How Ethyl Acetate Empowers Industry Synergy?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5, plays a crucial role in fostering industry synergy across various sectors. This colorless liquid ester, characterized by its fruity odor, is produced through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid. Its unique properties, including low toxicity, high solvency, and rapid evaporation rate, make it an indispensable component in numerous industrial applications.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various compounds, catalyzing the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and other specialty chemicals. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an excellent solvent for paints, coatings, and adhesives, contributing to the synergy between the chemical and manufacturing sectors.
The electronics industry benefits from ethyl acetate's cleaning properties, utilizing it in the production of circuit boards and semiconductor components. This application creates a bridge between the chemical and electronics industries, showcasing the compound's role in facilitating cross-sector collaboration.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl acetate finds application as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent. Its natural occurrence in fruits and wines allows for its use in creating artificial fruit flavors and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. This versatility demonstrates how ethyl acetate connects the chemical industry with food production and processing.
The pharmaceutical sector relies on ethyl acetate for drug formulation and as a reaction medium in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Its low toxicity and high purity standards make it suitable for use in various medicinal products, illustrating the compound's importance in linking chemical manufacturing with healthcare industries.
Ethyl acetate's role in the printing industry is significant, serving as a solvent in inks and coatings. Its fast evaporation rate and ability to dissolve various resins make it ideal for flexographic and gravure printing processes. This application highlights the synergy between chemical production and the printing and packaging industries.
The cosmetics and personal care industry utilizes ethyl acetate in nail polish removers and as a solvent in perfumes and other beauty products. This usage demonstrates how the compound bridges the gap between chemical manufacturing and consumer goods production.
In conclusion, ethyl acetate's diverse applications and unique properties enable it to act as a catalyst for industry synergy. By serving multiple sectors simultaneously, it creates interconnections and dependencies that drive innovation, efficiency, and collaboration across various industrial landscapes. This overview underscores the compound's significance in empowering cross-industry cooperation and technological advancement.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various compounds, catalyzing the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and other specialty chemicals. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an excellent solvent for paints, coatings, and adhesives, contributing to the synergy between the chemical and manufacturing sectors.
The electronics industry benefits from ethyl acetate's cleaning properties, utilizing it in the production of circuit boards and semiconductor components. This application creates a bridge between the chemical and electronics industries, showcasing the compound's role in facilitating cross-sector collaboration.
In the food and beverage industry, ethyl acetate finds application as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent. Its natural occurrence in fruits and wines allows for its use in creating artificial fruit flavors and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. This versatility demonstrates how ethyl acetate connects the chemical industry with food production and processing.
The pharmaceutical sector relies on ethyl acetate for drug formulation and as a reaction medium in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Its low toxicity and high purity standards make it suitable for use in various medicinal products, illustrating the compound's importance in linking chemical manufacturing with healthcare industries.
Ethyl acetate's role in the printing industry is significant, serving as a solvent in inks and coatings. Its fast evaporation rate and ability to dissolve various resins make it ideal for flexographic and gravure printing processes. This application highlights the synergy between chemical production and the printing and packaging industries.
The cosmetics and personal care industry utilizes ethyl acetate in nail polish removers and as a solvent in perfumes and other beauty products. This usage demonstrates how the compound bridges the gap between chemical manufacturing and consumer goods production.
In conclusion, ethyl acetate's diverse applications and unique properties enable it to act as a catalyst for industry synergy. By serving multiple sectors simultaneously, it creates interconnections and dependencies that drive innovation, efficiency, and collaboration across various industrial landscapes. This overview underscores the compound's significance in empowering cross-industry cooperation and technological advancement.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for ethyl acetate has been steadily growing, driven by its versatile applications across multiple industries. This solvent's unique properties make it indispensable in various sectors, creating a synergistic effect that boosts overall industrial productivity and innovation.
In the coatings and paints industry, ethyl acetate's demand is particularly robust. Its excellent solvency and low toxicity make it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking environmentally friendly alternatives. The global shift towards water-based and low-VOC formulations has further accelerated the adoption of ethyl acetate in this sector.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another significant market for ethyl acetate. Its use as a solvent in drug manufacturing processes and as an extraction medium for natural compounds has led to increased demand. The growing pharmaceutical sector, especially in emerging economies, is expected to drive further growth in ethyl acetate consumption.
