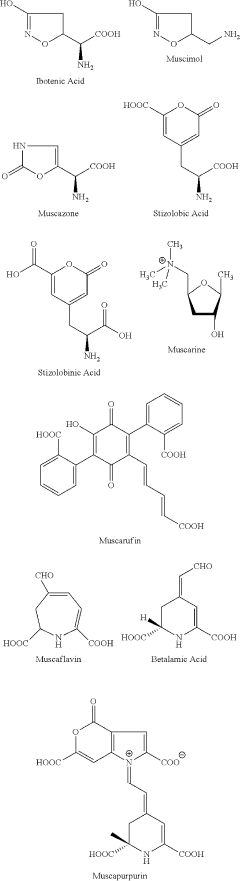
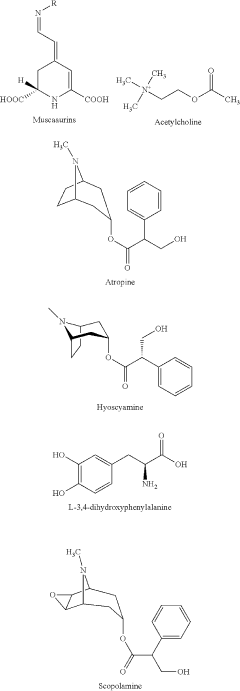
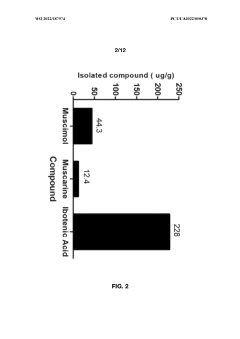
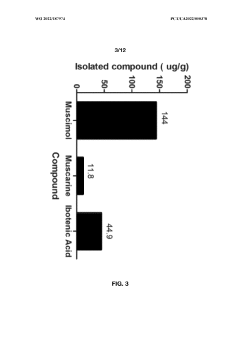
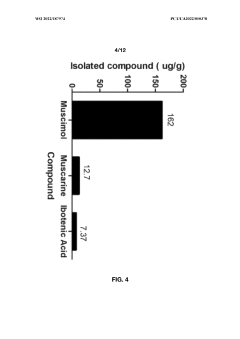
How Does Muscimol Contribute to Therapeutic Alignments?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has a rich history in both traditional medicine and modern neuroscience. Derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, commonly known as the fly agaric, muscimol has been used for centuries in various cultural and medicinal practices. Its psychoactive properties have long intrigued researchers and practitioners alike, leading to extensive studies on its potential therapeutic applications.
The chemical structure of muscimol was first elucidated in the 1960s, marking a significant milestone in understanding its pharmacological properties. This discovery paved the way for synthetic production and more controlled research into its effects on the central nervous system. Muscimol's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently has made it a valuable tool in neuroscience research, particularly in studying GABA-ergic systems.
In recent years, the focus on muscimol has shifted towards its potential therapeutic alignments. Its powerful GABA-A receptor activation properties have sparked interest in its use for various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Researchers have explored its potential in treating anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disturbances, among other conditions characterized by imbalances in inhibitory neurotransmission.
The unique pharmacokinetics of muscimol contribute to its therapeutic potential. Unlike many other GABA-A agonists, muscimol exhibits a relatively long half-life and sustained action in the brain. This characteristic makes it an attractive candidate for developing long-acting treatments for chronic conditions that require prolonged GABA-ergic modulation.
However, the development of muscimol-based therapies has faced challenges. Its potent psychoactive effects and potential for abuse have raised concerns about its safety profile. Researchers have been working on developing modified versions of muscimol or novel delivery methods to harness its therapeutic benefits while minimizing unwanted side effects.
The evolving understanding of muscimol's mechanism of action at the molecular level has opened new avenues for research. Recent studies have revealed its interactions with specific GABA-A receptor subunits, providing insights into its selective effects on different brain regions and functions. This knowledge is crucial for developing more targeted therapeutic approaches and understanding the full spectrum of muscimol's potential applications.
As research progresses, muscimol continues to be a subject of interest in both basic neuroscience and clinical research. Its unique properties and historical significance make it a fascinating compound at the intersection of traditional knowledge and modern pharmacology, holding promise for future therapeutic innovations.
The chemical structure of muscimol was first elucidated in the 1960s, marking a significant milestone in understanding its pharmacological properties. This discovery paved the way for synthetic production and more controlled research into its effects on the central nervous system. Muscimol's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently has made it a valuable tool in neuroscience research, particularly in studying GABA-ergic systems.
