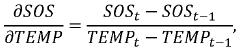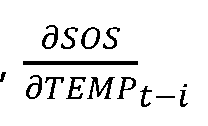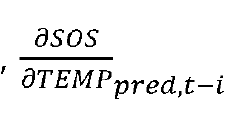Antifreeze and Its Critical Function in HVAC Systems
JUL 2, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HVAC Antifreeze Background
Antifreeze has been an integral component in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems for decades, playing a crucial role in maintaining system efficiency and preventing damage in extreme temperature conditions. The concept of using antifreeze in mechanical systems dates back to the early 20th century, with its application in HVAC systems becoming widespread in the 1950s and 1960s as central heating and cooling systems became more common in residential and commercial buildings.
The primary function of antifreeze in HVAC systems is to lower the freezing point of the water-based solution circulating through the system. This is particularly important in regions that experience cold winters, where the risk of water freezing and expanding within pipes and components can lead to severe damage and system failure. By preventing freezing, antifreeze ensures continuous operation of the HVAC system even in sub-zero temperatures.
Initially, methanol and ethylene glycol were the most commonly used antifreeze substances in HVAC systems. However, concerns about toxicity and environmental impact led to the development of safer alternatives. Propylene glycol emerged as a popular choice due to its lower toxicity profile and biodegradability, making it more suitable for use in residential and commercial settings.
The evolution of antifreeze formulations has been driven by the need for improved performance, longevity, and compatibility with modern HVAC materials. Modern antifreeze solutions often include corrosion inhibitors, pH buffers, and anti-foaming agents to protect system components and enhance overall efficiency. These additives help extend the lifespan of HVAC equipment by preventing internal corrosion and scale buildup.
As HVAC systems have become more sophisticated, the role of antifreeze has expanded beyond freeze protection. In closed-loop systems, such as those used in geothermal heat pumps, antifreeze solutions serve as heat transfer fluids, efficiently moving thermal energy between the ground and the building. This application has become increasingly important with the growing adoption of renewable energy technologies in HVAC systems.
The selection of the appropriate antifreeze solution for an HVAC system depends on various factors, including the specific system design, operating temperatures, and local climate conditions. Engineers and HVAC professionals must consider these factors to ensure optimal system performance and longevity. The ongoing research and development in antifreeze technology continue to focus on improving environmental sustainability, enhancing heat transfer properties, and extending the service life of HVAC systems.
The primary function of antifreeze in HVAC systems is to lower the freezing point of the water-based solution circulating through the system. This is particularly important in regions that experience cold winters, where the risk of water freezing and expanding within pipes and components can lead to severe damage and system failure. By preventing freezing, antifreeze ensures continuous operation of the HVAC system even in sub-zero temperatures.
Initially, methanol and ethylene glycol were the most commonly used antifreeze substances in HVAC systems. However, concerns about toxicity and environmental impact led to the development of safer alternatives. Propylene glycol emerged as a popular choice due to its lower toxicity profile and biodegradability, making it more suitable for use in residential and commercial settings.
The evolution of antifreeze formulations has been driven by the need for improved performance, longevity, and compatibility with modern HVAC materials. Modern antifreeze solutions often include corrosion inhibitors, pH buffers, and anti-foaming agents to protect system components and enhance overall efficiency. These additives help extend the lifespan of HVAC equipment by preventing internal corrosion and scale buildup.
As HVAC systems have become more sophisticated, the role of antifreeze has expanded beyond freeze protection. In closed-loop systems, such as those used in geothermal heat pumps, antifreeze solutions serve as heat transfer fluids, efficiently moving thermal energy between the ground and the building. This application has become increasingly important with the growing adoption of renewable energy technologies in HVAC systems.
The selection of the appropriate antifreeze solution for an HVAC system depends on various factors, including the specific system design, operating temperatures, and local climate conditions. Engineers and HVAC professionals must consider these factors to ensure optimal system performance and longevity. The ongoing research and development in antifreeze technology continue to focus on improving environmental sustainability, enhancing heat transfer properties, and extending the service life of HVAC systems.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for antifreeze in HVAC systems has been steadily growing, driven by the expansion of the global HVAC industry and increasing awareness of the importance of system maintenance. As climate control becomes more critical in both residential and commercial settings, the need for efficient and reliable HVAC systems has surged, consequently boosting the demand for antifreeze solutions.
