Carbolic Acid's Effectiveness in Developing Eco-Conscious Pest Management
JUL 22, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carbolic Acid in Pest Control: Background and Objectives
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has a long and storied history in pest control dating back to the late 19th century. Initially used as a disinfectant, its potent antimicrobial properties soon led to its application in managing various pests. The evolution of carbolic acid in pest management reflects the broader trajectory of agricultural and public health practices, moving from indiscriminate use towards more targeted and environmentally conscious approaches.
The primary objective in exploring carbolic acid's effectiveness in developing eco-conscious pest management is to harness its proven pest control capabilities while minimizing environmental impact. This goal aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices and the reduction of harmful chemical residues in ecosystems. By revisiting this traditional compound, researchers aim to innovate new formulations and application methods that balance efficacy with ecological responsibility.
Recent technological advancements have opened new avenues for optimizing carbolic acid's use in pest control. These include the development of slow-release formulations, targeted delivery systems, and synergistic combinations with other natural compounds. Such innovations seek to enhance the compound's effectiveness while reducing the overall quantity required, thereby lessening its environmental footprint.
The renewed interest in carbolic acid also stems from the increasing resistance of pests to conventional synthetic pesticides. As a natural compound with a complex mode of action, carbolic acid presents a potential alternative that may be less prone to resistance development. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for integrated pest management strategies, which aim to reduce reliance on single-compound solutions.
Furthermore, the exploration of carbolic acid in eco-conscious pest management is part of a broader trend towards "green chemistry" in agricultural practices. This approach emphasizes the use of naturally derived compounds and processes that minimize environmental harm. By investigating carbolic acid's potential in this context, researchers hope to contribute to the development of more sustainable pest control solutions that can meet the demands of modern agriculture while preserving ecological balance.
The technical objectives of this research include optimizing carbolic acid's formulation for maximum pest control efficacy and minimal environmental persistence, developing novel application techniques that reduce off-target effects, and investigating potential synergies with other eco-friendly pest management strategies. These goals reflect the multifaceted nature of modern pest control research, which must balance effectiveness, environmental stewardship, and economic viability.
The primary objective in exploring carbolic acid's effectiveness in developing eco-conscious pest management is to harness its proven pest control capabilities while minimizing environmental impact. This goal aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices and the reduction of harmful chemical residues in ecosystems. By revisiting this traditional compound, researchers aim to innovate new formulations and application methods that balance efficacy with ecological responsibility.
Recent technological advancements have opened new avenues for optimizing carbolic acid's use in pest control. These include the development of slow-release formulations, targeted delivery systems, and synergistic combinations with other natural compounds. Such innovations seek to enhance the compound's effectiveness while reducing the overall quantity required, thereby lessening its environmental footprint.
The renewed interest in carbolic acid also stems from the increasing resistance of pests to conventional synthetic pesticides. As a natural compound with a complex mode of action, carbolic acid presents a potential alternative that may be less prone to resistance development. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for integrated pest management strategies, which aim to reduce reliance on single-compound solutions.
Furthermore, the exploration of carbolic acid in eco-conscious pest management is part of a broader trend towards "green chemistry" in agricultural practices. This approach emphasizes the use of naturally derived compounds and processes that minimize environmental harm. By investigating carbolic acid's potential in this context, researchers hope to contribute to the development of more sustainable pest control solutions that can meet the demands of modern agriculture while preserving ecological balance.
The technical objectives of this research include optimizing carbolic acid's formulation for maximum pest control efficacy and minimal environmental persistence, developing novel application techniques that reduce off-target effects, and investigating potential synergies with other eco-friendly pest management strategies. These goals reflect the multifaceted nature of modern pest control research, which must balance effectiveness, environmental stewardship, and economic viability.
Market Analysis for Eco-Friendly Pest Management Solutions
The market for eco-friendly pest management solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness and stricter regulations on chemical pesticides. The global market for biopesticides, a key segment of eco-friendly pest control, was valued at $4.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 14.7%.
Consumer demand for organic produce and sustainable agricultural practices has been a major factor in this market expansion. Retailers and food manufacturers are increasingly requiring suppliers to adopt eco-friendly pest management methods to meet consumer preferences and comply with organic certification standards. This trend is particularly strong in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where organic food sales have consistently outpaced conventional food sales growth.
