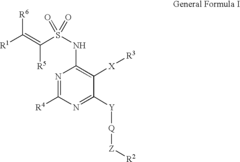
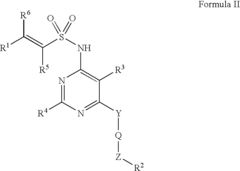
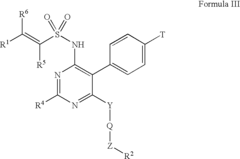
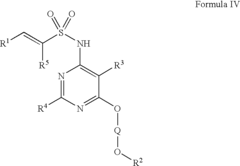
Unveiling Ethyl Acetate’s Role in Novel Pharmaceuticals
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate in Pharma: Background and Objectives
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, has been a staple in the pharmaceutical industry for decades. Its journey from a simple solvent to a key player in novel drug development showcases the evolving landscape of pharmaceutical research. This colorless liquid, with its characteristic sweet smell, has traditionally been utilized in various industrial applications, including as a solvent for paints, coatings, and adhesives. However, its role in pharmaceuticals has expanded significantly in recent years.
The pharmaceutical industry's growing interest in ethyl acetate stems from its unique properties that align well with the demands of modern drug development. Its low toxicity, high volatility, and excellent solvency make it an ideal candidate for various pharmaceutical processes. As the industry shifts towards more environmentally friendly and efficient practices, ethyl acetate's biodegradability and relatively low production costs have further elevated its importance.
In the context of novel pharmaceuticals, ethyl acetate is emerging as a crucial component in several cutting-edge applications. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds makes it invaluable in the synthesis and purification of new drug molecules. Additionally, its role in drug delivery systems is gaining attention, with researchers exploring its potential in enhancing the bioavailability and efficacy of various medications.
The objectives of investigating ethyl acetate's role in novel pharmaceuticals are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to exploit its unique chemical properties to develop more effective drug formulations. This includes improving drug solubility, stability, and absorption rates. Another key goal is to utilize ethyl acetate in the design of novel drug delivery systems, potentially revolutionizing how certain medications are administered and absorbed by the body.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry is keen on leveraging ethyl acetate's properties to streamline manufacturing processes. This involves developing more efficient extraction and purification methods, potentially reducing production costs and environmental impact. The exploration of ethyl acetate's role also extends to its potential in creating new drug combinations and formulations that were previously challenging or impossible to produce.
As we delve deeper into the potential of ethyl acetate in pharmaceuticals, it's clear that this compound is at the forefront of several technological advancements. From enhancing drug efficacy to revolutionizing production methods, ethyl acetate is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of pharmaceutical research and development. The ongoing exploration of its capabilities promises to unlock new possibilities in drug design, delivery, and manufacturing, potentially leading to more effective treatments and improved patient outcomes.
The pharmaceutical industry's growing interest in ethyl acetate stems from its unique properties that align well with the demands of modern drug development. Its low toxicity, high volatility, and excellent solvency make it an ideal candidate for various pharmaceutical processes. As the industry shifts towards more environmentally friendly and efficient practices, ethyl acetate's biodegradability and relatively low production costs have further elevated its importance.
In the context of novel pharmaceuticals, ethyl acetate is emerging as a crucial component in several cutting-edge applications. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds makes it invaluable in the synthesis and purification of new drug molecules. Additionally, its role in drug delivery systems is gaining attention, with researchers exploring its potential in enhancing the bioavailability and efficacy of various medications.
The objectives of investigating ethyl acetate's role in novel pharmaceuticals are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to exploit its unique chemical properties to develop more effective drug formulations. This includes improving drug solubility, stability, and absorption rates. Another key goal is to utilize ethyl acetate in the design of novel drug delivery systems, potentially revolutionizing how certain medications are administered and absorbed by the body.
Furthermore, the pharmaceutical industry is keen on leveraging ethyl acetate's properties to streamline manufacturing processes. This involves developing more efficient extraction and purification methods, potentially reducing production costs and environmental impact. The exploration of ethyl acetate's role also extends to its potential in creating new drug combinations and formulations that were previously challenging or impossible to produce.
