conventional agrochemicals can limit their adoption, especially in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for these products varies significantly across regions, potentially impacting market growth and product development strategies.
Current Challenges in Carboxylic Acid Agrochemical Development
The development of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals faces several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent instability of carboxylic acid moieties under various environmental conditions. These compounds are susceptible to degradation through hydrolysis, photolysis, and microbial action, which can significantly reduce their persistence in the field and overall effectiveness.
Another major challenge lies in the formulation of these agrochemicals. Carboxylic acids often exhibit poor solubility in water and organic solvents, making it difficult to create stable and effective formulations. This solubility issue not only affects the ease of application but also impacts the bioavailability of the active ingredients, potentially reducing their efficacy against target pests or pathogens.
The environmental impact of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is also a growing concern. While these compounds are generally considered more environmentally friendly than traditional pesticides, there are still concerns about their potential effects on non-target organisms and ecosystems. Developing formulations that maximize efficacy while minimizing environmental impact remains a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Regulatory hurdles present another obstacle in the development and commercialization of carboxylic acid agrochemicals. Stringent safety and efficacy requirements imposed by regulatory bodies worldwide necessitate extensive testing and documentation, which can be both time-consuming and costly. This regulatory burden can slow down the introduction of new products to the market and increase overall development costs.
The selectivity of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is another area that requires improvement. Enhancing the specificity of these compounds to target only harmful pests or pathogens while sparing beneficial organisms is crucial for their widespread acceptance and use in integrated pest management strategies.
Resistance management is an ongoing challenge in the agrochemical industry, and carboxylic acid-derived products are no exception. As with any pesticide, there is a risk of target organisms developing resistance over time, potentially reducing the long-term effectiveness of these compounds. Developing strategies to mitigate resistance and prolong the useful life of these agrochemicals is essential for their sustainable use.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals compared to conventional alternatives remains a challenge. While these compounds offer potential environmental benefits, their production costs and application requirements may be higher than traditional pesticides. Improving manufacturing processes and formulation technologies to reduce costs without compromising efficacy is crucial for the widespread adoption of these agrochemicals in commercial agriculture.
Another major challenge lies in the formulation of these agrochemicals. Carboxylic acids often exhibit poor solubility in water and organic solvents, making it difficult to create stable and effective formulations. This solubility issue not only affects the ease of application but also impacts the bioavailability of the active ingredients, potentially reducing their efficacy against target pests or pathogens.
The environmental impact of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is also a growing concern. While these compounds are generally considered more environmentally friendly than traditional pesticides, there are still concerns about their potential effects on non-target organisms and ecosystems. Developing formulations that maximize efficacy while minimizing environmental impact remains a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers.
Regulatory hurdles present another obstacle in the development and commercialization of carboxylic acid agrochemicals. Stringent safety and efficacy requirements imposed by regulatory bodies worldwide necessitate extensive testing and documentation, which can be both time-consuming and costly. This regulatory burden can slow down the introduction of new products to the market and increase overall development costs.
The selectivity of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is another area that requires improvement. Enhancing the specificity of these compounds to target only harmful pests or pathogens while sparing beneficial organisms is crucial for their widespread acceptance and use in integrated pest management strategies.
Resistance management is an ongoing challenge in the agrochemical industry, and carboxylic acid-derived products are no exception. As with any pesticide, there is a risk of target organisms developing resistance over time, potentially reducing the long-term effectiveness of these compounds. Developing strategies to mitigate resistance and prolong the useful life of these agrochemicals is essential for their sustainable use.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals compared to conventional alternatives remains a challenge. While these compounds offer potential environmental benefits, their production costs and application requirements may be higher than traditional pesticides. Improving manufacturing processes and formulation technologies to reduce costs without compromising efficacy is crucial for the widespread adoption of these agrochemicals in commercial agriculture.
Current Formulation Strategies for Carboxylic Acid Agrochemicals
01 Synthesis of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals
Various methods for synthesizing carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals are described. These processes involve the preparation of compounds with carboxylic acid functional groups that have potential applications in agriculture. The synthesis routes may include reactions such as oxidation, reduction, or substitution to obtain the desired carboxylic acid derivatives.- Synthesis of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals: Various methods for synthesizing carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals are described. These processes involve the formation of carboxylic acid derivatives through different chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution. The resulting compounds have potential applications as herbicides, fungicides, or insecticides in agriculture.