In the residential sector, the rising adoption of central heating and cooling systems in developing countries has significantly contributed to the market growth. Homeowners are increasingly recognizing the value of proper HVAC maintenance, including the use of antifreeze to protect their systems from freezing and corrosion. This trend is particularly evident in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, where the risk of system damage due to freezing is high.
The commercial and industrial sectors represent a substantial portion of the antifreeze market for HVAC systems. Large-scale facilities such as office buildings, shopping centers, and factories require robust climate control solutions, driving the demand for high-performance antifreeze products. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability in commercial buildings has also led to the development of eco-friendly antifreeze formulations, further expanding market opportunities.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has indirectly impacted the HVAC antifreeze market. As EVs rely more heavily on efficient thermal management systems, there is an increased demand for specialized antifreeze solutions that can maintain optimal battery temperatures while also supporting the vehicle's HVAC system.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for HVAC antifreeze, due to their well-established HVAC infrastructure and cold climates. However, rapid urbanization and improving living standards in Asia-Pacific countries, particularly China and India, are creating new growth opportunities for antifreeze manufacturers.
The market is also being shaped by technological advancements in antifreeze formulations. Manufacturers are developing products with enhanced thermal properties, extended service life, and improved compatibility with modern HVAC materials. This innovation is driven by the need for more efficient and reliable climate control systems in various applications, from data centers to renewable energy installations.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly antifreeze solutions. This trend is pushing manufacturers to develop biodegradable and less toxic alternatives to traditional ethylene glycol-based products, opening up new market segments for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
In the residential sector, the rising adoption of central heating and cooling systems in developing countries has significantly contributed to the market growth. Homeowners are increasingly recognizing the value of proper HVAC maintenance, including the use of antifreeze to protect their systems from freezing and corrosion. This trend is particularly evident in regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, where the risk of system damage due to freezing is high.
The commercial and industrial sectors represent a substantial portion of the antifreeze market for HVAC systems. Large-scale facilities such as office buildings, shopping centers, and factories require robust climate control solutions, driving the demand for high-performance antifreeze products. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability in commercial buildings has also led to the development of eco-friendly antifreeze formulations, further expanding market opportunities.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has indirectly impacted the HVAC antifreeze market. As EVs rely more heavily on efficient thermal management systems, there is an increased demand for specialized antifreeze solutions that can maintain optimal battery temperatures while also supporting the vehicle's HVAC system.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for HVAC antifreeze, due to their well-established HVAC infrastructure and cold climates. However, rapid urbanization and improving living standards in Asia-Pacific countries, particularly China and India, are creating new growth opportunities for antifreeze manufacturers.
The market is also being shaped by technological advancements in antifreeze formulations. Manufacturers are developing products with enhanced thermal properties, extended service life, and improved compatibility with modern HVAC materials. This innovation is driven by the need for more efficient and reliable climate control systems in various applications, from data centers to renewable energy installations.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly antifreeze solutions. This trend is pushing manufacturers to develop biodegradable and less toxic alternatives to traditional ethylene glycol-based products, opening up new market segments for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Current Challenges
The use of antifreeze in HVAC systems is critical for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing damage, yet it faces several significant challenges in current applications. One of the primary issues is the environmental impact of traditional antifreeze solutions. Many commonly used antifreeze formulations contain ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, which can be toxic to wildlife and contaminate soil and water sources if leaked or improperly disposed of. This has led to increased pressure for the development of more eco-friendly alternatives that maintain the same level of performance.
Another challenge lies in the corrosion protection capabilities of antifreeze solutions. While antifreeze is designed to prevent freezing and overheating, it must also protect the various metal components within HVAC systems from corrosion. However, the effectiveness of corrosion inhibitors in antifreeze can diminish over time, leading to potential system damage if not properly maintained or replaced. This necessitates regular testing and replacement of antifreeze solutions, which can be costly and time-consuming for system operators.