In recent years, the focus on muscimol has shifted towards its potential therapeutic alignments. Its powerful GABA-A receptor activation properties have sparked interest in its use for various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Researchers have explored its potential in treating anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disturbances, among other conditions characterized by imbalances in inhibitory neurotransmission.
The unique pharmacokinetics of muscimol contribute to its therapeutic potential. Unlike many other GABA-A agonists, muscimol exhibits a relatively long half-life and sustained action in the brain. This characteristic makes it an attractive candidate for developing long-acting treatments for chronic conditions that require prolonged GABA-ergic modulation.
However, the development of muscimol-based therapies has faced challenges. Its potent psychoactive effects and potential for abuse have raised concerns about its safety profile. Researchers have been working on developing modified versions of muscimol or novel delivery methods to harness its therapeutic benefits while minimizing unwanted side effects.
The evolving understanding of muscimol's mechanism of action at the molecular level has opened new avenues for research. Recent studies have revealed its interactions with specific GABA-A receptor subunits, providing insights into its selective effects on different brain regions and functions. This knowledge is crucial for developing more targeted therapeutic approaches and understanding the full spectrum of muscimol's potential applications.
As research progresses, muscimol continues to be a subject of interest in both basic neuroscience and clinical research. Its unique properties and historical significance make it a fascinating compound at the intersection of traditional knowledge and modern pharmacology, holding promise for future therapeutic innovations.
Therapeutic Demand
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has garnered significant attention in the therapeutic landscape due to its potential in addressing various neurological and psychiatric disorders. The market demand for muscimol-based therapies has been steadily increasing, driven by the rising prevalence of conditions such as anxiety, epilepsy, and sleep disorders.
The global neurology market, which encompasses many of the potential applications for muscimol, is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by an aging population, increased awareness of mental health issues, and the need for more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Anxiety disorders, one of the primary targets for muscimol-based therapies, affect a significant portion of the global population. The World Health Organization estimates that 264 million people worldwide suffer from anxiety disorders, creating a substantial market for novel treatments. The demand for anxiolytic drugs that can provide relief without the risk of dependence or severe side effects is particularly high.
Epilepsy, another condition where muscimol shows promise, affects approximately 50 million people globally. The current anti-epileptic drug market is substantial, but there is a persistent need for more effective treatments, especially for drug-resistant epilepsy. Muscimol's unique mechanism of action offers potential in addressing this unmet need.
Sleep disorders represent another significant market opportunity for muscimol-based therapies. With an estimated 50-70 million adults in the United States alone suffering from sleep disorders, the demand for safe and effective sleep aids is considerable. The current market is dominated by benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, which often come with side effects and the risk of dependence. Muscimol's potential to induce sleep without these drawbacks makes it an attractive alternative.
The pharmaceutical industry's growing interest in GABA-ergic compounds further underscores the market potential for muscimol. As research continues to elucidate the role of GABA in various neurological processes, the demand for drugs that can modulate this system is expected to increase.
Moreover, the shift towards personalized medicine and the search for targeted therapies have created a favorable environment for the development of muscimol-based treatments. The ability to tailor dosages and formulations to individual patient needs could significantly expand the therapeutic applications of muscimol.
In conclusion, the therapeutic demand for muscimol-based treatments is driven by the prevalence of neurological and psychiatric disorders, the limitations of current therapies, and the growing understanding of GABA's role in the central nervous system. As research progresses and clinical trials demonstrate efficacy, the market potential for muscimol is likely to expand, potentially revolutionizing treatment approaches in neurology and psychiatry.
The global neurology market, which encompasses many of the potential applications for muscimol, is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by an aging population, increased awareness of mental health issues, and the need for more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Anxiety disorders, one of the primary targets for muscimol-based therapies, affect a significant portion of the global population. The World Health Organization estimates that 264 million people worldwide suffer from anxiety disorders, creating a substantial market for novel treatments. The demand for anxiolytic drugs that can provide relief without the risk of dependence or severe side effects is particularly high.
Epilepsy, another condition where muscimol shows promise, affects approximately 50 million people globally. The current anti-epileptic drug market is substantial, but there is a persistent need for more effective treatments, especially for drug-resistant epilepsy. Muscimol's unique mechanism of action offers potential in addressing this unmet need.
