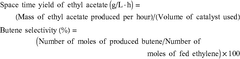How to Address Safety in Ethyl Acetate Manufacturing?
JUN 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ethyl Acetate Safety Overview
Ethyl acetate manufacturing poses significant safety challenges due to the chemical's flammable and volatile nature. This overview addresses key safety considerations in the production process. The primary hazards associated with ethyl acetate include fire, explosion, and exposure risks to workers and the environment.
Fire safety is paramount in ethyl acetate production. The chemical has a low flash point of -4°C (25°F), making it highly flammable. Proper ventilation, spark-proof equipment, and stringent fire suppression systems are essential. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive fire prevention strategies, including regular equipment maintenance, proper storage practices, and emergency response protocols.
Explosion risks are another critical concern. Ethyl acetate vapors can form explosive mixtures with air, particularly in confined spaces. To mitigate this risk, production facilities must maintain vapor concentrations below the lower explosive limit (LEL) through effective ventilation and monitoring systems. Explosion-proof electrical equipment and instrumentation are mandatory in areas where ethyl acetate is present.
Worker safety is a top priority. Exposure to ethyl acetate can cause irritation to eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection, must be provided and consistently used. Regular safety training and drills are crucial to ensure workers understand the risks and proper handling procedures.
Environmental safety is equally important. Ethyl acetate can be harmful to aquatic life and contribute to air pollution. Manufacturers must implement robust containment systems, spill prevention measures, and waste management protocols. Proper disposal of ethyl acetate waste and adherence to environmental regulations are essential to minimize ecological impact.
Process safety management (PSM) plays a vital role in ethyl acetate manufacturing. This systematic approach involves hazard identification, risk assessment, and implementation of control measures. Regular process hazard analyses (PHAs) help identify potential failure points and guide the development of preventive measures.
Continuous monitoring and control systems are crucial for maintaining safe operating conditions. Advanced instrumentation for temperature, pressure, and concentration monitoring, coupled with automated control systems, help prevent deviations that could lead to safety incidents. Emergency shutdown systems should be in place to quickly and safely halt operations if abnormal conditions are detected.
In conclusion, addressing safety in ethyl acetate manufacturing requires a multifaceted approach encompassing fire prevention, explosion mitigation, worker protection, environmental safeguards, and robust process safety management. By implementing comprehensive safety measures and fostering a culture of safety awareness, manufacturers can significantly reduce risks associated with ethyl acetate production.
Fire safety is paramount in ethyl acetate production. The chemical has a low flash point of -4°C (25°F), making it highly flammable. Proper ventilation, spark-proof equipment, and stringent fire suppression systems are essential. Manufacturers must implement comprehensive fire prevention strategies, including regular equipment maintenance, proper storage practices, and emergency response protocols.
Explosion risks are another critical concern. Ethyl acetate vapors can form explosive mixtures with air, particularly in confined spaces. To mitigate this risk, production facilities must maintain vapor concentrations below the lower explosive limit (LEL) through effective ventilation and monitoring systems. Explosion-proof electrical equipment and instrumentation are mandatory in areas where ethyl acetate is present.
Worker safety is a top priority. Exposure to ethyl acetate can cause irritation to eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and respiratory protection, must be provided and consistently used. Regular safety training and drills are crucial to ensure workers understand the risks and proper handling procedures.
Environmental safety is equally important. Ethyl acetate can be harmful to aquatic life and contribute to air pollution. Manufacturers must implement robust containment systems, spill prevention measures, and waste management protocols. Proper disposal of ethyl acetate waste and adherence to environmental regulations are essential to minimize ecological impact.
Process safety management (PSM) plays a vital role in ethyl acetate manufacturing. This systematic approach involves hazard identification, risk assessment, and implementation of control measures. Regular process hazard analyses (PHAs) help identify potential failure points and guide the development of preventive measures.
Continuous monitoring and control systems are crucial for maintaining safe operating conditions. Advanced instrumentation for temperature, pressure, and concentration monitoring, coupled with automated control systems, help prevent deviations that could lead to safety incidents. Emergency shutdown systems should be in place to quickly and safely halt operations if abnormal conditions are detected.
