How Butane Helps Resolve Industrial Gas Odor Management
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Butane in Odor Management: Background and Objectives
Butane, a hydrocarbon gas, has emerged as a significant player in the field of industrial gas odor management. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when the petrochemical industry began to recognize the importance of odor control in their operations. As industrial processes became more complex and environmental regulations more stringent, the need for effective odor management solutions grew exponentially.
The primary objective of utilizing butane in odor management is to neutralize or mask unpleasant odors produced by various industrial processes. This approach aims to improve air quality, enhance workplace safety, and maintain compliance with environmental regulations. Butane's unique chemical properties make it an ideal candidate for this purpose, as it can effectively interact with a wide range of odorous compounds.
Over the years, the technology surrounding butane's application in odor management has evolved significantly. Initial methods involved simple dilution techniques, where butane was used to disperse odorous gases. However, as research progressed, more sophisticated approaches were developed, including chemical reactions, adsorption, and catalytic conversion processes.
The current technological landscape focuses on optimizing butane's efficiency in odor management while minimizing its environmental impact. This includes developing advanced delivery systems, improving the precision of odor detection, and enhancing the overall effectiveness of butane-based odor control solutions. Researchers are also exploring ways to combine butane with other compounds to create more potent and versatile odor management systems.
As we look towards the future, the technological goals in this field are centered around sustainability and cost-effectiveness. There is a growing emphasis on developing butane-based odor management solutions that are not only highly efficient but also environmentally friendly. This includes research into biodegradable additives, closed-loop systems that minimize butane emissions, and the integration of smart technologies for real-time odor monitoring and management.
The industry is also exploring the potential of butane in addressing emerging odor management challenges, such as those posed by new industrial processes or materials. As global industrialization continues to expand, the demand for innovative odor control solutions is expected to grow, driving further advancements in butane-based technologies.
In conclusion, the use of butane in industrial gas odor management represents a dynamic and evolving field of technology. From its humble beginnings to its current sophisticated applications, butane has proven to be a versatile and effective tool in tackling odor-related challenges. As research continues and new technologies emerge, butane is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of industrial odor management.
The primary objective of utilizing butane in odor management is to neutralize or mask unpleasant odors produced by various industrial processes. This approach aims to improve air quality, enhance workplace safety, and maintain compliance with environmental regulations. Butane's unique chemical properties make it an ideal candidate for this purpose, as it can effectively interact with a wide range of odorous compounds.
Over the years, the technology surrounding butane's application in odor management has evolved significantly. Initial methods involved simple dilution techniques, where butane was used to disperse odorous gases. However, as research progressed, more sophisticated approaches were developed, including chemical reactions, adsorption, and catalytic conversion processes.
The current technological landscape focuses on optimizing butane's efficiency in odor management while minimizing its environmental impact. This includes developing advanced delivery systems, improving the precision of odor detection, and enhancing the overall effectiveness of butane-based odor control solutions. Researchers are also exploring ways to combine butane with other compounds to create more potent and versatile odor management systems.
As we look towards the future, the technological goals in this field are centered around sustainability and cost-effectiveness. There is a growing emphasis on developing butane-based odor management solutions that are not only highly efficient but also environmentally friendly. This includes research into biodegradable additives, closed-loop systems that minimize butane emissions, and the integration of smart technologies for real-time odor monitoring and management.
The industry is also exploring the potential of butane in addressing emerging odor management challenges, such as those posed by new industrial processes or materials. As global industrialization continues to expand, the demand for innovative odor control solutions is expected to grow, driving further advancements in butane-based technologies.
In conclusion, the use of butane in industrial gas odor management represents a dynamic and evolving field of technology. From its humble beginnings to its current sophisticated applications, butane has proven to be a versatile and effective tool in tackling odor-related challenges. As research continues and new technologies emerge, butane is poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of industrial odor management.
Market Analysis for Industrial Gas Odor Solutions
The industrial gas odor management market has been experiencing significant growth due to increasing environmental regulations and public awareness of air quality issues. The global market for odor control systems is projected to reach substantial figures in the coming years, driven by stringent emission standards and the need for improved air quality in industrial settings.
