Evaluating Future Demand for Ethyl Acetate in Various Sectors
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the formula CH3COOC2H5, is widely used across various industries due to its unique properties and applications. This colorless liquid ester is known for its characteristic sweet smell, reminiscent of pear drops or nail polish remover. It is produced through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, a process that can be carried out using different catalysts and reaction conditions.
The compound's low toxicity, high solvency, and moderate volatility make it an attractive choice for numerous applications. In the coatings industry, ethyl acetate serves as an excellent solvent for a wide range of resins, including nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, and various synthetic polymers. Its fast evaporation rate and ability to produce high-gloss finishes have made it a staple in the production of paints, varnishes, and lacquers.
The pharmaceutical sector relies on ethyl acetate for its role in the extraction and purification of antibiotics and other active pharmaceutical ingredients. Its use extends to the production of various drugs and as a solvent in tablet coating processes. In the food industry, ethyl acetate is employed as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. Its natural occurrence in fruits and wines contributes to its acceptance as a food additive.
The electronics industry utilizes ethyl acetate in the manufacture of printed circuit boards and in cleaning processes. Its ability to dissolve various resins makes it valuable in the production of flexible packaging materials and adhesives. Additionally, ethyl acetate finds applications in the cosmetics industry, particularly in nail polish removers and perfumes.
From an environmental perspective, ethyl acetate is considered less harmful compared to many other organic solvents. It is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment, making it a more sustainable choice in many applications. However, its flammability and potential for forming explosive mixtures with air necessitate careful handling and storage practices.
The global market for ethyl acetate has been steadily growing, driven by increasing demand from end-use industries, particularly in developing economies. Factors such as urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing industrial activities contribute to this trend. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, has emerged as a significant consumer and producer of ethyl acetate, reflecting the shift in manufacturing activities to these countries.
The compound's low toxicity, high solvency, and moderate volatility make it an attractive choice for numerous applications. In the coatings industry, ethyl acetate serves as an excellent solvent for a wide range of resins, including nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, and various synthetic polymers. Its fast evaporation rate and ability to produce high-gloss finishes have made it a staple in the production of paints, varnishes, and lacquers.
The pharmaceutical sector relies on ethyl acetate for its role in the extraction and purification of antibiotics and other active pharmaceutical ingredients. Its use extends to the production of various drugs and as a solvent in tablet coating processes. In the food industry, ethyl acetate is employed as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. Its natural occurrence in fruits and wines contributes to its acceptance as a food additive.
The electronics industry utilizes ethyl acetate in the manufacture of printed circuit boards and in cleaning processes. Its ability to dissolve various resins makes it valuable in the production of flexible packaging materials and adhesives. Additionally, ethyl acetate finds applications in the cosmetics industry, particularly in nail polish removers and perfumes.
From an environmental perspective, ethyl acetate is considered less harmful compared to many other organic solvents. It is biodegradable and does not persist in the environment, making it a more sustainable choice in many applications. However, its flammability and potential for forming explosive mixtures with air necessitate careful handling and storage practices.
The global market for ethyl acetate has been steadily growing, driven by increasing demand from end-use industries, particularly in developing economies. Factors such as urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing industrial activities contribute to this trend. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, has emerged as a significant consumer and producer of ethyl acetate, reflecting the shift in manufacturing activities to these countries.
Market Demand Analysis
The global market for ethyl acetate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. As a key solvent and intermediate in the production of numerous products, ethyl acetate's demand is closely tied to the performance of end-use sectors such as paints and coatings, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging.
In the paints and coatings industry, ethyl acetate serves as an essential solvent due to its excellent solvency and low toxicity. The construction boom in emerging economies and the increasing demand for eco-friendly coatings are expected to fuel the growth of this segment. The automotive sector, another significant consumer of paints and coatings, is likely to contribute to the rising demand for ethyl acetate as vehicle production continues to increase globally.