In conclusion, addressing safety in ethyl acetate manufacturing requires a multifaceted approach encompassing fire prevention, explosion mitigation, worker protection, environmental safeguards, and robust process safety management. By implementing comprehensive safety measures and fostering a culture of safety awareness, manufacturers can significantly reduce risks associated with ethyl acetate production.
Market Demand Analysis
The global market for ethyl acetate has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its widespread applications in various industries. The demand for ethyl acetate is primarily fueled by its use as a solvent in paints, coatings, adhesives, and the pharmaceutical industry. As safety concerns in manufacturing processes gain increasing attention, the market for safer ethyl acetate production methods is expanding rapidly.
In the paints and coatings industry, which accounts for a significant portion of ethyl acetate consumption, there is a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly and safe production processes. This trend is pushing manufacturers to adopt safer methods of ethyl acetate production, creating a substantial market opportunity for innovative safety solutions.
The pharmaceutical sector, another major consumer of ethyl acetate, is particularly sensitive to safety issues due to stringent regulatory requirements. As pharmaceutical companies strive to meet these standards, they are actively seeking safer ethyl acetate manufacturing processes, further driving the demand for advanced safety technologies.
The adhesives industry, which relies heavily on ethyl acetate as a solvent, is also showing increased interest in safer production methods. This is partly due to growing awareness of workplace safety and environmental concerns among end-users, creating pressure on adhesive manufacturers to source ethyl acetate from producers with robust safety practices.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the highest growth in ethyl acetate demand. This regional growth is accompanied by an increasing focus on industrial safety, creating a significant market for safety-oriented ethyl acetate manufacturing solutions in these emerging economies.
The market demand for safer ethyl acetate production is further bolstered by stringent government regulations and industry standards. Countries around the world are implementing stricter safety guidelines for chemical manufacturing, compelling ethyl acetate producers to invest in advanced safety technologies and processes.
Moreover, there is a growing trend towards sustainable and green chemistry practices in the chemical industry. This shift is creating additional demand for safer ethyl acetate production methods that not only address immediate safety concerns but also contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
As companies increasingly prioritize worker safety and environmental responsibility, there is a rising willingness to invest in advanced safety technologies for ethyl acetate production. This trend is expected to continue, providing a robust market for innovative safety solutions in the ethyl acetate manufacturing sector.
In the paints and coatings industry, which accounts for a significant portion of ethyl acetate consumption, there is a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly and safe production processes. This trend is pushing manufacturers to adopt safer methods of ethyl acetate production, creating a substantial market opportunity for innovative safety solutions.
The pharmaceutical sector, another major consumer of ethyl acetate, is particularly sensitive to safety issues due to stringent regulatory requirements. As pharmaceutical companies strive to meet these standards, they are actively seeking safer ethyl acetate manufacturing processes, further driving the demand for advanced safety technologies.
The adhesives industry, which relies heavily on ethyl acetate as a solvent, is also showing increased interest in safer production methods. This is partly due to growing awareness of workplace safety and environmental concerns among end-users, creating pressure on adhesive manufacturers to source ethyl acetate from producers with robust safety practices.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the highest growth in ethyl acetate demand. This regional growth is accompanied by an increasing focus on industrial safety, creating a significant market for safety-oriented ethyl acetate manufacturing solutions in these emerging economies.
The market demand for safer ethyl acetate production is further bolstered by stringent government regulations and industry standards. Countries around the world are implementing stricter safety guidelines for chemical manufacturing, compelling ethyl acetate producers to invest in advanced safety technologies and processes.
Moreover, there is a growing trend towards sustainable and green chemistry practices in the chemical industry. This shift is creating additional demand for safer ethyl acetate production methods that not only address immediate safety concerns but also contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
As companies increasingly prioritize worker safety and environmental responsibility, there is a rising willingness to invest in advanced safety technologies for ethyl acetate production. This trend is expected to continue, providing a robust market for innovative safety solutions in the ethyl acetate manufacturing sector.
Current Safety Challenges
Ethyl acetate manufacturing presents several significant safety challenges that require careful consideration and management. The primary concern stems from the highly flammable nature of ethyl acetate, which poses a constant risk of fire and explosion throughout the production process. This volatile organic compound has a low flash point and can form explosive mixtures with air, necessitating stringent control measures to prevent ignition sources and manage vapor concentrations.
