How Ethyl Acetate Facilitates Robust Industrial Innovations?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview and Applications
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5, plays a crucial role in various industrial applications. This colorless liquid, characterized by its fruity odor, has become an indispensable component in numerous manufacturing processes due to its unique properties and wide-ranging applicability.
In the realm of industrial solvents, ethyl acetate stands out for its excellent solvency power and low toxicity. It effectively dissolves a wide array of substances, making it a preferred choice in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. The compound's ability to evaporate quickly without leaving residues has made it particularly valuable in the printing industry, where it is used extensively in flexographic and gravure printing processes.
The pharmaceutical industry heavily relies on ethyl acetate for various applications. It serves as a crucial extraction solvent in the production of antibiotics and other pharmaceutical compounds. Its low toxicity and high purity make it suitable for use in the final stages of drug manufacturing, ensuring the quality and safety of medicinal products.
In the flavor and fragrance industry, ethyl acetate contributes significantly to the creation of synthetic fruit flavors. Its natural presence in many fruits, such as apples and pears, makes it an ideal component for replicating authentic fruit aromas in food and beverage products. This application extends to the cosmetics industry, where ethyl acetate is used in perfumes and personal care products to impart pleasant, fruity scents.
The electronics industry benefits from ethyl acetate's properties in the production of circuit boards and electronic components. Its use as a cleaning agent for removing flux residues and other contaminants from electronic assemblies ensures the reliability and longevity of electronic devices. Additionally, its role in the manufacture of flexible electronics and displays showcases its adaptability to emerging technologies.
Ethyl acetate's environmental profile adds to its industrial appeal. As a volatile organic compound (VOC) with relatively low toxicity and ozone depletion potential, it aligns well with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This characteristic has led to its increased adoption as a replacement for more harmful solvents in various industrial processes, contributing to greener manufacturing practices.
The compound's versatility extends to its use in the production of biodegradable plastics and sustainable packaging materials. As industries strive for more environmentally friendly alternatives, ethyl acetate's role in developing bio-based polymers and coatings positions it at the forefront of sustainable innovation.
In the realm of industrial solvents, ethyl acetate stands out for its excellent solvency power and low toxicity. It effectively dissolves a wide array of substances, making it a preferred choice in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. The compound's ability to evaporate quickly without leaving residues has made it particularly valuable in the printing industry, where it is used extensively in flexographic and gravure printing processes.
The pharmaceutical industry heavily relies on ethyl acetate for various applications. It serves as a crucial extraction solvent in the production of antibiotics and other pharmaceutical compounds. Its low toxicity and high purity make it suitable for use in the final stages of drug manufacturing, ensuring the quality and safety of medicinal products.
In the flavor and fragrance industry, ethyl acetate contributes significantly to the creation of synthetic fruit flavors. Its natural presence in many fruits, such as apples and pears, makes it an ideal component for replicating authentic fruit aromas in food and beverage products. This application extends to the cosmetics industry, where ethyl acetate is used in perfumes and personal care products to impart pleasant, fruity scents.
The electronics industry benefits from ethyl acetate's properties in the production of circuit boards and electronic components. Its use as a cleaning agent for removing flux residues and other contaminants from electronic assemblies ensures the reliability and longevity of electronic devices. Additionally, its role in the manufacture of flexible electronics and displays showcases its adaptability to emerging technologies.
Ethyl acetate's environmental profile adds to its industrial appeal. As a volatile organic compound (VOC) with relatively low toxicity and ozone depletion potential, it aligns well with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This characteristic has led to its increased adoption as a replacement for more harmful solvents in various industrial processes, contributing to greener manufacturing practices.
The compound's versatility extends to its use in the production of biodegradable plastics and sustainable packaging materials. As industries strive for more environmentally friendly alternatives, ethyl acetate's role in developing bio-based polymers and coatings positions it at the forefront of sustainable innovation.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for ethyl acetate has been steadily growing, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. This compound's unique properties make it an indispensable component in numerous industrial processes, contributing to robust innovations in multiple sectors.
In the coatings and paints industry, ethyl acetate serves as a crucial solvent due to its excellent solvency and low toxicity. The global paints and coatings market is projected to expand significantly, with a corresponding increase in demand for ethyl acetate. This growth is fueled by rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and the automotive industry's expansion, particularly in emerging economies.
