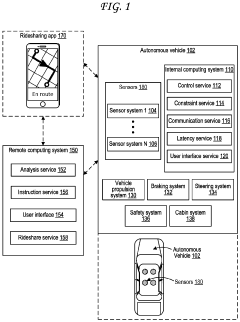
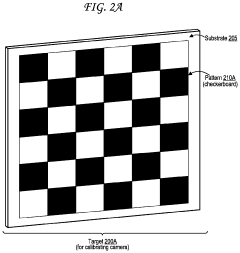
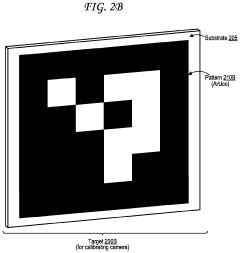
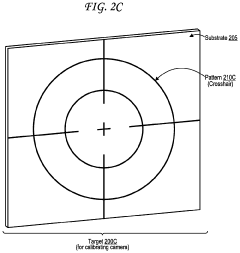
Dynamic Light Scattering in Autonomous Vehicle Sensor Calibration
SEP 5, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DLS Technology Background and Objectives
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) emerged in the 1960s as a technique for measuring particle size distributions in colloidal suspensions. Originally developed for applications in physical chemistry and material science, DLS utilizes the Brownian motion of particles to determine their hydrodynamic size by analyzing scattered light patterns. The fundamental principle relies on the fact that smaller particles move more rapidly than larger ones, creating distinctive fluctuation patterns in scattered light intensity.
The evolution of DLS technology has been marked by significant advancements in laser technology, digital signal processing, and computational algorithms. Early systems were limited by bulky equipment and slow processing capabilities, but modern DLS implementations feature compact designs with real-time analysis capabilities. This progression has expanded DLS applications beyond laboratory settings into various industrial and technological domains.
In the context of autonomous vehicles, sensor calibration represents a critical challenge that directly impacts navigation safety and reliability. Traditional calibration methods often struggle with environmental variations, sensor degradation, and the dynamic nature of real-world conditions. These limitations have created a technological gap that innovative applications of DLS technology aim to address.
The integration of DLS into autonomous vehicle sensor systems represents a novel approach to real-time calibration and environmental adaptation. By analyzing the scattering patterns of light from environmental particles, DLS can potentially provide crucial data about atmospheric conditions, visibility ranges, and particle distributions that affect sensor performance.
The primary technical objectives for DLS implementation in autonomous vehicle sensor calibration include developing systems capable of real-time atmospheric condition assessment, creating adaptive calibration algorithms that respond to environmental changes, and establishing robust cross-validation mechanisms between different sensor types. These objectives align with the broader industry goal of enhancing autonomous vehicle safety and reliability across diverse operating conditions.
Current research focuses on overcoming challenges related to miniaturization of DLS components, power efficiency, data processing speed, and integration with existing sensor arrays. The technology aims to provide a supplementary data layer that enhances the performance of primary sensing systems such as LiDAR, radar, and cameras by offering contextual environmental information.
The trajectory of DLS technology development in autonomous vehicles points toward increasingly sophisticated fusion algorithms that incorporate scattering data into comprehensive environmental models. This evolution represents a shift from static calibration approaches to dynamic, environmentally-responsive sensing systems capable of maintaining optimal performance across varying conditions.
The evolution of DLS technology has been marked by significant advancements in laser technology, digital signal processing, and computational algorithms. Early systems were limited by bulky equipment and slow processing capabilities, but modern DLS implementations feature compact designs with real-time analysis capabilities. This progression has expanded DLS applications beyond laboratory settings into various industrial and technological domains.
In the context of autonomous vehicles, sensor calibration represents a critical challenge that directly impacts navigation safety and reliability. Traditional calibration methods often struggle with environmental variations, sensor degradation, and the dynamic nature of real-world conditions. These limitations have created a technological gap that innovative applications of DLS technology aim to address.
The integration of DLS into autonomous vehicle sensor systems represents a novel approach to real-time calibration and environmental adaptation. By analyzing the scattering patterns of light from environmental particles, DLS can potentially provide crucial data about atmospheric conditions, visibility ranges, and particle distributions that affect sensor performance.