Another critical safety issue in ethyl acetate production is the potential for chemical exposure. The raw materials, intermediates, and final product can all cause severe health effects if workers come into contact with them. Inhalation of ethyl acetate vapors can lead to respiratory irritation, dizziness, and in extreme cases, unconsciousness. Skin contact may result in dermatitis, while eye exposure can cause serious damage. Implementing robust personal protective equipment (PPE) protocols and maintaining effective ventilation systems are essential to mitigate these risks.
Process safety management is a complex challenge in ethyl acetate manufacturing. The reaction between ethanol and acetic acid, catalyzed by sulfuric acid, requires precise control of temperature and pressure. Deviations from optimal conditions can lead to runaway reactions, potentially resulting in equipment failure and release of hazardous materials. Ensuring the integrity of reactor vessels, piping systems, and control mechanisms is crucial to prevent such incidents.
Storage and handling of large quantities of ethyl acetate and its precursors present additional safety concerns. Proper containment systems, including secondary containment for spills and leaks, must be in place to prevent environmental contamination and reduce fire hazards. The design and maintenance of storage tanks, transfer systems, and loading/unloading facilities require careful engineering to minimize the risk of accidents.
Waste management and disposal in ethyl acetate production also pose significant safety challenges. The process generates various by-products and waste streams that may be hazardous or environmentally harmful. Proper treatment, storage, and disposal of these materials are essential to comply with regulations and protect both workers and the environment.
Lastly, the potential for human error remains a persistent safety challenge in ethyl acetate manufacturing. Complex processes, high-pressure systems, and the handling of hazardous materials demand a well-trained workforce with a strong safety culture. Developing comprehensive training programs, implementing clear standard operating procedures, and fostering a culture of safety awareness are critical to addressing this human factor in industrial safety.
Another critical safety issue in ethyl acetate production is the potential for chemical exposure. The raw materials, intermediates, and final product can all cause severe health effects if workers come into contact with them. Inhalation of ethyl acetate vapors can lead to respiratory irritation, dizziness, and in extreme cases, unconsciousness. Skin contact may result in dermatitis, while eye exposure can cause serious damage. Implementing robust personal protective equipment (PPE) protocols and maintaining effective ventilation systems are essential to mitigate these risks.
Process safety management is a complex challenge in ethyl acetate manufacturing. The reaction between ethanol and acetic acid, catalyzed by sulfuric acid, requires precise control of temperature and pressure. Deviations from optimal conditions can lead to runaway reactions, potentially resulting in equipment failure and release of hazardous materials. Ensuring the integrity of reactor vessels, piping systems, and control mechanisms is crucial to prevent such incidents.
Storage and handling of large quantities of ethyl acetate and its precursors present additional safety concerns. Proper containment systems, including secondary containment for spills and leaks, must be in place to prevent environmental contamination and reduce fire hazards. The design and maintenance of storage tanks, transfer systems, and loading/unloading facilities require careful engineering to minimize the risk of accidents.
Waste management and disposal in ethyl acetate production also pose significant safety challenges. The process generates various by-products and waste streams that may be hazardous or environmentally harmful. Proper treatment, storage, and disposal of these materials are essential to comply with regulations and protect both workers and the environment.
Lastly, the potential for human error remains a persistent safety challenge in ethyl acetate manufacturing. Complex processes, high-pressure systems, and the handling of hazardous materials demand a well-trained workforce with a strong safety culture. Developing comprehensive training programs, implementing clear standard operating procedures, and fostering a culture of safety awareness are critical to addressing this human factor in industrial safety.
Existing Safety Solutions
01 Safety measures in industrial processes
Ethyl acetate safety in industrial processes involves implementing proper handling procedures, ventilation systems, and protective equipment. This includes using closed systems, monitoring vapor concentrations, and providing adequate personal protective equipment for workers to minimize exposure risks.- Safety measures in industrial processes: Ethyl acetate safety in industrial processes involves implementing proper handling procedures, ventilation systems, and protective equipment. This includes using closed systems, monitoring vapor concentrations, and providing adequate personal protective equipment to workers to minimize exposure risks during manufacturing, distillation, and purification processes.
- Environmental and disposal considerations: Proper disposal and environmental management of ethyl acetate are crucial for safety. This includes implementing recovery and recycling systems, treating waste streams, and using appropriate containment methods to prevent soil and water contamination. Adhering to local regulations and guidelines for chemical waste management is essential.