The food and beverage industry also contributes substantially to the market demand for ethyl acetate. Its application as a flavoring agent and in the production of artificial fruit essences has seen steady growth. The rising consumer preference for natural and organic products has paradoxically increased the demand for ethyl acetate in creating natural-identical flavors.
In the electronics industry, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the production of printed circuit boards and semiconductor devices. The ongoing digital transformation and the proliferation of electronic devices worldwide continue to fuel the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
The packaging industry, particularly flexible packaging, has emerged as a significant consumer of ethyl acetate. Its use in adhesives and printing inks for food packaging has grown due to its low toxicity and favorable regulatory status. The e-commerce boom and changing consumer preferences towards convenient, lightweight packaging solutions have further boosted this demand.
The automotive sector's demand for ethyl acetate has been increasing, primarily due to its use in automotive paints and coatings. The growing automotive industry in developing countries and the trend towards electric vehicles, which often require specialized coatings, are expected to sustain this demand.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of major end-use industries. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and increasing focus on sustainable chemical solutions.
The market demand analysis reveals a positive outlook for ethyl acetate, with its ability to empower industry synergy being a key driver. Its cross-industry applications create a network effect, where growth in one sector often leads to increased demand in others, fostering overall industrial development and innovation.
In the coatings and paints industry, ethyl acetate's demand is particularly robust. Its excellent solvency and low toxicity make it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking environmentally friendly alternatives. The global shift towards water-based and low-VOC formulations has further accelerated the adoption of ethyl acetate in this sector.
The pharmaceutical industry represents another significant market for ethyl acetate. Its use as a solvent in drug manufacturing processes and as an extraction medium for natural compounds has led to increased demand. The growing pharmaceutical sector, especially in emerging economies, is expected to drive further growth in ethyl acetate consumption.
The food and beverage industry also contributes substantially to the market demand for ethyl acetate. Its application as a flavoring agent and in the production of artificial fruit essences has seen steady growth. The rising consumer preference for natural and organic products has paradoxically increased the demand for ethyl acetate in creating natural-identical flavors.
In the electronics industry, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the production of printed circuit boards and semiconductor devices. The ongoing digital transformation and the proliferation of electronic devices worldwide continue to fuel the demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
The packaging industry, particularly flexible packaging, has emerged as a significant consumer of ethyl acetate. Its use in adhesives and printing inks for food packaging has grown due to its low toxicity and favorable regulatory status. The e-commerce boom and changing consumer preferences towards convenient, lightweight packaging solutions have further boosted this demand.
The automotive sector's demand for ethyl acetate has been increasing, primarily due to its use in automotive paints and coatings. The growing automotive industry in developing countries and the trend towards electric vehicles, which often require specialized coatings, are expected to sustain this demand.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest market for ethyl acetate, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the presence of major end-use industries. North America and Europe follow, with steady demand from established industries and increasing focus on sustainable chemical solutions.
The market demand analysis reveals a positive outlook for ethyl acetate, with its ability to empower industry synergy being a key driver. Its cross-industry applications create a network effect, where growth in one sector often leads to increased demand in others, fostering overall industrial development and innovation.
Technical Challenges
The development and application of ethyl acetate in industrial synergy face several technical challenges that require innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of production processes to enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Current manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive steps and generate significant waste, necessitating the development of more sustainable production techniques.
Another challenge lies in improving the purity and quality of ethyl acetate for specialized applications. As industries demand higher-grade solvents, there is a growing need for advanced purification technologies that can remove trace impurities without compromising the product's properties or increasing production costs significantly.
The storage and transportation of ethyl acetate present additional technical hurdles. Its volatile nature and flammability require sophisticated containment systems and safety protocols. Developing more stable formulations or innovative packaging solutions that mitigate these risks while maintaining the solvent's effectiveness is a critical area of research.
Furthermore, the integration of ethyl acetate production with other industrial processes to achieve true synergy is complex. Designing efficient systems that can utilize byproducts or waste streams from one process as feedstock for ethyl acetate production, or vice versa, requires advanced process engineering and careful consideration of material compatibility and reaction kinetics.
The recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate from industrial processes also pose significant technical challenges. Developing cost-effective and energy-efficient separation techniques to reclaim the solvent from various mixtures and matrices is crucial for promoting circular economy principles and reducing raw material consumption.
Addressing the environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate use is another major challenge. This includes developing bio-based alternatives or finding ways to produce ethyl acetate from renewable resources without compromising its performance or increasing costs. Additionally, mitigating volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during use and improving end-of-life management of ethyl acetate-containing products are areas requiring innovative solutions.