As we delve deeper into the potential of ethyl acetate in pharmaceuticals, it's clear that this compound is at the forefront of several technological advancements. From enhancing drug efficacy to revolutionizing production methods, ethyl acetate is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of pharmaceutical research and development. The ongoing exploration of its capabilities promises to unlock new possibilities in drug design, delivery, and manufacturing, potentially leading to more effective treatments and improved patient outcomes.
Market Demand Analysis for Ethyl Acetate-Based Drugs
The market demand for ethyl acetate-based drugs has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing need for innovative pharmaceutical solutions. This trend is particularly evident in the treatment of complex diseases and conditions that have proven resistant to traditional therapies. The global pharmaceutical industry's focus on developing novel drug delivery systems and formulations has further amplified the potential of ethyl acetate in drug development.
One of the key factors contributing to the rising demand for ethyl acetate-based drugs is their enhanced bioavailability and improved efficacy. Ethyl acetate's unique properties allow for better drug absorption and distribution within the body, leading to more effective treatments with potentially lower dosages. This characteristic is especially valuable in addressing issues related to poor drug solubility and permeability, which have long been challenges in pharmaceutical development.
The market for ethyl acetate-based drugs is also being propelled by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the aging global population. As healthcare systems worldwide grapple with the rising burden of conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders, there is a growing demand for more effective and targeted therapies. Ethyl acetate-based drugs offer promising solutions in these areas, potentially providing better patient outcomes and quality of life.
Furthermore, the shift towards personalized medicine and precision therapeutics has created new opportunities for ethyl acetate-based drug formulations. These drugs can be tailored to specific patient populations or genetic profiles, offering more targeted and effective treatments. This trend aligns with the broader movement in the pharmaceutical industry towards more patient-centric approaches to drug development and delivery.
The market potential for ethyl acetate-based drugs extends across various therapeutic areas. In oncology, for instance, these drugs show promise in improving the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents, potentially reducing side effects while enhancing efficacy. In the field of neurology, ethyl acetate-based formulations are being explored for their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively, opening up new possibilities for treating neurological disorders.
From a geographical perspective, the demand for ethyl acetate-based drugs is global, with significant growth expected in both developed and emerging markets. North America and Europe currently lead in terms of research and development activities, while Asia-Pacific regions are showing rapid growth in adoption and market expansion. This global distribution of demand underscores the universal appeal and potential of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical applications.
In conclusion, the market demand analysis for ethyl acetate-based drugs reveals a promising landscape with substantial growth potential. The combination of technological advancements, increasing disease burden, and the push for more effective and personalized treatments is creating a favorable environment for the development and adoption of these innovative pharmaceutical solutions.
One of the key factors contributing to the rising demand for ethyl acetate-based drugs is their enhanced bioavailability and improved efficacy. Ethyl acetate's unique properties allow for better drug absorption and distribution within the body, leading to more effective treatments with potentially lower dosages. This characteristic is especially valuable in addressing issues related to poor drug solubility and permeability, which have long been challenges in pharmaceutical development.
The market for ethyl acetate-based drugs is also being propelled by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the aging global population. As healthcare systems worldwide grapple with the rising burden of conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders, there is a growing demand for more effective and targeted therapies. Ethyl acetate-based drugs offer promising solutions in these areas, potentially providing better patient outcomes and quality of life.
Furthermore, the shift towards personalized medicine and precision therapeutics has created new opportunities for ethyl acetate-based drug formulations. These drugs can be tailored to specific patient populations or genetic profiles, offering more targeted and effective treatments. This trend aligns with the broader movement in the pharmaceutical industry towards more patient-centric approaches to drug development and delivery.
The market potential for ethyl acetate-based drugs extends across various therapeutic areas. In oncology, for instance, these drugs show promise in improving the delivery of chemotherapeutic agents, potentially reducing side effects while enhancing efficacy. In the field of neurology, ethyl acetate-based formulations are being explored for their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively, opening up new possibilities for treating neurological disorders.
