Exploring Licensing Requirements for Vehicle-to-Grid Providers
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V2G Technology Background and Objectives
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology represents a transformative approach to energy management that has evolved significantly over the past decade. The concept emerged in the late 1990s but gained substantial momentum after 2010 with the proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs) and smart grid technologies. V2G enables bidirectional power flow between EVs and the electricity grid, allowing vehicles to not only consume energy but also return it to the grid when needed.
The evolution of V2G technology has been driven by several factors, including the growing penetration of renewable energy sources, increasing grid instability issues, and the need for more flexible energy storage solutions. Early V2G implementations focused primarily on frequency regulation services, but the technology has since expanded to encompass peak shaving, demand response, and grid stabilization functions.
Current technological trends indicate a move toward more sophisticated V2G systems with enhanced communication protocols, improved power electronics, and advanced battery management systems. These developments aim to minimize battery degradation while maximizing the economic value of grid services provided by connected vehicles.
The primary technical objectives for V2G deployment include establishing standardized communication interfaces between vehicles and grid operators, developing robust cybersecurity frameworks to protect the integrity of both the energy system and vehicle operations, and creating efficient market mechanisms that fairly compensate vehicle owners for the grid services they provide.
Regulatory frameworks for V2G are still evolving globally, with significant variations across different jurisdictions. A key technical goal is to develop licensing requirements that balance the need for grid reliability and safety with the promotion of innovation and market entry for new V2G service providers.
From a technical perspective, V2G systems must address several critical challenges, including minimizing battery degradation from additional cycling, ensuring seamless integration with existing grid infrastructure, and developing predictive algorithms that optimize vehicle availability for both transportation and grid service needs.
The ultimate objective of V2G technology development is to create a decentralized, resilient energy ecosystem where millions of electric vehicles can collectively function as a massive distributed energy resource, providing critical grid services while generating additional revenue for vehicle owners and reducing the overall cost of transportation electrification.
The evolution of V2G technology has been driven by several factors, including the growing penetration of renewable energy sources, increasing grid instability issues, and the need for more flexible energy storage solutions. Early V2G implementations focused primarily on frequency regulation services, but the technology has since expanded to encompass peak shaving, demand response, and grid stabilization functions.
Current technological trends indicate a move toward more sophisticated V2G systems with enhanced communication protocols, improved power electronics, and advanced battery management systems. These developments aim to minimize battery degradation while maximizing the economic value of grid services provided by connected vehicles.
The primary technical objectives for V2G deployment include establishing standardized communication interfaces between vehicles and grid operators, developing robust cybersecurity frameworks to protect the integrity of both the energy system and vehicle operations, and creating efficient market mechanisms that fairly compensate vehicle owners for the grid services they provide.
Regulatory frameworks for V2G are still evolving globally, with significant variations across different jurisdictions. A key technical goal is to develop licensing requirements that balance the need for grid reliability and safety with the promotion of innovation and market entry for new V2G service providers.
From a technical perspective, V2G systems must address several critical challenges, including minimizing battery degradation from additional cycling, ensuring seamless integration with existing grid infrastructure, and developing predictive algorithms that optimize vehicle availability for both transportation and grid service needs.
The ultimate objective of V2G technology development is to create a decentralized, resilient energy ecosystem where millions of electric vehicles can collectively function as a massive distributed energy resource, providing critical grid services while generating additional revenue for vehicle owners and reducing the overall cost of transportation electrification.
Market Demand Analysis for V2G Services
The Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) market is experiencing significant growth potential as electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerates globally. Current market analysis indicates that the global V2G technology market is projected to reach $17.4 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 48% from 2020. This substantial growth is driven by increasing grid instability issues, rising renewable energy integration challenges, and the expanding EV fleet worldwide.
Primary market demand for V2G services stems from multiple stakeholders across the energy ecosystem. Utility companies represent a major demand segment, seeking V2G solutions to address peak load management, frequency regulation, and grid stabilization. These companies face mounting pressure to balance supply and demand fluctuations, particularly with the increasing penetration of intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
Fleet operators constitute another significant market segment, particularly those managing delivery vehicles, public transportation, and corporate fleets. These operators view V2G as an opportunity to generate additional revenue streams from their vehicle assets during idle periods, potentially offsetting the higher initial costs of electric vehicles.