Sleep disorders represent another significant market opportunity for muscimol-based therapies. With an estimated 50-70 million adults in the United States alone suffering from sleep disorders, the demand for safe and effective sleep aids is considerable. The current market is dominated by benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, which often come with side effects and the risk of dependence. Muscimol's potential to induce sleep without these drawbacks makes it an attractive alternative.
The pharmaceutical industry's growing interest in GABA-ergic compounds further underscores the market potential for muscimol. As research continues to elucidate the role of GABA in various neurological processes, the demand for drugs that can modulate this system is expected to increase.
Moreover, the shift towards personalized medicine and the search for targeted therapies have created a favorable environment for the development of muscimol-based treatments. The ability to tailor dosages and formulations to individual patient needs could significantly expand the therapeutic applications of muscimol.
In conclusion, the therapeutic demand for muscimol-based treatments is driven by the prevalence of neurological and psychiatric disorders, the limitations of current therapies, and the growing understanding of GABA's role in the central nervous system. As research progresses and clinical trials demonstrate efficacy, the market potential for muscimol is likely to expand, potentially revolutionizing treatment approaches in neurology and psychiatry.
Current Challenges
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, presents both promising therapeutic potential and significant challenges in its application for therapeutic alignments. One of the primary obstacles is the difficulty in achieving targeted delivery to specific brain regions. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) poses a substantial hurdle, limiting the ability of muscimol to reach its intended sites of action effectively. This challenge necessitates the development of advanced drug delivery systems or novel formulations to enhance BBB penetration without compromising safety.
Another critical challenge lies in managing the potent sedative effects of muscimol. While these effects can be beneficial in certain therapeutic contexts, such as treating insomnia or anxiety disorders, they can also limit the drug's applicability in conditions where cognitive function needs to be preserved. Striking the right balance between therapeutic efficacy and minimizing unwanted sedation remains a significant hurdle in muscimol's clinical development.
The potential for developing tolerance to muscimol's effects over time presents another substantial challenge. As with many GABA-ergic compounds, repeated administration may lead to reduced efficacy, necessitating dose escalation and potentially increasing the risk of side effects. This phenomenon complicates long-term treatment strategies and requires careful consideration in clinical trial design and patient management protocols.
Furthermore, the risk of adverse effects, particularly at higher doses, poses a significant challenge in muscimol's therapeutic application. These may include cognitive impairment, motor incoordination, and in severe cases, respiratory depression. Developing strategies to mitigate these risks while maintaining therapeutic efficacy is crucial for the successful clinical implementation of muscimol-based therapies.
The lack of comprehensive long-term safety data on muscimol use in humans represents another critical challenge. While preclinical studies and limited clinical trials have provided valuable insights, more extensive research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications of muscimol therapy, particularly in diverse patient populations and for chronic conditions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol presents unique challenges. As a compound with psychoactive properties and potential for abuse, navigating the regulatory requirements for clinical development and eventual market approval requires careful planning and extensive documentation. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, potentially slowing the progression of muscimol-based therapies from bench to bedside.
Another critical challenge lies in managing the potent sedative effects of muscimol. While these effects can be beneficial in certain therapeutic contexts, such as treating insomnia or anxiety disorders, they can also limit the drug's applicability in conditions where cognitive function needs to be preserved. Striking the right balance between therapeutic efficacy and minimizing unwanted sedation remains a significant hurdle in muscimol's clinical development.
The potential for developing tolerance to muscimol's effects over time presents another substantial challenge. As with many GABA-ergic compounds, repeated administration may lead to reduced efficacy, necessitating dose escalation and potentially increasing the risk of side effects. This phenomenon complicates long-term treatment strategies and requires careful consideration in clinical trial design and patient management protocols.
Furthermore, the risk of adverse effects, particularly at higher doses, poses a significant challenge in muscimol's therapeutic application. These may include cognitive impairment, motor incoordination, and in severe cases, respiratory depression. Developing strategies to mitigate these risks while maintaining therapeutic efficacy is crucial for the successful clinical implementation of muscimol-based therapies.
The lack of comprehensive long-term safety data on muscimol use in humans represents another critical challenge. While preclinical studies and limited clinical trials have provided valuable insights, more extensive research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications of muscimol therapy, particularly in diverse patient populations and for chronic conditions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding muscimol presents unique challenges. As a compound with psychoactive properties and potential for abuse, navigating the regulatory requirements for clinical development and eventual market approval requires careful planning and extensive documentation. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, potentially slowing the progression of muscimol-based therapies from bench to bedside.
