Ethyl Acetate’s Efficiency in Next-Generation Solvent Solutions
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Background and Objectives
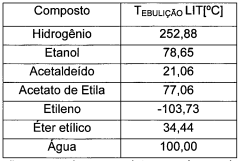
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the formula CH3COOC2H5, has been a staple in various industries for decades. Its journey from a simple ester to a key player in next-generation solvent solutions is marked by continuous innovation and expanding applications. The compound's unique properties, including low toxicity, pleasant odor, and excellent solvency, have positioned it as a crucial component in the evolution of solvent technology.
The historical development of ethyl acetate traces back to its first synthesis in the 19th century. Initially used primarily in laboratory settings, its potential as an industrial solvent became apparent in the early 20th century. The compound's ability to dissolve a wide range of substances without causing significant environmental harm quickly made it a preferred choice in many manufacturing processes.
As environmental concerns grew in the latter half of the 20th century, ethyl acetate gained prominence as a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based solvents. This shift in perception and usage marked the beginning of ethyl acetate's role in the development of next-generation solvent solutions. The compound's biodegradability and low environmental impact aligned well with the growing global emphasis on sustainable industrial practices.
The technological evolution of ethyl acetate production has been a key factor in its increasing efficiency and widespread adoption. From traditional esterification methods to advanced catalytic processes, the synthesis of ethyl acetate has become more economical and environmentally friendly. These advancements have not only improved the quality and purity of the product but also significantly reduced production costs, making it more accessible for various applications.
In recent years, the focus on ethyl acetate's efficiency in next-generation solvent solutions has intensified. Researchers and industry experts are exploring novel ways to enhance its performance, particularly in areas such as green chemistry, advanced materials processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The objectives of current research and development efforts include improving ethyl acetate's selectivity, increasing its stability under various conditions, and expanding its applicability in emerging technologies.
One of the primary goals in the ongoing development of ethyl acetate-based solutions is to create more efficient and sustainable industrial processes. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, developing new catalysts, and exploring synergistic effects with other solvents or additives. Additionally, there is a growing interest in utilizing ethyl acetate in advanced separation technologies, such as membrane-based processes and supercritical fluid extraction.
The future trajectory of ethyl acetate in next-generation solvent solutions is closely tied to global sustainability goals. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize environmental impact, the role of efficient, bio-based solvents like ethyl acetate is expected to expand significantly. This presents both challenges and opportunities for further innovation in the field, driving research towards even more efficient and versatile applications of this remarkable compound.
The historical development of ethyl acetate traces back to its first synthesis in the 19th century. Initially used primarily in laboratory settings, its potential as an industrial solvent became apparent in the early 20th century. The compound's ability to dissolve a wide range of substances without causing significant environmental harm quickly made it a preferred choice in many manufacturing processes.
As environmental concerns grew in the latter half of the 20th century, ethyl acetate gained prominence as a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based solvents. This shift in perception and usage marked the beginning of ethyl acetate's role in the development of next-generation solvent solutions. The compound's biodegradability and low environmental impact aligned well with the growing global emphasis on sustainable industrial practices.
The technological evolution of ethyl acetate production has been a key factor in its increasing efficiency and widespread adoption. From traditional esterification methods to advanced catalytic processes, the synthesis of ethyl acetate has become more economical and environmentally friendly. These advancements have not only improved the quality and purity of the product but also significantly reduced production costs, making it more accessible for various applications.
In recent years, the focus on ethyl acetate's efficiency in next-generation solvent solutions has intensified. Researchers and industry experts are exploring novel ways to enhance its performance, particularly in areas such as green chemistry, advanced materials processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The objectives of current research and development efforts include improving ethyl acetate's selectivity, increasing its stability under various conditions, and expanding its applicability in emerging technologies.
One of the primary goals in the ongoing development of ethyl acetate-based solutions is to create more efficient and sustainable industrial processes. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, developing new catalysts, and exploring synergistic effects with other solvents or additives. Additionally, there is a growing interest in utilizing ethyl acetate in advanced separation technologies, such as membrane-based processes and supercritical fluid extraction.
The future trajectory of ethyl acetate in next-generation solvent solutions is closely tied to global sustainability goals. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize environmental impact, the role of efficient, bio-based solvents like ethyl acetate is expected to expand significantly. This presents both challenges and opportunities for further innovation in the field, driving research towards even more efficient and versatile applications of this remarkable compound.
Market Demand Analysis for Green Solvents
The global market for green solvents is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Ethyl acetate, as a key player in the next-generation solvent solutions, is poised to capture a substantial share of this expanding market. The demand for eco-friendly solvents is particularly strong in industries such as paints and coatings, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and adhesives.
