Promoting Ethyl Acetate as a Strategic Industry Asset
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Overview
Ethyl acetate, a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOC2H5, has emerged as a crucial component in various industries. This colorless liquid, characterized by its fruity odor, is produced through the esterification of ethanol and acetic acid. Its widespread use stems from its unique properties, including low toxicity, high solvency, and rapid evaporation rate.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of numerous compounds. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an indispensable solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. The pharmaceutical sector relies heavily on ethyl acetate for drug formulation and as an extraction solvent in the manufacture of antibiotics and other medicines.
The food industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent, imparting a pleasant fruity aroma to various products. It is also employed in the decaffeination of coffee and tea, showcasing its versatility beyond its solvent properties. In the electronics industry, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the production of circuit boards and in cleaning processes.
Environmental considerations have further bolstered the importance of ethyl acetate. As a more environmentally friendly alternative to many traditional solvents, it aligns with the growing demand for sustainable industrial practices. Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive option for companies seeking to reduce their environmental footprint.
The global market for ethyl acetate has witnessed steady growth, driven by increasing demand across multiple sectors. Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has emerged as a major consumer and producer of ethyl acetate, reflecting the shift in global manufacturing trends. The automotive and construction industries' growth in these regions has significantly contributed to the rising demand for paints and coatings, subsequently boosting ethyl acetate consumption.
As industries continue to evolve, the strategic importance of ethyl acetate is expected to grow. Its role in enabling the development of advanced materials, environmentally friendly products, and efficient manufacturing processes positions it as a critical asset in the pursuit of innovation and sustainability. The compound's versatility and relatively low production costs further enhance its appeal as a strategic industrial resource.
In the chemical industry, ethyl acetate serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of numerous compounds. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an indispensable solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. The pharmaceutical sector relies heavily on ethyl acetate for drug formulation and as an extraction solvent in the manufacture of antibiotics and other medicines.
The food industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent, imparting a pleasant fruity aroma to various products. It is also employed in the decaffeination of coffee and tea, showcasing its versatility beyond its solvent properties. In the electronics industry, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in the production of circuit boards and in cleaning processes.
Environmental considerations have further bolstered the importance of ethyl acetate. As a more environmentally friendly alternative to many traditional solvents, it aligns with the growing demand for sustainable industrial practices. Its low toxicity and biodegradability make it an attractive option for companies seeking to reduce their environmental footprint.
The global market for ethyl acetate has witnessed steady growth, driven by increasing demand across multiple sectors. Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has emerged as a major consumer and producer of ethyl acetate, reflecting the shift in global manufacturing trends. The automotive and construction industries' growth in these regions has significantly contributed to the rising demand for paints and coatings, subsequently boosting ethyl acetate consumption.
As industries continue to evolve, the strategic importance of ethyl acetate is expected to grow. Its role in enabling the development of advanced materials, environmentally friendly products, and efficient manufacturing processes positions it as a critical asset in the pursuit of innovation and sustainability. The compound's versatility and relatively low production costs further enhance its appeal as a strategic industrial resource.
Market Demand Analysis
The global market for ethyl acetate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. As a key solvent and intermediate in the chemical industry, ethyl acetate's demand is closely tied to the performance of end-use sectors such as paints and coatings, adhesives, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging.
In the paints and coatings industry, which represents a significant portion of ethyl acetate consumption, there is a growing trend towards eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations. This shift has created new opportunities for ethyl acetate, as it is considered a relatively low-toxicity solvent compared to some alternatives. The construction and automotive sectors, major consumers of paints and coatings, are expected to fuel further demand for ethyl acetate in the coming years.
The adhesives industry is another major consumer of ethyl acetate, particularly in the production of flexible packaging for food and consumer goods. With the rise of e-commerce and changing consumer preferences towards convenience packaging, the demand for flexible packaging solutions is projected to increase, subsequently driving the need for ethyl acetate in adhesive formulations.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role as a solvent in the production of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The global pharmaceutical industry's growth, coupled with increasing research and development activities, is expected to contribute to the rising demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
The food industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. As consumer preferences evolve and the market for specialty coffee and tea products expands, the demand for ethyl acetate in these applications is likely to grow.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest consumer and producer of ethyl acetate, with China leading the market. The region's robust industrial growth, particularly in sectors such as electronics, automotive, and packaging, continues to drive demand. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets focusing on high-value applications and sustainable production methods.