The adhesives sector represents another substantial market for ethyl acetate. Its use in the production of flexible packaging adhesives, laminations, and pressure-sensitive adhesives has seen a surge in demand. The rise of e-commerce and changes in consumer packaging preferences have further boosted this trend, with ethyl acetate playing a pivotal role in creating innovative, sustainable packaging solutions.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent in the synthesis of various drugs and as an extraction medium. The growing pharmaceutical sector, driven by an aging population and increased healthcare spending, has led to a higher demand for ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing processes.
The electronics industry also contributes significantly to the market demand for ethyl acetate. Its application in the production of printed circuit boards and as a cleaning agent for electronic components has grown with the expansion of the electronics market, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific.
The food and beverage industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. With changing consumer preferences towards natural and organic products, the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector has seen steady growth.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have led to increased interest in bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources. This trend aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly industrial processes, opening new avenues for innovation and market expansion.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization and economic growth. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-quality, specialized applications of ethyl acetate in various industries.
In conclusion, the market demand for ethyl acetate is robust and diverse, spanning multiple industries and geographical regions. Its role in facilitating industrial innovations is evident across sectors, from coatings and adhesives to pharmaceuticals and electronics. The compound's versatility, coupled with growing environmental consciousness, positions ethyl acetate as a key component in driving sustainable industrial growth and innovation.
In the coatings and paints industry, ethyl acetate serves as a crucial solvent due to its excellent solvency and low toxicity. The global paints and coatings market is projected to expand significantly, with a corresponding increase in demand for ethyl acetate. This growth is fueled by rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and the automotive industry's expansion, particularly in emerging economies.
The adhesives sector represents another substantial market for ethyl acetate. Its use in the production of flexible packaging adhesives, laminations, and pressure-sensitive adhesives has seen a surge in demand. The rise of e-commerce and changes in consumer packaging preferences have further boosted this trend, with ethyl acetate playing a pivotal role in creating innovative, sustainable packaging solutions.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent in the synthesis of various drugs and as an extraction medium. The growing pharmaceutical sector, driven by an aging population and increased healthcare spending, has led to a higher demand for ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing processes.
The electronics industry also contributes significantly to the market demand for ethyl acetate. Its application in the production of printed circuit boards and as a cleaning agent for electronic components has grown with the expansion of the electronics market, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific.
The food and beverage industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. With changing consumer preferences towards natural and organic products, the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector has seen steady growth.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have led to increased interest in bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources. This trend aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly industrial processes, opening new avenues for innovation and market expansion.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to be the fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization and economic growth. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-quality, specialized applications of ethyl acetate in various industries.
In conclusion, the market demand for ethyl acetate is robust and diverse, spanning multiple industries and geographical regions. Its role in facilitating industrial innovations is evident across sectors, from coatings and adhesives to pharmaceuticals and electronics. The compound's versatility, coupled with growing environmental consciousness, positions ethyl acetate as a key component in driving sustainable industrial growth and innovation.
Technical Challenges and Limitations
Despite the widespread use of ethyl acetate in various industries, several technical challenges and limitations persist in its production and application. One of the primary concerns is the environmental impact associated with its synthesis. Traditional production methods often involve the use of petrochemical feedstocks, which contribute to carbon emissions and raise sustainability issues. Developing greener production processes that utilize renewable resources remains a significant challenge for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Another technical limitation lies in the purification of ethyl acetate. The presence of impurities, such as water and acetic acid, can significantly affect the quality and performance of the final product. Achieving high purity levels while maintaining cost-effectiveness in large-scale production is an ongoing challenge. Advanced separation techniques and innovative purification methods are needed to overcome this hurdle and meet the stringent quality requirements of various industries.
The volatility of ethyl acetate poses challenges in handling and storage. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it prone to evaporation, leading to potential product loss and environmental concerns. Developing improved containment systems and implementing effective vapor recovery technologies are crucial to mitigate these issues and ensure safe handling throughout the supply chain.
Ethyl acetate's flammability and potential for forming explosive mixtures with air present safety concerns in industrial settings. Implementing robust safety measures and engineering controls to prevent accidents and minimize risks during production, storage, and transportation is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers and end-users alike.
In terms of application limitations, ethyl acetate's compatibility with certain materials can be problematic. It may cause degradation or swelling of some plastics and rubbers, limiting its use in specific applications or requiring additional protective measures. Research into compatible materials and the development of resistant coatings or additives is necessary to expand its applicability across diverse industries.