From a geographical perspective, the demand for ethyl acetate-based drugs is global, with significant growth expected in both developed and emerging markets. North America and Europe currently lead in terms of research and development activities, while Asia-Pacific regions are showing rapid growth in adoption and market expansion. This global distribution of demand underscores the universal appeal and potential of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical applications.
In conclusion, the market demand analysis for ethyl acetate-based drugs reveals a promising landscape with substantial growth potential. The combination of technological advancements, increasing disease burden, and the push for more effective and personalized treatments is creating a favorable environment for the development and adoption of these innovative pharmaceutical solutions.
Current Challenges in Ethyl Acetate Pharmaceutical Applications
Despite the widespread use of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical applications, several challenges persist in its utilization for novel drug development and formulation. One of the primary concerns is the solvent's high volatility, which can lead to rapid evaporation during processing and storage. This characteristic not only affects the stability of pharmaceutical formulations but also poses potential safety risks in manufacturing environments.
Another significant challenge is the limited solubility of certain complex drug molecules in ethyl acetate. While the solvent is effective for many compounds, it may struggle to dissolve highly polar or large molecular weight substances, restricting its applicability in some advanced pharmaceutical developments. This limitation often necessitates the use of solvent mixtures or alternative solvents, complicating formulation processes and potentially increasing production costs.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate usage in pharmaceutical manufacturing is also a growing concern. Although it is considered less harmful than many other organic solvents, its production and disposal still contribute to environmental pollution. Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in pharmaceutical processes, putting pressure on manufacturers to find more sustainable alternatives or implement costly recovery systems.
Ethyl acetate's reactivity with certain drug compounds presents another challenge. In some cases, it may participate in unwanted side reactions or degradation processes, particularly during long-term storage or under specific environmental conditions. This reactivity can compromise the stability and efficacy of pharmaceutical products, necessitating extensive stability testing and potentially limiting shelf life.
The purity requirements for pharmaceutical-grade ethyl acetate pose additional challenges. Trace impurities can significantly impact drug quality and safety, requiring rigorous purification processes and quality control measures. These stringent requirements often lead to increased production costs and complexity in the supply chain management of pharmaceutical-grade ethyl acetate.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate use in pharmaceuticals is becoming increasingly complex. Different regions and countries may have varying guidelines and restrictions on its application in drug formulations, creating challenges for global pharmaceutical companies in maintaining consistent formulations across markets. Navigating these regulatory differences while ensuring product quality and safety adds another layer of complexity to ethyl acetate's use in novel pharmaceutical development.
Another significant challenge is the limited solubility of certain complex drug molecules in ethyl acetate. While the solvent is effective for many compounds, it may struggle to dissolve highly polar or large molecular weight substances, restricting its applicability in some advanced pharmaceutical developments. This limitation often necessitates the use of solvent mixtures or alternative solvents, complicating formulation processes and potentially increasing production costs.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate usage in pharmaceutical manufacturing is also a growing concern. Although it is considered less harmful than many other organic solvents, its production and disposal still contribute to environmental pollution. Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing the use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in pharmaceutical processes, putting pressure on manufacturers to find more sustainable alternatives or implement costly recovery systems.
Ethyl acetate's reactivity with certain drug compounds presents another challenge. In some cases, it may participate in unwanted side reactions or degradation processes, particularly during long-term storage or under specific environmental conditions. This reactivity can compromise the stability and efficacy of pharmaceutical products, necessitating extensive stability testing and potentially limiting shelf life.
The purity requirements for pharmaceutical-grade ethyl acetate pose additional challenges. Trace impurities can significantly impact drug quality and safety, requiring rigorous purification processes and quality control measures. These stringent requirements often lead to increased production costs and complexity in the supply chain management of pharmaceutical-grade ethyl acetate.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate use in pharmaceuticals is becoming increasingly complex. Different regions and countries may have varying guidelines and restrictions on its application in drug formulations, creating challenges for global pharmaceutical companies in maintaining consistent formulations across markets. Navigating these regulatory differences while ensuring product quality and safety adds another layer of complexity to ethyl acetate's use in novel pharmaceutical development.