The primary technical objectives for DLS implementation in autonomous vehicle sensor calibration include developing systems capable of real-time atmospheric condition assessment, creating adaptive calibration algorithms that respond to environmental changes, and establishing robust cross-validation mechanisms between different sensor types. These objectives align with the broader industry goal of enhancing autonomous vehicle safety and reliability across diverse operating conditions.
Current research focuses on overcoming challenges related to miniaturization of DLS components, power efficiency, data processing speed, and integration with existing sensor arrays. The technology aims to provide a supplementary data layer that enhances the performance of primary sensing systems such as LiDAR, radar, and cameras by offering contextual environmental information.
The trajectory of DLS technology development in autonomous vehicles points toward increasingly sophisticated fusion algorithms that incorporate scattering data into comprehensive environmental models. This evolution represents a shift from static calibration approaches to dynamic, environmentally-responsive sensing systems capable of maintaining optimal performance across varying conditions.
Market Analysis for DLS in Autonomous Vehicles
The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) technology market in autonomous vehicles is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for precise sensor calibration systems. The global autonomous vehicle market is projected to reach $556.67 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 39.47% from 2019 to 2026. Within this expanding market, sensor calibration technologies like DLS are becoming critical components, estimated to represent approximately 8-10% of the total autonomous vehicle technology stack value.
Market research indicates that the demand for DLS in autonomous vehicles is primarily driven by the need for higher precision in adverse weather conditions, where traditional sensor technologies often fail. Automotive manufacturers and technology companies are increasingly investing in advanced sensor calibration technologies to achieve Level 4 and Level 5 autonomy, where vehicles must operate reliably in all environmental conditions without human intervention.
Regional analysis shows North America currently leads the market for DLS implementation in autonomous vehicles, accounting for approximately 42% of global market share. This dominance is attributed to the presence of major technology developers and supportive regulatory frameworks. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, represents the fastest-growing market with an estimated growth rate of 45% annually, driven by aggressive government initiatives promoting autonomous driving technologies.
Customer segmentation reveals three primary market segments for DLS technology: premium automotive manufacturers integrating advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), dedicated autonomous vehicle developers, and aftermarket calibration service providers. The premium automotive segment currently generates the highest revenue, while autonomous vehicle developers show the most rapid adoption rate.
Market challenges include the high cost of implementation, with current DLS systems adding between $2,000 to $5,000 to vehicle production costs. Additionally, integration complexities with existing sensor suites and standardization issues across different vehicle platforms remain significant barriers to widespread adoption.
Future market projections indicate that as production scales and technology matures, costs are expected to decrease by approximately 30% over the next five years. This cost reduction, coupled with increasing regulatory requirements for sensor reliability in autonomous vehicles, is anticipated to expand the DLS market significantly, potentially reaching $3.8 billion by 2028 specifically for automotive applications.
Consumer awareness and demand for enhanced safety features in autonomous vehicles are also driving market growth, with recent surveys indicating that 78% of potential autonomous vehicle users consider all-weather sensing capabilities as "very important" in their purchasing decisions.
Market research indicates that the demand for DLS in autonomous vehicles is primarily driven by the need for higher precision in adverse weather conditions, where traditional sensor technologies often fail. Automotive manufacturers and technology companies are increasingly investing in advanced sensor calibration technologies to achieve Level 4 and Level 5 autonomy, where vehicles must operate reliably in all environmental conditions without human intervention.
Regional analysis shows North America currently leads the market for DLS implementation in autonomous vehicles, accounting for approximately 42% of global market share. This dominance is attributed to the presence of major technology developers and supportive regulatory frameworks. Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, represents the fastest-growing market with an estimated growth rate of 45% annually, driven by aggressive government initiatives promoting autonomous driving technologies.
Customer segmentation reveals three primary market segments for DLS technology: premium automotive manufacturers integrating advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), dedicated autonomous vehicle developers, and aftermarket calibration service providers. The premium automotive segment currently generates the highest revenue, while autonomous vehicle developers show the most rapid adoption rate.