The solvent properties of ethyl acetate, while beneficial in many applications, can also be a limitation in certain scenarios. Its high solvency power may lead to excessive dissolution or extraction of unwanted components in some processes, requiring careful control and optimization of usage parameters. Developing formulations that balance the solvent properties of ethyl acetate with other desired characteristics remains a challenge in various industrial applications.
Lastly, regulatory constraints and evolving environmental standards pose ongoing challenges for the ethyl acetate industry. Compliance with stringent emissions regulations and the need for sustainable production practices require continuous innovation in process technologies and waste management strategies. Adapting to these changing regulatory landscapes while maintaining economic viability is a significant challenge for manufacturers and users of ethyl acetate.
Another technical limitation lies in the purification of ethyl acetate. The presence of impurities, such as water and acetic acid, can significantly affect the quality and performance of the final product. Achieving high purity levels while maintaining cost-effectiveness in large-scale production is an ongoing challenge. Advanced separation techniques and innovative purification methods are needed to overcome this hurdle and meet the stringent quality requirements of various industries.
The volatility of ethyl acetate poses challenges in handling and storage. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it prone to evaporation, leading to potential product loss and environmental concerns. Developing improved containment systems and implementing effective vapor recovery technologies are crucial to mitigate these issues and ensure safe handling throughout the supply chain.
Ethyl acetate's flammability and potential for forming explosive mixtures with air present safety concerns in industrial settings. Implementing robust safety measures and engineering controls to prevent accidents and minimize risks during production, storage, and transportation is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers and end-users alike.
In terms of application limitations, ethyl acetate's compatibility with certain materials can be problematic. It may cause degradation or swelling of some plastics and rubbers, limiting its use in specific applications or requiring additional protective measures. Research into compatible materials and the development of resistant coatings or additives is necessary to expand its applicability across diverse industries.
The solvent properties of ethyl acetate, while beneficial in many applications, can also be a limitation in certain scenarios. Its high solvency power may lead to excessive dissolution or extraction of unwanted components in some processes, requiring careful control and optimization of usage parameters. Developing formulations that balance the solvent properties of ethyl acetate with other desired characteristics remains a challenge in various industrial applications.
Lastly, regulatory constraints and evolving environmental standards pose ongoing challenges for the ethyl acetate industry. Compliance with stringent emissions regulations and the need for sustainable production practices require continuous innovation in process technologies and waste management strategies. Adapting to these changing regulatory landscapes while maintaining economic viability is a significant challenge for manufacturers and users of ethyl acetate.
Current Industrial Solutions
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods are employed for the production and purification of ethyl acetate, including esterification reactions, distillation processes, and separation techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the manufacturing of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of catalysts. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate, which is an important industrial solvent and chemical intermediate.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a solvent for extractions, reactions, and formulations. It is particularly useful in the production of pharmaceuticals, coatings, and other specialty chemicals due to its favorable properties and relatively low toxicity.
- Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science: Ethyl acetate plays a role in polymer and material science applications, such as in the preparation of polymer solutions, as a component in adhesive formulations, and in the production of various composite materials. Its use can affect the properties and performance of the resulting materials.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Research and development efforts focus on improving the environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use. This includes developing greener production methods, enhancing recycling processes, and implementing safety measures for handling and storage of the compound.
- Novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate: Investigations into novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate aim to expand its potential applications and improve its properties. This includes the synthesis of new compounds based on ethyl acetate and the development of functionalized versions for specific industrial or research purposes.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent and reagent in various chemical processes. It finds applications in extraction, synthesis, and as a reaction medium in different industries, including pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fine chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in coating and adhesive formulations
Ethyl acetate is a key component in many coating and adhesive formulations. It is used as a solvent in paints, varnishes, and adhesives due to its excellent solvency properties and fast evaporation rate, contributing to the performance and application characteristics of these products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate
Processes for recovering and recycling ethyl acetate from industrial waste streams and spent solvents have been developed. These methods aim to reduce environmental impact and improve cost-effectiveness in industries that use large quantities of ethyl acetate.Expand Specific Solutions05 Ethyl acetate as a green solvent alternative
Ethyl acetate is being explored as a more environmentally friendly solvent alternative in various applications. Its relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and favorable physical properties make it an attractive option for replacing more hazardous solvents in certain processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The ethyl acetate market is in a mature growth stage, characterized by steady demand across various industrial applications. The global market size is estimated to be around $3-4 billion, with moderate annual growth projected. Technologically, ethyl acetate production is well-established, with major players like Celanese, Eastman Chemical, and SABIC having advanced manufacturing capabilities. However, innovation continues in areas like green production methods and new applications. Companies such as Resonac and Viridis Chemical are exploring bio-based ethyl acetate production, while research institutions like the University of Campinas and Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics are investigating novel catalysts and processes to improve efficiency and sustainability in ethyl acetate synthesis.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed an innovative process for ethyl acetate production using ethylene and acetic acid as raw materials. This method, known as the Celanese VA-Ethyl Acetate Process, offers significant advantages over traditional esterification routes. The process utilizes a unique catalyst system that allows for high selectivity and conversion rates, resulting in improved product quality and reduced energy consumption[1][3]. Additionally, Celanese has implemented advanced process control systems and heat integration techniques to optimize the production efficiency and minimize waste generation[2].