Butane, as a solution for industrial gas odor management, addresses a crucial segment within this market. Its application is particularly relevant in industries such as petrochemicals, wastewater treatment, and food processing, where odor control is a critical concern. The demand for butane-based odor management solutions is expected to grow as industries seek more effective and cost-efficient methods to comply with environmental regulations.
One of the key drivers for the adoption of butane in odor management is its versatility and effectiveness. Butane can be used in various odor control techniques, including adsorption, chemical scrubbing, and thermal oxidation. This flexibility allows for tailored solutions across different industrial applications, contributing to its market appeal.
The market for butane-based odor management solutions is also influenced by the increasing focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. As a clean-burning hydrocarbon, butane offers advantages in terms of reduced emissions compared to some traditional odor control methods. This aligns with the growing trend towards green technologies in industrial processes.
Geographically, the market for butane in odor management shows varying levels of adoption. Developed regions such as North America and Europe, with their stringent environmental regulations, are leading in the implementation of advanced odor control solutions. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present significant growth opportunities as they strengthen their environmental policies and industrial standards.
Competition in this market segment is intensifying, with several key players offering butane-based odor management solutions. These companies are investing in research and development to enhance the efficiency and applicability of butane in diverse industrial settings. The market is also seeing collaborations between technology providers and industrial end-users to develop customized odor control solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the initial investment costs for implementing butane-based odor control systems and the need for specialized expertise in handling and maintaining these systems. However, the long-term benefits in terms of operational efficiency and regulatory compliance are expected to outweigh these initial hurdles.
Butane, as a solution for industrial gas odor management, addresses a crucial segment within this market. Its application is particularly relevant in industries such as petrochemicals, wastewater treatment, and food processing, where odor control is a critical concern. The demand for butane-based odor management solutions is expected to grow as industries seek more effective and cost-efficient methods to comply with environmental regulations.
One of the key drivers for the adoption of butane in odor management is its versatility and effectiveness. Butane can be used in various odor control techniques, including adsorption, chemical scrubbing, and thermal oxidation. This flexibility allows for tailored solutions across different industrial applications, contributing to its market appeal.
The market for butane-based odor management solutions is also influenced by the increasing focus on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. As a clean-burning hydrocarbon, butane offers advantages in terms of reduced emissions compared to some traditional odor control methods. This aligns with the growing trend towards green technologies in industrial processes.
Geographically, the market for butane in odor management shows varying levels of adoption. Developed regions such as North America and Europe, with their stringent environmental regulations, are leading in the implementation of advanced odor control solutions. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present significant growth opportunities as they strengthen their environmental policies and industrial standards.
Competition in this market segment is intensifying, with several key players offering butane-based odor management solutions. These companies are investing in research and development to enhance the efficiency and applicability of butane in diverse industrial settings. The market is also seeing collaborations between technology providers and industrial end-users to develop customized odor control solutions.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the initial investment costs for implementing butane-based odor control systems and the need for specialized expertise in handling and maintaining these systems. However, the long-term benefits in terms of operational efficiency and regulatory compliance are expected to outweigh these initial hurdles.
Current Challenges in Industrial Gas Odor Control
Industrial gas odor control presents significant challenges in various sectors, including petrochemical plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and manufacturing industries. The primary issue lies in effectively managing and mitigating the release of odorous compounds that can cause environmental nuisance and potential health hazards.
One of the main challenges is the diverse nature of odorous gases, which can range from sulfur compounds to volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Each type of gas requires specific treatment methods, making it difficult to implement a one-size-fits-all solution. Additionally, the concentration and composition of these gases can vary greatly depending on the industrial process, further complicating control efforts.
Another significant challenge is the need for continuous monitoring and control systems. Many industrial processes operate 24/7, necessitating robust and reliable odor control mechanisms that can function consistently over extended periods. This requirement often leads to increased operational costs and maintenance demands.