Muscimol Applications
01 Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol
Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include formulations for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or sleep disorders. The muscimol-containing compositions can be prepared in different forms such as oral, topical, or injectable formulations.- Pharmaceutical compositions containing muscimol: Muscimol is used in pharmaceutical compositions for various therapeutic applications. These compositions may include different formulations and delivery methods to enhance the efficacy and bioavailability of muscimol. The compositions can be designed for treating neurological disorders, anxiety, or other conditions affected by GABA receptor modulation.
- Muscimol analogs and derivatives: Research focuses on developing and synthesizing muscimol analogs and derivatives. These modified compounds aim to improve upon the properties of muscimol, such as enhanced selectivity, potency, or reduced side effects. The analogs may be designed to target specific GABA receptor subtypes or to have improved pharmacokinetic profiles.
- Use of muscimol in neurostimulation therapies: Muscimol is explored in combination with neurostimulation techniques for treating neurological disorders. This approach may involve the use of muscimol to enhance or modulate the effects of electrical or magnetic stimulation of the brain. The combination therapy aims to improve outcomes in conditions such as epilepsy or movement disorders.
- Muscimol in drug delivery systems: Advanced drug delivery systems are developed to optimize the administration of muscimol. These may include controlled release formulations, targeted delivery mechanisms, or novel routes of administration. The goal is to improve the pharmacokinetics, reduce side effects, and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of muscimol-based treatments.
- Muscimol for treating anxiety and stress-related disorders: Research investigates the use of muscimol in treating anxiety and stress-related disorders. Studies explore its potential as an anxiolytic agent, possibly offering advantages over current treatments. The focus is on understanding its mechanism of action in anxiety reduction and developing optimal dosing strategies for clinical applications.
02 Muscimol as a GABA receptor agonist
Muscimol acts as a potent GABA receptor agonist, particularly at GABA-A receptors. This property makes it useful in treating conditions related to GABA dysfunction, such as epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and certain neurodegenerative diseases. Research focuses on developing muscimol derivatives with improved pharmacological profiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Muscimol in combination therapies
Muscimol is explored in combination therapies with other active ingredients to enhance therapeutic effects or reduce side effects. These combinations may target multiple pathways in neurological disorders or be used in pain management strategies. The synergistic effects of muscimol with other compounds are being investigated for various medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel delivery methods for muscimol
Innovative delivery methods are being developed to improve the efficacy and safety of muscimol administration. These include controlled-release formulations, transdermal patches, and targeted delivery systems that can cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively. Such methods aim to optimize the therapeutic potential of muscimol while minimizing systemic side effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Muscimol analogues and derivatives
Research is ongoing to develop muscimol analogues and derivatives with enhanced pharmacological properties. These modified compounds aim to improve selectivity for specific GABA receptor subtypes, increase bioavailability, or reduce unwanted side effects. Some derivatives may also have extended half-lives or improved stability compared to the parent compound.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The therapeutic potential of muscimol has sparked a competitive landscape in the pharmaceutical and research sectors. The industry is in an early development stage, with a growing market driven by increasing interest in novel neurological treatments. While the technology is still maturing, several key players are advancing research and development efforts. Companies like Celator Pharmaceuticals and PureTech Health are exploring muscimol's applications in drug delivery systems, while academic institutions such as the University of South Florida and Tianjin University are conducting foundational research. The involvement of established pharmaceutical giants like Teva Pharmaceutical Industries suggests a recognition of muscimol's potential, although the field remains open for innovative startups and research-driven organizations to make significant contributions.
Sepal Pharma Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sepal Pharma Ltd. is developing innovative muscimol-based therapeutics for neuropsychiatric disorders. Their approach involves creating novel formulations and delivery systems for muscimol to optimize its therapeutic potential while minimizing side effects. Sepal Pharma is exploring the use of muscimol in treating anxiety disorders, insomnia, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The company's research focuses on leveraging muscimol's rapid onset of action and its ability to modulate GABA-A receptors without causing tolerance or dependence[10]. Sepal Pharma is conducting preclinical studies to evaluate the efficacy of their muscimol formulations in animal models of anxiety and sleep disorders, with plans to initiate clinical trials in the near future[11].
Strengths: Focus on rapid-acting anxiolytic and hypnotic applications, potential for non-addictive alternatives to benzodiazepines, innovative drug delivery systems. Weaknesses: Early-stage development, potential regulatory hurdles for novel formulations, competition from established anxiolytic and hypnotic medications.