Strengths: High product purity, improved energy efficiency, and reduced environmental impact. Weaknesses: Potential higher initial capital investment and reliance on proprietary catalyst technology.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel ethyl acetate production process using a fixed-bed reactor system with a heterogeneous catalyst. This approach involves the direct addition of ethanol to acetic acid over a solid acid catalyst, achieving high conversion rates and selectivity. The process incorporates advanced heat recovery systems and utilizes a proprietary catalyst formulation that enhances reaction kinetics and reduces byproduct formation[4][5]. Sinopec has also implemented sophisticated process control algorithms to optimize reaction conditions and maintain consistent product quality across various feedstock compositions[6].
Strengths: Efficient use of raw materials, adaptability to different feedstocks, and improved process stability. Weaknesses: Potential catalyst deactivation issues and the need for periodic catalyst regeneration or replacement.
Innovative Ethyl Acetate Technologies
Direct and selective production of ethyl acetate from acetic acid utilizing a bimetal supported catalyst
PatentWO2010014145A2
Innovation
- A process utilizing a bimetallic catalyst supported on a suitable catalyst support, comprising metals like platinum, palladium, copper, and cobalt, which selectively hydrogenates acetic acid to ethyl acetate with high yield and selectivity, minimizing by-product formation.
Homogeneous iron catalysts for the conversion of ethanol to ethyl acetate and hydrogen
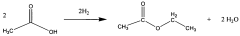
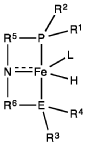
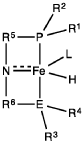
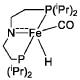
PatentWO2019027965A1
Innovation
- A process utilizing a homogeneous iron catalyst with a tridentate pincer ligand for dehydrogenative coupling of ethanol at moderate temperatures, producing ethyl acetate efficiently and selectively, with iron loadings as low as 0.001 mol%, allowing for continuous operation and easy separation of ethyl acetate from the catalyst.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ethyl acetate in industrial innovations reveals both positive and negative aspects that warrant careful consideration. On the positive side, ethyl acetate is generally considered less harmful to the environment compared to many other solvents used in industrial processes. Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it a more environmentally friendly option in various applications.
Ethyl acetate's volatility allows for easy recovery and recycling, reducing waste and minimizing environmental contamination. This characteristic aligns well with circular economy principles and sustainable manufacturing practices. Furthermore, its use as a replacement for more hazardous solvents in industries such as coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals contributes to overall reduction in environmental pollution and worker exposure to harmful chemicals.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate is not entirely benign. Its production process, typically involving the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, can generate byproducts and require energy inputs that contribute to carbon emissions. The large-scale industrial use of ethyl acetate also raises concerns about potential air and water pollution if not properly managed.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from ethyl acetate can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity. While less severe than many other industrial solvents, these emissions still require careful monitoring and control measures to mitigate their impact on air quality and human health.
Water contamination is another potential environmental risk associated with ethyl acetate use in industrial processes. Improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to the presence of ethyl acetate in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Although ethyl acetate is biodegradable, high concentrations can still pose temporary risks to aquatic life and water quality.
To address these environmental concerns, industries utilizing ethyl acetate are increasingly adopting closed-loop systems, improved recovery techniques, and enhanced emission control technologies. These measures aim to minimize the release of ethyl acetate into the environment and optimize its use in industrial processes.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers significant environmental advantages over many traditional industrial solvents, its widespread use still necessitates careful management and continuous improvement in handling practices. Balancing its benefits in facilitating robust industrial innovations with responsible environmental stewardship remains a key challenge for industries relying on this versatile compound.