The compatibility of antifreeze with new materials used in modern HVAC systems presents an additional challenge. As manufacturers innovate with new alloys and composite materials to improve system efficiency and reduce weight, the formulation of antifreeze must evolve to ensure it remains compatible with these materials without causing degradation or reducing their effectiveness. This requires ongoing research and development to create antifreeze solutions that can adapt to the changing landscape of HVAC system materials.
Heat transfer efficiency is another area of concern. While antifreeze is necessary to prevent freezing, it can also reduce the overall heat transfer efficiency of the system compared to water alone. This trade-off between freeze protection and thermal efficiency poses a challenge for system designers who must balance these competing factors to optimize performance, especially in regions with varying climate conditions.
Lastly, the storage and handling of antifreeze present logistical challenges. The liquid nature of most antifreeze solutions means they require careful storage to prevent spills and leaks. Additionally, the transportation and disposal of antifreeze must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, adding complexity and cost to HVAC system maintenance and operation. These factors collectively underscore the need for innovative solutions that can address the multifaceted challenges associated with antifreeze use in HVAC systems, driving the industry towards more sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly alternatives.
Another challenge lies in the corrosion protection capabilities of antifreeze solutions. While antifreeze is designed to prevent freezing and overheating, it must also protect the various metal components within HVAC systems from corrosion. However, the effectiveness of corrosion inhibitors in antifreeze can diminish over time, leading to potential system damage if not properly maintained or replaced. This necessitates regular testing and replacement of antifreeze solutions, which can be costly and time-consuming for system operators.
The compatibility of antifreeze with new materials used in modern HVAC systems presents an additional challenge. As manufacturers innovate with new alloys and composite materials to improve system efficiency and reduce weight, the formulation of antifreeze must evolve to ensure it remains compatible with these materials without causing degradation or reducing their effectiveness. This requires ongoing research and development to create antifreeze solutions that can adapt to the changing landscape of HVAC system materials.
Heat transfer efficiency is another area of concern. While antifreeze is necessary to prevent freezing, it can also reduce the overall heat transfer efficiency of the system compared to water alone. This trade-off between freeze protection and thermal efficiency poses a challenge for system designers who must balance these competing factors to optimize performance, especially in regions with varying climate conditions.
Lastly, the storage and handling of antifreeze present logistical challenges. The liquid nature of most antifreeze solutions means they require careful storage to prevent spills and leaks. Additionally, the transportation and disposal of antifreeze must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, adding complexity and cost to HVAC system maintenance and operation. These factors collectively underscore the need for innovative solutions that can address the multifaceted challenges associated with antifreeze use in HVAC systems, driving the industry towards more sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly alternatives.
Existing Antifreeze Solutions
01 Composition of antifreeze solutions
Antifreeze solutions typically consist of a mixture of water and chemical compounds designed to lower the freezing point of the solution. Common ingredients include glycols, alcohols, and corrosion inhibitors. These solutions are formulated to provide protection against freezing in various applications, such as automotive cooling systems and industrial processes.- Composition of antifreeze solutions: Antifreeze solutions typically consist of a mixture of water and chemical compounds designed to lower the freezing point of the solution. Common ingredients include glycols, alcohols, and corrosion inhibitors. These solutions are formulated to provide protection against freezing in various applications, such as automotive cooling systems and industrial processes.
- Environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations: Development of eco-friendly antifreeze solutions focuses on using biodegradable and less toxic ingredients. These formulations may incorporate plant-based glycols, natural corrosion inhibitors, and other sustainable components to reduce environmental impact while maintaining effective freeze protection properties.
- Antifreeze recycling and purification methods: Techniques for recycling and purifying used antifreeze solutions have been developed to reduce waste and conserve resources. These methods may involve filtration, distillation, chemical treatment, or a combination of processes to remove contaminants and restore the antifreeze to a reusable condition.
- Antifreeze applications in specific industries: Specialized antifreeze formulations have been developed for use in various industries beyond automotive applications. These include solutions for solar thermal systems, wind turbines, and other renewable energy technologies, as well as antifreeze products tailored for use in food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Antifreeze testing and monitoring systems: Innovations in antifreeze testing and monitoring systems allow for real-time assessment of antifreeze quality and performance. These technologies may include sensors, analytical devices, or automated systems that can detect contamination, measure freeze protection levels, or alert users to the need for antifreeze replacement or maintenance.