Residential consumers with EVs represent an emerging but potentially massive market. Consumer surveys indicate growing interest in energy independence and cost reduction opportunities, with approximately 67% of EV owners expressing willingness to participate in V2G programs if properly incentivized. This segment is particularly sensitive to financial benefits, with research suggesting that monetary incentives of 10-15% reduction in electricity costs could drive widespread adoption.
Geographic distribution of V2G market demand shows concentration in regions with high renewable energy penetration and progressive energy policies. Western Europe, particularly Denmark, the Netherlands, and the UK, demonstrates strong market readiness due to supportive regulatory frameworks. North America shows significant potential, especially in California and northeastern states with established carbon reduction goals and grid modernization initiatives.
Market barriers affecting demand include consumer concerns about battery degradation, with studies indicating that approximately 58% of potential V2G participants cite battery lifespan as their primary concern. Additionally, complex tariff structures and the absence of standardized compensation models limit market growth in many regions.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily slowed market development but simultaneously accelerated interest in grid resilience and energy independence, creating new opportunities for V2G service providers. Post-pandemic economic recovery plans in many countries have specifically allocated funding for grid modernization and clean energy initiatives, potentially accelerating V2G adoption timelines.
Primary market demand for V2G services stems from multiple stakeholders across the energy ecosystem. Utility companies represent a major demand segment, seeking V2G solutions to address peak load management, frequency regulation, and grid stabilization. These companies face mounting pressure to balance supply and demand fluctuations, particularly with the increasing penetration of intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
Fleet operators constitute another significant market segment, particularly those managing delivery vehicles, public transportation, and corporate fleets. These operators view V2G as an opportunity to generate additional revenue streams from their vehicle assets during idle periods, potentially offsetting the higher initial costs of electric vehicles.
Residential consumers with EVs represent an emerging but potentially massive market. Consumer surveys indicate growing interest in energy independence and cost reduction opportunities, with approximately 67% of EV owners expressing willingness to participate in V2G programs if properly incentivized. This segment is particularly sensitive to financial benefits, with research suggesting that monetary incentives of 10-15% reduction in electricity costs could drive widespread adoption.
Geographic distribution of V2G market demand shows concentration in regions with high renewable energy penetration and progressive energy policies. Western Europe, particularly Denmark, the Netherlands, and the UK, demonstrates strong market readiness due to supportive regulatory frameworks. North America shows significant potential, especially in California and northeastern states with established carbon reduction goals and grid modernization initiatives.
Market barriers affecting demand include consumer concerns about battery degradation, with studies indicating that approximately 58% of potential V2G participants cite battery lifespan as their primary concern. Additionally, complex tariff structures and the absence of standardized compensation models limit market growth in many regions.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily slowed market development but simultaneously accelerated interest in grid resilience and energy independence, creating new opportunities for V2G service providers. Post-pandemic economic recovery plans in many countries have specifically allocated funding for grid modernization and clean energy initiatives, potentially accelerating V2G adoption timelines.
Current Regulatory Landscape and Challenges
The Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) regulatory landscape remains fragmented and complex across different jurisdictions, creating significant challenges for service providers seeking to enter this emerging market. In the United States, regulatory frameworks vary substantially by state, with California leading through its Rule 21 interconnection standards that specifically address bidirectional power flow. However, most states lack clear V2G-specific regulations, forcing providers to navigate through a patchwork of existing electricity market rules designed primarily for traditional generators.
The European Union has made more coordinated progress through its Clean Energy Package, which recognizes energy storage as a distinct market activity and provides some foundational regulatory principles for V2G services. The UK has implemented specific V2G demonstration regulatory sandboxes, allowing controlled testing of business models while developing appropriate licensing frameworks.
A primary challenge in the current landscape is the dual classification problem: V2G providers often fall between traditional regulatory categories, simultaneously functioning as both electricity consumers and generators. This creates uncertainty regarding which licensing requirements apply and which regulatory body has jurisdiction. For instance, in many markets, V2G providers must obtain both supply licenses and generation permits, significantly increasing compliance costs and administrative burdens.