Existing Pharmaceutical Solutions Utilizing Ethyl Acetate
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods and processes for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification reactions, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts or reactants to improve yield and purity.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds. Its applications span across multiple industries such as pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: The use of ethyl acetate as an extraction solvent or in separation processes is explored. This includes its application in liquid-liquid extraction, chromatography, and other purification techniques for various compounds and materials.
- Ethyl acetate-based formulations and compositions: Development of formulations and compositions containing ethyl acetate for specific applications. These may include adhesives, coatings, cleaning solutions, or other products where ethyl acetate's properties are beneficial.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate use: Addressing environmental and safety aspects related to ethyl acetate usage, including waste management, emission control, and safe handling practices. This may involve developing greener processes or alternative solvents to replace ethyl acetate in certain applications.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in diverse chemical processes, such as solvent extraction, as a reaction medium, and in the production of various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for use in pharmaceuticals, coatings, and other industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science
Ethyl acetate plays a role in polymer synthesis, material processing, and the development of novel materials. It is used in the preparation of polymers, as a solvent in material formulations, and in the modification of material properties.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, reducing emissions, and enhancing handling and storage practices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for ethyl acetate
Various analytical techniques and methods are employed for the detection, quantification, and characterization of ethyl acetate in different matrices. These methods are crucial for quality control, process monitoring, and research applications involving ethyl acetate.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Ethyl Acetate-Based Pharmaceutical Research
The development of novel pharmaceuticals utilizing ethyl acetate is in a nascent stage, with the market showing significant growth potential. The global pharmaceutical industry, valued at over $1 trillion, is increasingly exploring innovative applications of ethyl acetate in drug formulation and delivery. Companies like Novartis AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche are at the forefront of this research, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. While the technology is still evolving, early-stage clinical trials and patent filings indicate a growing interest in ethyl acetate-based drug solutions. The competitive landscape is characterized by collaborations between pharmaceutical giants and specialized chemical companies, aiming to overcome formulation challenges and enhance drug efficacy.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has been exploring the use of ethyl acetate in novel pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in the development of controlled-release drug delivery systems. Their approach involves utilizing ethyl acetate as a solvent in the preparation of polymeric nanoparticles, which can encapsulate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) for targeted and sustained release[1]. The company has developed a patented process that uses ethyl acetate in a green chemistry approach, reducing the environmental impact of drug manufacturing[2]. This method allows for the creation of nanoparticles with improved bioavailability and stability of APIs, especially for poorly water-soluble drugs[3]. Novartis has also investigated the use of ethyl acetate in the synthesis of novel pharmaceutical intermediates, leveraging its properties as a versatile organic solvent[4].
Strengths: Improved drug bioavailability, environmentally friendly manufacturing process, and enhanced stability of APIs. Weaknesses: Potential residual solvent concerns and the need for specialized equipment for nanoparticle production.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Technical Solution: Boehringer Ingelheim has been pioneering the use of ethyl acetate in continuous flow chemistry for pharmaceutical synthesis. Their innovative approach involves using ethyl acetate as both a solvent and a reagent in multi-step synthesis processes[1]. This method allows for more efficient and scalable production of complex pharmaceutical compounds. The company has developed a proprietary microreactor technology that optimizes the use of ethyl acetate in flow chemistry, resulting in higher yields and purity of final products[2]. Additionally, Boehringer Ingelheim has explored the use of ethyl acetate in the development of novel drug delivery systems, particularly for inhalation therapies[3]. Their research has shown that ethyl acetate can be used to create fine, uniform particles of APIs, improving lung deposition and therapeutic efficacy[4].
Strengths: Increased efficiency in drug synthesis, improved scalability of production, and enhanced drug delivery for inhalation therapies. Weaknesses: Requires significant investment in specialized equipment and potential challenges in regulatory approval for novel manufacturing processes.
Innovative Approaches in Ethyl Acetate Drug Formulations
Arylethene-sulfonamides
PatentInactiveUS6951856B2
Innovation
- Development of arylethene-sulfonamides with specific structural formulas that inhibit endothelin binding to ETA and ETB receptors, offering improved potency and efficacy as demonstrated by IC50 values and functional inhibitory potency in endothelin-induced contraction assays.