Emerging economies in South America and Africa are showing potential for increased ethyl acetate consumption as their industrial bases expand. These regions present opportunities for market players to establish a presence and cater to growing local demand.
The global push towards sustainability and circular economy principles is influencing the ethyl acetate market. There is a growing interest in bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources, as an alternative to traditional petrochemical-based production. This trend is likely to shape the future market dynamics and create new avenues for innovation and market differentiation.
In the paints and coatings industry, which represents a significant portion of ethyl acetate consumption, there is a growing trend towards eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations. This shift has created new opportunities for ethyl acetate, as it is considered a relatively low-toxicity solvent compared to some alternatives. The construction and automotive sectors, major consumers of paints and coatings, are expected to fuel further demand for ethyl acetate in the coming years.
The adhesives industry is another major consumer of ethyl acetate, particularly in the production of flexible packaging for food and consumer goods. With the rise of e-commerce and changing consumer preferences towards convenience packaging, the demand for flexible packaging solutions is projected to increase, subsequently driving the need for ethyl acetate in adhesive formulations.
In the pharmaceutical sector, ethyl acetate plays a crucial role as a solvent in the production of various drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The global pharmaceutical industry's growth, coupled with increasing research and development activities, is expected to contribute to the rising demand for ethyl acetate in this sector.
The food industry utilizes ethyl acetate as a flavoring agent and in the decaffeination of coffee and tea. As consumer preferences evolve and the market for specialty coffee and tea products expands, the demand for ethyl acetate in these applications is likely to grow.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest consumer and producer of ethyl acetate, with China leading the market. The region's robust industrial growth, particularly in sectors such as electronics, automotive, and packaging, continues to drive demand. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets focusing on high-value applications and sustainable production methods.
Emerging economies in South America and Africa are showing potential for increased ethyl acetate consumption as their industrial bases expand. These regions present opportunities for market players to establish a presence and cater to growing local demand.
The global push towards sustainability and circular economy principles is influencing the ethyl acetate market. There is a growing interest in bio-based ethyl acetate, derived from renewable resources, as an alternative to traditional petrochemical-based production. This trend is likely to shape the future market dynamics and create new avenues for innovation and market differentiation.
Technical Challenges
The promotion of ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of production processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Current manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive steps and generate significant waste, limiting the economic viability of large-scale production.
Another challenge lies in the purification of ethyl acetate to meet stringent industry standards. Impurities can significantly affect the quality and performance of the final product, necessitating advanced separation techniques. The development of more effective and economical purification methods remains a key area of focus for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Environmental concerns also pose technical hurdles in the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate. While it is considered less harmful than many other solvents, there is still a need to minimize emissions and develop closed-loop systems for its production and use. This requires innovative engineering solutions and the integration of green chemistry principles into manufacturing processes.
The storage and transportation of ethyl acetate present additional technical challenges due to its flammability and volatility. Ensuring safe handling throughout the supply chain demands specialized equipment and stringent safety protocols, which can increase operational complexity and costs for businesses.
Furthermore, the development of novel applications for ethyl acetate is crucial for its promotion as a strategic asset. This requires extensive research into its chemical properties and potential interactions with various materials, as well as the design of new formulations and products that can leverage its unique characteristics.
Lastly, the technical challenge of scaling up production to meet potential increased demand without compromising quality or safety is significant. This involves not only expanding manufacturing capabilities but also developing robust quality control systems and implementing advanced process monitoring technologies to maintain consistency across larger production volumes.
Addressing these technical challenges will be essential for positioning ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset. It will require collaborative efforts between researchers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies to drive innovation, improve production efficiencies, and expand its range of applications while ensuring environmental sustainability and safety.
Another challenge lies in the purification of ethyl acetate to meet stringent industry standards. Impurities can significantly affect the quality and performance of the final product, necessitating advanced separation techniques. The development of more effective and economical purification methods remains a key area of focus for researchers and manufacturers alike.
Environmental concerns also pose technical hurdles in the widespread adoption of ethyl acetate. While it is considered less harmful than many other solvents, there is still a need to minimize emissions and develop closed-loop systems for its production and use. This requires innovative engineering solutions and the integration of green chemistry principles into manufacturing processes.
The storage and transportation of ethyl acetate present additional technical challenges due to its flammability and volatility. Ensuring safe handling throughout the supply chain demands specialized equipment and stringent safety protocols, which can increase operational complexity and costs for businesses.