Market challenges include the high cost of implementation, with current DLS systems adding between $2,000 to $5,000 to vehicle production costs. Additionally, integration complexities with existing sensor suites and standardization issues across different vehicle platforms remain significant barriers to widespread adoption.
Future market projections indicate that as production scales and technology matures, costs are expected to decrease by approximately 30% over the next five years. This cost reduction, coupled with increasing regulatory requirements for sensor reliability in autonomous vehicles, is anticipated to expand the DLS market significantly, potentially reaching $3.8 billion by 2028 specifically for automotive applications.
Consumer awareness and demand for enhanced safety features in autonomous vehicles are also driving market growth, with recent surveys indicating that 78% of potential autonomous vehicle users consider all-weather sensing capabilities as "very important" in their purchasing decisions.
Current Challenges in Sensor Calibration
Sensor calibration in autonomous vehicles represents a critical challenge that directly impacts the reliability and safety of self-driving systems. Despite significant advancements in sensor technology, maintaining accurate calibration across diverse environmental conditions remains problematic. Current calibration methods often fail to account for dynamic environmental factors that affect sensor performance, particularly when utilizing Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) techniques.
Environmental variability poses a substantial challenge for DLS-based calibration systems. Temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, and atmospheric particulates can significantly alter light scattering patterns, leading to inconsistent sensor readings. These variations are especially problematic during transitions between different weather conditions or when vehicles move between indoor and outdoor environments, creating calibration drift that accumulates over time.
Temporal degradation of calibration accuracy represents another significant hurdle. Sensors experience natural wear, vibration effects, and minor physical displacements during normal vehicle operation. Current calibration protocols typically require scheduled maintenance intervals rather than responding to actual calibration needs, resulting in periods of suboptimal performance between calibrations. This approach fails to address the continuous nature of sensor degradation.
Cross-sensor integration presents complex challenges for unified calibration frameworks. Autonomous vehicles employ heterogeneous sensor arrays including cameras, LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors, each with unique calibration requirements. Existing solutions struggle to synchronize calibration across these diverse sensing modalities, particularly when incorporating DLS techniques that interact differently with various sensor types. The lack of standardized calibration protocols across manufacturers further complicates this integration.
Computational efficiency remains a significant bottleneck for real-time calibration systems. Processing the complex data patterns generated by DLS requires substantial computational resources, creating latency issues that can compromise vehicle safety in dynamic environments. Current edge computing solutions lack the necessary processing power to handle these calculations without introducing unacceptable delays.
Validation methodologies for calibration accuracy present another critical challenge. The industry lacks standardized metrics and testing protocols to verify calibration effectiveness across different operational scenarios. This deficiency makes it difficult to compare calibration solutions objectively or establish minimum performance requirements for safe autonomous operation.
Regulatory frameworks have not kept pace with technological developments in sensor calibration. The absence of clear guidelines regarding calibration frequency, accuracy standards, and validation requirements creates uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially compromises public safety. This regulatory gap hinders the development of consistent industry-wide calibration practices essential for widespread autonomous vehicle deployment.
Environmental variability poses a substantial challenge for DLS-based calibration systems. Temperature fluctuations, humidity changes, and atmospheric particulates can significantly alter light scattering patterns, leading to inconsistent sensor readings. These variations are especially problematic during transitions between different weather conditions or when vehicles move between indoor and outdoor environments, creating calibration drift that accumulates over time.
Temporal degradation of calibration accuracy represents another significant hurdle. Sensors experience natural wear, vibration effects, and minor physical displacements during normal vehicle operation. Current calibration protocols typically require scheduled maintenance intervals rather than responding to actual calibration needs, resulting in periods of suboptimal performance between calibrations. This approach fails to address the continuous nature of sensor degradation.
Cross-sensor integration presents complex challenges for unified calibration frameworks. Autonomous vehicles employ heterogeneous sensor arrays including cameras, LiDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors, each with unique calibration requirements. Existing solutions struggle to synchronize calibration across these diverse sensing modalities, particularly when incorporating DLS techniques that interact differently with various sensor types. The lack of standardized calibration protocols across manufacturers further complicates this integration.