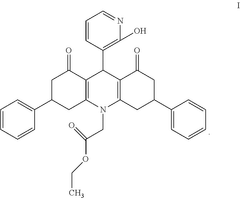
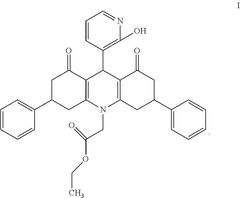
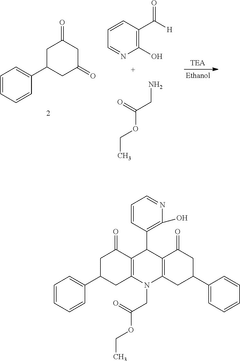
Ethyl 2-[9-(2-hydroxypyridin-3-yl)-3,6-diphenyl-1,8-dioxo-3,4,9,10-tetrahydroacridine-10-yl]-acetate as an antimicrobial compound
PatentActiveUS20250145583A1
Innovation
- The development of the ethyl 2-[9-(2-hydroxypyridin-3-yl)-3,6-diphenyl-1,8-dioxo-3,4,9,10-tetrahydroacridine-10-yl]-acetate compound, synthesized via a three-component reaction, which has been characterized and shown to possess significant antibacterial and antifungal activity.
Regulatory Considerations for Ethyl Acetate in Pharmaceuticals
The regulatory landscape for ethyl acetate in pharmaceuticals is complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration by manufacturers and regulatory bodies alike. As a widely used solvent in pharmaceutical production, ethyl acetate falls under the scrutiny of various regulatory agencies worldwide, each with its own set of guidelines and requirements.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical applications. The FDA classifies ethyl acetate as a Class 3 solvent, which is considered to have low toxic potential to human health. This classification allows for its use in pharmaceutical products, but with specific limitations on residual levels. Manufacturers must adhere to the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Q3C guidelines, which set permissible daily exposure (PDE) limits for ethyl acetate.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) also follows the ICH Q3C guidelines, aligning its regulatory approach with global standards. However, the EMA may impose additional requirements for certain pharmaceutical products, particularly those intended for sensitive populations or specific therapeutic areas.
In Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) enforces similar regulations, emphasizing the importance of controlling residual solvent levels in finished pharmaceutical products. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with Japanese Pharmacopoeia standards, which include specific tests for residual solvents.
Regulatory bodies in emerging markets, such as China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and India's Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), are increasingly aligning their regulations with international standards. However, they may have additional country-specific requirements that pharmaceutical companies must navigate.
A critical aspect of regulatory compliance is the development and validation of analytical methods for detecting and quantifying ethyl acetate residues in pharmaceutical products. Manufacturers must implement robust quality control processes and maintain detailed documentation of solvent usage and removal during production.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines on the handling, storage, and disposal of organic solvents, including ethyl acetate, to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approach to ethyl acetate and other solvents. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these changes and be prepared to adapt their processes accordingly. This may include exploring alternative solvents or developing new formulation techniques that reduce reliance on ethyl acetate while maintaining product efficacy and safety.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical applications. The FDA classifies ethyl acetate as a Class 3 solvent, which is considered to have low toxic potential to human health. This classification allows for its use in pharmaceutical products, but with specific limitations on residual levels. Manufacturers must adhere to the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Q3C guidelines, which set permissible daily exposure (PDE) limits for ethyl acetate.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) also follows the ICH Q3C guidelines, aligning its regulatory approach with global standards. However, the EMA may impose additional requirements for certain pharmaceutical products, particularly those intended for sensitive populations or specific therapeutic areas.
In Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) enforces similar regulations, emphasizing the importance of controlling residual solvent levels in finished pharmaceutical products. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with Japanese Pharmacopoeia standards, which include specific tests for residual solvents.
Regulatory bodies in emerging markets, such as China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and India's Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), are increasingly aligning their regulations with international standards. However, they may have additional country-specific requirements that pharmaceutical companies must navigate.