- Novel carboxylic acid-based agrochemical compounds: New carboxylic acid-derived compounds with agrochemical properties are presented. These compounds feature unique structural modifications that enhance their efficacy as pesticides, herbicides, or plant growth regulators. The novel structures may include specific functional groups or substitutions that improve their biological activity or environmental stability.
- Formulation of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals: Techniques for formulating carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals into effective and stable products are discussed. These formulations may include additives, surfactants, or other ingredients to improve solubility, dispersibility, or adherence to plant surfaces. The formulations aim to enhance the efficacy and ease of application of the active ingredients.
- Applications of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals: Various applications of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals in agriculture are explored. These compounds may be used for weed control, pest management, disease prevention, or plant growth regulation. The specific uses depend on the chemical structure and properties of the carboxylic acid derivatives.
- Environmental and safety aspects of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals: Studies on the environmental impact and safety of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals are presented. This includes research on biodegradability, ecotoxicology, and potential effects on non-target organisms. Additionally, methods for reducing environmental risks and improving the safety profile of these compounds are discussed.
02 Formulation of carboxylic acid-based pesticides
Carboxylic acid derivatives are formulated into effective pesticide compositions. These formulations may include additional components such as surfactants, carriers, or other active ingredients to enhance their efficacy and stability. The resulting products are designed for various agricultural applications, including insecticides, herbicides, or fungicides.Expand Specific Solutions03 Novel carboxylic acid compounds with agrochemical properties
New carboxylic acid-derived compounds are developed and characterized for their potential use as agrochemicals. These novel compounds may exhibit improved efficacy, reduced environmental impact, or enhanced selectivity compared to existing agrochemicals. Structure-activity relationships are often explored to optimize the desired properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application methods for carboxylic acid-based agrochemicals
Various techniques for applying carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals are described. These may include methods for foliar application, soil treatment, or seed coating. The application methods are designed to maximize the effectiveness of the agrochemicals while minimizing environmental impact and ensuring safe handling.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations of carboxylic acid agrochemicals
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental profile and safety of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. This includes studies on biodegradability, ecotoxicology, and human health impacts. Strategies for reducing potential risks associated with these compounds in agricultural use are also explored.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Carboxylic Acid Agrochemical Industry
The field of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is experiencing significant advancements, with major players like Bayer CropScience, Syngenta, and BASF leading the way. The industry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable agricultural solutions. The global market for these agrochemicals is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 5-7% over the next five years. Technological maturity varies across different product categories, with established companies like Corteva Agriscience and Solvay pushing innovation boundaries. Emerging players such as Jiangsu Yangnong Chemical and Qingdao Kingagroot Chemical are also contributing to the competitive landscape, focusing on novel formulations and improved efficacy.
Corteva Agriscience LLC
Technical Solution: Corteva Agriscience has focused on developing next-generation carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals with enhanced selectivity and reduced environmental persistence. Their research includes the design of carboxylic acid-based herbicides that target specific plant metabolic pathways, providing effective weed control while minimizing crop injury[9]. Corteva has also developed innovative carboxylic acid derivatives as seed treatments, which can improve seedling vigor and early-season crop protection[10]. Furthermore, they have invested in precision agriculture technologies that optimize the application of these compounds, reducing overall chemical use and improving farm profitability[11].
Strengths: Strong integration of chemistry and biotechnology, extensive field trial network, and focus on digital agriculture solutions. Weaknesses: Dependence on commodity crop markets and potential regulatory challenges in some regions.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG has made significant advancements in carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals, focusing on developing novel compounds with enhanced efficacy and environmental safety. Their research includes the synthesis of new carboxylic acid-based herbicides that target specific plant enzymes, reducing the impact on non-target organisms. Bayer has also developed innovative formulations that improve the uptake and translocation of these compounds in plants, increasing their effectiveness at lower application rates[1]. Additionally, they have invested in the development of carboxylic acid-derived fungicides that disrupt pathogen cell membranes, providing broad-spectrum disease control in various crops[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, extensive patent portfolio, and global market presence. Weaknesses: High development costs and regulatory challenges for new compounds.