- Fire and explosion prevention: Ethyl acetate is highly flammable, necessitating specific fire and explosion prevention measures. This includes proper storage in cool, well-ventilated areas away from ignition sources, using explosion-proof electrical equipment, and implementing fire suppression systems. Regular safety inspections and maintenance of storage facilities are crucial.
- Health hazards and exposure control: Ethyl acetate can pose health risks through inhalation, skin contact, and ingestion. Safety measures include providing adequate ventilation, using appropriate personal protective equipment, and implementing exposure monitoring programs. Regular health check-ups for workers and maintaining safety data sheets are important for managing potential health hazards.
- Transportation and storage safety: Safe transportation and storage of ethyl acetate require specific precautions. This includes using appropriate containers, labeling according to hazardous material regulations, and following proper loading and unloading procedures. Implementing spill prevention and response plans, as well as training personnel in safe handling practices, are essential for maintaining safety during transport and storage.
02 Fire and explosion prevention
Due to its flammable nature, ethyl acetate requires specific fire and explosion prevention measures. These include proper storage in fire-resistant containers, implementing grounding and bonding procedures to prevent static electricity buildup, and using explosion-proof electrical equipment in areas where ethyl acetate is present.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and health considerations
Ethyl acetate can have environmental and health impacts if not properly managed. Safety measures include implementing proper disposal methods, using emission control systems to reduce air pollution, and conducting regular health monitoring for workers exposed to ethyl acetate vapors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safe handling in laboratory settings
In laboratory environments, ethyl acetate safety involves using fume hoods for handling, proper labeling and storage of containers, and implementing spill response procedures. Additionally, proper training for laboratory personnel on the safe use and disposal of ethyl acetate is essential.Expand Specific Solutions05 Transportation and storage safety
Ensuring the safe transportation and storage of ethyl acetate involves using appropriate containers, following proper labeling and documentation procedures, and implementing storage facility safety measures. This includes temperature control, segregation from incompatible materials, and regular inspections of storage areas.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The ethyl acetate manufacturing industry is in a mature stage, characterized by established production processes and a stable market demand. The global market size for ethyl acetate is substantial, driven by its widespread use in various industries such as coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Technologically, the production process is well-developed, with major players like Celanese International Corp., BASF Corp., and Eastman Chemical Co. continuously refining their methods for improved efficiency and safety. Companies such as Johnson Matthey Davy Technologies Ltd. and UOP LLC are at the forefront of developing advanced catalysts and process technologies. Emerging players like Nantong Acetic Acid Chemical Co., Ltd. and Jiangsu Baichuan High-Tech New Materials Co., Ltd. are also contributing to the industry's growth, particularly in the Asian market.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has implemented a holistic safety approach in their ethyl acetate manufacturing process, combining advanced engineering controls with robust operational procedures. Their system includes state-of-the-art pressure relief systems, flame arrestors, and inert gas blanketing to prevent fire and explosion risks. Celanese has developed a sophisticated process safety information system that integrates real-time data from multiple sources to provide early warning of potential safety issues[5]. They have also implemented a rigorous management of change process to ensure that safety is maintained during any modifications to the production process or equipment[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive safety systems, strong focus on process safety information, effective change management. Weaknesses: Potential for system complexity, high reliance on technology for safety management.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a comprehensive safety approach for ethyl acetate manufacturing, focusing on process safety management and inherently safer design. Their method includes advanced process control systems, real-time monitoring of critical parameters, and automated safety interlocks. BASF employs a multi-layered safety strategy, incorporating risk assessment tools like HAZOP and LOPA[1]. They have implemented a closed-loop production system to minimize exposure risks and reduce emissions. Additionally, BASF has invested in employee training programs and regular safety audits to maintain a strong safety culture[2].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach, advanced technology integration, strong safety culture. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial implementation costs, complexity in managing multiple safety layers.