A critical aspect of regulatory compliance is the development and validation of analytical methods for detecting and quantifying ethyl acetate residues in pharmaceutical products. Manufacturers must implement robust quality control processes and maintain detailed documentation of solvent usage and removal during production.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of ethyl acetate in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines on the handling, storage, and disposal of organic solvents, including ethyl acetate, to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approach to ethyl acetate and other solvents. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these changes and be prepared to adapt their processes accordingly. This may include exploring alternative solvents or developing new formulation techniques that reduce reliance on ethyl acetate while maintaining product efficacy and safety.
Environmental Impact of Ethyl Acetate in Drug Manufacturing
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing is a critical consideration for the pharmaceutical industry. As a widely used solvent in various stages of drug production, ethyl acetate's environmental footprint extends from its synthesis to its disposal.
During the manufacturing process, ethyl acetate emissions can contribute to air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, it reacts with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, forming ground-level ozone and other photochemical oxidants. These compounds are key components of smog, which can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems.
Water pollution is another concern associated with ethyl acetate use in pharmaceutical production. Improper handling or disposal can lead to contamination of water bodies. Although ethyl acetate is biodegradable and has low toxicity to aquatic life, high concentrations can still disrupt aquatic ecosystems and potentially affect drinking water sources.
The production of ethyl acetate itself has environmental implications. Traditional methods of synthesis often involve petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, recent advancements in green chemistry have led to more sustainable production routes, such as the use of bioethanol as a starting material, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint.
Waste management in pharmaceutical manufacturing is crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of ethyl acetate. Many facilities employ solvent recovery systems to recycle and reuse ethyl acetate, reducing both waste and the need for fresh solvent production. Advanced treatment technologies, such as activated carbon adsorption and catalytic oxidation, are also employed to minimize emissions and effluents.
The pharmaceutical industry is increasingly adopting green chemistry principles to address the environmental concerns associated with solvents like ethyl acetate. This includes exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents, optimizing reaction conditions to reduce solvent use, and implementing continuous flow chemistry techniques that can dramatically decrease solvent consumption.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and limits for ethyl acetate emissions and disposal. Compliance with these regulations drives innovation in cleaner production methods and more efficient solvent management practices. As a result, many pharmaceutical companies are investing in research and development to improve their environmental performance related to solvent use.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate plays a vital role in drug manufacturing, its environmental impact necessitates careful management and ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable practices. The industry's focus on green chemistry and circular economy principles is gradually transforming the environmental profile of ethyl acetate use in pharmaceutical production.
During the manufacturing process, ethyl acetate emissions can contribute to air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, it reacts with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, forming ground-level ozone and other photochemical oxidants. These compounds are key components of smog, which can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems.
Water pollution is another concern associated with ethyl acetate use in pharmaceutical production. Improper handling or disposal can lead to contamination of water bodies. Although ethyl acetate is biodegradable and has low toxicity to aquatic life, high concentrations can still disrupt aquatic ecosystems and potentially affect drinking water sources.
The production of ethyl acetate itself has environmental implications. Traditional methods of synthesis often involve petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, recent advancements in green chemistry have led to more sustainable production routes, such as the use of bioethanol as a starting material, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint.
Waste management in pharmaceutical manufacturing is crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of ethyl acetate. Many facilities employ solvent recovery systems to recycle and reuse ethyl acetate, reducing both waste and the need for fresh solvent production. Advanced treatment technologies, such as activated carbon adsorption and catalytic oxidation, are also employed to minimize emissions and effluents.
The pharmaceutical industry is increasingly adopting green chemistry principles to address the environmental concerns associated with solvents like ethyl acetate. This includes exploring alternative, more environmentally friendly solvents, optimizing reaction conditions to reduce solvent use, and implementing continuous flow chemistry techniques that can dramatically decrease solvent consumption.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and limits for ethyl acetate emissions and disposal. Compliance with these regulations drives innovation in cleaner production methods and more efficient solvent management practices. As a result, many pharmaceutical companies are investing in research and development to improve their environmental performance related to solvent use.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate plays a vital role in drug manufacturing, its environmental impact necessitates careful management and ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable practices. The industry's focus on green chemistry and circular economy principles is gradually transforming the environmental profile of ethyl acetate use in pharmaceutical production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!