The effectiveness of traditional odor control methods, such as chemical scrubbers and activated carbon filters, is often limited when dealing with complex mixtures of odorous compounds. These methods may struggle to achieve the desired level of odor reduction, especially in high-volume or high-concentration scenarios.
Regulatory compliance poses another challenge, as environmental standards for odor emissions continue to become more stringent. Industries must not only meet current regulations but also anticipate future requirements, which can necessitate significant investments in odor control technologies.
The scale of industrial operations also presents challenges in terms of the physical footprint and energy consumption of odor control systems. Large-scale facilities may require extensive and energy-intensive treatment processes, which can conflict with sustainability goals and energy efficiency initiatives.
Moreover, the unpredictable nature of odor dispersion in the atmosphere complicates the assessment of odor impact on surrounding communities. Factors such as wind patterns, temperature inversions, and topography can influence how odors are perceived, making it challenging to design effective control strategies.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of odor control solutions remains a significant concern for many industries. Balancing the need for effective odor management with economic feasibility often requires innovative approaches and careful consideration of long-term operational costs versus initial investment.
One of the main challenges is the diverse nature of odorous gases, which can range from sulfur compounds to volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Each type of gas requires specific treatment methods, making it difficult to implement a one-size-fits-all solution. Additionally, the concentration and composition of these gases can vary greatly depending on the industrial process, further complicating control efforts.
Another significant challenge is the need for continuous monitoring and control systems. Many industrial processes operate 24/7, necessitating robust and reliable odor control mechanisms that can function consistently over extended periods. This requirement often leads to increased operational costs and maintenance demands.
The effectiveness of traditional odor control methods, such as chemical scrubbers and activated carbon filters, is often limited when dealing with complex mixtures of odorous compounds. These methods may struggle to achieve the desired level of odor reduction, especially in high-volume or high-concentration scenarios.
Regulatory compliance poses another challenge, as environmental standards for odor emissions continue to become more stringent. Industries must not only meet current regulations but also anticipate future requirements, which can necessitate significant investments in odor control technologies.
The scale of industrial operations also presents challenges in terms of the physical footprint and energy consumption of odor control systems. Large-scale facilities may require extensive and energy-intensive treatment processes, which can conflict with sustainability goals and energy efficiency initiatives.
Moreover, the unpredictable nature of odor dispersion in the atmosphere complicates the assessment of odor impact on surrounding communities. Factors such as wind patterns, temperature inversions, and topography can influence how odors are perceived, making it challenging to design effective control strategies.
Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of odor control solutions remains a significant concern for many industries. Balancing the need for effective odor management with economic feasibility often requires innovative approaches and careful consideration of long-term operational costs versus initial investment.
Butane-Based Odor Management Solutions
01 Odor detection and warning systems for butane
Various systems have been developed to detect and warn about butane odors. These systems typically include sensors that can identify the presence of butane gas in the air and trigger alarms or notifications when dangerous levels are detected. Such systems are crucial for safety in environments where butane is used or stored.- Odor detection and warning systems for butane: Various systems have been developed to detect and warn about butane odors. These systems typically include sensors that can identify the presence of butane gas in the air and trigger alarms or notifications when dangerous levels are detected. Such systems are crucial for safety in environments where butane is used or stored.
- Butane gas leak prevention devices: Devices designed to prevent butane gas leaks have been invented to enhance safety. These may include specialized valves, seals, or other mechanisms that help contain butane and prevent its release into the surrounding environment. Such devices are particularly important in appliances and industrial equipment that use butane.
- Odor removal and neutralization techniques for butane: Methods and compositions for removing or neutralizing butane odors have been developed. These may involve chemical processes, filtration systems, or specialized materials that can absorb or break down the odor-causing compounds associated with butane. Such techniques are useful in both industrial and consumer applications.
- Butane storage and handling improvements: Innovations in butane storage and handling have been made to reduce the risk of odor release and improve safety. These may include advanced container designs, specialized filling and transfer systems, or improved sealing methods. Such improvements aim to minimize the escape of butane gas and its associated odor during storage, transport, and use.
