Benefits of V12 Engines in Long-Range Military Applications
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V12 Engine Evolution
The V12 engine has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for luxury automobiles and aircraft, the V12 configuration has found its way into various military applications, particularly in long-range vehicles and equipment. The evolution of V12 engines for military use has been driven by the need for increased power, reliability, and efficiency in demanding operational environments.
In the early stages of V12 engine development, the focus was primarily on increasing power output and improving durability. World War II saw a surge in V12 engine production for military aircraft, tanks, and naval vessels. These engines were characterized by their high power-to-weight ratio and smooth operation, making them ideal for long-range missions and heavy-duty applications.
Post-war advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques led to the development of more robust V12 engines capable of withstanding extreme conditions. The introduction of turbocharging and supercharging technologies in the 1960s and 1970s further enhanced the power output and efficiency of V12 engines, making them even more suitable for long-range military applications.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a shift towards electronic fuel injection systems and computer-controlled engine management, significantly improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. These advancements allowed V12 engines to maintain their power advantage while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
In recent decades, the focus of V12 engine evolution has been on weight reduction, fuel efficiency, and integration with hybrid technologies. Advanced materials such as lightweight alloys and composites have been employed to reduce engine weight without compromising strength. Innovations in combustion technology, such as direct injection and variable valve timing, have further improved fuel efficiency and power delivery.
The latest generation of V12 engines for military applications incorporates sophisticated thermal management systems, advanced lubrication technologies, and modular designs for easier maintenance and repair in the field. These engines are also being designed with multi-fuel capabilities, allowing them to operate on a variety of fuel types, enhancing operational flexibility in diverse environments.
Looking ahead, the evolution of V12 engines for long-range military applications is likely to focus on further integration with electric powertrains, development of more efficient cooling systems, and the use of artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance and performance optimization. These advancements will ensure that V12 engines continue to play a crucial role in military vehicles and equipment, providing the power and reliability needed for extended operations in challenging conditions.
In the early stages of V12 engine development, the focus was primarily on increasing power output and improving durability. World War II saw a surge in V12 engine production for military aircraft, tanks, and naval vessels. These engines were characterized by their high power-to-weight ratio and smooth operation, making them ideal for long-range missions and heavy-duty applications.
Post-war advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques led to the development of more robust V12 engines capable of withstanding extreme conditions. The introduction of turbocharging and supercharging technologies in the 1960s and 1970s further enhanced the power output and efficiency of V12 engines, making them even more suitable for long-range military applications.
The 1980s and 1990s saw a shift towards electronic fuel injection systems and computer-controlled engine management, significantly improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. These advancements allowed V12 engines to maintain their power advantage while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
In recent decades, the focus of V12 engine evolution has been on weight reduction, fuel efficiency, and integration with hybrid technologies. Advanced materials such as lightweight alloys and composites have been employed to reduce engine weight without compromising strength. Innovations in combustion technology, such as direct injection and variable valve timing, have further improved fuel efficiency and power delivery.
The latest generation of V12 engines for military applications incorporates sophisticated thermal management systems, advanced lubrication technologies, and modular designs for easier maintenance and repair in the field. These engines are also being designed with multi-fuel capabilities, allowing them to operate on a variety of fuel types, enhancing operational flexibility in diverse environments.
Looking ahead, the evolution of V12 engines for long-range military applications is likely to focus on further integration with electric powertrains, development of more efficient cooling systems, and the use of artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance and performance optimization. These advancements will ensure that V12 engines continue to play a crucial role in military vehicles and equipment, providing the power and reliability needed for extended operations in challenging conditions.
Military Demand Analysis
The military sector has shown a consistent and growing demand for long-range applications, particularly in the realm of aircraft and ground vehicles. This demand is driven by the need for extended operational capabilities, increased mission endurance, and enhanced strategic flexibility. V12 engines have emerged as a compelling solution to meet these requirements, offering a unique combination of power, efficiency, and reliability.
In the aviation sector, long-range military aircraft such as strategic bombers, maritime patrol aircraft, and aerial refueling tankers require engines capable of sustained high-performance over extended periods. The V12 configuration provides the necessary power output while maintaining fuel efficiency, a critical factor for missions that can span thousands of miles. The ability to operate for prolonged durations without refueling enhances the strategic reach of military forces, allowing for global power projection and rapid response capabilities.