The adhesives industry represents another major market for ethyl acetate. With the growth of e-commerce and the packaging industry, the demand for adhesives in flexible packaging applications is projected to rise. This trend is particularly evident in the food and beverage sector, where ethyl acetate is used in the production of laminating adhesives for food packaging materials.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role as a solvent in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The expanding pharmaceutical industry, driven by an aging population and increasing healthcare expenditure, is expected to contribute significantly to the growth of ethyl acetate demand.
The food industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. As consumer preferences shift towards healthier and more natural products, the demand for decaffeinated beverages is likely to increase, potentially boosting ethyl acetate consumption in this sector.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to remain the largest and fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate. The region's rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sector, and increasing population are the primary drivers of this growth. China and India, in particular, are anticipated to be key contributors to the rising demand.
However, the market for ethyl acetate is not without challenges. Environmental concerns and stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions may impact its usage in certain applications. This has led to increased research and development efforts focused on bio-based alternatives and more sustainable production methods for ethyl acetate.
In conclusion, the future demand for ethyl acetate across various sectors appears promising, with growth opportunities in multiple industries. The market is expected to evolve in response to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and environmental regulations, potentially opening up new applications and driving innovation in production processes.
In the paints and coatings industry, ethyl acetate serves as an essential solvent due to its excellent solvency and low toxicity. The construction boom in emerging economies and the increasing demand for eco-friendly coatings are expected to fuel the growth of this segment. The automotive sector, another significant consumer of paints and coatings, is likely to contribute to the rising demand for ethyl acetate as vehicle production continues to increase globally.
The adhesives industry represents another major market for ethyl acetate. With the growth of e-commerce and the packaging industry, the demand for adhesives in flexible packaging applications is projected to rise. This trend is particularly evident in the food and beverage sector, where ethyl acetate is used in the production of laminating adhesives for food packaging materials.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role as a solvent in the synthesis of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The expanding pharmaceutical industry, driven by an aging population and increasing healthcare expenditure, is expected to contribute significantly to the growth of ethyl acetate demand.
The food industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. As consumer preferences shift towards healthier and more natural products, the demand for decaffeinated beverages is likely to increase, potentially boosting ethyl acetate consumption in this sector.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to remain the largest and fastest-growing market for ethyl acetate. The region's rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing sector, and increasing population are the primary drivers of this growth. China and India, in particular, are anticipated to be key contributors to the rising demand.
However, the market for ethyl acetate is not without challenges. Environmental concerns and stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions may impact its usage in certain applications. This has led to increased research and development efforts focused on bio-based alternatives and more sustainable production methods for ethyl acetate.
In conclusion, the future demand for ethyl acetate across various sectors appears promising, with growth opportunities in multiple industries. The market is expected to evolve in response to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and environmental regulations, potentially opening up new applications and driving innovation in production processes.
Industry Challenges
The ethyl acetate industry faces several significant challenges that could impact its future demand across various sectors. One of the primary concerns is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly ethanol and acetic acid. These fluctuations can lead to unpredictable production costs, affecting the overall profitability and stability of manufacturers in the ethyl acetate market.
Environmental regulations pose another substantial challenge for the industry. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies, ethyl acetate producers must adapt to more stringent emission controls and waste management practices. This may require significant investments in cleaner production technologies and processes, potentially increasing operational costs and affecting market competitiveness.
The industry also grapples with the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. As consumers and businesses become more environmentally conscious, there is a rising demand for bio-based and renewable solvents. This shift in preference could potentially reduce the market share of traditional ethyl acetate, derived from petrochemical sources, in favor of more sustainable options.
Competition from alternative solvents presents another challenge. Products such as methyl acetate, isopropyl alcohol, and other emerging solvents are gaining traction in various applications, potentially eroding ethyl acetate's market share in certain sectors. Manufacturers must continuously innovate and improve their products to maintain their competitive edge in the face of these alternatives.
The global economic landscape and trade tensions also contribute to the industry's challenges. Tariffs, trade restrictions, and geopolitical uncertainties can disrupt supply chains and affect the international trade of ethyl acetate. This can lead to market fragmentation and regional price disparities, complicating global market dynamics for producers and consumers alike.