02 Environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations
There is a growing focus on developing eco-friendly antifreeze solutions that minimize environmental impact. These formulations often utilize biodegradable components and reduce the use of toxic substances. Research in this area aims to maintain or improve the performance of traditional antifreeze while addressing environmental concerns.Expand Specific Solutions03 Antifreeze recycling and purification methods
Various techniques have been developed for recycling and purifying used antifreeze solutions. These methods aim to remove contaminants, restore the antifreeze properties, and extend the useful life of the product. Processes may include filtration, distillation, and chemical treatment to separate and purify the antifreeze components.Expand Specific Solutions04 Antifreeze applications in specific industries
Antifreeze solutions are utilized in various industries beyond automotive applications. Specialized formulations are developed for use in renewable energy systems, such as solar thermal and geothermal installations. Additionally, antifreeze products are designed for use in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial processes where low-temperature protection is required.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and quality control of antifreeze products
Methods and equipment for testing and ensuring the quality of antifreeze solutions are crucial for maintaining product effectiveness. These may include techniques for measuring freezing point depression, corrosion protection, and overall performance. Quality control processes are implemented to ensure consistency and reliability of antifreeze products across different batches and applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The antifreeze market in HVAC systems is in a mature stage, with a steady global demand driven by the growing HVAC industry. The market size is substantial, reflecting the essential role of antifreeze in preventing system damage and ensuring efficient operation. Technologically, antifreeze solutions are well-established, but ongoing research focuses on improving environmental sustainability and performance. Key players like Daikin, Trane, and Carrier are investing in advanced formulations, while companies such as Arteco NV specialize in developing innovative coolants. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of HVAC manufacturers and specialized chemical companies, with a trend towards eco-friendly and energy-efficient antifreeze solutions.
DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd.
Technical Solution: Daikin has developed advanced antifreeze solutions for HVAC systems, focusing on environmentally friendly refrigerants. Their VRV (Variable Refrigerant Volume) technology incorporates a unique antifreeze circuit that prevents freezing in low ambient temperatures, allowing for efficient operation in cold climates[1]. The company has also introduced a water-based antifreeze solution for their air-to-water heat pump systems, which provides excellent heat transfer properties while minimizing environmental impact[2]. Daikin's antifreeze technologies are designed to work seamlessly with their energy-efficient heat exchangers, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of HVAC equipment even in extreme weather conditions[3].
Strengths: Advanced VRV technology, environmentally friendly solutions, and excellent cold climate performance. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial costs and system complexity compared to traditional HVAC systems.
LG Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: LG Electronics has developed innovative antifreeze technologies for their HVAC systems, particularly focusing on heat pumps and air conditioners. Their THERMA V series incorporates a low-temperature heating operation mode that utilizes an advanced antifreeze solution to prevent system freezing in temperatures as low as -25°C[1]. LG's antifreeze technology includes a smart defrost control system that optimizes defrosting cycles, reducing energy consumption and improving overall system efficiency[2]. Additionally, LG has implemented a dual injection technology in their compressors, which enhances the antifreeze capabilities by ensuring proper refrigerant flow and preventing ice formation in critical components[3].
Strengths: Excellent low-temperature performance, energy-efficient defrost control, and advanced compressor technology. Weaknesses: May require more frequent maintenance due to complex systems and potential for higher costs in initial installation.