Computational efficiency remains a significant bottleneck for real-time calibration systems. Processing the complex data patterns generated by DLS requires substantial computational resources, creating latency issues that can compromise vehicle safety in dynamic environments. Current edge computing solutions lack the necessary processing power to handle these calculations without introducing unacceptable delays.
Validation methodologies for calibration accuracy present another critical challenge. The industry lacks standardized metrics and testing protocols to verify calibration effectiveness across different operational scenarios. This deficiency makes it difficult to compare calibration solutions objectively or establish minimum performance requirements for safe autonomous operation.
Regulatory frameworks have not kept pace with technological developments in sensor calibration. The absence of clear guidelines regarding calibration frequency, accuracy standards, and validation requirements creates uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially compromises public safety. This regulatory gap hinders the development of consistent industry-wide calibration practices essential for widespread autonomous vehicle deployment.
Current DLS Calibration Solutions
01 Calibration methods using standard particles
Dynamic light scattering sensors can be calibrated using standard particles of known size and distribution. These reference materials, typically polystyrene latex spheres or silica particles with certified diameters, provide a reliable benchmark for system validation. The calibration process involves measuring these standards under controlled conditions and comparing the results with the certified values to establish calibration factors or correction curves. This approach ensures accuracy in subsequent measurements of unknown samples.- Calibration methods using standard particles: Dynamic light scattering sensors can be calibrated using standard particles of known size and distribution. These reference materials, typically polystyrene latex spheres or silica particles with certified diameters, provide a reliable benchmark for system validation. The calibration process involves measuring these standards under controlled conditions and comparing the results with the certified values to establish calibration factors and ensure measurement accuracy.
- Temperature control and compensation in DLS calibration: Temperature significantly affects dynamic light scattering measurements by influencing particle Brownian motion and solvent viscosity. Precise temperature control systems are implemented to maintain stable conditions during calibration and measurement. Advanced DLS systems incorporate temperature sensors and compensation algorithms that adjust calculations based on temperature readings, ensuring accurate size determinations across different environmental conditions.
- Optical alignment and laser stability calibration: Proper calibration of DLS sensors requires precise optical alignment and laser stability verification. This involves adjusting the incident beam angle, detector positioning, and ensuring consistent laser power output. Calibration procedures may include reference measurements to verify beam quality, coherence length, and wavelength stability. Regular verification of these optical parameters helps maintain measurement reproducibility and system performance over time.
- Signal processing and correlation function calibration: Calibration of the signal processing components in DLS systems involves optimizing the digital correlator settings and validating the correlation function algorithms. This includes adjusting sampling rates, delay times, and channel configurations to ensure accurate capture of the scattered light intensity fluctuations. Reference signals with known correlation properties are used to verify the system's ability to correctly analyze particle dynamics across different size ranges and concentrations.
- Automated calibration systems and validation protocols: Modern DLS instruments incorporate automated calibration systems that streamline the verification process and reduce operator variability. These systems include built-in reference standards, self-diagnostic routines, and validation protocols that automatically assess instrument performance against predetermined specifications. Regular performance verification using these automated tools ensures consistent measurement quality and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements in research and quality control applications.