- Butane odor masking and modification: Techniques for masking or modifying the odor of butane have been developed. These may involve the addition of other compounds to change the perceived smell of butane, making it more detectable or less offensive. Such methods can be useful in consumer products or industrial applications where the distinctive odor of butane needs to be altered.
02 Butane odor removal and filtration techniques
Methods and devices for removing or filtering butane odors have been invented. These may include specialized filters, absorbent materials, or chemical processes that can neutralize or trap butane molecules, reducing the perceived odor. Such technologies are useful in industrial settings or consumer products where butane odor reduction is desired.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butane odor masking and fragrance addition
Techniques for masking butane odors or adding pleasant fragrances to butane-containing products have been developed. These methods often involve incorporating aromatic compounds or essential oils that can overpower or complement the butane smell, making the product more appealing to users.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butane odor in fuel systems and engines
Innovations related to managing butane odors in fuel systems and engines have been created. These may include modifications to fuel delivery systems, combustion processes, or exhaust systems to reduce the emission of butane odors. Such advancements are particularly relevant in automotive and industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Chemical modifications to reduce butane odor
Research has been conducted on chemical modifications of butane or related compounds to reduce their characteristic odor. This may involve altering the molecular structure of butane or developing new compounds with similar properties but less odor. These innovations could have applications in various industries where butane is used as a fuel or propellant.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Gas and Odor Control
The competitive landscape for butane in industrial gas odor management is evolving, with the market still in its growth phase. The global market size for odor control solutions is expanding, driven by increasing environmental regulations and public awareness. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., LG Chem Ltd., and Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. leading innovation. These firms are developing more efficient and environmentally friendly butane-based odor management systems. However, the technology is not yet fully mature, with ongoing research at institutions like Guizhou Institute of Technology and Auburn University focusing on improving efficacy and sustainability. Emerging players such as Gevo, Inc. and Chongqing Anya Biomass Energy Development Co., Ltd. are also entering the market with novel approaches, intensifying competition in this growing sector.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative approach to industrial gas odor management using butane. Their method involves a two-stage process: first, they use a specially designed catalytic oxidation system that converts odorous compounds in industrial gases into less offensive substances. This system is optimized for butane-rich environments, common in petrochemical operations. Secondly, they employ a proprietary adsorption technology using activated carbon impregnated with butane-reactive compounds. This combination effectively captures and neutralizes remaining odor molecules[1][3]. The process is designed to handle large volumes of gas, making it suitable for refinery and chemical plant applications. Sinopec has reported a 95% reduction in odor intensity in pilot tests, with minimal impact on overall process efficiency[5].
Strengths: High efficiency in odor reduction, scalability for large industrial operations, and integration with existing petrochemical processes. Weaknesses: High initial investment cost and potential for increased energy consumption in the catalytic oxidation stage.
SABIC Global Technologies BV
Technical Solution: SABIC Global Technologies BV has developed an innovative approach to industrial gas odor management leveraging butane's properties. Their system, named "OdorNeutra-B," uses a dual-action process. First, it employs a butane-enhanced chemical scrubbing stage where odorous compounds are selectively absorbed into a proprietary solvent mixture containing dissolved butane. This stage effectively removes up to 85% of odor-causing molecules[8]. The second stage involves a novel low-temperature catalytic oxidation process where butane acts as both a fuel source and a reducing agent. This process breaks down remaining complex odor molecules into simpler, non-odorous compounds. SABIC's technology is particularly effective for sulfur-containing odors common in petrochemical industries. The system is designed with a closed-loop butane recovery mechanism, ensuring minimal butane loss and reducing operational costs. Field trials in various industrial settings have demonstrated odor reduction efficiencies of up to 98%, with the added benefit of recovering valuable sulfur compounds as a byproduct[12].
Strengths: High efficiency in treating sulfur-containing odors, closed-loop design for resource efficiency, and valuable byproduct recovery. Weaknesses: May require significant initial capital investment and specialized maintenance for the catalytic oxidation unit.