Ground-based military vehicles, including heavy-duty trucks and armored personnel carriers, also benefit from V12 engines in long-range applications. These vehicles often need to traverse vast distances in challenging terrains, carrying heavy loads of personnel, equipment, and supplies. The V12 engine's high torque output at low RPMs makes it ideal for such demanding conditions, providing the necessary pulling power while maintaining fuel economy.
The military's emphasis on logistics and supply chain efficiency further underscores the importance of V12 engines in long-range applications. By enabling vehicles to cover greater distances on a single fuel load, these engines reduce the frequency of refueling stops, minimizing vulnerabilities and improving operational tempo. This capability is particularly valuable in remote or hostile environments where establishing and protecting supply lines can be challenging and resource-intensive.
Moreover, the reliability and durability of V12 engines align well with military requirements for equipment longevity and reduced maintenance needs. The robust design of these engines, coupled with their ability to operate efficiently under various conditions, translates to lower lifecycle costs and increased operational readiness – both critical factors in military planning and budgeting.
The demand for V12 engines in long-range military applications is also influenced by geopolitical factors and evolving defense strategies. As nations seek to expand their sphere of influence and respond to global security challenges, the need for long-range capabilities becomes increasingly pronounced. This trend is evident in the development of next-generation long-range bombers, advanced reconnaissance aircraft, and multi-role combat vehicles, all of which could potentially benefit from V12 engine technology.
In the aviation sector, long-range military aircraft such as strategic bombers, maritime patrol aircraft, and aerial refueling tankers require engines capable of sustained high-performance over extended periods. The V12 configuration provides the necessary power output while maintaining fuel efficiency, a critical factor for missions that can span thousands of miles. The ability to operate for prolonged durations without refueling enhances the strategic reach of military forces, allowing for global power projection and rapid response capabilities.
Ground-based military vehicles, including heavy-duty trucks and armored personnel carriers, also benefit from V12 engines in long-range applications. These vehicles often need to traverse vast distances in challenging terrains, carrying heavy loads of personnel, equipment, and supplies. The V12 engine's high torque output at low RPMs makes it ideal for such demanding conditions, providing the necessary pulling power while maintaining fuel economy.
The military's emphasis on logistics and supply chain efficiency further underscores the importance of V12 engines in long-range applications. By enabling vehicles to cover greater distances on a single fuel load, these engines reduce the frequency of refueling stops, minimizing vulnerabilities and improving operational tempo. This capability is particularly valuable in remote or hostile environments where establishing and protecting supply lines can be challenging and resource-intensive.
Moreover, the reliability and durability of V12 engines align well with military requirements for equipment longevity and reduced maintenance needs. The robust design of these engines, coupled with their ability to operate efficiently under various conditions, translates to lower lifecycle costs and increased operational readiness – both critical factors in military planning and budgeting.
The demand for V12 engines in long-range military applications is also influenced by geopolitical factors and evolving defense strategies. As nations seek to expand their sphere of influence and respond to global security challenges, the need for long-range capabilities becomes increasingly pronounced. This trend is evident in the development of next-generation long-range bombers, advanced reconnaissance aircraft, and multi-role combat vehicles, all of which could potentially benefit from V12 engine technology.
V12 Tech Challenges
The implementation of V12 engines in long-range military applications presents several significant technical challenges. One of the primary issues is the complexity of the engine design itself. With twelve cylinders arranged in a V-configuration, these engines require intricate cooling systems, precise fuel injection, and sophisticated engine management systems to operate efficiently and reliably.
Weight is another critical factor that poses challenges for military applications. V12 engines are inherently heavier than their smaller counterparts, which can impact the overall weight distribution and payload capacity of military vehicles or aircraft. This increased weight may necessitate additional structural reinforcements, potentially compromising the vehicle's agility and maneuverability.
Fuel efficiency remains a persistent challenge for V12 engines, particularly in long-range operations. The high fuel consumption of these powerful engines can limit operational range and increase the logistical burden of fuel transport and storage. This issue becomes even more pronounced in remote or hostile environments where fuel resupply may be difficult or dangerous.