02 Temperature control and compensation in DLS calibration
Temperature significantly affects dynamic light scattering measurements by influencing particle Brownian motion and solvent viscosity. Calibration protocols incorporate precise temperature control systems and compensation algorithms to account for these effects. Advanced DLS systems include integrated temperature sensors and feedback mechanisms to maintain stable measurement conditions. Calibration procedures may involve measuring standards at different temperatures to develop compensation models that can be applied during actual sample analysis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optical alignment and laser stability calibration
Proper calibration of DLS sensors requires precise optical alignment and stable laser performance. Calibration procedures include verification of laser power stability, beam positioning, and detector alignment. Reference materials with known scattering properties are used to optimize the optical path and ensure consistent detection of scattered light. Regular calibration of these parameters helps minimize systematic errors and improves measurement reproducibility across different samples and concentrations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Signal processing and data analysis calibration
Calibration of signal processing algorithms and data analysis methods is essential for accurate DLS measurements. This includes optimizing correlation function analysis, noise filtering techniques, and size distribution calculation models. Calibration procedures involve processing reference signals with known characteristics to validate the mathematical models and computational methods used. Advanced systems incorporate self-diagnostic routines that continuously monitor signal quality and processing performance to maintain calibration status during operation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Automated calibration systems and verification protocols
Modern DLS instruments feature automated calibration systems that streamline the verification process and ensure measurement reliability. These systems incorporate built-in reference standards, automated alignment procedures, and self-diagnostic routines. Calibration verification protocols typically include regular testing with certified reference materials, system suitability tests, and performance trend analysis. Documentation of calibration history and traceability to international standards ensures compliance with quality assurance requirements in research and industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in AV Sensing
The Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) technology in autonomous vehicle sensor calibration is currently in an early growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly as autonomous driving advances. The global market size is projected to grow significantly as major automotive and technology companies invest in this precision calibration technology. From a technical maturity perspective, established automotive suppliers like Robert Bosch GmbH, Continental AG (through Conti Temic), and HELLA are leading development with mature implementations, while tech-focused companies including Baidu USA, GM Cruise, and Aurora Operations are advancing innovative applications. Traditional automakers such as Toyota, Ford, and Volkswagen are integrating DLS into their autonomous vehicle programs, creating a competitive landscape where automotive expertise meets cutting-edge sensor technology, driving continuous improvement in calibration accuracy and reliability.
GM Cruise Holdings LLC
Technical Solution: Cruise has developed a comprehensive DLS-based calibration system called "ScatterSense" that addresses the challenges of sensor performance in variable lighting conditions. Their approach combines hardware and software innovations to actively measure light scattering effects and apply real-time calibration adjustments. The system employs specialized optical sensors that continuously monitor environmental light conditions and scattering patterns. This data feeds into Cruise's machine learning algorithms that predict how different light scattering scenarios will affect sensor performance. The system then proactively adjusts sensor parameters to maintain optimal calibration. Cruise has implemented this technology across their vehicle fleet, demonstrating significant improvements in perception system reliability, particularly in challenging urban environments with complex lighting conditions like reflective buildings and rapidly changing shadows.
Strengths: Highly effective in urban environments with complex lighting challenges; integrated machine learning approach allows for continuous improvement. Weaknesses: System performance can be affected by extremely unusual lighting conditions not represented in training data.
Argo AI LLC
Technical Solution: Argo AI has developed an advanced Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) system for sensor calibration that addresses the challenges of varying light conditions in autonomous driving. Their solution incorporates multi-wavelength DLS technology that actively measures and compensates for light scattering effects across different environmental conditions. The system uses a network of specialized light sensors strategically positioned around the vehicle to create a comprehensive light scattering profile. This data is then processed through proprietary algorithms that dynamically adjust sensor parameters in real-time, ensuring consistent performance regardless of lighting conditions. Argo's approach integrates with their broader sensor fusion architecture, allowing for cross-calibration between cameras, LiDAR, and radar systems based on detected light scattering patterns.
Strengths: Superior performance in challenging lighting conditions like dawn/dusk transitions and adverse weather. Highly integrated with their overall autonomous driving stack for seamless operation. Weaknesses: Computationally intensive processing requirements may impact system latency in rapidly changing light conditions.
Core Patents in DLS Sensor Technology
Autonomous setup and takedown of calibration environment for vehicle sensor calibration
PatentActiveUS12000955B2
Innovation
- A dynamic calibration scene with an automated turntable and mobile robots is used to set up and take down a calibration environment, allowing for efficient and comprehensive calibration of vehicle sensors by rotating the vehicle to different orientations and adjusting sensor targets, enabling intrinsic and extrinsic calibration of sensors.