Lastly, the adaptation of ethyl acetate for emerging technologies and applications presents ongoing challenges. As new industries and processes emerge, there is a constant need to tailor the properties and formulations of ethyl acetate to meet specific requirements, whether in advanced materials manufacturing, nanotechnology, or biotechnology applications.
Another challenge lies in improving the purity and quality of ethyl acetate for specialized applications. As industries demand higher-grade solvents, there is a growing need for advanced purification technologies that can remove trace impurities without compromising the product's properties or increasing production costs significantly.
The storage and transportation of ethyl acetate present additional technical hurdles. Its volatile nature and flammability require sophisticated containment systems and safety protocols. Developing more stable formulations or innovative packaging solutions that mitigate these risks while maintaining the solvent's effectiveness is a critical area of research.
Furthermore, the integration of ethyl acetate production with other industrial processes to achieve true synergy is complex. Designing efficient systems that can utilize byproducts or waste streams from one process as feedstock for ethyl acetate production, or vice versa, requires advanced process engineering and careful consideration of material compatibility and reaction kinetics.
The recovery and recycling of ethyl acetate from industrial processes also pose significant technical challenges. Developing cost-effective and energy-efficient separation techniques to reclaim the solvent from various mixtures and matrices is crucial for promoting circular economy principles and reducing raw material consumption.
Addressing the environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate use is another major challenge. This includes developing bio-based alternatives or finding ways to produce ethyl acetate from renewable resources without compromising its performance or increasing costs. Additionally, mitigating volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during use and improving end-of-life management of ethyl acetate-containing products are areas requiring innovative solutions.
Lastly, the adaptation of ethyl acetate for emerging technologies and applications presents ongoing challenges. As new industries and processes emerge, there is a constant need to tailor the properties and formulations of ethyl acetate to meet specific requirements, whether in advanced materials manufacturing, nanotechnology, or biotechnology applications.
Current Applications
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The processes aim to optimize the production of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described. These include esterification processes, distillation techniques, and the use of specific catalysts to improve yield and purity. The production methods aim to optimize the synthesis of ethyl acetate from ethanol and acetic acid or other precursors.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate. It finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The versatility of ethyl acetate in different chemical reactions and its role in industrial processes are highlighted.
- Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes: Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various compounds. Its use as a solvent in liquid-liquid extraction, chromatography, and other separation techniques is described. The effectiveness of ethyl acetate in isolating specific compounds from complex mixtures is emphasized.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: The environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use are addressed. This includes methods for reducing emissions, improving process safety, and developing more sustainable production routes. Techniques for handling, storing, and disposing of ethyl acetate in an environmentally friendly manner are also discussed.
- Novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate: Research into novel derivatives and modifications of ethyl acetate is presented. This includes the development of new compounds based on ethyl acetate, as well as modifications to its structure to enhance certain properties or create new functionalities. The potential applications of these novel derivatives in various industries are explored.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes and industries. It serves as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials. Its versatility makes it valuable in diverse applications across different sectors.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various compounds. Its properties make it suitable for liquid-liquid extraction, chromatography, and other separation techniques. These processes are used in the purification of natural products, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
The use and handling of ethyl acetate involve environmental and safety considerations. This includes methods for reducing emissions, improving workplace safety, and developing more sustainable production processes. Efforts are made to minimize the environmental impact of ethyl acetate production and use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and formulations of ethyl acetate
Research into new applications and formulations of ethyl acetate is ongoing. This includes its use in novel materials, coatings, and specialty chemicals. Innovations in formulation and application techniques aim to expand the utility of ethyl acetate in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The ethyl acetate industry is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established production processes. The global market size is projected to reach $4.3 billion by 2026, driven by increasing applications in various sectors. Technologically, the industry is well-developed, with major players like Celanese International Corp., China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Eastman Chemical Co. leading innovation. These companies are focusing on improving production efficiency and developing bio-based alternatives. Emerging players such as LanzaTech NZ, Inc. are exploring novel fermentation technologies, while established chemical giants like BASF Corp. and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA are integrating ethyl acetate into their diverse product portfolios, fostering industry synergy across multiple sectors.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed an innovative process for ethyl acetate production using ethylene and acetic acid as raw materials. This method, known as the Celanese VA-EA Process, integrates vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) and ethyl acetate production, resulting in significant synergies[1]. The process involves the reaction of ethylene with acetic acid in the presence of a palladium-based catalyst, followed by hydrogenation to produce ethyl acetate. This integrated approach allows for efficient use of raw materials and energy, reducing overall production costs[2]. Additionally, Celanese has implemented advanced process control systems and heat integration techniques to further optimize the production process, resulting in improved yield and reduced environmental impact[3].