Technological advancements in end-use industries may also pose challenges. As industries such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and packaging evolve, their requirements for solvents may change. Ethyl acetate producers must stay abreast of these developments and adapt their products to meet new specifications and performance criteria.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges related to capacity utilization and market saturation in certain regions. Overproduction in some areas, particularly in Asia, can lead to price pressures and reduced profit margins. Balancing supply with demand fluctuations across different geographical markets remains a persistent challenge for ethyl acetate manufacturers.
Environmental regulations pose another substantial challenge for the industry. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental policies, ethyl acetate producers must adapt to more stringent emission controls and waste management practices. This may require significant investments in cleaner production technologies and processes, potentially increasing operational costs and affecting market competitiveness.
The industry also grapples with the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives. As consumers and businesses become more environmentally conscious, there is a rising demand for bio-based and renewable solvents. This shift in preference could potentially reduce the market share of traditional ethyl acetate, derived from petrochemical sources, in favor of more sustainable options.
Competition from alternative solvents presents another challenge. Products such as methyl acetate, isopropyl alcohol, and other emerging solvents are gaining traction in various applications, potentially eroding ethyl acetate's market share in certain sectors. Manufacturers must continuously innovate and improve their products to maintain their competitive edge in the face of these alternatives.
The global economic landscape and trade tensions also contribute to the industry's challenges. Tariffs, trade restrictions, and geopolitical uncertainties can disrupt supply chains and affect the international trade of ethyl acetate. This can lead to market fragmentation and regional price disparities, complicating global market dynamics for producers and consumers alike.
Technological advancements in end-use industries may also pose challenges. As industries such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and packaging evolve, their requirements for solvents may change. Ethyl acetate producers must stay abreast of these developments and adapt their products to meet new specifications and performance criteria.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges related to capacity utilization and market saturation in certain regions. Overproduction in some areas, particularly in Asia, can lead to price pressures and reduced profit margins. Balancing supply with demand fluctuations across different geographical markets remains a persistent challenge for ethyl acetate manufacturers.
Current Applications
01 Production methods for ethyl acetate
Various methods are employed for the production of ethyl acetate, including esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, dehydrogenation of ethanol, and oxidation of ethylene. These processes aim to meet the increasing demand for ethyl acetate in different industries.- Production methods for ethyl acetate: Various methods are employed for the production of ethyl acetate, including esterification of ethanol and acetic acid, dehydrogenation of ethanol, and oxidation of ethylene. These processes aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product to meet increasing demand.
- Purification and separation techniques: Purification and separation techniques are crucial in ethyl acetate production to meet quality standards and increase yield. These may include distillation, extraction, and membrane separation processes, which are continually being improved to enhance efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
- Applications driving demand: The demand for ethyl acetate is driven by its diverse applications in various industries. It is widely used as a solvent in paints, coatings, adhesives, and the pharmaceutical industry. Additionally, it finds applications in food packaging, flexible packaging, and as a flavoring agent in the food industry.
- Market trends and demand analysis: Market trends indicate a growing demand for ethyl acetate, particularly in emerging economies. Factors such as increasing industrialization, growth in end-use industries, and the shift towards eco-friendly solvents contribute to this trend. Market analysis also considers factors like raw material availability and price fluctuations.
- Sustainable production and bio-based alternatives: With increasing focus on sustainability, research is being conducted on bio-based production of ethyl acetate and other environmentally friendly alternatives. This includes the use of renewable feedstocks, development of bio-catalysts, and exploration of green chemistry principles to meet the growing demand while reducing environmental impact.