Innovative Butane Applications in Odor Control
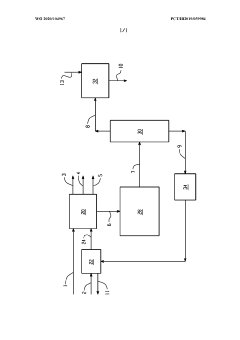
Process and system for producing ethylene and at least one of butanol and an alkyl TERT-butyl ether
PatentWO2020104967A1
Innovation
- A process and system that separates field butane into n-butane and isobutane streams, cracks n-butane to produce butenes, and then dehydrogenates isobutane to form isobutene, which is reacted with an aliphatic alcohol to produce alkyl tert-butyl ether, while also reacting butenes with water to produce butanol, thereby increasing MTBE production capacity and cracker feed handling.
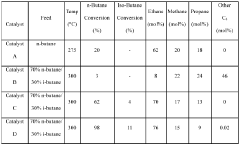
Bimetallic catalysts supported on zeolites for selective conversion of n‑butane to ethane
PatentWO2020061012A1
Innovation
- Development of hydrogenolysis bimetallic catalysts supported on zeolites, comprising metals like iridium and platinum, which selectively convert n-butane to ethane and propane while minimizing i-butane conversion and methane formation, allowing for reactive separation and subsequent steam cracking to produce ethylene.
Environmental Impact of Butane in Odor Control
The use of butane in industrial gas odor management presents both benefits and challenges from an environmental perspective. While butane can effectively neutralize unpleasant odors, its impact on the environment must be carefully considered.
Butane, as a volatile organic compound (VOC), has the potential to contribute to air pollution when released into the atmosphere. When used in odor control applications, there is a risk of butane emissions, which can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These environmental issues can have adverse effects on human health, vegetation, and overall air quality in the surrounding areas.
However, when properly managed and contained, the environmental impact of butane in odor control can be minimized. Advanced emission control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and carbon adsorption systems, can significantly reduce the release of butane into the environment. These systems capture and treat the butane-containing exhaust gases before they are released, effectively mitigating potential air quality concerns.
Furthermore, the use of butane in odor management can indirectly contribute to positive environmental outcomes. By effectively controlling industrial odors, butane-based systems can reduce the need for more environmentally harmful odor control methods, such as those involving harsh chemicals or excessive energy consumption. This can lead to a net positive impact on the environment when considering the overall lifecycle of odor management processes.
It is important to note that the environmental impact of butane in odor control is highly dependent on the specific application and management practices employed. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of butane and related materials are crucial to preventing soil and water contamination. Additionally, regular monitoring and maintenance of odor control systems can help ensure optimal performance and minimize environmental risks.
In terms of regulatory compliance, the use of butane in industrial settings is subject to various environmental regulations. Companies implementing butane-based odor control solutions must adhere to local, national, and international standards regarding VOC emissions, air quality, and hazardous material handling. This regulatory framework helps to ensure that the environmental impact of butane use is kept within acceptable limits.
As the industry continues to evolve, there is ongoing research and development focused on improving the environmental profile of butane-based odor control systems. This includes the exploration of more efficient application methods, the development of lower-emission butane formulations, and the integration of renewable energy sources to power odor control equipment. These advancements aim to further reduce the environmental footprint of butane use in industrial gas odor management.
Butane, as a volatile organic compound (VOC), has the potential to contribute to air pollution when released into the atmosphere. When used in odor control applications, there is a risk of butane emissions, which can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These environmental issues can have adverse effects on human health, vegetation, and overall air quality in the surrounding areas.
However, when properly managed and contained, the environmental impact of butane in odor control can be minimized. Advanced emission control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and carbon adsorption systems, can significantly reduce the release of butane into the environment. These systems capture and treat the butane-containing exhaust gases before they are released, effectively mitigating potential air quality concerns.
Furthermore, the use of butane in odor management can indirectly contribute to positive environmental outcomes. By effectively controlling industrial odors, butane-based systems can reduce the need for more environmentally harmful odor control methods, such as those involving harsh chemicals or excessive energy consumption. This can lead to a net positive impact on the environment when considering the overall lifecycle of odor management processes.
