Historical Evolution of V12 Engine Configurations
AUG 5, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V12 Engine Origins and Objectives
The V12 engine configuration has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. Its development was driven by the pursuit of power, smoothness, and prestige in automotive and aviation applications. The V12 layout emerged as engineers sought to combine the benefits of inline and V-shaped engine designs, aiming to create a powerplant that could deliver high output while maintaining a relatively compact form factor.
The origins of the V12 can be traced to the pioneering work of Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (DMG) in 1909, when they introduced the first V12 engine for use in racing boats. This early innovation set the stage for the engine's adoption in luxury automobiles and aircraft. The primary objectives behind the V12's development were to achieve greater power output, improved balance, and reduced vibration compared to existing engine configurations.
As the automotive industry evolved, the V12 engine became synonymous with high-performance and luxury vehicles. Manufacturers like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln in the United States, along with European brands such as Rolls-Royce, Daimler, and Ferrari, embraced the V12 configuration to power their flagship models. The engine's ability to produce substantial power while operating smoothly made it ideal for large, prestigious automobiles.
In the aviation sector, the V12 engine played a crucial role during World War I and II. Aircraft manufacturers adopted V12 designs to power fighter planes and bombers, valuing the engine's high power-to-weight ratio and reliability. The Rolls-Royce Merlin, a famous V12 aero engine, became iconic for its use in the Supermarine Spitfire and other Allied aircraft during World War II.
Throughout its evolution, the V12 engine has undergone numerous refinements and innovations. Engineers have continuously worked to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance performance. The introduction of technologies such as fuel injection, variable valve timing, and turbocharging has allowed V12 engines to remain relevant in an era of increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations.
The objectives driving V12 engine development have shifted over time. While power and prestige remain important factors, modern V12 engines also focus on meeting strict emissions standards, improving fuel economy, and integrating with hybrid powertrains. These goals reflect the changing landscape of the automotive industry and the need to balance performance with environmental responsibility.
The origins of the V12 can be traced to the pioneering work of Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (DMG) in 1909, when they introduced the first V12 engine for use in racing boats. This early innovation set the stage for the engine's adoption in luxury automobiles and aircraft. The primary objectives behind the V12's development were to achieve greater power output, improved balance, and reduced vibration compared to existing engine configurations.
As the automotive industry evolved, the V12 engine became synonymous with high-performance and luxury vehicles. Manufacturers like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln in the United States, along with European brands such as Rolls-Royce, Daimler, and Ferrari, embraced the V12 configuration to power their flagship models. The engine's ability to produce substantial power while operating smoothly made it ideal for large, prestigious automobiles.
In the aviation sector, the V12 engine played a crucial role during World War I and II. Aircraft manufacturers adopted V12 designs to power fighter planes and bombers, valuing the engine's high power-to-weight ratio and reliability. The Rolls-Royce Merlin, a famous V12 aero engine, became iconic for its use in the Supermarine Spitfire and other Allied aircraft during World War II.
Throughout its evolution, the V12 engine has undergone numerous refinements and innovations. Engineers have continuously worked to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance performance. The introduction of technologies such as fuel injection, variable valve timing, and turbocharging has allowed V12 engines to remain relevant in an era of increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations.
The objectives driving V12 engine development have shifted over time. While power and prestige remain important factors, modern V12 engines also focus on meeting strict emissions standards, improving fuel economy, and integrating with hybrid powertrains. These goals reflect the changing landscape of the automotive industry and the need to balance performance with environmental responsibility.
Market Demand Analysis for V12 Engines
The market demand for V12 engines has undergone significant shifts over the past decades, reflecting changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and regulatory pressures. Historically, V12 engines were synonymous with luxury, power, and prestige, finding their place in high-end automobiles, racing cars, and even aircraft.
In the automotive sector, V12 engines have maintained a niche but passionate market. Luxury car manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley, and Ferrari have consistently offered V12 options to cater to discerning customers who prioritize performance and exclusivity. These engines are often the flagship powerplants in their respective lineups, commanding premium prices and attracting enthusiasts and collectors alike.