The agricultural sector remains the largest end-user of eco-friendly pest management solutions, accounting for approximately 60% of the market share. However, there is growing adoption in urban and residential settings, driven by concerns over the health impacts of traditional chemical pesticides on humans and pets.
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has emerged as a potential eco-friendly alternative in pest management. Its effectiveness against a wide range of pests, coupled with its lower environmental persistence compared to many synthetic pesticides, has attracted interest from both researchers and industry players. The market for carbolic acid-based pest control products is still nascent but shows promise for rapid growth.
Regulatory support for eco-friendly pest management solutions varies globally but is generally trending towards more stringent controls on chemical pesticides and incentives for bio-based alternatives. The European Union's Farm to Fork Strategy, for instance, aims to reduce the use of chemical pesticides by 50% by 2030, creating significant opportunities for eco-friendly alternatives.
Challenges in the market include the higher cost of many eco-friendly solutions compared to conventional pesticides, variability in efficacy under different environmental conditions, and the need for farmer education on proper application techniques. However, ongoing research and development efforts are addressing these issues, with a focus on improving formulation stability, enhancing pest-specific targeting, and developing integrated pest management strategies that combine multiple eco-friendly approaches.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established agrochemical companies diversifying into eco-friendly solutions and innovative startups specializing in biopesticides and other natural pest control methods. Strategic partnerships between research institutions, technology providers, and distribution networks are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to accelerate product development and market penetration.
Consumer demand for organic produce and sustainable agricultural practices has been a major factor in this market expansion. Retailers and food manufacturers are increasingly requiring suppliers to adopt eco-friendly pest management methods to meet consumer preferences and comply with organic certification standards. This trend is particularly strong in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where organic food sales have consistently outpaced conventional food sales growth.
The agricultural sector remains the largest end-user of eco-friendly pest management solutions, accounting for approximately 60% of the market share. However, there is growing adoption in urban and residential settings, driven by concerns over the health impacts of traditional chemical pesticides on humans and pets.
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has emerged as a potential eco-friendly alternative in pest management. Its effectiveness against a wide range of pests, coupled with its lower environmental persistence compared to many synthetic pesticides, has attracted interest from both researchers and industry players. The market for carbolic acid-based pest control products is still nascent but shows promise for rapid growth.
Regulatory support for eco-friendly pest management solutions varies globally but is generally trending towards more stringent controls on chemical pesticides and incentives for bio-based alternatives. The European Union's Farm to Fork Strategy, for instance, aims to reduce the use of chemical pesticides by 50% by 2030, creating significant opportunities for eco-friendly alternatives.
Challenges in the market include the higher cost of many eco-friendly solutions compared to conventional pesticides, variability in efficacy under different environmental conditions, and the need for farmer education on proper application techniques. However, ongoing research and development efforts are addressing these issues, with a focus on improving formulation stability, enhancing pest-specific targeting, and developing integrated pest management strategies that combine multiple eco-friendly approaches.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established agrochemical companies diversifying into eco-friendly solutions and innovative startups specializing in biopesticides and other natural pest control methods. Strategic partnerships between research institutions, technology providers, and distribution networks are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to accelerate product development and market penetration.
Current State and Challenges in Carbolic Acid-Based Pest Control
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has been utilized in pest management for decades due to its potent antimicrobial and insecticidal properties. However, its current state in eco-conscious pest control presents both promising advancements and significant challenges.
The global shift towards sustainable agriculture and environmentally friendly pest management has led to increased scrutiny of traditional chemical pesticides, including carbolic acid. While it remains effective against a wide range of pests, concerns about its environmental impact and potential health risks have prompted researchers and industry professionals to reevaluate its role in modern pest control strategies.
One of the primary challenges facing carbolic acid-based pest control is its persistence in the environment. Unlike some newer, more targeted pesticides, carbolic acid can remain active in soil and water for extended periods, potentially affecting non-target organisms and disrupting ecosystems. This persistence has led to stricter regulations on its use in many countries, limiting its application in certain agricultural and urban settings.
Another significant challenge is the development of pest resistance to carbolic acid. As with many long-used pesticides, some insect populations have shown increased tolerance to phenol-based treatments over time. This resistance not only reduces the effectiveness of carbolic acid but also necessitates higher application rates, exacerbating environmental concerns.