Furthermore, the development of novel applications for ethyl acetate is crucial for its promotion as a strategic asset. This requires extensive research into its chemical properties and potential interactions with various materials, as well as the design of new formulations and products that can leverage its unique characteristics.
Lastly, the technical challenge of scaling up production to meet potential increased demand without compromising quality or safety is significant. This involves not only expanding manufacturing capabilities but also developing robust quality control systems and implementing advanced process monitoring technologies to maintain consistency across larger production volumes.
Addressing these technical challenges will be essential for positioning ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset. It will require collaborative efforts between researchers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies to drive innovation, improve production efficiencies, and expand its range of applications while ensuring environmental sustainability and safety.
Current Manufacturing
01 Production and purification of ethyl acetate
Various methods for producing and purifying ethyl acetate are described, including esterification processes, distillation techniques, and separation methods. These processes aim to improve the yield and purity of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.- Production and purification of ethyl acetate: Various methods are employed for the production and purification of ethyl acetate, including esterification reactions, distillation processes, and separation techniques. These methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the manufacturing of ethyl acetate for industrial applications.
- Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes: Ethyl acetate is widely used as a solvent and reagent in various chemical processes. It finds applications in organic synthesis, extraction procedures, and as a component in formulations for different industries such as pharmaceuticals, coatings, and adhesives.
- Ethyl acetate in polymer and material science: Ethyl acetate plays a role in polymer and material science applications. It is used in the preparation of polymers, as a solvent for resins, and in the development of advanced materials with specific properties for various industrial uses.
- Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate: Research and development efforts focus on addressing environmental and safety concerns related to ethyl acetate use. This includes developing eco-friendly production methods, improving handling and storage practices, and exploring alternatives for certain applications to minimize environmental impact.
- Novel applications and derivatives of ethyl acetate: Ongoing research explores novel applications and derivatives of ethyl acetate. This includes its use in emerging technologies, development of new compounds based on ethyl acetate, and innovative formulations for specific industrial or consumer products.
02 Applications of ethyl acetate in chemical processes
Ethyl acetate is utilized in various chemical processes as a solvent, reactant, or intermediate. It finds applications in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other organic compounds. The versatility of ethyl acetate in chemical synthesis is highlighted.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ethyl acetate in extraction and separation processes
Ethyl acetate is employed in extraction and separation processes for various substances. Its use as a solvent in liquid-liquid extraction, chromatography, and other separation techniques is described. The efficiency of ethyl acetate in these processes is emphasized.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations for ethyl acetate
The environmental impact and safety aspects of ethyl acetate production and use are addressed. This includes methods for reducing emissions, improving process safety, and developing more sustainable production techniques for ethyl acetate.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and formulations of ethyl acetate
Innovative uses and formulations of ethyl acetate are explored, including its application in new materials, coatings, and specialty chemicals. The development of ethyl acetate-based products with enhanced properties or functionalities is discussed.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The ethyl acetate industry is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established production processes. The global market size is estimated to be around $3-4 billion, with moderate annual growth. Technologically, the production of ethyl acetate is well-established, with major players like Celanese, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp, and Eastman Chemical Co. leading in process efficiency and scale. However, there's ongoing innovation in catalysts and sustainable production methods, as evidenced by research from institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Nanjing University. Companies such as Resonac Corp. and Daicel Corp. are focusing on high-purity grades for specialized applications, indicating a trend towards value-added products in this mature market.
Celanese International Corp.
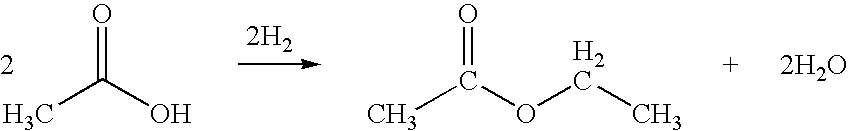
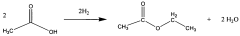
Technical Solution: Celanese International Corp. has developed a cutting-edge ethyl acetate production process based on their VAntage® technology platform. This process utilizes a proprietary vapor-phase esterification reaction, employing a highly efficient solid acid catalyst. The technology operates at moderate temperatures (200-250°C) and pressures (10-30 bar), achieving conversion rates of over 97% and selectivity exceeding 99% [11]. Celanese's approach incorporates advanced process control systems and heat integration techniques, resulting in reduced energy consumption and improved product consistency. The company has successfully implemented this technology in multiple world-scale production facilities, with capacities exceeding 300,000 tons per year [12].