The racing industry has also been a significant driver of V12 engine demand. Formula 1, in particular, saw extensive use of V12 configurations during the 1990s, with iconic manufacturers like Ferrari and Lamborghini pushing the boundaries of engine technology. This racing heritage has translated into sustained interest from motorsport enthusiasts and collectors of high-performance vehicles.
However, the market for V12 engines has faced challenges in recent years. Stringent emissions regulations and a global push towards fuel efficiency have put pressure on manufacturers to downsize engines or explore alternative powertrains. This has led to a decline in the number of V12-powered models available, particularly in mainstream vehicle segments.
Despite these challenges, there remains a dedicated market for V12 engines, particularly in the ultra-luxury and supercar segments. Manufacturers have responded by developing more efficient and technologically advanced V12 engines, often incorporating hybrid systems to meet emissions standards while maintaining the power and character that enthusiasts demand.
The marine industry represents another significant market for V12 engines, with large yachts and commercial vessels utilizing these powerful powerplants. In this sector, the demand for V12 engines has remained relatively stable, driven by the need for high power output and reliability in marine applications.
Looking ahead, the market for V12 engines is likely to become increasingly specialized. While overall volumes may decrease, there is expected to be continued demand from niche markets that value the unique characteristics of V12 configurations. This includes collectors, enthusiasts, and ultra-high-net-worth individuals seeking exclusive, high-performance vehicles.
In conclusion, while facing challenges from regulatory pressures and changing market dynamics, V12 engines continue to hold a significant place in specific market segments. Their future lies in balancing traditional appeal with technological innovation to meet evolving consumer and regulatory demands.
In the automotive sector, V12 engines have maintained a niche but passionate market. Luxury car manufacturers such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley, and Ferrari have consistently offered V12 options to cater to discerning customers who prioritize performance and exclusivity. These engines are often the flagship powerplants in their respective lineups, commanding premium prices and attracting enthusiasts and collectors alike.
The racing industry has also been a significant driver of V12 engine demand. Formula 1, in particular, saw extensive use of V12 configurations during the 1990s, with iconic manufacturers like Ferrari and Lamborghini pushing the boundaries of engine technology. This racing heritage has translated into sustained interest from motorsport enthusiasts and collectors of high-performance vehicles.
However, the market for V12 engines has faced challenges in recent years. Stringent emissions regulations and a global push towards fuel efficiency have put pressure on manufacturers to downsize engines or explore alternative powertrains. This has led to a decline in the number of V12-powered models available, particularly in mainstream vehicle segments.
Despite these challenges, there remains a dedicated market for V12 engines, particularly in the ultra-luxury and supercar segments. Manufacturers have responded by developing more efficient and technologically advanced V12 engines, often incorporating hybrid systems to meet emissions standards while maintaining the power and character that enthusiasts demand.
The marine industry represents another significant market for V12 engines, with large yachts and commercial vessels utilizing these powerful powerplants. In this sector, the demand for V12 engines has remained relatively stable, driven by the need for high power output and reliability in marine applications.
Looking ahead, the market for V12 engines is likely to become increasingly specialized. While overall volumes may decrease, there is expected to be continued demand from niche markets that value the unique characteristics of V12 configurations. This includes collectors, enthusiasts, and ultra-high-net-worth individuals seeking exclusive, high-performance vehicles.
In conclusion, while facing challenges from regulatory pressures and changing market dynamics, V12 engines continue to hold a significant place in specific market segments. Their future lies in balancing traditional appeal with technological innovation to meet evolving consumer and regulatory demands.
Current V12 Technology and Challenges
The V12 engine configuration has long been synonymous with luxury, performance, and engineering excellence. In recent years, however, this iconic engine layout has faced significant challenges and technological shifts. Current V12 engines typically displace between 5.2 and 6.75 liters, producing power outputs ranging from 500 to over 800 horsepower. These engines are primarily found in high-end luxury and sports cars, with manufacturers like Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Rolls-Royce continuing to champion the V12 configuration.