Grid interconnection requirements present another substantial hurdle. Technical standards for safely connecting V2G systems to the electricity grid remain inconsistent across regions, with many jurisdictions still applying conventional generator interconnection rules that are ill-suited for the dynamic, distributed nature of vehicle batteries. This misalignment often results in unnecessarily stringent technical requirements that increase implementation costs.
Market participation rules further complicate the landscape. In many wholesale electricity markets, minimum capacity thresholds and response time requirements were designed for conventional power plants, effectively excluding smaller V2G aggregators. While some markets have begun implementing aggregator frameworks, these often contain restrictive operational parameters that limit V2G economic viability.
Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations add another layer of complexity. V2G operations involve sensitive customer data and critical infrastructure connections, triggering multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously. Providers must navigate GDPR-like privacy requirements alongside critical infrastructure protection standards, often with unclear guidance on how these frameworks interact in the V2G context.
The absence of standardized carbon accounting methodologies for V2G services also creates uncertainty regarding how these services can participate in carbon markets or renewable energy credit systems, potentially limiting revenue streams that could enhance business model viability.
The European Union has made more coordinated progress through its Clean Energy Package, which recognizes energy storage as a distinct market activity and provides some foundational regulatory principles for V2G services. The UK has implemented specific V2G demonstration regulatory sandboxes, allowing controlled testing of business models while developing appropriate licensing frameworks.
A primary challenge in the current landscape is the dual classification problem: V2G providers often fall between traditional regulatory categories, simultaneously functioning as both electricity consumers and generators. This creates uncertainty regarding which licensing requirements apply and which regulatory body has jurisdiction. For instance, in many markets, V2G providers must obtain both supply licenses and generation permits, significantly increasing compliance costs and administrative burdens.
Grid interconnection requirements present another substantial hurdle. Technical standards for safely connecting V2G systems to the electricity grid remain inconsistent across regions, with many jurisdictions still applying conventional generator interconnection rules that are ill-suited for the dynamic, distributed nature of vehicle batteries. This misalignment often results in unnecessarily stringent technical requirements that increase implementation costs.
Market participation rules further complicate the landscape. In many wholesale electricity markets, minimum capacity thresholds and response time requirements were designed for conventional power plants, effectively excluding smaller V2G aggregators. While some markets have begun implementing aggregator frameworks, these often contain restrictive operational parameters that limit V2G economic viability.
Data privacy and cybersecurity regulations add another layer of complexity. V2G operations involve sensitive customer data and critical infrastructure connections, triggering multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously. Providers must navigate GDPR-like privacy requirements alongside critical infrastructure protection standards, often with unclear guidance on how these frameworks interact in the V2G context.
The absence of standardized carbon accounting methodologies for V2G services also creates uncertainty regarding how these services can participate in carbon markets or renewable energy credit systems, potentially limiting revenue streams that could enhance business model viability.
Current Licensing Frameworks and Solutions
01 Regulatory compliance for V2G technology
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology requires compliance with various regulatory frameworks before implementation. These include obtaining necessary permits, adhering to grid connection standards, and meeting safety certifications. Regulatory bodies may require specific licensing for entities operating V2G systems, particularly regarding electricity trading and grid interaction capabilities. Compliance documentation must be maintained and updated as regulations evolve.- Regulatory compliance for V2G technology: Vehicle-to-Grid technology requires compliance with various regulatory frameworks and licensing requirements before implementation. These regulations ensure the safe and standardized operation of V2G systems across different jurisdictions. Compliance involves meeting technical standards, grid connection protocols, and obtaining necessary permits from energy regulatory bodies. The licensing process typically includes certification of equipment, verification of safety measures, and adherence to local electrical codes.
- Intellectual property management for V2G systems: Managing intellectual property rights is crucial for V2G technology deployment. This includes obtaining patents for innovative V2G components, securing software licenses for grid communication protocols, and establishing licensing agreements for proprietary energy management algorithms. Companies developing V2G solutions must navigate complex IP landscapes to ensure freedom to operate while protecting their innovations through appropriate licensing structures and technology transfer agreements.