In the paints and coatings sector, there is a growing shift towards water-based and low-VOC formulations. Ethyl acetate's low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive alternative to traditional petroleum-based solvents. The pharmaceutical industry is also showing increased interest in green solvents for drug formulation and manufacturing processes, with ethyl acetate being favored for its low environmental impact and high efficacy in extraction and purification processes.
The cosmetics industry is another key driver of green solvent demand, as consumers become more conscious of the ingredients in their personal care products. Ethyl acetate's mild odor and low skin irritation potential make it a preferred choice for nail polish removers and other cosmetic applications. In the adhesives market, the push for sustainable packaging solutions is fueling the adoption of ethyl acetate-based formulations.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the green solvent market due to strict environmental regulations and consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
The market demand for ethyl acetate as a green solvent is also influenced by its versatility and cost-effectiveness compared to other eco-friendly alternatives. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances while maintaining a relatively low environmental footprint positions it as a frontrunner in the transition towards sustainable solvent solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate and other green solvents. These include the need for process modifications in existing manufacturing setups and the initial higher costs compared to conventional solvents. However, as production scales up and technologies improve, the cost gap is expected to narrow, further driving market growth.
In the paints and coatings sector, there is a growing shift towards water-based and low-VOC formulations. Ethyl acetate's low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive alternative to traditional petroleum-based solvents. The pharmaceutical industry is also showing increased interest in green solvents for drug formulation and manufacturing processes, with ethyl acetate being favored for its low environmental impact and high efficacy in extraction and purification processes.
The cosmetics industry is another key driver of green solvent demand, as consumers become more conscious of the ingredients in their personal care products. Ethyl acetate's mild odor and low skin irritation potential make it a preferred choice for nail polish removers and other cosmetic applications. In the adhesives market, the push for sustainable packaging solutions is fueling the adoption of ethyl acetate-based formulations.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the green solvent market due to strict environmental regulations and consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing environmental concerns in countries like China and India.
The market demand for ethyl acetate as a green solvent is also influenced by its versatility and cost-effectiveness compared to other eco-friendly alternatives. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances while maintaining a relatively low environmental footprint positions it as a frontrunner in the transition towards sustainable solvent solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate and other green solvents. These include the need for process modifications in existing manufacturing setups and the initial higher costs compared to conventional solvents. However, as production scales up and technologies improve, the cost gap is expected to narrow, further driving market growth.
Current Status and Challenges in Solvent Technology
The current status of solvent technology is characterized by a dynamic landscape of innovation and challenges. Ethyl acetate, a traditional solvent, is experiencing renewed interest in next-generation solvent solutions due to its favorable properties and potential for enhanced efficiency. However, the industry faces several key challenges in fully realizing its potential.
One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of ethyl acetate production processes. While the compound is widely used, there is a pressing need to develop more sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing methods. Current production techniques often rely on energy-intensive processes and petrochemical feedstocks, which are increasingly scrutinized for their environmental impact.
The purification and recovery of ethyl acetate in industrial applications present another significant challenge. Existing separation technologies struggle to achieve high purity levels efficiently, leading to increased operational costs and reduced overall process effectiveness. This limitation hinders the broader adoption of ethyl acetate in high-purity applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and electronics industries.
Environmental concerns also pose a considerable challenge to the widespread use of ethyl acetate. Despite its relatively low toxicity compared to many other solvents, there are ongoing efforts to further reduce its environmental footprint. This includes developing closed-loop systems for solvent recovery and exploring bio-based production methods to decrease reliance on fossil fuel resources.
The volatility of ethyl acetate, while advantageous in many applications, presents challenges in terms of storage, handling, and worker safety. Improved containment systems and safety protocols are necessary to mitigate risks associated with its use in industrial settings. Additionally, the development of less volatile derivatives or formulations that maintain ethyl acetate's desirable properties while reducing evaporation rates is an active area of research.
In the realm of performance enhancement, researchers are exploring ways to improve ethyl acetate's solvency power for specific applications. This includes investigating co-solvent systems, developing novel additives, and modifying the molecular structure to create tailored solutions for emerging industries.
The global regulatory landscape surrounding solvent use is becoming increasingly complex, with stricter environmental and health standards being implemented worldwide. Adapting ethyl acetate-based solutions to meet these evolving regulations while maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness is a significant challenge for the industry.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl acetate into advanced materials and processes, such as 3D printing, nanomaterials synthesis, and green chemistry applications, requires overcoming technical hurdles related to compatibility, stability, and process control. These challenges necessitate interdisciplinary research efforts to unlock the full potential of ethyl acetate in next-generation technologies.