Core Antifreeze Innovations
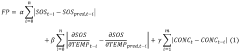
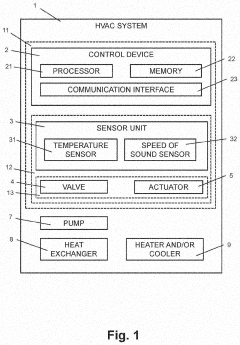
Method and device for determining antifreeze content in a fluid of an HVAC system
PatentWO2021219627A1
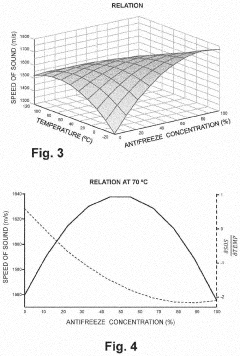
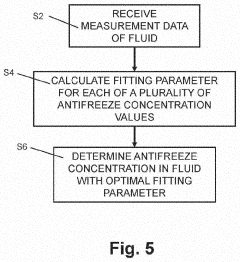
Innovation
- A method and device using a processor to determine antifreeze content in HVAC systems by measuring temperature and speed of sound, calculating fitting parameters, and identifying the optimal antifreeze concentration and type through iterative processes and weighted comparisons with previous data.
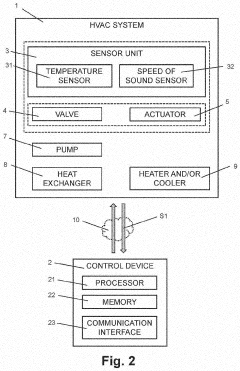
Method and device for determining antifreeze content in a fluid of an HVAC system
PatentActiveUS20230146901A1
Innovation
- A method and device using a processor to calculate antifreeze concentration in HVAC systems by analyzing measured temperature and speed of sound data, incorporating previous measurement and concentration data to determine optimal fitting parameters and identify antifreeze type.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the use and management of antifreeze in HVAC systems. These regulations are designed to protect human health and the environment from potential hazards associated with antifreeze chemicals. The primary focus of these regulations is on the proper handling, storage, and disposal of antifreeze solutions.
One of the key aspects of environmental regulations concerning antifreeze is the classification of used antifreeze as hazardous waste. This classification is due to the presence of heavy metals and other toxic substances that can accumulate in antifreeze during its use in HVAC systems. As a result, strict guidelines are in place for the disposal of used antifreeze, prohibiting its release into the environment through sewers, storm drains, or on the ground.
Many jurisdictions require that used antifreeze be recycled or properly disposed of through authorized waste management facilities. Recycling of antifreeze has become increasingly common, as it reduces the environmental impact and conserves resources. The recycling process typically involves removing contaminants and restoring the antifreeze to its original chemical composition.
The Clean Water Act and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States are two primary federal regulations that impact antifreeze management. These acts set standards for the discharge of pollutants into water bodies and regulate the handling of hazardous waste, respectively. State and local regulations may impose additional requirements, such as mandatory recycling programs or specific disposal procedures.
Environmental regulations also address the chemical composition of antifreeze. There has been a shift towards more environmentally friendly formulations, with a focus on reducing the use of toxic substances like ethylene glycol. Propylene glycol-based antifreeze, which is less toxic, has gained popularity as an alternative in some applications.
The impact of these regulations extends to HVAC system design and maintenance practices. Manufacturers and service providers must ensure that their systems and procedures comply with environmental standards. This includes implementing proper containment measures to prevent leaks, using appropriate materials for storage and transport, and maintaining accurate records of antifreeze handling and disposal.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, it is likely that regulations surrounding antifreeze in HVAC systems will become more stringent. Future trends may include stricter limits on the types of chemicals used in antifreeze formulations, increased emphasis on recycling and recovery programs, and more comprehensive reporting requirements for antifreeze usage and disposal.
One of the key aspects of environmental regulations concerning antifreeze is the classification of used antifreeze as hazardous waste. This classification is due to the presence of heavy metals and other toxic substances that can accumulate in antifreeze during its use in HVAC systems. As a result, strict guidelines are in place for the disposal of used antifreeze, prohibiting its release into the environment through sewers, storm drains, or on the ground.
Many jurisdictions require that used antifreeze be recycled or properly disposed of through authorized waste management facilities. Recycling of antifreeze has become increasingly common, as it reduces the environmental impact and conserves resources. The recycling process typically involves removing contaminants and restoring the antifreeze to its original chemical composition.
The Clean Water Act and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States are two primary federal regulations that impact antifreeze management. These acts set standards for the discharge of pollutants into water bodies and regulate the handling of hazardous waste, respectively. State and local regulations may impose additional requirements, such as mandatory recycling programs or specific disposal procedures.