- Grid integration certification requirements: V2G systems must meet specific certification requirements for grid integration to ensure compatibility with existing power infrastructure. These certifications verify that V2G equipment can safely interact with the electrical grid without causing disruptions or safety hazards. Requirements typically include testing for power quality, response to grid signals, islanding detection, and compliance with communication protocols. Certification processes vary by region and may involve testing by independent laboratories or utility approval procedures.
- Data security and privacy compliance: V2G technology involves significant data exchange between vehicles, charging infrastructure, and grid operators, necessitating robust security measures and privacy compliance. Licensing requirements often include data protection protocols, secure authentication mechanisms, and compliance with privacy regulations. Operators must implement encryption standards, secure access controls, and transparent data handling practices to protect sensitive information about energy usage patterns, vehicle location, and user behavior.
- Commercial licensing models for V2G services: Various commercial licensing models have emerged for V2G technology deployment, including subscription-based services, revenue-sharing arrangements, and platform licensing. These models define how V2G service providers, vehicle owners, and grid operators share benefits and responsibilities. Licensing agreements typically address compensation for grid services, equipment usage rights, maintenance responsibilities, and liability allocation. The selection of appropriate licensing models impacts the economic viability and market adoption of V2G technology.
02 Intellectual property licensing for V2G systems
Implementing V2G technology often requires licensing of intellectual property rights from patent holders. This includes licensing agreements for proprietary communication protocols, energy management algorithms, and hardware interfaces. Companies must navigate complex IP landscapes to ensure they have proper rights to use the technology commercially. Cross-licensing agreements between automotive manufacturers and energy companies are common in this space.Expand Specific Solutions03 Technical certification requirements for grid connection
V2G systems must meet specific technical certification requirements to connect to the electrical grid. These include standards for power quality, response times, and communication protocols. Certification processes typically involve testing for grid stability impact, electromagnetic compatibility, and cybersecurity measures. Equipment must demonstrate compliance with international standards such as ISO/IEC and regional grid codes before receiving operational licenses.Expand Specific Solutions04 Data security and privacy compliance
V2G technology involves significant data exchange between vehicles, charging infrastructure, and grid operators, necessitating compliance with data protection regulations. Licensing requirements often include demonstrating robust data security measures, user consent mechanisms, and privacy protection frameworks. Operators must implement encryption standards, access controls, and secure authentication methods to protect sensitive information while maintaining operational efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Software licensing for V2G management platforms
V2G systems rely heavily on software platforms that manage energy flow, billing, and grid integration. These platforms require specific software licensing agreements that cover usage rights, modification capabilities, and distribution limitations. Cloud-based V2G management solutions often operate under subscription models with specific terms regarding data ownership and service levels. Open-source components may be incorporated but must comply with their respective license requirements.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Stakeholders
The Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) licensing landscape is currently in an emerging growth phase, characterized by increasing market interest but limited standardized regulatory frameworks. The global V2G market is projected to expand significantly, driven by renewable energy integration and grid stability needs. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across different regions. Leading automotive manufacturers like Toyota, Honda, Volkswagen, and Hyundai are advancing V2G capabilities in their electric vehicle portfolios, while energy sector players such as State Grid Corporation of China are developing supporting infrastructure. Technology companies including IBM and Qualcomm are contributing communication and data management solutions. The competitive environment features cross-industry collaboration between automotive OEMs, utility providers, and technology firms, with regulatory harmonization emerging as a critical success factor.
State Grid Corp. of China
Technical Solution: State Grid has developed a comprehensive V2G licensing framework that integrates with China's national energy infrastructure. Their approach includes a tiered licensing system based on provider capacity and grid impact. The system implements real-time monitoring protocols for V2G operations through their proprietary Grid Integration Management Platform (GIMP), which handles bidirectional energy flow authentication and verification. State Grid has established standardized technical requirements for V2G providers, including communication protocols, safety measures, and grid stability parameters that must be met before licensing approval. Their framework also incorporates a regulatory compliance module that automatically updates as regional regulations change, helping providers maintain compliance across different Chinese provinces with varying requirements. The company has successfully implemented this system across pilot programs in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen, demonstrating scalability and adaptability to different regional grid characteristics.