One of the main challenges facing V12 engines is the increasing pressure to meet stringent emissions regulations. Manufacturers have had to implement advanced technologies such as direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Some V12 engines now incorporate hybrid systems to further enhance performance while reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Another significant challenge is the trend towards downsizing and turbocharging in the automotive industry. Many manufacturers are moving away from large-displacement naturally aspirated engines in favor of smaller, turbocharged units that can deliver similar power outputs with improved fuel efficiency. This shift has led to a reduction in the number of V12-powered vehicles on the market.
The complexity and cost of V12 engines present additional challenges. These engines require extensive engineering resources to develop and maintain, and their production costs are significantly higher than those of smaller engines. This factor limits their application to ultra-luxury and high-performance vehicles, where price is less of a concern for consumers.
Despite these challenges, V12 engines continue to evolve. Recent advancements include the use of lightweight materials such as aluminum and carbon fiber to reduce engine weight, improved thermal management systems to enhance efficiency, and the integration of advanced electronic control systems for optimized performance and emissions control.
The future of V12 engines remains uncertain, with some manufacturers committing to their continued development while others are phasing them out in favor of alternative powertrains. The increasing focus on electrification poses a significant threat to the long-term viability of V12 engines, as electric motors can deliver instant torque and high power outputs without the emissions concerns associated with large-displacement internal combustion engines.
In conclusion, while V12 engines continue to represent the pinnacle of internal combustion engine technology, they face substantial challenges in the current automotive landscape. Their survival will likely depend on continued innovation in areas such as materials science, combustion efficiency, and hybridization, as well as the willingness of manufacturers and consumers to support this iconic engine configuration in an increasingly electrified world.
One of the main challenges facing V12 engines is the increasing pressure to meet stringent emissions regulations. Manufacturers have had to implement advanced technologies such as direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Some V12 engines now incorporate hybrid systems to further enhance performance while reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Another significant challenge is the trend towards downsizing and turbocharging in the automotive industry. Many manufacturers are moving away from large-displacement naturally aspirated engines in favor of smaller, turbocharged units that can deliver similar power outputs with improved fuel efficiency. This shift has led to a reduction in the number of V12-powered vehicles on the market.
The complexity and cost of V12 engines present additional challenges. These engines require extensive engineering resources to develop and maintain, and their production costs are significantly higher than those of smaller engines. This factor limits their application to ultra-luxury and high-performance vehicles, where price is less of a concern for consumers.
Despite these challenges, V12 engines continue to evolve. Recent advancements include the use of lightweight materials such as aluminum and carbon fiber to reduce engine weight, improved thermal management systems to enhance efficiency, and the integration of advanced electronic control systems for optimized performance and emissions control.
The future of V12 engines remains uncertain, with some manufacturers committing to their continued development while others are phasing them out in favor of alternative powertrains. The increasing focus on electrification poses a significant threat to the long-term viability of V12 engines, as electric motors can deliver instant torque and high power outputs without the emissions concerns associated with large-displacement internal combustion engines.
In conclusion, while V12 engines continue to represent the pinnacle of internal combustion engine technology, they face substantial challenges in the current automotive landscape. Their survival will likely depend on continued innovation in areas such as materials science, combustion efficiency, and hybridization, as well as the willingness of manufacturers and consumers to support this iconic engine configuration in an increasingly electrified world.
Contemporary V12 Design Solutions
01 V12 Engine Design and Configuration
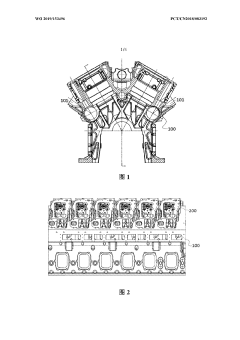
V12 engines are characterized by their unique configuration of twelve cylinders arranged in two banks of six, forming a V-shape. This design allows for a compact engine layout while providing high power output and smooth operation. The V12 configuration is often used in high-performance and luxury vehicles due to its balance of power and refinement.- V12 Engine Design and Configuration: V12 engines are designed with 12 cylinders arranged in two banks of six, forming a V shape. This configuration allows for a compact design while providing high power output and smooth operation. The V12 layout is often used in high-performance and luxury vehicles due to its balance of power and refinement.
- V12 Engine Control Systems: Advanced control systems are implemented in V12 engines to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. These systems may include electronic fuel injection, variable valve timing, and engine management units that continuously adjust engine parameters based on driving conditions and user input.