Environmental regulations also address the chemical composition of antifreeze. There has been a shift towards more environmentally friendly formulations, with a focus on reducing the use of toxic substances like ethylene glycol. Propylene glycol-based antifreeze, which is less toxic, has gained popularity as an alternative in some applications.
The impact of these regulations extends to HVAC system design and maintenance practices. Manufacturers and service providers must ensure that their systems and procedures comply with environmental standards. This includes implementing proper containment measures to prevent leaks, using appropriate materials for storage and transport, and maintaining accurate records of antifreeze handling and disposal.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, it is likely that regulations surrounding antifreeze in HVAC systems will become more stringent. Future trends may include stricter limits on the types of chemicals used in antifreeze formulations, increased emphasis on recycling and recovery programs, and more comprehensive reporting requirements for antifreeze usage and disposal.
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations are paramount when dealing with antifreeze in HVAC systems. The primary concern is the toxicity of many antifreeze solutions, particularly those containing ethylene glycol. Ingestion of ethylene glycol can lead to severe health consequences, including kidney damage and potentially fatal outcomes. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement proper handling and storage protocols. This includes clearly labeling all containers, securing storage areas to prevent unauthorized access, and providing adequate ventilation in areas where antifreeze is used or stored.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for workers handling antifreeze. This typically includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate clothing to prevent skin contact. In case of spills, immediate clean-up procedures should be followed, and contaminated materials must be disposed of according to local regulations. It is also vital to have eyewash stations and safety showers readily accessible in areas where antifreeze is handled.
Environmental considerations are equally important. Antifreeze solutions can be harmful to aquatic life and contaminate water sources if not properly disposed of. Many jurisdictions classify used antifreeze as hazardous waste, requiring specific disposal methods. Implementing a recycling program for used antifreeze can help reduce environmental impact and comply with regulations.
Regular maintenance and inspection of HVAC systems are crucial to prevent leaks and ensure the safe operation of antifreeze-containing components. This includes checking for signs of corrosion, inspecting hoses and connections, and monitoring antifreeze levels. Proper training for all personnel involved in handling or working with antifreeze-containing systems is essential to ensure they understand the associated risks and safety procedures.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards using less toxic alternatives, such as propylene glycol-based antifreeze solutions. While these are generally considered safer for humans and animals, they still require proper handling and disposal. When selecting an antifreeze solution, it is important to consider not only its performance characteristics but also its safety profile and environmental impact.
Emergency response planning is another critical aspect of antifreeze safety in HVAC systems. This includes having clearly defined procedures for dealing with spills, leaks, or accidental exposure. Staff should be trained in these procedures and have access to necessary emergency equipment and contact information for relevant authorities or medical services.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for workers handling antifreeze. This typically includes chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and appropriate clothing to prevent skin contact. In case of spills, immediate clean-up procedures should be followed, and contaminated materials must be disposed of according to local regulations. It is also vital to have eyewash stations and safety showers readily accessible in areas where antifreeze is handled.
Environmental considerations are equally important. Antifreeze solutions can be harmful to aquatic life and contaminate water sources if not properly disposed of. Many jurisdictions classify used antifreeze as hazardous waste, requiring specific disposal methods. Implementing a recycling program for used antifreeze can help reduce environmental impact and comply with regulations.
Regular maintenance and inspection of HVAC systems are crucial to prevent leaks and ensure the safe operation of antifreeze-containing components. This includes checking for signs of corrosion, inspecting hoses and connections, and monitoring antifreeze levels. Proper training for all personnel involved in handling or working with antifreeze-containing systems is essential to ensure they understand the associated risks and safety procedures.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards using less toxic alternatives, such as propylene glycol-based antifreeze solutions. While these are generally considered safer for humans and animals, they still require proper handling and disposal. When selecting an antifreeze solution, it is important to consider not only its performance characteristics but also its safety profile and environmental impact.
Emergency response planning is another critical aspect of antifreeze safety in HVAC systems. This includes having clearly defined procedures for dealing with spills, leaks, or accidental exposure. Staff should be trained in these procedures and have access to necessary emergency equipment and contact information for relevant authorities or medical services.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!