Strengths: Comprehensive integration with existing national grid infrastructure; scalable across diverse regional requirements; strong technical standardization. Weaknesses: Primarily designed for Chinese regulatory environment; may require significant adaptation for international markets; heavy emphasis on centralized control that may limit innovation from smaller V2G providers.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford has developed the "BlueOval V2G Licensing Navigator," a comprehensive solution designed to help vehicle-to-grid providers navigate the complex licensing landscape. Their approach focuses on creating standardized technical packages that meet or exceed regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions. The system includes a proprietary compliance assessment tool that evaluates V2G hardware and software against current regulations in target markets, identifying gaps and providing remediation pathways. Ford's framework incorporates a "Regulatory Requirements Database" that tracks licensing requirements across all 50 U.S. states and major international markets, updated quarterly to reflect changing regulations. Their approach emphasizes vehicle-side certification, leveraging Ford's established relationships with utility regulators to create pre-approved vehicle configurations that simplify the licensing process for V2G providers using Ford vehicles. The company has also developed standardized testing protocols for bidirectional charging equipment that align with both automotive safety standards and utility interconnection requirements, addressing a key regulatory gap in many jurisdictions. Ford has successfully implemented this framework through pilot programs with utilities in California, Michigan, and the UK, demonstrating its adaptability across different regulatory environments.
Strengths: Strong integration with vehicle certification processes; comprehensive cross-jurisdictional database; established relationships with utility regulators. Weaknesses: Primarily optimized for Ford vehicles; limited focus on smaller-scale V2G applications; requires significant ongoing investment to maintain regulatory database currency.
Critical Regulatory Standards and Compliance
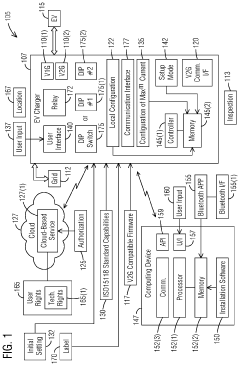
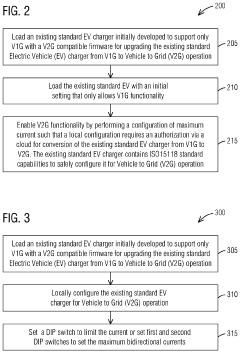
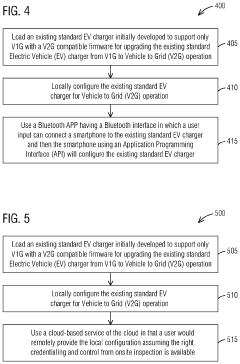
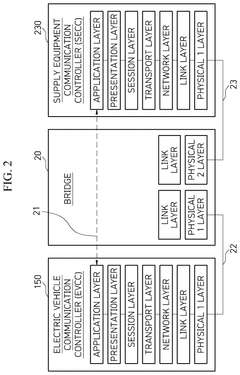
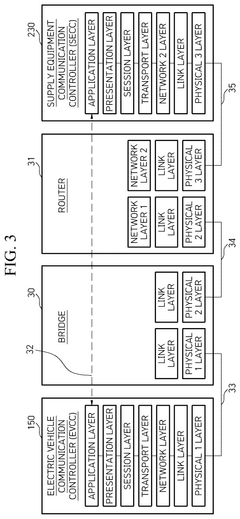
Upgrading an existing standard electric vehicle (EV) charger from grid to vehicle (V1G) to v1g plus vehicle to grid (V2G) operation
PatentPendingUS20240201974A1
Innovation
- A method to locally configure existing standard AC EV chargers with ISO15118 capabilities for V2G operation by loading V2G compatible firmware, authorizing via the cloud, and configuring maximum current, allowing bi-directional charging/discharging through a communication interface.