- V12 Engine Cooling and Lubrication: Efficient cooling and lubrication systems are crucial for V12 engines due to their high power output and heat generation. These systems may incorporate advanced coolant circulation, oil cooling, and precision-engineered components to maintain optimal operating temperatures and reduce wear on engine parts.
- V12 Engine Applications in Vehicles: V12 engines are commonly used in high-end luxury cars, sports cars, and racing vehicles. Their application extends to marine engines for large yachts and some specialized industrial equipment. The choice of a V12 engine often signifies a focus on performance, prestige, and engineering excellence in the vehicle design.
- V12 Engine Emissions and Efficiency Improvements: Modern V12 engines incorporate various technologies to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions while maintaining high performance. These may include start-stop systems, cylinder deactivation, lightweight materials, and advanced exhaust after-treatment systems to meet stringent environmental regulations.
02 V12 Engine Performance Optimization
Various techniques are employed to optimize the performance of V12 engines, including advanced fuel injection systems, variable valve timing, and turbocharging. These technologies help improve power output, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Engineers focus on balancing the engine for minimal vibration and maximizing power-to-weight ratio.Expand Specific Solutions03 V12 Engine Applications in Vehicles
V12 engines are commonly used in high-end luxury cars, sports cars, and racing vehicles. They are also found in some marine applications and specialized industrial equipment. The choice of a V12 engine often signifies a vehicle's premium status and performance capabilities, offering a combination of power, smoothness, and prestige.Expand Specific Solutions04 V12 Engine Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Effective cooling and lubrication are crucial for V12 engines due to their high power output and complex design. Advanced cooling systems may include multiple radiators, oil coolers, and precise temperature management. Lubrication systems are designed to ensure proper oil distribution to all moving parts, even under high-stress conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 V12 Engine Manufacturing and Assembly
The production of V12 engines involves sophisticated manufacturing processes and precision assembly techniques. This includes advanced casting methods for engine blocks, precision machining of components, and careful balancing of rotating assemblies. Quality control measures are particularly stringent to ensure reliability and performance standards are met.Expand Specific Solutions
Major V12 Engine Manufacturers
The historical evolution of V12 engine configurations represents a mature technology within the automotive industry, with a relatively niche market due to its high-performance and luxury applications. The competitive landscape is dominated by established players like Honda Motor Co., Ltd., GM Global Technology Operations LLC, and Toyota Motor Corp., who have invested heavily in refining V12 technology over decades. The market size remains limited, primarily catering to high-end sports cars and luxury vehicles. Technological advancements have focused on improving efficiency and reducing emissions while maintaining the distinctive power and prestige associated with V12 engines. However, the shift towards electrification in the automotive sector poses challenges for the long-term growth of V12 engines.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: General Motors has played a crucial role in the historical evolution of V12 engine configurations. GM's approach to V12 engines has varied over time, with significant contributions in both automotive and marine applications. In the automotive sector, GM's Cadillac division was known for its V12 engines in the 1930s, which were praised for their smoothness and power[3]. More recently, GM has explored V12 configurations for high-performance applications, including concept cars and racing engines. Their V12 designs have incorporated advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and lightweight materials to improve performance and efficiency[4].
Strengths: High prestige, excellent power-to-weight ratio, smooth operation. Weaknesses: High production costs, limited market demand in modern automotive landscape, fuel efficiency challenges.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honda's involvement in the historical evolution of V12 engine configurations has been primarily focused on their Formula 1 racing program. Honda developed a series of V12 engines for F1 racing in the 1960s and early 1990s, showcasing their engineering prowess in high-performance applications. Their RA121E V12 engine, used in the 1991 F1 season, was particularly notable for its compact design and high power output[5]. While Honda has not produced V12 engines for road cars, their racing V12s have contributed to advancements in areas such as lightweight design, high-rpm operation, and thermal efficiency. These developments have indirectly influenced broader engine design trends[6].
Strengths: High-revving capability, compact design, racing pedigree. Weaknesses: Limited application outside of motorsports, high development costs, lack of road car V12 experience.