Despite these challenges, recent research has shown promising developments in mitigating the negative impacts of carbolic acid while maintaining its pest control efficacy. Formulation improvements have led to more targeted delivery systems, reducing overall environmental exposure. Additionally, the integration of carbolic acid into comprehensive Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programs has shown potential in minimizing resistance development and environmental impact.
Nanotechnology has emerged as a potential game-changer in carbolic acid-based pest control. Nanoencapsulation techniques have demonstrated the ability to enhance the stability and controlled release of carbolic acid, potentially reducing the required dosage and environmental persistence. However, the long-term effects of nanomaterials in the environment remain a subject of ongoing research and debate.
The regulatory landscape surrounding carbolic acid usage continues to evolve, with many countries implementing stricter guidelines on its application. This regulatory pressure has spurred innovation in alternative, eco-friendly pest control methods, including biopesticides and cultural practices. However, the transition away from traditional chemical pesticides presents its own set of challenges, including efficacy, cost, and farmer adoption.
In conclusion, while carbolic acid remains an effective tool in pest management, its current state is characterized by a complex interplay of environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and technological advancements. The challenge lies in balancing its proven efficacy with the growing demand for sustainable, eco-conscious pest control solutions. Future developments in this field will likely focus on enhancing the targeted delivery of carbolic acid, minimizing environmental impact, and integrating it into holistic, sustainable pest management strategies.
The global shift towards sustainable agriculture and environmentally friendly pest management has led to increased scrutiny of traditional chemical pesticides, including carbolic acid. While it remains effective against a wide range of pests, concerns about its environmental impact and potential health risks have prompted researchers and industry professionals to reevaluate its role in modern pest control strategies.
One of the primary challenges facing carbolic acid-based pest control is its persistence in the environment. Unlike some newer, more targeted pesticides, carbolic acid can remain active in soil and water for extended periods, potentially affecting non-target organisms and disrupting ecosystems. This persistence has led to stricter regulations on its use in many countries, limiting its application in certain agricultural and urban settings.
Another significant challenge is the development of pest resistance to carbolic acid. As with many long-used pesticides, some insect populations have shown increased tolerance to phenol-based treatments over time. This resistance not only reduces the effectiveness of carbolic acid but also necessitates higher application rates, exacerbating environmental concerns.
Despite these challenges, recent research has shown promising developments in mitigating the negative impacts of carbolic acid while maintaining its pest control efficacy. Formulation improvements have led to more targeted delivery systems, reducing overall environmental exposure. Additionally, the integration of carbolic acid into comprehensive Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programs has shown potential in minimizing resistance development and environmental impact.
Nanotechnology has emerged as a potential game-changer in carbolic acid-based pest control. Nanoencapsulation techniques have demonstrated the ability to enhance the stability and controlled release of carbolic acid, potentially reducing the required dosage and environmental persistence. However, the long-term effects of nanomaterials in the environment remain a subject of ongoing research and debate.
The regulatory landscape surrounding carbolic acid usage continues to evolve, with many countries implementing stricter guidelines on its application. This regulatory pressure has spurred innovation in alternative, eco-friendly pest control methods, including biopesticides and cultural practices. However, the transition away from traditional chemical pesticides presents its own set of challenges, including efficacy, cost, and farmer adoption.
In conclusion, while carbolic acid remains an effective tool in pest management, its current state is characterized by a complex interplay of environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and technological advancements. The challenge lies in balancing its proven efficacy with the growing demand for sustainable, eco-conscious pest control solutions. Future developments in this field will likely focus on enhancing the targeted delivery of carbolic acid, minimizing environmental impact, and integrating it into holistic, sustainable pest management strategies.
Existing Carbolic Acid Formulations for Pest Control
01 Antimicrobial properties of carbolic acid
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, demonstrates strong antimicrobial effectiveness against various pathogens. It is widely used in disinfectants and antiseptics due to its ability to kill bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The compound's effectiveness in sterilization and sanitization makes it valuable in medical and industrial applications.- Antimicrobial properties of carbolic acid: Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, exhibits strong antimicrobial properties. It is effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This makes it useful in various applications such as disinfectants, antiseptics, and preservatives.