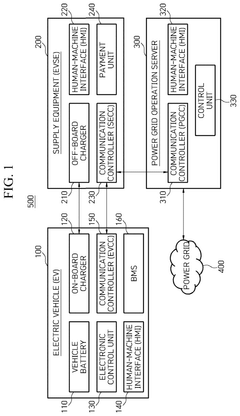
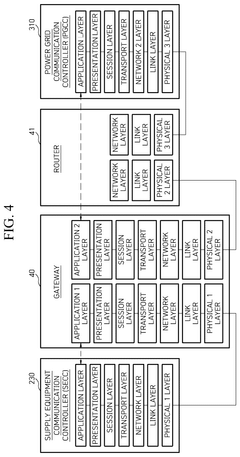
Communication method between electric vehicle, supply equipment and power grid operation server and power transmission device embedded in electric vehicle
PatentPendingUS20240383364A1
Innovation
- A communication method and system that enables electric vehicles to transmit discharge schedules and costs to supply equipment and power grid controllers, facilitating authorization and efficient energy transfer, including a human-machine interface, on-board charger, and electric vehicle communication controller for managing energy transfer and billing.
Cross-Jurisdictional Licensing Comparison
The licensing frameworks for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) providers vary significantly across different jurisdictions, creating a complex regulatory landscape that requires careful navigation. In the United States, licensing requirements are primarily determined at the state level, with California leading the way through its Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) certification program, which specifically addresses V2G capabilities. California requires V2G providers to obtain both utility interconnection approval and certification for bidirectional charging equipment, setting a precedent that other states are beginning to follow.
The European Union has established a more harmonized approach through its Network Code on Demand Connection (DCC), which includes provisions for V2G services. However, implementation details still vary by member state. Germany, for instance, requires V2G providers to register as "flexibility service providers" under the Energy Industry Act, while France has created a specialized "auto-consumption collective" license category that accommodates V2G operations within local energy communities.
Japan has pioneered a unified national licensing framework through its "Aggregator Business Registration System," which explicitly includes V2G providers. This system requires compliance with technical standards for grid connection and cybersecurity protocols, but offers a streamlined single-application process that has accelerated market entry for many providers.
In contrast, China has adopted a pilot-based approach, with different licensing requirements across designated demonstration zones. Shanghai's pilot program requires V2G providers to partner with established utility companies, while Shenzhen has created a new "distributed energy resource aggregator" license category with independent operational authority.
The United Kingdom has developed perhaps the most V2G-specific licensing framework through its Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (Ofgem). The UK system distinguishes between "V2G equipment providers" who require product certification and "V2G service operators" who must obtain an electricity supply license with specific V2G provisions or qualify for the "license lite" regime designed for smaller operators.
Cross-jurisdictional analysis reveals that licensing requirements generally fall into four categories: grid interconnection standards, equipment certification, operational permits, and market participation rules. The most progressive frameworks, such as those in the UK and Japan, have created V2G-specific pathways that recognize the unique dual nature of these services as both consumers and producers of electricity.
For multinational V2G providers, these varying requirements present significant compliance challenges, with some companies reporting that licensing processes account for up to 30% of their market entry costs in new jurisdictions.
The European Union has established a more harmonized approach through its Network Code on Demand Connection (DCC), which includes provisions for V2G services. However, implementation details still vary by member state. Germany, for instance, requires V2G providers to register as "flexibility service providers" under the Energy Industry Act, while France has created a specialized "auto-consumption collective" license category that accommodates V2G operations within local energy communities.
Japan has pioneered a unified national licensing framework through its "Aggregator Business Registration System," which explicitly includes V2G providers. This system requires compliance with technical standards for grid connection and cybersecurity protocols, but offers a streamlined single-application process that has accelerated market entry for many providers.
In contrast, China has adopted a pilot-based approach, with different licensing requirements across designated demonstration zones. Shanghai's pilot program requires V2G providers to partner with established utility companies, while Shenzhen has created a new "distributed energy resource aggregator" license category with independent operational authority.
The United Kingdom has developed perhaps the most V2G-specific licensing framework through its Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (Ofgem). The UK system distinguishes between "V2G equipment providers" who require product certification and "V2G service operators" who must obtain an electricity supply license with specific V2G provisions or qualify for the "license lite" regime designed for smaller operators.
Cross-jurisdictional analysis reveals that licensing requirements generally fall into four categories: grid interconnection standards, equipment certification, operational permits, and market participation rules. The most progressive frameworks, such as those in the UK and Japan, have created V2G-specific pathways that recognize the unique dual nature of these services as both consumers and producers of electricity.