Psyched Wellness Ltd.
Technical Solution: Psyched Wellness Ltd. has developed a proprietary extraction and purification process for muscimol from Amanita muscaria mushrooms. Their approach focuses on creating a standardized, safe, and legal muscimol extract for therapeutic use. The company's flagship product, AME-1, is a muscimol-based tincture designed to promote stress relief, relaxation, and restful sleep[1][2]. Psyched Wellness is conducting preclinical studies to evaluate muscimol's potential in treating various conditions, including anxiety, depression, and addiction. Their research aims to leverage muscimol's GABA-A receptor agonist properties to achieve therapeutic alignments without the hallucinogenic effects associated with other psychedelic compounds[3].
Strengths: Proprietary extraction process, focus on legal and standardized muscimol products, potential for wide-ranging therapeutic applications. Weaknesses: Limited clinical data, regulatory challenges in some markets, potential competition from synthetic GABA-A agonists.
Core Mechanisms
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
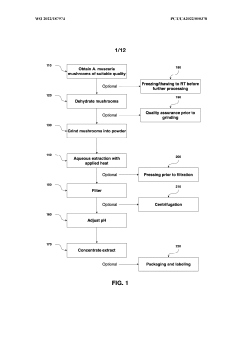
Processes for extracting muscimol from amanita muscaria
PatentWO2022187974A1
Innovation
- Aqueous extraction methods involving heat, pH reduction, and concentration techniques such as distillation and refluxing are employed to decrease ibotenic acid content and increase muscimol content in the extract, including steps like grinding the mushroom biomass, filtering, and acidification to facilitate decarboxylation of ibotenic acid to muscimol.
Safety Regulations
The safety regulations surrounding muscimol and its therapeutic applications are crucial for ensuring patient well-being and regulatory compliance. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushroom species, has shown potential in various therapeutic alignments. However, its use is subject to strict oversight due to its potent effects on the central nervous system.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, have established comprehensive guidelines for the research, development, and clinical use of muscimol-based therapies. These regulations encompass several key areas, including quality control, dosage standardization, and adverse effect monitoring.
Quality control measures are paramount in the production and handling of muscimol-containing substances. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent purity and potency. This includes rigorous testing protocols to detect contaminants and verify the concentration of active compounds.
Dosage standardization is another critical aspect of safety regulations. Given muscimol's potent effects, precise dosing is essential to minimize risks while maximizing therapeutic benefits. Clinical trials must establish safe and effective dose ranges for different indications, taking into account factors such as patient age, weight, and medical history.
Adverse effect monitoring is a continuous process throughout the development and use of muscimol-based therapies. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive pharmacovigilance programs to track and report any unexpected side effects or interactions. This data informs ongoing safety assessments and potential label updates.
The controlled substance status of muscimol in many jurisdictions adds another layer of regulatory complexity. Researchers and healthcare providers must comply with strict protocols for storage, handling, and administration. This often includes secure storage facilities, detailed record-keeping, and limited access to authorized personnel only.
Patient informed consent is a critical component of safety regulations for muscimol therapies. Given the compound's psychoactive properties, patients must be fully informed of potential risks and effects before treatment. This includes detailed discussions about possible alterations in perception, mood, and cognition during therapy sessions.
Long-term safety studies are mandated by regulatory agencies to assess the potential for dependency, tolerance, or other cumulative effects from prolonged muscimol use. These studies inform guidelines for treatment duration and potential restrictions on repeated courses of therapy.
As research into muscimol's therapeutic potential continues to evolve, safety regulations are likely to be refined and updated. Regulatory bodies maintain ongoing dialogue with researchers and clinicians to ensure that safety standards keep pace with scientific advancements and clinical experiences.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, have established comprehensive guidelines for the research, development, and clinical use of muscimol-based therapies. These regulations encompass several key areas, including quality control, dosage standardization, and adverse effect monitoring.
Quality control measures are paramount in the production and handling of muscimol-containing substances. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent purity and potency. This includes rigorous testing protocols to detect contaminants and verify the concentration of active compounds.
Dosage standardization is another critical aspect of safety regulations. Given muscimol's potent effects, precise dosing is essential to minimize risks while maximizing therapeutic benefits. Clinical trials must establish safe and effective dose ranges for different indications, taking into account factors such as patient age, weight, and medical history.