- Use in medical and dental applications: Carbolic acid's effectiveness extends to medical and dental applications. It is used in various formulations for wound care, oral hygiene products, and surgical preparations. Its ability to kill harmful microorganisms helps prevent infections and promote healing.
- Industrial and environmental applications: The effectiveness of carbolic acid is utilized in industrial and environmental applications. It is used in water treatment processes, as a component in cleaning agents, and in the production of various chemicals. Its strong disinfectant properties make it valuable for maintaining hygiene in industrial settings.
- Formulation and delivery methods: Various formulation and delivery methods have been developed to enhance the effectiveness of carbolic acid. These include encapsulation techniques, controlled release systems, and combination with other active ingredients. Such methods aim to improve the stability, efficacy, and safety of carbolic acid-based products.
- Safety considerations and alternatives: While carbolic acid is effective, its use comes with safety considerations due to its corrosive nature and potential toxicity. Research has focused on developing safer alternatives or modified versions that maintain effectiveness while reducing risks. This includes exploring natural compounds with similar properties and creating synergistic blends.
02 Carbolic acid in medical treatments
Carbolic acid has been utilized in various medical treatments due to its effectiveness. It has applications in wound care, dental procedures, and as a topical anesthetic. The compound's ability to reduce pain and prevent infection has made it a valuable component in certain medical formulations and procedures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Industrial applications of carbolic acid
The effectiveness of carbolic acid extends to various industrial applications. It is used in the production of plastics, resins, and other synthetic materials. Its properties make it useful in water treatment, as a precursor in chemical synthesis, and in the manufacturing of dyes and pharmaceuticals.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact and safety considerations
While carbolic acid is effective in many applications, its use requires careful consideration of environmental impact and safety. Proper handling, storage, and disposal methods are essential due to its corrosive and toxic nature. Research focuses on developing safer alternatives or improved formulations to mitigate potential risks associated with carbolic acid use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovations in carbolic acid formulations
Ongoing research aims to enhance the effectiveness of carbolic acid through innovative formulations. This includes developing controlled-release mechanisms, combining it with other active ingredients for synergistic effects, and creating novel delivery systems. These advancements seek to improve the compound's efficacy while potentially reducing its concentration and associated risks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Eco-Conscious Pest Management Industry
The competitive landscape for carbolic acid's effectiveness in developing eco-conscious pest management is evolving rapidly. The industry is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by rising demand for sustainable agricultural practices. The global market for eco-friendly pest management solutions is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Bayer AG, BASF SE, and Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. leading research efforts. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to develop innovative, environmentally-friendly formulations. However, the technology is not yet fully mature, with ongoing challenges in balancing efficacy and environmental impact. Smaller players like Globachem NV and Shandong Weifang Rainbow Chemical Co., Ltd. are also contributing to technological advancements, intensifying competition in this niche market.
Bayer AG
Technical Solution: Bayer AG has pioneered a carbolic acid-based pest management system that focuses on sustainability and eco-friendliness. Their approach involves the development of microencapsulated carbolic acid derivatives that provide controlled release of the active ingredients[2]. This technology allows for lower application rates while maintaining pest control efficacy. Bayer has also incorporated plant-based adjuvants to enhance the performance of their carbolic acid formulations, reducing the overall chemical load in the environment[4]. Additionally, they have developed a comprehensive integrated pest management (IPM) program that combines their eco-conscious carbolic acid products with biological control agents and cultural practices[6].
Strengths: Reduced chemical usage, enhanced efficacy through controlled release, and comprehensive IPM approach. Weaknesses: Potential for higher initial costs and the need for farmer education on new application methods.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Chemical has developed an eco-friendly pest management solution utilizing carbolic acid derivatives. Their approach focuses on the synthesis of bio-based phenolic compounds derived from renewable resources, reducing reliance on petrochemical-based ingredients[1]. The company has also implemented a green chemistry process for manufacturing these compounds, significantly reducing waste and energy consumption[3]. Sumitomo's formulation includes synergistic plant extracts that enhance the efficacy of carbolic acid derivatives while minimizing environmental impact[5]. They have also developed a novel delivery system that improves the targeted application of the pest control agents, reducing off-target effects on beneficial insects[7].
Strengths: Use of renewable resources, reduced environmental footprint in production, and enhanced targeting of pest species. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in pest spectrum coverage and higher production costs.