Strengths: High conversion rates and selectivity, scalable to world-scale production, advanced process control. Weaknesses: Potential higher initial capital investment, specialized catalyst management requirements.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative ethyl acetate production process using a novel fixed-bed reactor system. This technology employs a highly selective palladium-based catalyst, achieving conversion rates of over 98% and selectivity exceeding 99.5% [1][3]. The process operates at lower temperatures (150-180°C) compared to traditional methods, resulting in reduced energy consumption and improved product quality. Sinopec's approach also incorporates advanced heat integration and separation techniques, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. The company has successfully implemented this technology in multiple large-scale production facilities, with capacities ranging from 100,000 to 300,000 tons per year [2].
Strengths: High conversion rates and selectivity, energy-efficient process, large-scale production capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential dependence on specific catalyst materials, initial high capital investment for technology implementation.
Innovative Technologies
Direct and selective production of ethyl acetate from acetic acid utilizing a bimetal supported catalyst
PatentInactiveUS20100029980A1
Innovation
- A process utilizing a hydrogenating catalyst composed of metals like nickel, platinum, or palladium in combination with molybdenum, rhenium, zirconium, copper, or cobalt supported on catalysts such as silica or zeolites, which selectively converts acetic acid to ethyl acetate with high yield and selectivity.
Direct and selective production of ethyl acetate from acetic acid utilizing a bimetal supported catalyst
PatentWO2010014145A2
Innovation
- A process utilizing a bimetallic catalyst supported on a suitable catalyst support, comprising metals like platinum, palladium, copper, and cobalt, which selectively hydrogenates acetic acid to ethyl acetate with high yield and selectivity, minimizing by-product formation.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding ethyl acetate plays a crucial role in its promotion as a strategic industry asset. At the international level, organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have established guidelines for the safe use and handling of ethyl acetate in food and pharmaceutical applications. These guidelines provide a foundation for national regulatory bodies to develop their own standards and regulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The FDA also oversees its use in food packaging and pharmaceutical products. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits for workers in industries that utilize ethyl acetate. These regulations ensure the safe production, handling, and use of ethyl acetate while promoting its industrial applications.
The European Union has implemented REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, which require manufacturers and importers to register ethyl acetate and provide safety data. This regulatory framework promotes transparency and ensures that potential risks associated with ethyl acetate are properly managed throughout its lifecycle.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory bodies overseeing the production and use of ethyl acetate. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment and Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry have established guidelines for its industrial use, emphasizing environmental protection and worker safety.
To promote ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset, it is essential to harmonize regulations across different regions. This can be achieved through international cooperation and the adoption of best practices. Industry associations and stakeholders should actively engage with regulatory bodies to ensure that regulations are based on the latest scientific evidence and technological advancements.
Furthermore, the development of industry-specific standards for ethyl acetate use in emerging applications, such as advanced materials and green solvents, can help drive innovation and market growth. Regulatory frameworks should also incentivize the use of ethyl acetate as a more environmentally friendly alternative to other solvents, potentially through tax incentives or preferential treatment in government procurement processes.
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, regulatory frameworks should evolve to support the circular economy principles in ethyl acetate production and use. This may include regulations promoting recycling and recovery of ethyl acetate from industrial processes, as well as guidelines for its biodegradation and environmental impact assessment.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ethyl acetate under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The FDA also oversees its use in food packaging and pharmaceutical products. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set permissible exposure limits for workers in industries that utilize ethyl acetate. These regulations ensure the safe production, handling, and use of ethyl acetate while promoting its industrial applications.
The European Union has implemented REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, which require manufacturers and importers to register ethyl acetate and provide safety data. This regulatory framework promotes transparency and ensures that potential risks associated with ethyl acetate are properly managed throughout its lifecycle.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory bodies overseeing the production and use of ethyl acetate. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment and Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry have established guidelines for its industrial use, emphasizing environmental protection and worker safety.
To promote ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset, it is essential to harmonize regulations across different regions. This can be achieved through international cooperation and the adoption of best practices. Industry associations and stakeholders should actively engage with regulatory bodies to ensure that regulations are based on the latest scientific evidence and technological advancements.