One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of ethyl acetate production processes. While the compound is widely used, there is a pressing need to develop more sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing methods. Current production techniques often rely on energy-intensive processes and petrochemical feedstocks, which are increasingly scrutinized for their environmental impact.
The purification and recovery of ethyl acetate in industrial applications present another significant challenge. Existing separation technologies struggle to achieve high purity levels efficiently, leading to increased operational costs and reduced overall process effectiveness. This limitation hinders the broader adoption of ethyl acetate in high-purity applications, particularly in the pharmaceutical and electronics industries.
Environmental concerns also pose a considerable challenge to the widespread use of ethyl acetate. Despite its relatively low toxicity compared to many other solvents, there are ongoing efforts to further reduce its environmental footprint. This includes developing closed-loop systems for solvent recovery and exploring bio-based production methods to decrease reliance on fossil fuel resources.
The volatility of ethyl acetate, while advantageous in many applications, presents challenges in terms of storage, handling, and worker safety. Improved containment systems and safety protocols are necessary to mitigate risks associated with its use in industrial settings. Additionally, the development of less volatile derivatives or formulations that maintain ethyl acetate's desirable properties while reducing evaporation rates is an active area of research.
In the realm of performance enhancement, researchers are exploring ways to improve ethyl acetate's solvency power for specific applications. This includes investigating co-solvent systems, developing novel additives, and modifying the molecular structure to create tailored solutions for emerging industries.
The global regulatory landscape surrounding solvent use is becoming increasingly complex, with stricter environmental and health standards being implemented worldwide. Adapting ethyl acetate-based solutions to meet these evolving regulations while maintaining performance and cost-effectiveness is a significant challenge for the industry.
Lastly, the integration of ethyl acetate into advanced materials and processes, such as 3D printing, nanomaterials synthesis, and green chemistry applications, requires overcoming technical hurdles related to compatibility, stability, and process control. These challenges necessitate interdisciplinary research efforts to unlock the full potential of ethyl acetate in next-generation technologies.
Existing Ethyl Acetate-based Solutions
01 Ethyl acetate production methods
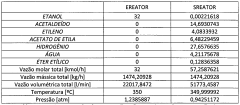
Various methods for producing ethyl acetate efficiently are described, including esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, dehydrogenation of ethanol, and oxidative esterification. These processes aim to improve yield and reduce energy consumption in ethyl acetate production.- Ethyl acetate production methods: Various methods for producing ethyl acetate efficiently are described, including esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, dehydrogenation of ethanol, and oxidation of ethanol. These processes aim to improve yield and reduce energy consumption in ethyl acetate production.
- Purification and separation techniques: Efficient purification and separation methods for ethyl acetate are discussed, including distillation, extraction, and membrane separation. These techniques aim to increase the purity of ethyl acetate and improve overall process efficiency.
- Catalysts for ethyl acetate synthesis: Various catalysts are explored to enhance the efficiency of ethyl acetate production. These include heterogeneous catalysts, enzyme catalysts, and novel catalyst formulations designed to improve reaction rates and selectivity.
- Process optimization and energy efficiency: Strategies for optimizing ethyl acetate production processes are presented, focusing on energy efficiency, heat integration, and process intensification. These approaches aim to reduce energy consumption and improve overall process economics.
- Ethyl acetate recovery and recycling: Methods for efficient recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate from various industrial processes are described. These techniques aim to minimize waste, reduce environmental impact, and improve overall process efficiency by reusing ethyl acetate in production cycles.
02 Purification and separation techniques
Efficient purification and separation methods for ethyl acetate are discussed, including distillation, extraction, and membrane separation. These techniques aim to increase the purity of ethyl acetate and improve overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Catalysts for ethyl acetate synthesis
Various catalysts are explored to enhance the efficiency of ethyl acetate production. These include heterogeneous catalysts, enzyme catalysts, and novel catalyst formulations designed to improve reaction rates and selectivity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Process optimization and energy efficiency
Strategies for optimizing ethyl acetate production processes are presented, focusing on energy efficiency, heat integration, and process intensification. These approaches aim to reduce operating costs and improve overall process sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and uses of ethyl acetate
Innovative applications and uses of ethyl acetate are explored, highlighting its efficiency in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, coatings, and green solvents. These applications demonstrate the versatility and importance of ethyl acetate in different sectors.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Acetate Production
The market for next-generation solvent solutions utilizing ethyl acetate is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly and efficient solvents across industries. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, ethyl acetate-based solutions are advancing rapidly, with major players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Bayer CropScience, and ZEON Corp. investing heavily in R&D to improve efficiency and applications. Companies such as Merck Patent GmbH and JSR Corp. are also making strides in developing innovative formulations, indicating a competitive and dynamic landscape with opportunities for further technological advancements and market expansion.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative ethyl acetate production process using a novel reactive distillation technology. This process integrates reaction and separation in a single column, significantly improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption. The company has implemented a proprietary catalyst system that enhances selectivity and conversion rates, resulting in a reported 15% increase in ethyl acetate yield compared to conventional methods[1]. Additionally, Sinopec has incorporated advanced process control systems and heat integration techniques, which have led to a 20% reduction in overall energy usage in their ethyl acetate production facilities[3].