Ethyl acetate's volatility allows for easy recovery and recycling, reducing waste and minimizing environmental contamination. This characteristic aligns well with circular economy principles and sustainable manufacturing practices. Furthermore, its use as a replacement for more hazardous solvents in industries such as coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals contributes to overall reduction in environmental pollution and worker exposure to harmful chemicals.
However, the environmental impact of ethyl acetate is not entirely benign. Its production process, typically involving the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, can generate byproducts and require energy inputs that contribute to carbon emissions. The large-scale industrial use of ethyl acetate also raises concerns about potential air and water pollution if not properly managed.
Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from ethyl acetate can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, particularly in urban areas with high industrial activity. While less severe than many other industrial solvents, these emissions still require careful monitoring and control measures to mitigate their impact on air quality and human health.
Water contamination is another potential environmental risk associated with ethyl acetate use in industrial processes. Improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to the presence of ethyl acetate in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Although ethyl acetate is biodegradable, high concentrations can still pose temporary risks to aquatic life and water quality.
To address these environmental concerns, industries utilizing ethyl acetate are increasingly adopting closed-loop systems, improved recovery techniques, and enhanced emission control technologies. These measures aim to minimize the release of ethyl acetate into the environment and optimize its use in industrial processes.
In conclusion, while ethyl acetate offers significant environmental advantages over many traditional industrial solvents, its widespread use still necessitates careful management and continuous improvement in handling practices. Balancing its benefits in facilitating robust industrial innovations with responsible environmental stewardship remains a key challenge for industries relying on this versatile compound.
Regulatory Compliance Landscape
The regulatory compliance landscape for ethyl acetate is complex and multifaceted, reflecting its widespread use across various industries. As a solvent and intermediate in numerous applications, ethyl acetate is subject to a range of regulations aimed at ensuring safety, environmental protection, and quality control.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA inventory, requiring manufacturers and importers to comply with reporting, recordkeeping, and testing requirements. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets permissible exposure limits for workers handling ethyl acetate in industrial settings.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of ethyl acetate within its member states. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers must register ethyl acetate with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide comprehensive safety data. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) regulation further ensures that hazards associated with ethyl acetate are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate's use as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent is regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Both agencies have established guidelines for its use in food products, including maximum residue limits and specific applications where it is permitted.
The pharmaceutical sector faces stringent regulations regarding the use of ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing processes. The FDA's Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations and the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) guidelines on quality of medicines require strict control and documentation of solvents used in pharmaceutical production, including ethyl acetate.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in the ethyl acetate compliance landscape. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its emissions are regulated under various clean air acts globally. Industries using ethyl acetate must often implement emission control technologies and monitoring systems to comply with air quality standards.
Internationally, the transport of ethyl acetate is subject to regulations set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Air Transport Association (IATA), given its classification as a flammable liquid. These regulations dictate packaging, labeling, and handling requirements for safe transportation.
As industries continue to innovate with ethyl acetate, staying abreast of evolving regulations across different jurisdictions remains crucial. Companies must invest in robust compliance management systems to navigate this complex regulatory landscape effectively, ensuring their innovations remain both legally compliant and commercially viable.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA inventory, requiring manufacturers and importers to comply with reporting, recordkeeping, and testing requirements. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets permissible exposure limits for workers handling ethyl acetate in industrial settings.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of ethyl acetate within its member states. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers must register ethyl acetate with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide comprehensive safety data. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) regulation further ensures that hazards associated with ethyl acetate are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate's use as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent is regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Both agencies have established guidelines for its use in food products, including maximum residue limits and specific applications where it is permitted.
The pharmaceutical sector faces stringent regulations regarding the use of ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing processes. The FDA's Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations and the European Medicines Agency's (EMA) guidelines on quality of medicines require strict control and documentation of solvents used in pharmaceutical production, including ethyl acetate.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in the ethyl acetate compliance landscape. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), its emissions are regulated under various clean air acts globally. Industries using ethyl acetate must often implement emission control technologies and monitoring systems to comply with air quality standards.
Internationally, the transport of ethyl acetate is subject to regulations set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the International Air Transport Association (IATA), given its classification as a flammable liquid. These regulations dictate packaging, labeling, and handling requirements for safe transportation.
As industries continue to innovate with ethyl acetate, staying abreast of evolving regulations across different jurisdictions remains crucial. Companies must invest in robust compliance management systems to navigate this complex regulatory landscape effectively, ensuring their innovations remain both legally compliant and commercially viable.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!