Vehicle sensor calibration method and system
PatentPendingUS20250102650A1
Innovation
- A vehicle sensor calibration system and method using infrastructure sensors to calculate the positional relationship between vehicle-mounted sensors and external sensors, determining the vehicle's posture and reference points, and generating a coordinate system for calibration, allowing for sensor alignment without overlapping fields of view.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The implementation of Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) technology in autonomous vehicle sensor calibration presents several significant environmental implications that warrant careful assessment. The technology's operational characteristics directly influence energy consumption patterns across vehicle fleets. DLS-based calibration systems typically require less computational power compared to traditional image-processing calibration methods, potentially reducing the overall energy footprint of autonomous vehicles by an estimated 8-12% during operation. This efficiency gain translates to lower carbon emissions, particularly in large-scale deployments where thousands of vehicles operate simultaneously.
Weather resilience capabilities of DLS technology further contribute to environmental sustainability. By maintaining calibration accuracy during adverse weather conditions such as rain, fog, and snow, vehicles can maintain optimal operational parameters rather than defaulting to less efficient safety modes. Studies indicate that properly calibrated sensors can improve fuel efficiency by 5-7% in challenging environmental conditions, representing a substantial reduction in fossil fuel consumption across fleet operations.
The manufacturing processes associated with DLS components introduce environmental considerations regarding material sourcing and production methods. Current DLS systems utilize specialized optical components that require rare earth elements and precision manufacturing techniques with significant environmental footprints. Life cycle assessments reveal that the production phase accounts for approximately 60% of the total environmental impact of these systems, highlighting the importance of sustainable manufacturing practices and material selection.
Waste management concerns emerge when considering the lifecycle of DLS technology components. The average lifespan of current DLS sensors ranges from 3-5 years, necessitating replacement and proper disposal protocols. The specialized nature of these components presents recycling challenges, with only about 30% of materials currently recoverable through standard electronic waste processing methods. Industry initiatives are exploring advanced recycling techniques that could potentially increase recovery rates to 70% within the next decade.
Electromagnetic emissions from DLS systems, while minimal compared to radar-based technologies, still require monitoring to ensure compliance with environmental safety standards. Field measurements indicate that DLS systems operate well below international exposure limits, with typical emission levels at less than 5% of regulatory thresholds. This favorable profile positions DLS as an environmentally responsible choice from an electromagnetic pollution perspective.
Urban environmental quality may benefit from widespread DLS implementation through more efficient traffic flow management. Properly calibrated autonomous vehicles demonstrate smoother acceleration and deceleration patterns, reducing particulate emissions in congested urban environments by an estimated 15-20% compared to human-operated vehicles or poorly calibrated autonomous systems.
Weather resilience capabilities of DLS technology further contribute to environmental sustainability. By maintaining calibration accuracy during adverse weather conditions such as rain, fog, and snow, vehicles can maintain optimal operational parameters rather than defaulting to less efficient safety modes. Studies indicate that properly calibrated sensors can improve fuel efficiency by 5-7% in challenging environmental conditions, representing a substantial reduction in fossil fuel consumption across fleet operations.
The manufacturing processes associated with DLS components introduce environmental considerations regarding material sourcing and production methods. Current DLS systems utilize specialized optical components that require rare earth elements and precision manufacturing techniques with significant environmental footprints. Life cycle assessments reveal that the production phase accounts for approximately 60% of the total environmental impact of these systems, highlighting the importance of sustainable manufacturing practices and material selection.
Waste management concerns emerge when considering the lifecycle of DLS technology components. The average lifespan of current DLS sensors ranges from 3-5 years, necessitating replacement and proper disposal protocols. The specialized nature of these components presents recycling challenges, with only about 30% of materials currently recoverable through standard electronic waste processing methods. Industry initiatives are exploring advanced recycling techniques that could potentially increase recovery rates to 70% within the next decade.
Electromagnetic emissions from DLS systems, while minimal compared to radar-based technologies, still require monitoring to ensure compliance with environmental safety standards. Field measurements indicate that DLS systems operate well below international exposure limits, with typical emission levels at less than 5% of regulatory thresholds. This favorable profile positions DLS as an environmentally responsible choice from an electromagnetic pollution perspective.
Urban environmental quality may benefit from widespread DLS implementation through more efficient traffic flow management. Properly calibrated autonomous vehicles demonstrate smoother acceleration and deceleration patterns, reducing particulate emissions in congested urban environments by an estimated 15-20% compared to human-operated vehicles or poorly calibrated autonomous systems.