Innovative Carboxylic Acid Derivatives in Crop Protection
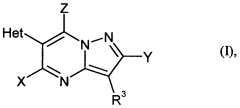
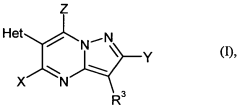
Heterocyclically substituted heterocyclyl carboxylic acid derivatives
PatentWO2008151735A2
Innovation
- Development of heterocyclic carboxylic acid derivatives with specific structural features, including various substituents, which are suitable for use as pesticides, acaricides, and fungicides, and their agrochemically active salts, potentially enhanced by the addition of ammonium or phosphonium salts and penetrants.
Heterocyclically substituted heterocyclylcarboxylic acid derivatives
PatentInactiveUS20100167931A1
Innovation
- Development of heterocyclic carboxylic acid derivatives and their agrochemically active salts, which are used in compositions for controlling animal pests and phytopathogenic harmful fungi, enhanced by the addition of ammonium or phosphonium salts and penetrants, to improve their insecticidal, acaricidal, and fungicidal activity.
Environmental Impact of Carboxylic Acid-Based Agrochemicals
The environmental impact of carboxylic acid-based agrochemicals is a critical consideration in the development and application of these compounds. These agrochemicals, derived from carboxylic acids, have become increasingly prevalent in modern agriculture due to their effectiveness in pest control and crop management. However, their widespread use has raised concerns about potential ecological consequences.
One of the primary environmental impacts of carboxylic acid-based agrochemicals is their effect on soil health. These compounds can alter soil pH levels, potentially affecting microbial communities and nutrient availability. Long-term application may lead to changes in soil structure and fertility, impacting the overall ecosystem balance. Additionally, the persistence of these chemicals in soil can vary, with some compounds degrading rapidly while others may accumulate over time.
Water contamination is another significant concern associated with carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. Runoff from treated fields can introduce these compounds into nearby water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. The impact on water quality may include changes in pH levels and the introduction of chemical residues, which can have cascading effects on aquatic flora and fauna.
Biodiversity is also at risk from the extensive use of these agrochemicals. While designed to target specific pests, carboxylic acid-based compounds may have unintended effects on non-target organisms. This can include beneficial insects, pollinators, and soil-dwelling organisms that play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance. The potential for bioaccumulation in food chains is another aspect that requires careful consideration.
Air quality can be affected by the volatilization of certain carboxylic acid-based agrochemicals. Atmospheric transport of these compounds may lead to their deposition in non-target areas, potentially impacting ecosystems far from the original application sites. This long-range transport can contribute to broader environmental concerns, including potential effects on human health in surrounding communities.
The environmental fate of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is influenced by various factors, including their chemical properties, application methods, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate negative impacts. Efforts to improve formulations, optimize application techniques, and enhance degradation processes are ongoing to reduce environmental persistence and off-target effects.
Regulatory frameworks play a vital role in managing the environmental impact of these agrochemicals. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for their use, including restrictions on application rates, timing, and methods. Environmental monitoring programs are essential for assessing long-term impacts and informing policy decisions. The development of more environmentally friendly alternatives and integrated pest management strategies is also being pursued to reduce reliance on chemical interventions.
One of the primary environmental impacts of carboxylic acid-based agrochemicals is their effect on soil health. These compounds can alter soil pH levels, potentially affecting microbial communities and nutrient availability. Long-term application may lead to changes in soil structure and fertility, impacting the overall ecosystem balance. Additionally, the persistence of these chemicals in soil can vary, with some compounds degrading rapidly while others may accumulate over time.
Water contamination is another significant concern associated with carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals. Runoff from treated fields can introduce these compounds into nearby water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. The impact on water quality may include changes in pH levels and the introduction of chemical residues, which can have cascading effects on aquatic flora and fauna.
Biodiversity is also at risk from the extensive use of these agrochemicals. While designed to target specific pests, carboxylic acid-based compounds may have unintended effects on non-target organisms. This can include beneficial insects, pollinators, and soil-dwelling organisms that play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance. The potential for bioaccumulation in food chains is another aspect that requires careful consideration.