Innovative Safety Measures
Method for producing ethyl acetate production catalyst
PatentPendingUS20230330636A1
Innovation
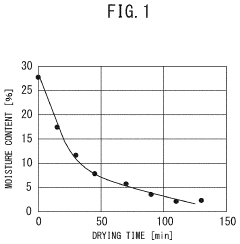
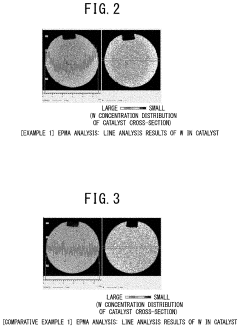
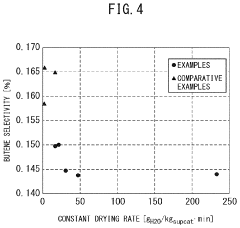
- A method involving impregnating a silica carrier with an aqueous solution of heteropolyacid or its salt at a volume close to 100% of the carrier's water absorption capacity, followed by drying at a controlled rate of 5 to 300 gH2O/kgsupcat·min, ensures a high amount of active ingredient is supported on the carrier surface, enhancing catalyst activity and selectivity.
Method for producing ethyl acetate
PatentPendingUS20250002441A1
Innovation
- Controlling the palladium content in the catalyst within the range of 0.1 to 14 ppb by mass in a heteropolyacid or its salt supported on a carrier, such as silica, suppresses side reactions and ensures stable long-term operation.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of addressing safety in ethyl acetate manufacturing. The production of this widely used solvent is subject to stringent regulations and standards set by various governmental and industry bodies. Manufacturers must adhere to these regulations to ensure the safety of workers, the environment, and end-users of ethyl acetate products.
One of the primary regulatory frameworks governing ethyl acetate production is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States. OSHA mandates specific safety measures, including proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols. Compliance with these standards is essential to minimize the risk of workplace accidents and exposure to hazardous chemicals.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in ethyl acetate manufacturing safety. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces strict guidelines on emissions control, waste management, and spill prevention. Manufacturers must implement robust environmental management systems to comply with these regulations, which may include installing air pollution control devices, implementing proper waste disposal procedures, and developing comprehensive spill response plans.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another crucial compliance requirement for ethyl acetate manufacturers operating in or exporting to European markets. REACH mandates thorough documentation of chemical properties, safety assessments, and risk management measures. Compliance with REACH ensures that ethyl acetate production meets the EU's high standards for chemical safety and environmental protection.
Industry-specific standards, such as those set by the American Chemistry Council's Responsible Care program, provide additional guidelines for safe ethyl acetate manufacturing. These voluntary standards often go beyond regulatory requirements, promoting best practices in process safety, product stewardship, and community engagement.
To ensure regulatory compliance, ethyl acetate manufacturers must implement comprehensive management systems that integrate safety considerations into all aspects of their operations. This includes regular audits, employee training programs, and continuous improvement initiatives. Documentation and record-keeping are crucial components of compliance, as they demonstrate adherence to regulations and facilitate inspections by regulatory authorities.
Staying up-to-date with evolving regulations is essential for maintaining compliance in ethyl acetate manufacturing. Companies must actively monitor changes in regulatory landscapes across different jurisdictions and adapt their processes accordingly. This may involve participating in industry associations, engaging with regulatory bodies, and investing in compliance management software to streamline regulatory tracking and reporting.
One of the primary regulatory frameworks governing ethyl acetate production is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards in the United States. OSHA mandates specific safety measures, including proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols. Compliance with these standards is essential to minimize the risk of workplace accidents and exposure to hazardous chemicals.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in ethyl acetate manufacturing safety. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces strict guidelines on emissions control, waste management, and spill prevention. Manufacturers must implement robust environmental management systems to comply with these regulations, which may include installing air pollution control devices, implementing proper waste disposal procedures, and developing comprehensive spill response plans.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation is another crucial compliance requirement for ethyl acetate manufacturers operating in or exporting to European markets. REACH mandates thorough documentation of chemical properties, safety assessments, and risk management measures. Compliance with REACH ensures that ethyl acetate production meets the EU's high standards for chemical safety and environmental protection.
Industry-specific standards, such as those set by the American Chemistry Council's Responsible Care program, provide additional guidelines for safe ethyl acetate manufacturing. These voluntary standards often go beyond regulatory requirements, promoting best practices in process safety, product stewardship, and community engagement.