For multinational V2G providers, these varying requirements present significant compliance challenges, with some companies reporting that licensing processes account for up to 30% of their market entry costs in new jurisdictions.
Grid Integration and Security Requirements
The integration of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) systems into existing power infrastructure presents significant technical challenges that must be addressed through comprehensive security and operational requirements. Power grid operators must establish robust technical specifications to ensure V2G providers can safely connect to and interact with the electrical grid without compromising system stability or security. These requirements typically include compliance with grid codes, communication protocols, and response time parameters that maintain grid reliability during bidirectional energy flows.
Security considerations form a critical component of V2G integration requirements. Providers must implement multi-layered cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential cyber attacks that could compromise grid operations. This includes end-to-end encryption of communication channels, secure authentication mechanisms, and regular security audits. The increasing digitalization of grid infrastructure amplifies these concerns, necessitating continuous security updates and vulnerability assessments.
Interoperability standards represent another essential aspect of grid integration. V2G providers must ensure their systems can communicate seamlessly with various grid management systems, smart meters, and other grid-connected devices. Standards such as IEEE 2030.5, OpenADR, and IEC 61850 are increasingly being adopted to facilitate this interoperability, allowing for standardized information exchange between V2G systems and grid operators.
Grid stability protection mechanisms must be incorporated into V2G systems to prevent adverse impacts on power quality and reliability. These include frequency regulation capabilities, voltage support functions, and anti-islanding protection. V2G providers must demonstrate through testing and certification that their systems can respond appropriately to grid disturbances without exacerbating instability issues. This often requires sophisticated power electronics with fast response times and precise control algorithms.
Data management requirements for V2G integration encompass both operational and privacy considerations. Providers must establish secure data handling procedures that comply with relevant privacy regulations while still enabling effective grid management. This includes protocols for collecting, storing, and transmitting energy usage data, vehicle charging patterns, and grid interaction metrics. Grid operators typically require access to specific operational data to forecast available capacity and manage grid resources effectively.
Emergency response protocols constitute a final critical element of grid integration requirements. V2G systems must be capable of responding to grid emergencies according to predefined procedures, potentially including rapid disconnection during critical events or providing emergency power during outages. These capabilities must be thoroughly tested and documented as part of the licensing process to ensure grid resilience and public safety during exceptional circumstances.
Security considerations form a critical component of V2G integration requirements. Providers must implement multi-layered cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential cyber attacks that could compromise grid operations. This includes end-to-end encryption of communication channels, secure authentication mechanisms, and regular security audits. The increasing digitalization of grid infrastructure amplifies these concerns, necessitating continuous security updates and vulnerability assessments.
Interoperability standards represent another essential aspect of grid integration. V2G providers must ensure their systems can communicate seamlessly with various grid management systems, smart meters, and other grid-connected devices. Standards such as IEEE 2030.5, OpenADR, and IEC 61850 are increasingly being adopted to facilitate this interoperability, allowing for standardized information exchange between V2G systems and grid operators.
Grid stability protection mechanisms must be incorporated into V2G systems to prevent adverse impacts on power quality and reliability. These include frequency regulation capabilities, voltage support functions, and anti-islanding protection. V2G providers must demonstrate through testing and certification that their systems can respond appropriately to grid disturbances without exacerbating instability issues. This often requires sophisticated power electronics with fast response times and precise control algorithms.
Data management requirements for V2G integration encompass both operational and privacy considerations. Providers must establish secure data handling procedures that comply with relevant privacy regulations while still enabling effective grid management. This includes protocols for collecting, storing, and transmitting energy usage data, vehicle charging patterns, and grid interaction metrics. Grid operators typically require access to specific operational data to forecast available capacity and manage grid resources effectively.
Emergency response protocols constitute a final critical element of grid integration requirements. V2G systems must be capable of responding to grid emergencies according to predefined procedures, potentially including rapid disconnection during critical events or providing emergency power during outages. These capabilities must be thoroughly tested and documented as part of the licensing process to ensure grid resilience and public safety during exceptional circumstances.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!