Adverse effect monitoring is a continuous process throughout the development and use of muscimol-based therapies. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive pharmacovigilance programs to track and report any unexpected side effects or interactions. This data informs ongoing safety assessments and potential label updates.
The controlled substance status of muscimol in many jurisdictions adds another layer of regulatory complexity. Researchers and healthcare providers must comply with strict protocols for storage, handling, and administration. This often includes secure storage facilities, detailed record-keeping, and limited access to authorized personnel only.
Patient informed consent is a critical component of safety regulations for muscimol therapies. Given the compound's psychoactive properties, patients must be fully informed of potential risks and effects before treatment. This includes detailed discussions about possible alterations in perception, mood, and cognition during therapy sessions.
Long-term safety studies are mandated by regulatory agencies to assess the potential for dependency, tolerance, or other cumulative effects from prolonged muscimol use. These studies inform guidelines for treatment duration and potential restrictions on repeated courses of therapy.
As research into muscimol's therapeutic potential continues to evolve, safety regulations are likely to be refined and updated. Regulatory bodies maintain ongoing dialogue with researchers and clinicians to ensure that safety standards keep pace with scientific advancements and clinical experiences.
Ethical Considerations
The use of muscimol in therapeutic alignments raises several important ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. Firstly, the potential for abuse and addiction associated with GABA receptor agonists like muscimol necessitates strict controls and monitoring protocols. Healthcare providers must ensure that patients fully understand the risks and benefits, and implement safeguards against misuse or diversion.
Additionally, the psychoactive effects of muscimol, including altered consciousness and potential hallucinations, raise questions about informed consent and decision-making capacity. Protocols must be established to assess a patient's ability to provide informed consent before initiating treatment, and to monitor their cognitive state throughout the therapeutic process.
The long-term effects of muscimol on brain function and neuroplasticity are not yet fully understood. Ethical research practices must be employed to gather more data on long-term outcomes while protecting participants' rights and well-being. This includes transparent reporting of both positive and negative results to inform future clinical applications.
There are also concerns about equitable access to muscimol-based therapies. As a novel treatment, it may initially be expensive and limited in availability. Healthcare systems and policymakers must consider how to ensure fair distribution and prevent exacerbation of existing healthcare disparities.
The use of muscimol in vulnerable populations, such as those with severe mental illness or neurological disorders, requires additional ethical scrutiny. Extra precautions must be taken to protect these individuals from potential exploitation or undue influence in clinical trials or treatment programs.
Furthermore, the cultural and spiritual significance of muscimol-containing mushrooms in some indigenous traditions must be respected. Any commercialization or medical use of muscimol should involve consultation with and consideration of the rights of indigenous communities.
Lastly, as research progresses, there is a need for ongoing ethical review and adaptation of guidelines. This should involve multidisciplinary input from neuroscientists, ethicists, clinicians, and patient advocates to ensure that the therapeutic use of muscimol aligns with evolving ethical standards and societal values.
Additionally, the psychoactive effects of muscimol, including altered consciousness and potential hallucinations, raise questions about informed consent and decision-making capacity. Protocols must be established to assess a patient's ability to provide informed consent before initiating treatment, and to monitor their cognitive state throughout the therapeutic process.
The long-term effects of muscimol on brain function and neuroplasticity are not yet fully understood. Ethical research practices must be employed to gather more data on long-term outcomes while protecting participants' rights and well-being. This includes transparent reporting of both positive and negative results to inform future clinical applications.
There are also concerns about equitable access to muscimol-based therapies. As a novel treatment, it may initially be expensive and limited in availability. Healthcare systems and policymakers must consider how to ensure fair distribution and prevent exacerbation of existing healthcare disparities.
The use of muscimol in vulnerable populations, such as those with severe mental illness or neurological disorders, requires additional ethical scrutiny. Extra precautions must be taken to protect these individuals from potential exploitation or undue influence in clinical trials or treatment programs.
Furthermore, the cultural and spiritual significance of muscimol-containing mushrooms in some indigenous traditions must be respected. Any commercialization or medical use of muscimol should involve consultation with and consideration of the rights of indigenous communities.
Lastly, as research progresses, there is a need for ongoing ethical review and adaptation of guidelines. This should involve multidisciplinary input from neuroscientists, ethicists, clinicians, and patient advocates to ensure that the therapeutic use of muscimol aligns with evolving ethical standards and societal values.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!