02 Purification and separation techniques
Efficient purification and separation techniques are crucial in ethyl acetate production to meet quality standards and increase yield. These may include distillation, extraction, and membrane separation processes to remove impurities and achieve high-purity ethyl acetate.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications driving demand
The growing demand for ethyl acetate is driven by its diverse applications in various industries. It is widely used as a solvent in paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, it finds applications in the food industry as a flavoring agent and in the production of flexible packaging materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sustainable production and bio-based alternatives
To address environmental concerns and meet the increasing demand, research is focused on developing sustainable production methods and bio-based alternatives for ethyl acetate. This includes the use of renewable feedstocks, enzymatic processes, and the development of bio-ethyl acetate from agricultural waste materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market trends and demand analysis
The global ethyl acetate market is experiencing steady growth due to increasing industrial applications and consumer demand. Factors such as urbanization, growing disposable income, and the expansion of end-use industries contribute to the rising demand for ethyl acetate. Market analysis and forecasting play crucial roles in understanding and meeting this demand.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Market Players
The ethyl acetate market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size expected to reach $4.3 billion by 2026. The industry is characterized by established production processes and applications across various sectors, including paints, coatings, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging. Key players like Celanese International Corp., China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Eastman Chemical Co. dominate the market with their advanced production capabilities and extensive distribution networks. The technology for ethyl acetate production is well-developed, with ongoing research focused on improving efficiency and sustainability. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Tech University and Tianjin University collaborate with industry leaders to drive innovation in production methods and applications, indicating a steady progression in technological maturity.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has developed an advanced acetyl chain technology for ethyl acetate production. Their process utilizes acetic acid and ethanol as raw materials, employing a highly efficient catalyst system that allows for continuous production with high selectivity[1]. The company has implemented process intensification techniques, resulting in reduced energy consumption and improved yield. Celanese's technology also incorporates an innovative purification system that minimizes waste and ensures high-quality ethyl acetate suitable for various applications, including coatings, pharmaceuticals, and electronics[2].
Strengths: Highly efficient process, reduced energy consumption, high-quality product. Weaknesses: Dependence on acetic acid and ethanol availability, potential sensitivity to raw material price fluctuations.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: Sinopec has developed a novel ethyl acetate production process using a reactive distillation technology. This integrated approach combines reaction and separation in a single unit, significantly improving process efficiency[3]. The company's method utilizes ethanol and acetic acid as feedstocks, with a proprietary catalyst that enhances conversion rates. Sinopec's process also incorporates advanced heat integration strategies, reducing overall energy consumption by up to 30% compared to conventional methods[4]. Additionally, they have implemented a sophisticated control system that optimizes production parameters in real-time, ensuring consistent product quality and maximizing yield.
Strengths: Highly integrated process, reduced energy consumption, improved product consistency. Weaknesses: Complex operation requiring specialized expertise, potentially higher initial capital investment.
Technological Innovations
Process of low energy consumption for preparing a carboxylic acid ester
PatentWO2012123279A1
Innovation
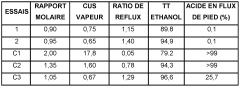
- A process involving the reaction of ethyl alcohol with acetic acid in the presence of a solid acid catalyst, using a reactive distillation system with a centrally placed reaction zone between upper and lower separation zones, optimizing the molar ratio of acetic acid to ethyl alcohol between 0.85 and 0.97, and controlling the reflux ratio between 1.0 and 1.5, significantly reduces energy costs and minimizes acetic acid at the column bottom.
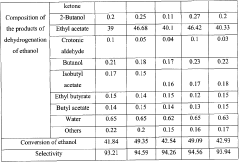
Catalyst for vapor-phase heterogeneous catalytic dehydrogenation of ethanol to ethyl acetate, method for producing ethyl acetate and method for removing impurities from ethanol dehydrogenation reaction
PatentWO2022066136A1
Innovation
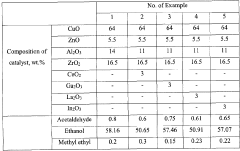
- A catalyst comprising a mixture of CuO, ZnO, ZrO2, and Al2O3 oxides with additional metal oxides like Ce, Ga, La, or In, used for vapor-phase heterogeneous catalytic dehydrogenation at lower temperatures and pressures, achieving high selectivity and conversion of ethyl acetate from technical-grade ethanol with up to 10 wt.% water content.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future demand for ethyl acetate across various sectors. As governments worldwide increasingly prioritize sustainability and environmental protection, industries using ethyl acetate are compelled to adapt their practices and seek alternatives where necessary.