To ensure regulatory compliance, ethyl acetate manufacturers must implement comprehensive management systems that integrate safety considerations into all aspects of their operations. This includes regular audits, employee training programs, and continuous improvement initiatives. Documentation and record-keeping are crucial components of compliance, as they demonstrate adherence to regulations and facilitate inspections by regulatory authorities.
Staying up-to-date with evolving regulations is essential for maintaining compliance in ethyl acetate manufacturing. Companies must actively monitor changes in regulatory landscapes across different jurisdictions and adapt their processes accordingly. This may involve participating in industry associations, engaging with regulatory bodies, and investing in compliance management software to streamline regulatory tracking and reporting.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of ethyl acetate manufacturing is a critical consideration in addressing safety concerns within the industry. The production process involves several potential environmental hazards that require careful management and mitigation strategies. One of the primary environmental risks is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Ethyl acetate itself is a VOC, and its production can lead to emissions of other VOCs as well. These compounds contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on both human health and ecosystems.
Water pollution is another significant environmental concern in ethyl acetate manufacturing. The process generates wastewater that may contain organic solvents, acids, and other chemical contaminants. If not properly treated, this wastewater can harm aquatic ecosystems and potentially contaminate groundwater sources. Additionally, the production of ethyl acetate requires substantial energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change if fossil fuels are the primary energy source.
To address these environmental impacts, manufacturers must implement comprehensive pollution control measures. Advanced air pollution control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers or carbon adsorption systems, can effectively reduce VOC emissions. For wastewater management, on-site treatment facilities employing biological and chemical processes can significantly reduce the pollutant load before discharge. Energy efficiency improvements and the adoption of renewable energy sources can help mitigate the carbon footprint associated with ethyl acetate production.
Waste reduction and recycling initiatives are also crucial in minimizing environmental impact. Implementing closed-loop systems and optimizing production processes can reduce raw material consumption and waste generation. Recovery and reuse of solvents and by-products not only minimize environmental impact but also improve economic efficiency. Furthermore, adopting green chemistry principles in the design of production processes can lead to inherently safer and more environmentally friendly manufacturing methods.
Regulatory compliance and continuous monitoring are essential components of environmental impact management. Manufacturers must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations, which often require regular reporting of emissions and waste management practices. Implementing robust environmental management systems, such as ISO 14001, can help ensure ongoing compliance and drive continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Lastly, life cycle assessment (LCA) of ethyl acetate production can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental impact of the manufacturing process. By considering the entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to product disposal, manufacturers can identify opportunities for improvement and make informed decisions to reduce their environmental footprint. This holistic approach is crucial for developing sustainable and safe manufacturing practices in the ethyl acetate industry.
Water pollution is another significant environmental concern in ethyl acetate manufacturing. The process generates wastewater that may contain organic solvents, acids, and other chemical contaminants. If not properly treated, this wastewater can harm aquatic ecosystems and potentially contaminate groundwater sources. Additionally, the production of ethyl acetate requires substantial energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change if fossil fuels are the primary energy source.
To address these environmental impacts, manufacturers must implement comprehensive pollution control measures. Advanced air pollution control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers or carbon adsorption systems, can effectively reduce VOC emissions. For wastewater management, on-site treatment facilities employing biological and chemical processes can significantly reduce the pollutant load before discharge. Energy efficiency improvements and the adoption of renewable energy sources can help mitigate the carbon footprint associated with ethyl acetate production.
Waste reduction and recycling initiatives are also crucial in minimizing environmental impact. Implementing closed-loop systems and optimizing production processes can reduce raw material consumption and waste generation. Recovery and reuse of solvents and by-products not only minimize environmental impact but also improve economic efficiency. Furthermore, adopting green chemistry principles in the design of production processes can lead to inherently safer and more environmentally friendly manufacturing methods.
Regulatory compliance and continuous monitoring are essential components of environmental impact management. Manufacturers must adhere to local, national, and international environmental regulations, which often require regular reporting of emissions and waste management practices. Implementing robust environmental management systems, such as ISO 14001, can help ensure ongoing compliance and drive continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Lastly, life cycle assessment (LCA) of ethyl acetate production can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental impact of the manufacturing process. By considering the entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to product disposal, manufacturers can identify opportunities for improvement and make informed decisions to reduce their environmental footprint. This holistic approach is crucial for developing sustainable and safe manufacturing practices in the ethyl acetate industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!