Key V12 Engine Innovations
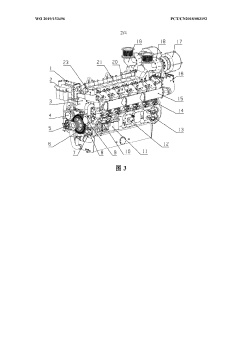
V-type 12-cylinder diesel engine
PatentWO2019153496A1
Innovation
- It adopts a V-shaped 12-cylinder diesel engine design, including a V-shaped cylinder block, 12 single cylinder heads, an electronically controlled single pump diesel supply system, an air intake system and a high and low temperature water separate cooling system to achieve double-sided oil supply, supercharged cooling and Classified cooling to improve the power and performance of diesel engines.
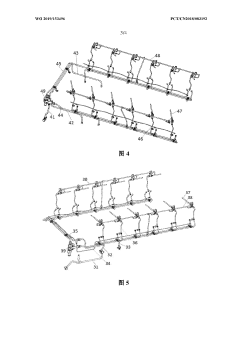
Transmission with dual input and output shafts
PatentInactiveUS20160245382A1
Innovation
- A transmission design with dual input shafts, a differential gear assembly, and half synchronizer clutches that allows for non-rotatable connections between gears and lay shafts, enabling torque transmission while reducing the need for external differentials and simplifying the power train architecture.
Environmental Impact of V12 Engines
The environmental impact of V12 engines has been a subject of increasing concern as awareness of climate change and air pollution has grown. V12 engines, known for their power and smooth operation, have traditionally been associated with high-performance luxury vehicles and racing cars. However, their significant fuel consumption and emissions have placed them under scrutiny in recent years.
V12 engines typically produce higher levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to smaller engine configurations due to their larger displacement and fuel requirements. The average V12 engine can emit between 300 to 500 grams of CO2 per kilometer, significantly exceeding the emissions of more common four or six-cylinder engines. This high carbon footprint has led to increased pressure on manufacturers to improve efficiency or phase out V12 engines in favor of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
In addition to CO2 emissions, V12 engines also contribute to other forms of air pollution. They tend to produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which are harmful to human health and the environment. These emissions have become a particular concern in urban areas, where air quality standards are increasingly stringent.
The manufacturing process of V12 engines also has environmental implications. The production of these complex powerplants requires more resources and energy compared to simpler engine configurations. This increased resource consumption contributes to the overall environmental footprint of vehicles equipped with V12 engines.
In response to environmental concerns and tightening regulations, manufacturers have implemented various technologies to mitigate the environmental impact of V12 engines. These include the adoption of direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation systems. Some luxury car makers have also introduced hybrid V12 powertrains, combining the traditional engine with electric motors to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Despite these improvements, the long-term sustainability of V12 engines remains questionable. Many countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines, including V12s, in favor of electric vehicles. This shift is driven by the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality in urban areas.
The environmental impact of V12 engines extends beyond their operational phase. The disposal and recycling of these engines at the end of their life cycle present additional challenges due to their complex construction and use of various materials. Proper recycling and disposal procedures are crucial to minimize the environmental impact of decommissioned V12 engines.
V12 engines typically produce higher levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to smaller engine configurations due to their larger displacement and fuel requirements. The average V12 engine can emit between 300 to 500 grams of CO2 per kilometer, significantly exceeding the emissions of more common four or six-cylinder engines. This high carbon footprint has led to increased pressure on manufacturers to improve efficiency or phase out V12 engines in favor of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
In addition to CO2 emissions, V12 engines also contribute to other forms of air pollution. They tend to produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which are harmful to human health and the environment. These emissions have become a particular concern in urban areas, where air quality standards are increasingly stringent.
The manufacturing process of V12 engines also has environmental implications. The production of these complex powerplants requires more resources and energy compared to simpler engine configurations. This increased resource consumption contributes to the overall environmental footprint of vehicles equipped with V12 engines.