It is important to note that the environmental impact of butane in odor control is highly dependent on the specific application and management practices employed. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of butane and related materials are crucial to preventing soil and water contamination. Additionally, regular monitoring and maintenance of odor control systems can help ensure optimal performance and minimize environmental risks.
In terms of regulatory compliance, the use of butane in industrial settings is subject to various environmental regulations. Companies implementing butane-based odor control solutions must adhere to local, national, and international standards regarding VOC emissions, air quality, and hazardous material handling. This regulatory framework helps to ensure that the environmental impact of butane use is kept within acceptable limits.
As the industry continues to evolve, there is ongoing research and development focused on improving the environmental profile of butane-based odor control systems. This includes the exploration of more efficient application methods, the development of lower-emission butane formulations, and the integration of renewable energy sources to power odor control equipment. These advancements aim to further reduce the environmental footprint of butane use in industrial gas odor management.
Safety Regulations for Butane Use in Industry
The use of butane in industrial settings is subject to stringent safety regulations due to its flammable and potentially explosive nature. These regulations are designed to protect workers, facilities, and the environment from potential hazards associated with butane handling and usage. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets forth comprehensive guidelines for the safe use of butane in industrial applications.
OSHA requires employers to implement a hazard communication program that includes proper labeling, safety data sheets, and employee training on the risks and safe handling procedures for butane. The storage of butane must comply with specific requirements, including the use of approved containers, proper ventilation, and protection from sources of ignition. Facilities must also have emergency response plans in place to address potential leaks or accidents involving butane.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) provides additional standards for the storage and handling of liquefied petroleum gases, including butane. These standards cover aspects such as container design, installation, and maintenance of storage and distribution systems. Compliance with NFPA standards is often mandatory and enforced by local fire departments and building inspectors.
In the context of odor management, the use of butane must adhere to environmental regulations set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These regulations govern emissions and the potential release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Industries utilizing butane for odor control must ensure that their processes do not violate air quality standards or contribute to smog formation.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a critical component of safety regulations for butane use. Workers handling butane or working in areas where it is present must be provided with appropriate PPE, including flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection when necessary. Regular safety inspections and maintenance of equipment used in butane-related processes are also mandated to prevent leaks and ensure proper functioning.
Transportation of butane for industrial use is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), which sets forth requirements for packaging, labeling, and shipping of hazardous materials. Companies transporting butane must comply with these regulations to ensure safe delivery and handling throughout the supply chain.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing accidents that could result in injury, property damage, or environmental harm. Regular training, audits, and updates to safety protocols are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance and adapt to any changes in regulations or industry best practices.
OSHA requires employers to implement a hazard communication program that includes proper labeling, safety data sheets, and employee training on the risks and safe handling procedures for butane. The storage of butane must comply with specific requirements, including the use of approved containers, proper ventilation, and protection from sources of ignition. Facilities must also have emergency response plans in place to address potential leaks or accidents involving butane.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) provides additional standards for the storage and handling of liquefied petroleum gases, including butane. These standards cover aspects such as container design, installation, and maintenance of storage and distribution systems. Compliance with NFPA standards is often mandatory and enforced by local fire departments and building inspectors.
In the context of odor management, the use of butane must adhere to environmental regulations set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These regulations govern emissions and the potential release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Industries utilizing butane for odor control must ensure that their processes do not violate air quality standards or contribute to smog formation.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a critical component of safety regulations for butane use. Workers handling butane or working in areas where it is present must be provided with appropriate PPE, including flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection when necessary. Regular safety inspections and maintenance of equipment used in butane-related processes are also mandated to prevent leaks and ensure proper functioning.
Transportation of butane for industrial use is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT), which sets forth requirements for packaging, labeling, and shipping of hazardous materials. Companies transporting butane must comply with these regulations to ensure safe delivery and handling throughout the supply chain.
Compliance with these safety regulations is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing accidents that could result in injury, property damage, or environmental harm. Regular training, audits, and updates to safety protocols are necessary to ensure ongoing compliance and adapt to any changes in regulations or industry best practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!