In recent years, many countries have implemented stricter volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards, directly impacting the use of ethyl acetate in industries such as coatings, adhesives, and printing inks. The European Union's VOC Solvents Emissions Directive and similar regulations in North America have led to a shift towards water-based or low-VOC formulations, potentially reducing ethyl acetate demand in these sectors.
However, ethyl acetate's relatively low toxicity compared to other solvents has positioned it favorably in some regulatory frameworks. It is often considered a safer alternative to more harmful solvents, which may drive increased demand in certain applications where substitution is necessary to meet environmental standards.
The pharmaceutical industry, a significant consumer of ethyl acetate, faces stringent regulations regarding solvent residues in final products. While this has led to increased scrutiny of ethyl acetate use, its status as a Class 3 solvent (low toxic potential) under ICH guidelines ensures its continued importance in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate's use as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent is subject to regulations such as the FDA's Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status and the European Food Safety Authority's guidelines. These regulations generally support its use but may impose limits on residual levels in final products.
Emerging environmental concerns, such as the circular economy and lifecycle assessment, are likely to influence future regulations. This could lead to increased focus on the recyclability and biodegradability of ethyl acetate-based products, potentially driving innovation in recovery and reuse technologies.
As climate change mitigation becomes a global priority, regulations aimed at reducing carbon footprints may indirectly affect ethyl acetate demand. Industries may be incentivized to seek bio-based alternatives or improve production efficiencies to meet carbon reduction targets.
The evolving regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for ethyl acetate producers and consumers. While some sectors may see decreased demand due to stricter environmental controls, others may experience growth as ethyl acetate replaces more harmful substances. Staying abreast of regulatory developments and proactively adapting to changing standards will be crucial for stakeholders in the ethyl acetate market.
In recent years, many countries have implemented stricter volatile organic compound (VOC) emission standards, directly impacting the use of ethyl acetate in industries such as coatings, adhesives, and printing inks. The European Union's VOC Solvents Emissions Directive and similar regulations in North America have led to a shift towards water-based or low-VOC formulations, potentially reducing ethyl acetate demand in these sectors.
However, ethyl acetate's relatively low toxicity compared to other solvents has positioned it favorably in some regulatory frameworks. It is often considered a safer alternative to more harmful solvents, which may drive increased demand in certain applications where substitution is necessary to meet environmental standards.
The pharmaceutical industry, a significant consumer of ethyl acetate, faces stringent regulations regarding solvent residues in final products. While this has led to increased scrutiny of ethyl acetate use, its status as a Class 3 solvent (low toxic potential) under ICH guidelines ensures its continued importance in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
In the food industry, ethyl acetate's use as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent is subject to regulations such as the FDA's Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status and the European Food Safety Authority's guidelines. These regulations generally support its use but may impose limits on residual levels in final products.
Emerging environmental concerns, such as the circular economy and lifecycle assessment, are likely to influence future regulations. This could lead to increased focus on the recyclability and biodegradability of ethyl acetate-based products, potentially driving innovation in recovery and reuse technologies.
As climate change mitigation becomes a global priority, regulations aimed at reducing carbon footprints may indirectly affect ethyl acetate demand. Industries may be incentivized to seek bio-based alternatives or improve production efficiencies to meet carbon reduction targets.
The evolving regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for ethyl acetate producers and consumers. While some sectors may see decreased demand due to stricter environmental controls, others may experience growth as ethyl acetate replaces more harmful substances. Staying abreast of regulatory developments and proactively adapting to changing standards will be crucial for stakeholders in the ethyl acetate market.