Maintenance and reliability are also significant concerns. The complexity of V12 engines often translates to more frequent maintenance requirements and a higher likelihood of mechanical issues. In military applications, where operational readiness is crucial, this can lead to increased downtime and higher maintenance costs.
Heat management presents another technical hurdle. V12 engines generate substantial heat during operation, necessitating advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance. This is particularly challenging in extreme environments or during prolonged high-output operations typical in military scenarios.
Emissions control is an emerging challenge, even in military applications. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, military vehicles are not exempt from the need to reduce emissions. Balancing the power output of V12 engines with increasingly strict emissions standards requires innovative solutions in engine design and exhaust treatment systems.
Lastly, the integration of V12 engines with modern military technologies poses unique challenges. This includes compatibility with advanced electronic systems, adaptation to various fuel types for operational flexibility, and the ability to operate effectively in a wide range of environmental conditions, from arctic cold to desert heat.
Weight is another critical factor that poses challenges for military applications. V12 engines are inherently heavier than their smaller counterparts, which can impact the overall weight distribution and payload capacity of military vehicles or aircraft. This increased weight may necessitate additional structural reinforcements, potentially compromising the vehicle's agility and maneuverability.
Fuel efficiency remains a persistent challenge for V12 engines, particularly in long-range operations. The high fuel consumption of these powerful engines can limit operational range and increase the logistical burden of fuel transport and storage. This issue becomes even more pronounced in remote or hostile environments where fuel resupply may be difficult or dangerous.
Maintenance and reliability are also significant concerns. The complexity of V12 engines often translates to more frequent maintenance requirements and a higher likelihood of mechanical issues. In military applications, where operational readiness is crucial, this can lead to increased downtime and higher maintenance costs.
Heat management presents another technical hurdle. V12 engines generate substantial heat during operation, necessitating advanced cooling systems to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance. This is particularly challenging in extreme environments or during prolonged high-output operations typical in military scenarios.
Emissions control is an emerging challenge, even in military applications. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, military vehicles are not exempt from the need to reduce emissions. Balancing the power output of V12 engines with increasingly strict emissions standards requires innovative solutions in engine design and exhaust treatment systems.
Lastly, the integration of V12 engines with modern military technologies poses unique challenges. This includes compatibility with advanced electronic systems, adaptation to various fuel types for operational flexibility, and the ability to operate effectively in a wide range of environmental conditions, from arctic cold to desert heat.
Current V12 Solutions
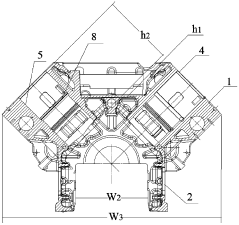
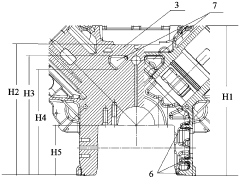
01 V12 Engine Design and Configuration
V12 engines are typically designed with two banks of six cylinders arranged in a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact engine design while providing high power output and smooth operation. The V-angle between cylinder banks can vary, with common angles including 60 and 90 degrees. V12 engines are often used in high-performance vehicles, luxury cars, and some marine applications due to their power and refinement.- V12 Engine Design and Configuration: V12 engines are typically designed with two banks of six cylinders arranged in a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact engine design while providing high power output and smooth operation. The V-angle between the cylinder banks can vary, with common angles including 60 degrees and 90 degrees.
- Performance Optimization in V12 Engines: Various techniques are employed to optimize the performance of V12 engines, including advanced fuel injection systems, variable valve timing, and turbocharging. These technologies help improve power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions control in high-performance applications.
- Control Systems for V12 Engines: Modern V12 engines utilize sophisticated electronic control systems to manage engine operation. These systems may include engine control units (ECUs), sensors, and actuators to optimize performance, fuel economy, and emissions across various operating conditions.
- Manufacturing and Assembly Processes: Specialized manufacturing and assembly processes are employed in the production of V12 engines. These may include precision machining of engine components, advanced casting techniques for engine blocks, and automated assembly lines to ensure consistent quality and performance.