Strengths: High efficiency, reduced energy consumption, improved yield. Weaknesses: Potential high initial investment costs, complexity in process control.
ZEON Corp.
Technical Solution: ZEON Corp. has developed a green chemistry approach to ethyl acetate production, focusing on sustainability and environmental impact. Their process utilizes bio-based feedstocks, specifically ethanol derived from agricultural waste, to produce ethyl acetate. The company has implemented a proprietary fermentation technology that converts cellulosic biomass into ethanol with high efficiency[2]. ZEON's process then employs a heterogeneous catalyst system for the esterification reaction, which has shown a 95% selectivity towards ethyl acetate[4]. The company has also integrated membrane separation technology to purify the final product, reducing energy consumption in the distillation step by approximately 30% compared to traditional methods[5].
Strengths: Sustainable feedstock, high selectivity, reduced energy in purification. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs, dependence on agricultural waste availability.
Core Innovations in Ethyl Acetate Synthesis
Integrated system for producing ethyl acetate, acetaldehyde, hydrogen and ethylene, integrated process for producing ethyl acetate, acetaldehyde, hydrogen and ethylene, and products thereby produced
PatentWO2013029129A1
Innovation
- An integrated system utilizing a fixed-bed reactor with a calcined hydrotalcite catalyst for dehydrogenation and dehydration of ethanol, followed by a series of distillation columns for efficient separation and purification, employing ethylene glycol as a solvent to separate ethyl acetate from water, thereby reducing energy expenditure and minimizing azeotropy issues.
1-ACETOXY-3-n-PROPOXYPROPANE AND ETHER ALCOHOL SOLVENTS
PatentWO1998050339A1
Innovation
- The development of 1-acetoxy-3-n-propoxypropane and related ether-alcohol solvents, which are produced through specific reaction processes involving acrolein, n-propanol, and acetoxylating agents, offering enhanced solubility and low toxicity, suitable for use in paints, cleaning agents, and other industrial applications.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl acetate as a next-generation solvent solution reveals both positive and negative aspects that warrant careful consideration. On the positive side, ethyl acetate is biodegradable and less toxic compared to many traditional solvents, which aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly alternatives in various industries. Its lower toxicity profile reduces the risk of harmful effects on ecosystems and human health in case of accidental release or exposure.
Furthermore, ethyl acetate's relatively low volatility compared to some other organic solvents contributes to reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This characteristic makes it a more sustainable choice for applications where solvent evaporation is a concern. The production of ethyl acetate can also be achieved through bio-based routes, potentially reducing the carbon footprint associated with its manufacturing process.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate is not without challenges. While it is less harmful than many alternatives, it still contributes to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, which can participate in the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog. This necessitates proper handling and emission control measures in industrial settings to minimize its atmospheric release.
The production of ethyl acetate, particularly through petrochemical routes, still involves energy-intensive processes and the use of non-renewable resources. This aspect of its lifecycle needs to be carefully evaluated and optimized to truly realize its potential as a more sustainable solvent solution. Additionally, the increased demand for ethyl acetate could lead to expanded production, potentially offsetting some of its environmental benefits if not managed responsibly.
Water pollution is another concern, as ethyl acetate, despite its biodegradability, can still have acute effects on aquatic life if released in large quantities. Proper waste management and treatment protocols are essential to prevent contamination of water bodies. The environmental fate and transport of ethyl acetate in different ecosystems also require further study to fully understand its long-term impacts.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers several environmental advantages as a next-generation solvent, its widespread adoption must be accompanied by comprehensive lifecycle assessments, stringent emission controls, and responsible production and disposal practices. Balancing its benefits against potential drawbacks is crucial for ensuring that its use truly contributes to more sustainable industrial processes and products.