Air quality can be affected by the volatilization of certain carboxylic acid-based agrochemicals. Atmospheric transport of these compounds may lead to their deposition in non-target areas, potentially impacting ecosystems far from the original application sites. This long-range transport can contribute to broader environmental concerns, including potential effects on human health in surrounding communities.
The environmental fate of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals is influenced by various factors, including their chemical properties, application methods, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate negative impacts. Efforts to improve formulations, optimize application techniques, and enhance degradation processes are ongoing to reduce environmental persistence and off-target effects.
Regulatory frameworks play a vital role in managing the environmental impact of these agrochemicals. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for their use, including restrictions on application rates, timing, and methods. Environmental monitoring programs are essential for assessing long-term impacts and informing policy decisions. The development of more environmentally friendly alternatives and integrated pest management strategies is also being pursued to reduce reliance on chemical interventions.
Regulatory Framework for Novel Agrochemical Compounds
The regulatory framework for novel agrochemical compounds derived from carboxylic acids is a complex and evolving landscape. As advancements in carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals continue to emerge, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their policies to ensure the safety and efficacy of these innovative products.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating novel agrochemicals. The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) provides the primary legal framework for pesticide regulation. Under FIFRA, carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals must undergo rigorous testing and evaluation before receiving approval for commercial use. This process includes assessing potential environmental impacts, human health risks, and efficacy against target pests.
The European Union (EU) has implemented a stringent regulatory system through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive approach requires manufacturers and importers of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals to provide detailed safety data and risk assessments. Additionally, the EU's Plant Protection Products Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 sets specific criteria for the approval of active substances and the authorization of plant protection products.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have also established robust regulatory frameworks for novel agrochemicals. China's Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture (ICAMA) oversees the registration and management of pesticides, including carboxylic acid-derived compounds. Japan's Agricultural Chemicals Regulation Law requires extensive safety and efficacy data for new agrochemical products.
International organizations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provide guidelines and standards for the evaluation of pesticide residues and toxicology. These guidelines influence national regulatory policies and promote harmonization of safety standards across borders.
As the field of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals advances, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. This has led to the development of fast-track approval processes for biopesticides and low-risk substances, which may benefit certain carboxylic acid-derived compounds that demonstrate favorable environmental profiles.
Regulatory compliance for novel agrochemicals requires substantial investment in research, development, and testing. Companies developing carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals must navigate complex regulatory pathways, often involving multiple jurisdictions with varying requirements. This complexity underscores the importance of early engagement with regulatory authorities and careful planning throughout the product development lifecycle.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating novel agrochemicals. The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) provides the primary legal framework for pesticide regulation. Under FIFRA, carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals must undergo rigorous testing and evaluation before receiving approval for commercial use. This process includes assessing potential environmental impacts, human health risks, and efficacy against target pests.
The European Union (EU) has implemented a stringent regulatory system through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This comprehensive approach requires manufacturers and importers of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals to provide detailed safety data and risk assessments. Additionally, the EU's Plant Protection Products Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 sets specific criteria for the approval of active substances and the authorization of plant protection products.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have also established robust regulatory frameworks for novel agrochemicals. China's Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture (ICAMA) oversees the registration and management of pesticides, including carboxylic acid-derived compounds. Japan's Agricultural Chemicals Regulation Law requires extensive safety and efficacy data for new agrochemical products.
International organizations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provide guidelines and standards for the evaluation of pesticide residues and toxicology. These guidelines influence national regulatory policies and promote harmonization of safety standards across borders.
As the field of carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals advances, regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. This has led to the development of fast-track approval processes for biopesticides and low-risk substances, which may benefit certain carboxylic acid-derived compounds that demonstrate favorable environmental profiles.
Regulatory compliance for novel agrochemicals requires substantial investment in research, development, and testing. Companies developing carboxylic acid-derived agrochemicals must navigate complex regulatory pathways, often involving multiple jurisdictions with varying requirements. This complexity underscores the importance of early engagement with regulatory authorities and careful planning throughout the product development lifecycle.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!