Innovations in Carbolic Acid-Based Pest Management
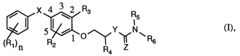
Carbamic acid amide derivatives and their use as pesticides
PatentInactiveEP0584046A1
Innovation
- Compounds of a specific formula, which can form acid addition salts and agrochemically advantageous salts, are developed to provide effective pest control by targeting insects and Acarina, with specific structural features such as halogen, alkyl, alkoxy, and cyano groups on a phenyl ring, and varying substituents for enhanced biological activity.
Active ingredient combinations having insecticidal and acaricidal properties
PatentInactiveEP2410847A1
Innovation
- Combining specific known compounds with organophosphates or carbamates to create synergistic active substance combinations that enhance insecticidal and acaricidal efficacy, reducing dosage requirements and expanding pest control spectrum while improving plant compatibility and safety.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Carbolic Acid Use
The environmental impact assessment of carbolic acid use in pest management is a critical aspect of developing eco-conscious solutions. Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has been utilized in various industrial and agricultural applications, including pest control. However, its potential environmental consequences require thorough evaluation.
Carbolic acid can persist in soil and water, potentially affecting ecosystems and non-target organisms. When released into the environment, it may contaminate groundwater and surface water, posing risks to aquatic life. Studies have shown that carbolic acid can be toxic to fish, invertebrates, and microorganisms at certain concentrations, disrupting the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
In soil, carbolic acid can impact microbial communities, potentially altering nutrient cycling and soil fertility. This may have cascading effects on plant growth and overall ecosystem health. Additionally, the compound can be absorbed by plants, raising concerns about its potential accumulation in the food chain.
Atmospheric release of carbolic acid through volatilization or improper handling can contribute to air pollution. While its atmospheric half-life is relatively short, it may still contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and other air quality issues in localized areas.
The biodegradation of carbolic acid in the environment is an important consideration. Under aerobic conditions, it can be broken down by certain microorganisms, but the rate of degradation varies depending on environmental factors such as temperature, pH, and microbial populations. In anaerobic environments, the degradation process is typically slower, potentially leading to longer-term environmental persistence.
Assessing the environmental impact of carbolic acid use also involves considering its potential for bioaccumulation in organisms. While carbolic acid does not typically bioaccumulate to a significant degree in most species, some studies have shown limited bioaccumulation in certain aquatic organisms, warranting further investigation.
The use of carbolic acid in pest management may also have indirect environmental impacts. For instance, its application could affect beneficial insects and pollinators, potentially disrupting ecosystem services and agricultural productivity. Furthermore, the development of pest resistance to carbolic acid-based treatments could lead to increased application rates or the use of alternative, potentially more harmful pesticides.
To mitigate these environmental risks, it is essential to develop and implement best practices for the use of carbolic acid in pest management. This includes proper application techniques, appropriate dosing, and the use of protective measures to minimize environmental exposure. Additionally, exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly pest control methods should be a priority in developing truly eco-conscious pest management strategies.
Carbolic acid can persist in soil and water, potentially affecting ecosystems and non-target organisms. When released into the environment, it may contaminate groundwater and surface water, posing risks to aquatic life. Studies have shown that carbolic acid can be toxic to fish, invertebrates, and microorganisms at certain concentrations, disrupting the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
In soil, carbolic acid can impact microbial communities, potentially altering nutrient cycling and soil fertility. This may have cascading effects on plant growth and overall ecosystem health. Additionally, the compound can be absorbed by plants, raising concerns about its potential accumulation in the food chain.
Atmospheric release of carbolic acid through volatilization or improper handling can contribute to air pollution. While its atmospheric half-life is relatively short, it may still contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and other air quality issues in localized areas.
The biodegradation of carbolic acid in the environment is an important consideration. Under aerobic conditions, it can be broken down by certain microorganisms, but the rate of degradation varies depending on environmental factors such as temperature, pH, and microbial populations. In anaerobic environments, the degradation process is typically slower, potentially leading to longer-term environmental persistence.
Assessing the environmental impact of carbolic acid use also involves considering its potential for bioaccumulation in organisms. While carbolic acid does not typically bioaccumulate to a significant degree in most species, some studies have shown limited bioaccumulation in certain aquatic organisms, warranting further investigation.