Supply Chain Dynamics
The supply chain dynamics of ethyl acetate play a crucial role in determining its future demand across various sectors. As a versatile solvent and intermediate, ethyl acetate's supply chain is influenced by several factors that impact its availability, pricing, and market distribution.
Raw material availability is a key driver in the ethyl acetate supply chain. The primary feedstocks for ethyl acetate production are ethanol and acetic acid. Fluctuations in the supply and pricing of these raw materials can significantly affect the production costs and, consequently, the market price of ethyl acetate. The increasing focus on bio-based ethanol production may introduce new dynamics in the raw material supply chain, potentially impacting the overall ethyl acetate market.
Production capacity and geographical distribution of manufacturing facilities are essential elements in the supply chain dynamics. Major producers of ethyl acetate are strategically located in regions with access to raw materials and proximity to key end-use markets. The concentration of production facilities in certain regions can lead to supply chain vulnerabilities, especially in the face of geopolitical tensions or natural disasters.
Transportation and logistics play a vital role in the ethyl acetate supply chain. As a flammable liquid, ethyl acetate requires specialized handling and transportation methods, which can impact its distribution efficiency and costs. The global nature of the ethyl acetate market necessitates a robust international logistics network, including sea freight for long-distance transportation and road or rail for regional distribution.
Inventory management is another critical aspect of the ethyl acetate supply chain. Given the volatile nature of demand in some end-use sectors, maintaining optimal inventory levels is crucial for both producers and consumers. Just-in-time inventory practices in industries like paints and coatings can lead to sudden spikes in demand, potentially causing short-term supply chain disruptions.
The increasing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles is reshaping the ethyl acetate supply chain. There is a growing interest in developing recycling and recovery processes for ethyl acetate, particularly in industries where it is used as a solvent. This trend could potentially lead to the emergence of new players in the supply chain, focusing on ethyl acetate recycling and purification.
Regulatory factors also significantly influence the ethyl acetate supply chain. Changes in environmental regulations, safety standards, or trade policies can impact the production, transportation, and use of ethyl acetate across different regions. Compliance with these regulations often requires adaptations in the supply chain, potentially affecting costs and market dynamics.
Raw material availability is a key driver in the ethyl acetate supply chain. The primary feedstocks for ethyl acetate production are ethanol and acetic acid. Fluctuations in the supply and pricing of these raw materials can significantly affect the production costs and, consequently, the market price of ethyl acetate. The increasing focus on bio-based ethanol production may introduce new dynamics in the raw material supply chain, potentially impacting the overall ethyl acetate market.
Production capacity and geographical distribution of manufacturing facilities are essential elements in the supply chain dynamics. Major producers of ethyl acetate are strategically located in regions with access to raw materials and proximity to key end-use markets. The concentration of production facilities in certain regions can lead to supply chain vulnerabilities, especially in the face of geopolitical tensions or natural disasters.
Transportation and logistics play a vital role in the ethyl acetate supply chain. As a flammable liquid, ethyl acetate requires specialized handling and transportation methods, which can impact its distribution efficiency and costs. The global nature of the ethyl acetate market necessitates a robust international logistics network, including sea freight for long-distance transportation and road or rail for regional distribution.
Inventory management is another critical aspect of the ethyl acetate supply chain. Given the volatile nature of demand in some end-use sectors, maintaining optimal inventory levels is crucial for both producers and consumers. Just-in-time inventory practices in industries like paints and coatings can lead to sudden spikes in demand, potentially causing short-term supply chain disruptions.
The increasing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles is reshaping the ethyl acetate supply chain. There is a growing interest in developing recycling and recovery processes for ethyl acetate, particularly in industries where it is used as a solvent. This trend could potentially lead to the emergence of new players in the supply chain, focusing on ethyl acetate recycling and purification.
Regulatory factors also significantly influence the ethyl acetate supply chain. Changes in environmental regulations, safety standards, or trade policies can impact the production, transportation, and use of ethyl acetate across different regions. Compliance with these regulations often requires adaptations in the supply chain, potentially affecting costs and market dynamics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!