Furthermore, ethyl acetate's relatively low volatility compared to some other organic solvents contributes to reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This characteristic makes it a more sustainable choice for applications where solvent evaporation is a concern. The production of ethyl acetate can also be achieved through bio-based routes, potentially reducing the carbon footprint associated with its manufacturing process.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate is not without challenges. While it is less harmful than many alternatives, it still contributes to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, which can participate in the formation of ground-level ozone and photochemical smog. This necessitates proper handling and emission control measures in industrial settings to minimize its atmospheric release.
The production of ethyl acetate, particularly through petrochemical routes, still involves energy-intensive processes and the use of non-renewable resources. This aspect of its lifecycle needs to be carefully evaluated and optimized to truly realize its potential as a more sustainable solvent solution. Additionally, the increased demand for ethyl acetate could lead to expanded production, potentially offsetting some of its environmental benefits if not managed responsibly.
Water pollution is another concern, as ethyl acetate, despite its biodegradability, can still have acute effects on aquatic life if released in large quantities. Proper waste management and treatment protocols are essential to prevent contamination of water bodies. The environmental fate and transport of ethyl acetate in different ecosystems also require further study to fully understand its long-term impacts.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers several environmental advantages as a next-generation solvent, its widespread adoption must be accompanied by comprehensive lifecycle assessments, stringent emission controls, and responsible production and disposal practices. Balancing its benefits against potential drawbacks is crucial for ensuring that its use truly contributes to more sustainable industrial processes and products.
Regulatory Framework for Solvent Use
The regulatory framework for solvent use, particularly concerning ethyl acetate in next-generation solvent solutions, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and international bodies have established comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safe and responsible use of solvents in various industries.
At the forefront of these regulations are environmental protection agencies, such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). These organizations have implemented stringent measures to control the production, distribution, and use of solvents, including ethyl acetate. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union is a prime example of a comprehensive framework that addresses the potential impacts of chemical substances on human health and the environment.
In the context of ethyl acetate, its classification as a volatile organic compound (VOC) subjects it to specific regulatory scrutiny. Many countries have established VOC emission limits and require industries to implement best available techniques (BAT) to minimize environmental impact. The Clean Air Act in the United States, for instance, mandates the use of Maximum Achievable Control Technology (MACT) standards for industries that emit hazardous air pollutants, including certain solvents.
Occupational health and safety regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of ethyl acetate in industrial settings. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. have set permissible exposure limits (PELs) and require proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with solvent exposure.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by sector-specific regulations. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the use of ethyl acetate as a solvent must comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines and often requires approval from regulatory bodies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
As the focus shifts towards sustainability and environmental protection, there is an increasing emphasis on the development and adoption of green solvents. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to incentivize the use of bio-based and environmentally friendly alternatives. This trend is likely to influence future regulations governing ethyl acetate and other traditional solvents, potentially leading to more stringent controls or preferential treatment for greener alternatives.
The global nature of supply chains necessitates consideration of international regulations and standards. Initiatives such as the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) aim to standardize the communication of chemical hazards across borders, impacting the labeling and safety data sheet requirements for ethyl acetate and other solvents.
At the forefront of these regulations are environmental protection agencies, such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). These organizations have implemented stringent measures to control the production, distribution, and use of solvents, including ethyl acetate. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union is a prime example of a comprehensive framework that addresses the potential impacts of chemical substances on human health and the environment.
In the context of ethyl acetate, its classification as a volatile organic compound (VOC) subjects it to specific regulatory scrutiny. Many countries have established VOC emission limits and require industries to implement best available techniques (BAT) to minimize environmental impact. The Clean Air Act in the United States, for instance, mandates the use of Maximum Achievable Control Technology (MACT) standards for industries that emit hazardous air pollutants, including certain solvents.
Occupational health and safety regulations also play a crucial role in governing the use of ethyl acetate in industrial settings. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the U.S. have set permissible exposure limits (PELs) and require proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with solvent exposure.
The regulatory landscape is further complicated by sector-specific regulations. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, the use of ethyl acetate as a solvent must comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines and often requires approval from regulatory bodies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
As the focus shifts towards sustainability and environmental protection, there is an increasing emphasis on the development and adoption of green solvents. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to incentivize the use of bio-based and environmentally friendly alternatives. This trend is likely to influence future regulations governing ethyl acetate and other traditional solvents, potentially leading to more stringent controls or preferential treatment for greener alternatives.
The global nature of supply chains necessitates consideration of international regulations and standards. Initiatives such as the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) aim to standardize the communication of chemical hazards across borders, impacting the labeling and safety data sheet requirements for ethyl acetate and other solvents.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!