Strengths: Integrated production process, efficient use of raw materials, reduced production costs. Weaknesses: Dependence on ethylene availability, potential catalyst deactivation issues.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a novel ethyl acetate production technology based on the direct etherification of ethanol. This process utilizes a proprietary solid acid catalyst that enables high conversion rates and selectivity[4]. The technology incorporates a reactive distillation column, which combines reaction and separation in a single unit, leading to improved process efficiency and reduced energy consumption[5]. Sinopec has also implemented advanced process intensification techniques, such as microchannel reactors, to enhance heat and mass transfer, resulting in higher yields and reduced equipment footprint[6]. Furthermore, the company has integrated this ethyl acetate production process with its existing petrochemical complexes, creating synergies in raw material supply and utility management.
Strengths: High conversion rates, energy-efficient process, integration with existing petrochemical infrastructure. Weaknesses: Reliance on ethanol as feedstock, potential catalyst deactivation over time.
Innovative Formulations
Process for the production of esters
PatentWO2012162321A2
Innovation
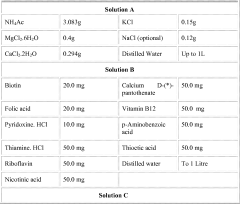
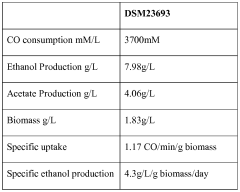
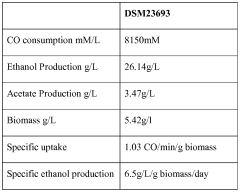
- A process involving anaerobic microbial fermentation of CO to produce ethanol and acetic acid, followed by an esterification reaction to form ethyl acetate, which can be optimized through continuous removal of water and use of reactive distillation to enhance conversion rates.
Process for the production of ethyle acetate
PatentInactiveEP0339330A3
Innovation
- A process utilizing citric acid as a natural catalyst, combined with biologically produced ethanol and acetic acid, eliminates the need for mineral acids, employing a reactor system with specific heating and condensation steps to achieve high purity ethyl acetate production.
Environmental Impact
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound, plays a significant role in various industries, but its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. The production and use of ethyl acetate have both positive and negative effects on the environment, requiring careful consideration and management.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate is its contribution to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. As a volatile substance, ethyl acetate can easily evaporate into the atmosphere, potentially contributing to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. This can have adverse effects on air quality, particularly in urban and industrial areas where its use is more prevalent.
However, compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate is considered relatively less harmful to the environment. It has a lower ozone depletion potential and global warming potential than many chlorinated solvents. Additionally, ethyl acetate is biodegradable, breaking down naturally in the environment over time, which reduces its long-term impact on ecosystems.
The production of ethyl acetate also has environmental implications. Traditional manufacturing processes often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to fossil fuel consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. However, recent advancements in bio-based production methods offer more sustainable alternatives. Ethyl acetate can be produced from renewable resources such as ethanol derived from agricultural waste, potentially reducing its carbon footprint.
Water pollution is another environmental concern related to ethyl acetate. Improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems. While ethyl acetate is less toxic to aquatic life compared to many other solvents, high concentrations can still be harmful. Proper handling, storage, and disposal practices are crucial to mitigate these risks.
In terms of waste management, ethyl acetate presents both challenges and opportunities. As a widely used solvent in various industries, it generates significant amounts of waste. However, its relatively low boiling point allows for efficient recovery and recycling through distillation processes. This not only reduces waste but also minimizes the need for fresh solvent production, contributing to a more circular economy.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate extends to its role in promoting industry synergy. By enabling more efficient processes and serving as a versatile intermediate in various chemical reactions, ethyl acetate can indirectly contribute to reduced energy consumption and waste generation across multiple industries. This synergistic effect has the potential to yield net positive environmental outcomes when considered in a broader industrial context.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ethyl acetate is its contribution to volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. As a volatile substance, ethyl acetate can easily evaporate into the atmosphere, potentially contributing to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. This can have adverse effects on air quality, particularly in urban and industrial areas where its use is more prevalent.