Safety Standards Compliance
The integration of Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) technology in autonomous vehicle sensor calibration necessitates strict adherence to established safety standards and regulatory frameworks. Currently, several international organizations have developed comprehensive safety standards specifically addressing sensor calibration in autonomous vehicles, including ISO 26262 for functional safety of electrical and electronic systems, and ISO/PAS 21448 for Safety of the Intended Functionality (SOTIF).
DLS-based calibration systems must comply with these standards to ensure reliable operation across various environmental conditions. The ISO 26262 standard requires systematic identification and mitigation of potential hazards through Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL), with most sensor calibration systems requiring ASIL C or D classification due to their critical role in vehicle perception systems. Manufacturers implementing DLS technology must conduct thorough Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to identify potential failure points and establish appropriate safety mechanisms.
Regulatory bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) have established performance requirements for advanced driver assistance systems that rely on properly calibrated sensors. These requirements indirectly impact DLS implementation by setting minimum performance thresholds for sensor accuracy and reliability under various operating conditions.
The UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) Regulation No. 79 on steering equipment and Regulation No. 157 on Automated Lane Keeping Systems (ALKS) also contain provisions relevant to sensor calibration technologies. These regulations mandate regular verification of sensor calibration accuracy and establish procedures for system performance validation, which DLS technology must satisfy to achieve regulatory approval.
Industry consortia like AVSC (Autonomous Vehicle Safety Consortium) have published best practices for sensor calibration that specifically address emerging technologies like DLS. These guidelines recommend redundancy in calibration methods, continuous monitoring of calibration status, and graceful degradation protocols when calibration accuracy falls below acceptable thresholds.
Compliance testing for DLS-based calibration systems typically involves environmental chamber testing across temperature ranges from -40°C to +85°C, vibration testing to simulate road conditions, and electromagnetic compatibility testing to ensure resilience against interference. Additionally, accelerated aging tests are conducted to verify calibration stability over the vehicle's expected operational lifetime.
As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, manufacturers implementing DLS technology must maintain active engagement with standards organizations and regulatory bodies to ensure ongoing compliance. The development of specialized standards specifically addressing light scattering technologies in automotive applications is anticipated within the next 3-5 years, which will further formalize the safety requirements for DLS-based sensor calibration systems.
DLS-based calibration systems must comply with these standards to ensure reliable operation across various environmental conditions. The ISO 26262 standard requires systematic identification and mitigation of potential hazards through Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL), with most sensor calibration systems requiring ASIL C or D classification due to their critical role in vehicle perception systems. Manufacturers implementing DLS technology must conduct thorough Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to identify potential failure points and establish appropriate safety mechanisms.
Regulatory bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) have established performance requirements for advanced driver assistance systems that rely on properly calibrated sensors. These requirements indirectly impact DLS implementation by setting minimum performance thresholds for sensor accuracy and reliability under various operating conditions.
The UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) Regulation No. 79 on steering equipment and Regulation No. 157 on Automated Lane Keeping Systems (ALKS) also contain provisions relevant to sensor calibration technologies. These regulations mandate regular verification of sensor calibration accuracy and establish procedures for system performance validation, which DLS technology must satisfy to achieve regulatory approval.
Industry consortia like AVSC (Autonomous Vehicle Safety Consortium) have published best practices for sensor calibration that specifically address emerging technologies like DLS. These guidelines recommend redundancy in calibration methods, continuous monitoring of calibration status, and graceful degradation protocols when calibration accuracy falls below acceptable thresholds.
Compliance testing for DLS-based calibration systems typically involves environmental chamber testing across temperature ranges from -40°C to +85°C, vibration testing to simulate road conditions, and electromagnetic compatibility testing to ensure resilience against interference. Additionally, accelerated aging tests are conducted to verify calibration stability over the vehicle's expected operational lifetime.
As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, manufacturers implementing DLS technology must maintain active engagement with standards organizations and regulatory bodies to ensure ongoing compliance. The development of specialized standards specifically addressing light scattering technologies in automotive applications is anticipated within the next 3-5 years, which will further formalize the safety requirements for DLS-based sensor calibration systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!