- Historical Development of V12 Engines: The development of V12 engines has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. Early designs focused on aircraft and luxury automobile applications, with subsequent advancements in materials, manufacturing techniques, and engine management systems leading to improved performance and efficiency over time.
02 Fuel Injection and Combustion Systems
Modern V12 engines often incorporate advanced fuel injection and combustion systems to optimize performance and efficiency. These may include direct injection technology, variable valve timing, and sophisticated engine management systems. Such technologies help improve fuel economy, reduce emissions, and enhance power delivery across the engine's operating range.Expand Specific Solutions03 Engine Control and Management
V12 engines typically employ complex control systems to manage various aspects of engine operation. This includes electronic control units (ECUs) that monitor and adjust parameters such as fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and valve operation. Advanced engine management systems may also incorporate features like cylinder deactivation for improved efficiency at lower loads.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Due to their size and power output, V12 engines require sophisticated cooling and lubrication systems. This may involve advanced coolant circulation designs, oil cooling systems, and precision-engineered components to ensure proper heat management and lubrication throughout the engine. Efficient cooling and lubrication are crucial for maintaining performance and longevity in high-output V12 engines.Expand Specific Solutions05 Historical Development and Innovations
The development of V12 engines has a rich history, with numerous innovations contributing to their evolution. Early designs focused on achieving smooth operation and high power output, while more recent developments have emphasized efficiency and emissions reduction. Innovations in materials, manufacturing techniques, and engine design have continually improved the performance and reliability of V12 engines over time.Expand Specific Solutions
Key V12 Manufacturers
The competition landscape for V12 engines in long-range military applications is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing technological advancements. The market size is significant, driven by defense spending and the need for high-performance engines in military vehicles and aircraft. Key players like Ford Global Technologies, GM Global Technology Operations, and Progress Rail Locomotive are at the forefront of V12 engine development, leveraging their extensive automotive and locomotive expertise. Companies such as Airbus Defence & Space and China Academy of Aerospace Aerodynamics are also contributing to the field, focusing on aerospace applications. The technology's maturity is evident, with continuous improvements in power output, fuel efficiency, and reliability being pursued by these industry leaders.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford's approach to V12 engines for long-range military applications focuses on advanced fuel efficiency and durability. Their V12 design incorporates direct fuel injection and variable valve timing, optimizing combustion for extended range missions[1]. The engine features a high-strength aluminum alloy block to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity. Ford has also implemented advanced thermal management systems to ensure consistent performance in extreme conditions, crucial for military operations[3]. The company's V12 engine utilizes a twin-turbocharging system, providing high power output and improved fuel economy, essential for long-range missions where refueling opportunities may be limited[5].
Strengths: High power-to-weight ratio, excellent fuel efficiency, and proven durability in harsh environments. Weaknesses: Complex design may increase maintenance requirements and potential for mechanical issues in remote locations.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM's V12 engine technology for military long-range applications emphasizes reliability and adaptability. Their V12 design features a modular architecture that allows for easy maintenance and part replacement in the field[2]. The engine incorporates advanced materials such as ceramic-coated cylinder liners to reduce friction and improve heat dissipation, enhancing overall efficiency and longevity[4]. GM has also developed a sophisticated engine control unit (ECU) that continuously optimizes performance based on mission parameters and environmental conditions. The V12 engine is designed with a high compression ratio and multi-stage forced induction, delivering exceptional torque across a wide RPM range, crucial for military vehicles operating in diverse terrains[6].
Strengths: Modular design for easy maintenance, advanced ECU for mission-specific optimization, and high torque output. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost due to advanced technologies and materials used.
V12 Core Innovations
Unmanned Aircraft and Operation Method for the Same
PatentActiveUS20180283292A1
Innovation
- A hybrid propulsion system combining a diesel or kerosene internal combustion engine with an electric motor and energy storage device, featuring a charger device that utilizes exhaust gas energy and mechanical charging, allowing for selective operation of the internal combustion engine and electric motor in parallel or series, and controlled by a controller based on flight parameters.