In response to environmental concerns and tightening regulations, manufacturers have implemented various technologies to mitigate the environmental impact of V12 engines. These include the adoption of direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation systems. Some luxury car makers have also introduced hybrid V12 powertrains, combining the traditional engine with electric motors to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Despite these improvements, the long-term sustainability of V12 engines remains questionable. Many countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines, including V12s, in favor of electric vehicles. This shift is driven by the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality in urban areas.
The environmental impact of V12 engines extends beyond their operational phase. The disposal and recycling of these engines at the end of their life cycle present additional challenges due to their complex construction and use of various materials. Proper recycling and disposal procedures are crucial to minimize the environmental impact of decommissioned V12 engines.
V12 Engine Sound Engineering
The sound engineering of V12 engines has played a crucial role in their historical evolution and popularity. V12 engines are renowned for their distinctive, powerful, and harmonious sound, which has become an integral part of their appeal in high-performance vehicles and luxury automobiles.
The unique sound characteristics of V12 engines stem from their configuration. With twelve cylinders arranged in two banks of six, typically in a 60-degree V-shape, these engines produce a complex and balanced exhaust note. The firing order of the cylinders creates a smooth, continuous sound that is often described as melodious and refined.
Over the years, sound engineers have worked tirelessly to enhance and perfect the V12 engine's acoustic properties. In the early days of V12 engines, the focus was primarily on performance and power output. However, as automotive technology advanced, manufacturers began to recognize the importance of engine sound in creating a premium driving experience.
The development of advanced exhaust systems has been a key factor in shaping the V12 engine's sound. Engineers have experimented with various exhaust manifold designs, pipe lengths, and muffler configurations to optimize the engine's acoustic output. The introduction of variable valve timing and lift systems has also allowed for greater control over the engine's sound at different RPM ranges.
In recent decades, the advent of active exhaust systems has revolutionized V12 engine sound engineering. These systems use electronically controlled valves to alter the exhaust flow and, consequently, the engine's sound. This technology allows drivers to switch between different sound profiles, from a more subdued tone for everyday driving to a more aggressive note for performance-oriented situations.
The pursuit of the perfect V12 sound has led to collaborations between automotive engineers and audio specialists. Some luxury car manufacturers have partnered with high-end audio companies to fine-tune the in-cabin sound experience, using sophisticated sound design techniques to amplify and enhance the natural engine notes.
As environmental regulations have become more stringent, sound engineers have faced new challenges in preserving the iconic V12 sound while meeting noise emission standards. This has led to innovative solutions, such as sound symposers and active noise control systems, which aim to maintain the engine's characteristic sound without exceeding legal limits.
The unique sound characteristics of V12 engines stem from their configuration. With twelve cylinders arranged in two banks of six, typically in a 60-degree V-shape, these engines produce a complex and balanced exhaust note. The firing order of the cylinders creates a smooth, continuous sound that is often described as melodious and refined.
Over the years, sound engineers have worked tirelessly to enhance and perfect the V12 engine's acoustic properties. In the early days of V12 engines, the focus was primarily on performance and power output. However, as automotive technology advanced, manufacturers began to recognize the importance of engine sound in creating a premium driving experience.
The development of advanced exhaust systems has been a key factor in shaping the V12 engine's sound. Engineers have experimented with various exhaust manifold designs, pipe lengths, and muffler configurations to optimize the engine's acoustic output. The introduction of variable valve timing and lift systems has also allowed for greater control over the engine's sound at different RPM ranges.
In recent decades, the advent of active exhaust systems has revolutionized V12 engine sound engineering. These systems use electronically controlled valves to alter the exhaust flow and, consequently, the engine's sound. This technology allows drivers to switch between different sound profiles, from a more subdued tone for everyday driving to a more aggressive note for performance-oriented situations.
The pursuit of the perfect V12 sound has led to collaborations between automotive engineers and audio specialists. Some luxury car manufacturers have partnered with high-end audio companies to fine-tune the in-cabin sound experience, using sophisticated sound design techniques to amplify and enhance the natural engine notes.
As environmental regulations have become more stringent, sound engineers have faced new challenges in preserving the iconic V12 sound while meeting noise emission standards. This has led to innovative solutions, such as sound symposers and active noise control systems, which aim to maintain the engine's characteristic sound without exceeding legal limits.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!