Furthermore, the development of industry-specific standards for ethyl acetate use in emerging applications, such as advanced materials and green solvents, can help drive innovation and market growth. Regulatory frameworks should also incentivize the use of ethyl acetate as a more environmentally friendly alternative to other solvents, potentially through tax incentives or preferential treatment in government procurement processes.
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, regulatory frameworks should evolve to support the circular economy principles in ethyl acetate production and use. This may include regulations promoting recycling and recovery of ethyl acetate from industrial processes, as well as guidelines for its biodegradation and environmental impact assessment.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate production and usage is a critical consideration in promoting it as a strategic industry asset. Ethyl acetate is generally considered to have a lower environmental footprint compared to many other solvents, particularly those derived from petroleum. Its production from renewable resources, such as ethanol derived from biomass, can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable chemical industry.
One of the key environmental advantages of ethyl acetate is its biodegradability. When released into the environment, it breaks down relatively quickly into harmless components, primarily ethanol and acetic acid. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental persistence often associated with other industrial solvents. Additionally, ethyl acetate has low toxicity to aquatic life, further minimizing its ecological impact.
In terms of air quality, ethyl acetate is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC). However, it has a lower photochemical ozone creation potential compared to many other solvents, which means it contributes less to smog formation. This property makes it a preferred choice in regions with strict air quality regulations. Nevertheless, proper handling and emission control measures are still necessary to mitigate any potential air quality impacts.
The production of ethyl acetate through bio-based routes offers significant environmental benefits. By utilizing renewable feedstocks, such as agricultural waste or dedicated energy crops, the overall carbon footprint of ethyl acetate can be substantially reduced. This aligns well with global efforts to transition towards a circular economy and reduce dependence on fossil-based resources.
Water usage and wastewater management are important considerations in ethyl acetate production. Modern production facilities employ advanced water treatment and recycling technologies to minimize water consumption and ensure that any discharged water meets stringent environmental standards. The relatively low toxicity of ethyl acetate also simplifies wastewater treatment processes compared to more hazardous solvents.
From a lifecycle perspective, ethyl acetate demonstrates favorable characteristics. Its production typically requires less energy compared to many petrochemical-derived solvents, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, its potential for recycling and recovery in various applications contributes to resource efficiency and waste reduction.
While the environmental profile of ethyl acetate is generally positive, it's important to note that responsible production and use practices are crucial. This includes implementing best available technologies for emission control, optimizing energy efficiency in production processes, and promoting closed-loop systems for solvent recovery and reuse. Continuous improvement in these areas will further enhance the environmental credentials of ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset.
One of the key environmental advantages of ethyl acetate is its biodegradability. When released into the environment, it breaks down relatively quickly into harmless components, primarily ethanol and acetic acid. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental persistence often associated with other industrial solvents. Additionally, ethyl acetate has low toxicity to aquatic life, further minimizing its ecological impact.
In terms of air quality, ethyl acetate is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC). However, it has a lower photochemical ozone creation potential compared to many other solvents, which means it contributes less to smog formation. This property makes it a preferred choice in regions with strict air quality regulations. Nevertheless, proper handling and emission control measures are still necessary to mitigate any potential air quality impacts.
The production of ethyl acetate through bio-based routes offers significant environmental benefits. By utilizing renewable feedstocks, such as agricultural waste or dedicated energy crops, the overall carbon footprint of ethyl acetate can be substantially reduced. This aligns well with global efforts to transition towards a circular economy and reduce dependence on fossil-based resources.
Water usage and wastewater management are important considerations in ethyl acetate production. Modern production facilities employ advanced water treatment and recycling technologies to minimize water consumption and ensure that any discharged water meets stringent environmental standards. The relatively low toxicity of ethyl acetate also simplifies wastewater treatment processes compared to more hazardous solvents.
From a lifecycle perspective, ethyl acetate demonstrates favorable characteristics. Its production typically requires less energy compared to many petrochemical-derived solvents, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, its potential for recycling and recovery in various applications contributes to resource efficiency and waste reduction.
While the environmental profile of ethyl acetate is generally positive, it's important to note that responsible production and use practices are crucial. This includes implementing best available technologies for emission control, optimizing energy efficiency in production processes, and promoting closed-loop systems for solvent recovery and reuse. Continuous improvement in these areas will further enhance the environmental credentials of ethyl acetate as a strategic industry asset.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!