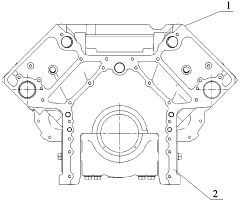
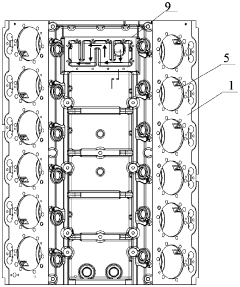
V-shaped twelve-cylinder cylinder block
PatentActiveCN109899172A
Innovation
- A V-shaped 12-cylinder cylinder block is designed, including two rows of left and right cylinders, multiple V-shaped reinforcing plates and two crankcase ventilation channels. U-shaped reinforcing ribs are set at the bottom, and an oil and gas separation structure is added inside the cylinder block. Reasonable parameter design improves the strength and stiffness of the cylinder block.
Fuel Efficiency Impact
The fuel efficiency impact of V12 engines in long-range military applications is a critical consideration that significantly influences operational capabilities and costs. V12 engines, while known for their power output, have traditionally been associated with higher fuel consumption compared to smaller engine configurations. However, in the context of long-range military applications, the fuel efficiency of V12 engines must be evaluated through a more nuanced lens.
V12 engines can achieve improved fuel efficiency in long-range scenarios due to their ability to operate at lower RPMs while maintaining high power output. This characteristic allows for sustained cruising speeds without pushing the engine to its limits, resulting in more economical fuel consumption over extended periods. The larger displacement of V12 engines also enables them to generate substantial torque at lower engine speeds, which is particularly beneficial for heavy military vehicles and aircraft operating in diverse terrains and altitudes.
Advanced technologies have further enhanced the fuel efficiency of modern V12 engines. Variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation systems have been implemented to optimize fuel consumption based on operational demands. These innovations allow V12 engines to adapt their performance characteristics in real-time, balancing power output with fuel efficiency as mission requirements dictate.
In long-range military applications, the fuel efficiency of V12 engines translates to extended operational range and reduced logistical burden. This increased range can be crucial for strategic missions, allowing military assets to cover vast distances without refueling. The reduced frequency of refueling not only enhances mission flexibility but also minimizes vulnerabilities associated with fuel supply chains in hostile environments.
Moreover, the fuel efficiency of V12 engines in military applications must be considered in the context of power-to-weight ratios. While V12 engines may consume more fuel in absolute terms, their ability to generate high power output relative to their weight can result in overall system efficiency gains. This is particularly relevant in aviation applications, where the trade-off between engine weight, fuel capacity, and power output is critical.
It is important to note that the fuel efficiency impact of V12 engines varies depending on the specific military platform and operational profile. For instance, in naval applications, the consistent power delivery of V12 engines can lead to more efficient long-range cruising compared to alternative propulsion systems. In land-based vehicles, the fuel efficiency benefits may be more pronounced in scenarios requiring sustained high-speed travel or heavy load transportation over extended distances.
V12 engines can achieve improved fuel efficiency in long-range scenarios due to their ability to operate at lower RPMs while maintaining high power output. This characteristic allows for sustained cruising speeds without pushing the engine to its limits, resulting in more economical fuel consumption over extended periods. The larger displacement of V12 engines also enables them to generate substantial torque at lower engine speeds, which is particularly beneficial for heavy military vehicles and aircraft operating in diverse terrains and altitudes.
Advanced technologies have further enhanced the fuel efficiency of modern V12 engines. Variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation systems have been implemented to optimize fuel consumption based on operational demands. These innovations allow V12 engines to adapt their performance characteristics in real-time, balancing power output with fuel efficiency as mission requirements dictate.
In long-range military applications, the fuel efficiency of V12 engines translates to extended operational range and reduced logistical burden. This increased range can be crucial for strategic missions, allowing military assets to cover vast distances without refueling. The reduced frequency of refueling not only enhances mission flexibility but also minimizes vulnerabilities associated with fuel supply chains in hostile environments.
Moreover, the fuel efficiency of V12 engines in military applications must be considered in the context of power-to-weight ratios. While V12 engines may consume more fuel in absolute terms, their ability to generate high power output relative to their weight can result in overall system efficiency gains. This is particularly relevant in aviation applications, where the trade-off between engine weight, fuel capacity, and power output is critical.