The use of carbolic acid in pest management may also have indirect environmental impacts. For instance, its application could affect beneficial insects and pollinators, potentially disrupting ecosystem services and agricultural productivity. Furthermore, the development of pest resistance to carbolic acid-based treatments could lead to increased application rates or the use of alternative, potentially more harmful pesticides.
To mitigate these environmental risks, it is essential to develop and implement best practices for the use of carbolic acid in pest management. This includes proper application techniques, appropriate dosing, and the use of protective measures to minimize environmental exposure. Additionally, exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly pest control methods should be a priority in developing truly eco-conscious pest management strategies.
Regulatory Framework for Biopesticides and Natural Compounds
The regulatory framework for biopesticides and natural compounds plays a crucial role in the development and implementation of eco-conscious pest management strategies, particularly concerning the use of carbolic acid. This framework encompasses a complex set of guidelines, standards, and procedures established by various governmental and international bodies to ensure the safe and effective use of these substances.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory authority for biopesticides and natural compounds. The EPA's Biopesticides and Pollution Prevention Division (BPPD) oversees the registration and regulation of these products under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This act requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their products are safe for human health and the environment before they can be marketed.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory system for biopesticides through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). The EU's regulatory framework is based on the principle of precaution, requiring extensive safety and efficacy data before approval. This approach has led to stricter regulations compared to some other regions, potentially impacting the adoption of certain biopesticides.
In the context of carbolic acid's use in pest management, regulatory bodies typically classify it as a synthetic organic compound rather than a biopesticide. However, its potential integration into eco-conscious pest management strategies necessitates consideration within the broader regulatory landscape of both synthetic and natural pest control agents.
Regulatory requirements for carbolic acid and similar compounds often include extensive toxicological studies, environmental impact assessments, and efficacy trials. These requirements aim to ensure that the use of such substances does not pose unacceptable risks to human health, non-target organisms, or the environment. Additionally, regulations may stipulate specific application methods, dosage limits, and safety precautions to minimize potential adverse effects.
The global nature of pest management challenges has led to efforts to harmonize regulatory approaches across different countries and regions. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has been instrumental in developing guidelines for the registration of biopesticides and promoting regulatory cooperation among member countries. These efforts aim to streamline the approval process for new products while maintaining high safety standards.
As the field of eco-conscious pest management evolves, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate innovative approaches and technologies. This includes the development of specific guidelines for novel biopesticides, natural compounds, and integrated pest management strategies that may incorporate substances like carbolic acid. The ongoing challenge for regulators is to balance the need for rigorous safety assessments with the imperative to facilitate the adoption of more sustainable pest control methods.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory authority for biopesticides and natural compounds. The EPA's Biopesticides and Pollution Prevention Division (BPPD) oversees the registration and regulation of these products under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This act requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their products are safe for human health and the environment before they can be marketed.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory system for biopesticides through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). The EU's regulatory framework is based on the principle of precaution, requiring extensive safety and efficacy data before approval. This approach has led to stricter regulations compared to some other regions, potentially impacting the adoption of certain biopesticides.
In the context of carbolic acid's use in pest management, regulatory bodies typically classify it as a synthetic organic compound rather than a biopesticide. However, its potential integration into eco-conscious pest management strategies necessitates consideration within the broader regulatory landscape of both synthetic and natural pest control agents.
Regulatory requirements for carbolic acid and similar compounds often include extensive toxicological studies, environmental impact assessments, and efficacy trials. These requirements aim to ensure that the use of such substances does not pose unacceptable risks to human health, non-target organisms, or the environment. Additionally, regulations may stipulate specific application methods, dosage limits, and safety precautions to minimize potential adverse effects.
The global nature of pest management challenges has led to efforts to harmonize regulatory approaches across different countries and regions. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has been instrumental in developing guidelines for the registration of biopesticides and promoting regulatory cooperation among member countries. These efforts aim to streamline the approval process for new products while maintaining high safety standards.
As the field of eco-conscious pest management evolves, regulatory frameworks are adapting to accommodate innovative approaches and technologies. This includes the development of specific guidelines for novel biopesticides, natural compounds, and integrated pest management strategies that may incorporate substances like carbolic acid. The ongoing challenge for regulators is to balance the need for rigorous safety assessments with the imperative to facilitate the adoption of more sustainable pest control methods.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!