However, compared to some other solvents, ethyl acetate is considered relatively less harmful to the environment. It has a lower ozone depletion potential and global warming potential than many chlorinated solvents. Additionally, ethyl acetate is biodegradable, breaking down naturally in the environment over time, which reduces its long-term impact on ecosystems.
The production of ethyl acetate also has environmental implications. Traditional manufacturing processes often rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to fossil fuel consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. However, recent advancements in bio-based production methods offer more sustainable alternatives. Ethyl acetate can be produced from renewable resources such as ethanol derived from agricultural waste, potentially reducing its carbon footprint.
Water pollution is another environmental concern related to ethyl acetate. Improper disposal or accidental spills can lead to contamination of water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems. While ethyl acetate is less toxic to aquatic life compared to many other solvents, high concentrations can still be harmful. Proper handling, storage, and disposal practices are crucial to mitigate these risks.
In terms of waste management, ethyl acetate presents both challenges and opportunities. As a widely used solvent in various industries, it generates significant amounts of waste. However, its relatively low boiling point allows for efficient recovery and recycling through distillation processes. This not only reduces waste but also minimizes the need for fresh solvent production, contributing to a more circular economy.
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate extends to its role in promoting industry synergy. By enabling more efficient processes and serving as a versatile intermediate in various chemical reactions, ethyl acetate can indirectly contribute to reduced energy consumption and waste generation across multiple industries. This synergistic effect has the potential to yield net positive environmental outcomes when considered in a broader industrial context.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in shaping its industrial applications and synergies. As a widely used solvent and chemical intermediate, ethyl acetate is subject to various regulations across different regions and sectors. These regulations primarily focus on ensuring safety, environmental protection, and quality control throughout the production, handling, and use of ethyl acetate.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA inventory, which means it has been assessed for potential risks to human health and the environment. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for ethyl acetate in workplace settings to protect workers from potential health hazards.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to ethyl acetate. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register the substance and provide safety data. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) maintains a comprehensive database of registered substances, including ethyl acetate, which provides valuable information on its properties, hazards, and safe use.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate is regulated as a food additive in many countries. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved its use as a synthetic flavoring substance and adjuvant. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated ethyl acetate and deemed it safe for use in food applications within specified limits.
The pharmaceutical industry is subject to stringent regulations regarding the use of solvents like ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, enforced by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), set standards for the quality and purity of solvents used in pharmaceutical production.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the ethyl acetate industry. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards that affect the use and handling of ethyl acetate. These regulations aim to reduce air pollution and protect public health by limiting the release of VOCs into the atmosphere.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important focus, regulations promoting the circular economy and waste reduction are influencing the ethyl acetate industry. This has led to increased interest in bio-based ethyl acetate production and recycling initiatives, which are subject to their own set of regulations and incentives in various jurisdictions.
The global nature of the chemical industry necessitates compliance with international agreements and standards. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards, which is crucial for the safe transport and handling of ethyl acetate across borders.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The substance is listed on the TSCA inventory, which means it has been assessed for potential risks to human health and the environment. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits for ethyl acetate in workplace settings to protect workers from potential health hazards.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to ethyl acetate. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register the substance and provide safety data. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) maintains a comprehensive database of registered substances, including ethyl acetate, which provides valuable information on its properties, hazards, and safe use.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate is regulated as a food additive in many countries. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved its use as a synthetic flavoring substance and adjuvant. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated ethyl acetate and deemed it safe for use in food applications within specified limits.
The pharmaceutical industry is subject to stringent regulations regarding the use of solvents like ethyl acetate in drug manufacturing. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, enforced by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), set standards for the quality and purity of solvents used in pharmaceutical production.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the ethyl acetate industry. Many countries have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards that affect the use and handling of ethyl acetate. These regulations aim to reduce air pollution and protect public health by limiting the release of VOCs into the atmosphere.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important focus, regulations promoting the circular economy and waste reduction are influencing the ethyl acetate industry. This has led to increased interest in bio-based ethyl acetate production and recycling initiatives, which are subject to their own set of regulations and incentives in various jurisdictions.
The global nature of the chemical industry necessitates compliance with international agreements and standards. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards, which is crucial for the safe transport and handling of ethyl acetate across borders.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!