It is important to note that the fuel efficiency impact of V12 engines varies depending on the specific military platform and operational profile. For instance, in naval applications, the consistent power delivery of V12 engines can lead to more efficient long-range cruising compared to alternative propulsion systems. In land-based vehicles, the fuel efficiency benefits may be more pronounced in scenarios requiring sustained high-speed travel or heavy load transportation over extended distances.
Environmental Concerns
The environmental impact of V12 engines in long-range military applications is a significant concern that requires careful consideration. These powerful engines, while offering substantial benefits in terms of performance and reliability, also pose challenges in terms of fuel consumption and emissions. V12 engines typically consume more fuel than smaller engine configurations, leading to increased carbon dioxide emissions and contributing to the overall carbon footprint of military operations.
The high fuel consumption of V12 engines also raises concerns about resource depletion and the long-term sustainability of their use in military applications. As global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensify, military organizations face increasing pressure to adopt more environmentally friendly technologies. This has led to a growing interest in alternative propulsion systems, such as hybrid or electric powertrains, which could potentially replace or supplement V12 engines in certain applications.
Noise pollution is another environmental issue associated with V12 engines. The loud operation of these engines can have detrimental effects on local ecosystems, particularly in sensitive environments where military operations may take place. This can disrupt wildlife habitats and contribute to overall environmental degradation in operational areas.
However, it is important to note that advancements in engine technology have led to improvements in the environmental performance of V12 engines. Modern V12 engines often incorporate features such as advanced fuel injection systems, turbocharging, and exhaust after-treatment technologies, which can help reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. These improvements, while not eliminating environmental concerns entirely, do mitigate some of the negative impacts associated with V12 engine use.
The environmental impact of V12 engines must also be considered in the context of their specific military applications. In long-range missions, the extended operational capabilities provided by V12 engines may actually result in fewer overall missions, potentially reducing the cumulative environmental impact compared to multiple shorter-range operations. Additionally, the durability and reliability of V12 engines can lead to longer service lives for military vehicles, reducing the environmental costs associated with frequent vehicle replacements.
As military organizations strive to balance operational requirements with environmental responsibilities, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further improving the environmental performance of V12 engines. This includes exploring the use of alternative fuels, developing more efficient combustion processes, and integrating advanced materials to reduce weight and improve overall efficiency. These efforts aim to address environmental concerns while maintaining the performance advantages that make V12 engines valuable in long-range military applications.
The high fuel consumption of V12 engines also raises concerns about resource depletion and the long-term sustainability of their use in military applications. As global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensify, military organizations face increasing pressure to adopt more environmentally friendly technologies. This has led to a growing interest in alternative propulsion systems, such as hybrid or electric powertrains, which could potentially replace or supplement V12 engines in certain applications.
Noise pollution is another environmental issue associated with V12 engines. The loud operation of these engines can have detrimental effects on local ecosystems, particularly in sensitive environments where military operations may take place. This can disrupt wildlife habitats and contribute to overall environmental degradation in operational areas.
However, it is important to note that advancements in engine technology have led to improvements in the environmental performance of V12 engines. Modern V12 engines often incorporate features such as advanced fuel injection systems, turbocharging, and exhaust after-treatment technologies, which can help reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. These improvements, while not eliminating environmental concerns entirely, do mitigate some of the negative impacts associated with V12 engine use.
The environmental impact of V12 engines must also be considered in the context of their specific military applications. In long-range missions, the extended operational capabilities provided by V12 engines may actually result in fewer overall missions, potentially reducing the cumulative environmental impact compared to multiple shorter-range operations. Additionally, the durability and reliability of V12 engines can lead to longer service lives for military vehicles, reducing the environmental costs associated with frequent vehicle replacements.
As military organizations strive to balance operational requirements with environmental responsibilities, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on further improving the environmental performance of V12 engines. This includes exploring the use of alternative fuels, developing more efficient combustion processes, and integrating advanced materials to reduce weight and improve overall efficiency. These efforts aim to address environmental concerns while maintaining the performance advantages that make V12 engines valuable in long-range military applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!