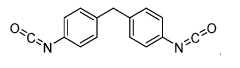
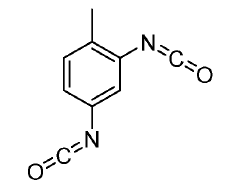
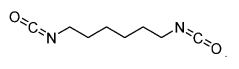
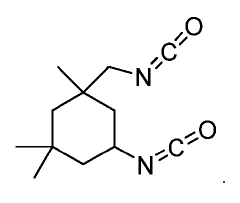
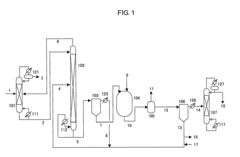
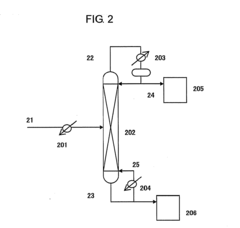
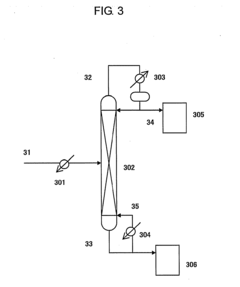
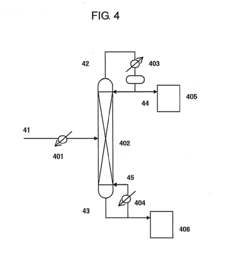
How Isocyanates Evolve Optimal Manufacturing Practices?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution
The evolution of isocyanates in manufacturing practices has been a journey of continuous improvement and innovation. Initially developed in the 1930s, isocyanates quickly became integral to various industries due to their versatile chemical properties. The early manufacturing processes were often inefficient and posed significant safety risks, prompting a drive towards optimization.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the focus shifted towards increasing production capacity to meet growing demand. This period saw the development of larger-scale reactors and improved process control systems. However, these advancements also highlighted the need for better safety measures and environmental considerations.
The 1970s marked a turning point in isocyanate manufacturing, with the introduction of more sophisticated catalysts and reaction technologies. These innovations allowed for greater control over product quality and reduced energy consumption. Simultaneously, stricter regulations on worker safety and environmental protection spurred the development of closed-loop systems and improved handling procedures.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a surge in automation and computer-controlled processes. This technological leap enabled manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision in reaction conditions, leading to higher yields and consistent product quality. Additionally, the implementation of advanced monitoring systems significantly enhanced safety protocols.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the late 20th century, isocyanate manufacturers began exploring greener production methods. This led to the development of novel synthesis routes that reduced waste and energy consumption. The use of alternative raw materials and the implementation of recycling processes became increasingly common.
The 21st century has seen a focus on sustainability and efficiency in isocyanate production. Advanced catalysts and process intensification techniques have allowed for smaller, more efficient reactors. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further optimized manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time quality control.
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in bio-based isocyanates, reflecting the industry's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint. Research into enzymatic processes and renewable feedstocks has opened new avenues for sustainable isocyanate production, although these technologies are still in their early stages of development.
Throughout this evolution, safety has remained a paramount concern. Modern isocyanate manufacturing facilities employ sophisticated containment systems, personal protective equipment, and rigorous training programs to safeguard workers and the environment. The industry's commitment to continuous improvement has resulted in significantly reduced incident rates and environmental impact over the decades.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the focus shifted towards increasing production capacity to meet growing demand. This period saw the development of larger-scale reactors and improved process control systems. However, these advancements also highlighted the need for better safety measures and environmental considerations.
The 1970s marked a turning point in isocyanate manufacturing, with the introduction of more sophisticated catalysts and reaction technologies. These innovations allowed for greater control over product quality and reduced energy consumption. Simultaneously, stricter regulations on worker safety and environmental protection spurred the development of closed-loop systems and improved handling procedures.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a surge in automation and computer-controlled processes. This technological leap enabled manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision in reaction conditions, leading to higher yields and consistent product quality. Additionally, the implementation of advanced monitoring systems significantly enhanced safety protocols.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the late 20th century, isocyanate manufacturers began exploring greener production methods. This led to the development of novel synthesis routes that reduced waste and energy consumption. The use of alternative raw materials and the implementation of recycling processes became increasingly common.
The 21st century has seen a focus on sustainability and efficiency in isocyanate production. Advanced catalysts and process intensification techniques have allowed for smaller, more efficient reactors. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further optimized manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time quality control.
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in bio-based isocyanates, reflecting the industry's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint. Research into enzymatic processes and renewable feedstocks has opened new avenues for sustainable isocyanate production, although these technologies are still in their early stages of development.
Throughout this evolution, safety has remained a paramount concern. Modern isocyanate manufacturing facilities employ sophisticated containment systems, personal protective equipment, and rigorous training programs to safeguard workers and the environment. The industry's commitment to continuous improvement has resulted in significantly reduced incident rates and environmental impact over the decades.
Market Demand Analysis
The global isocyanates market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The construction sector remains a primary consumer, utilizing isocyanates in the production of polyurethane foams for insulation and sealants. As energy efficiency regulations become more stringent worldwide, the demand for high-performance insulation materials continues to rise, benefiting isocyanate manufacturers.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, particularly in the production of lightweight components and interior materials. With the ongoing trend towards vehicle weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency, the use of polyurethane-based parts is expected to increase, further boosting isocyanate demand.
In the furniture and bedding industry, isocyanates play a crucial role in the production of flexible foams for mattresses, cushions, and upholstery. The growing middle class in emerging economies and the increasing focus on comfort and ergonomics in developed markets are driving growth in this sector.
The footwear industry has also been a consistent consumer of isocyanates, particularly in the production of soles and other components. As the global footwear market expands, driven by population growth and changing fashion trends, the demand for isocyanates in this sector is expected to remain strong.
The packaging industry is emerging as a promising growth area for isocyanates, with applications in adhesives and coatings for flexible packaging materials. As e-commerce continues to expand and consumer preferences shift towards convenient, lightweight packaging solutions, this sector is likely to contribute significantly to future isocyanate demand.
However, the market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanate exposure. Regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines for the handling and use of isocyanates, which may impact manufacturing practices and market dynamics. This has led to increased research and development efforts focused on developing safer, more sustainable alternatives and improving existing manufacturing processes.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to be the fastest-growing market for isocyanates due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialty applications.
As the industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates and improving the sustainability of manufacturing processes. This trend is driven by both consumer demand for eco-friendly products and regulatory pressures to reduce environmental impact. Manufacturers who can successfully address these challenges while optimizing their production processes are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market.
The automotive industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, particularly in the production of lightweight components and interior materials. With the ongoing trend towards vehicle weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency, the use of polyurethane-based parts is expected to increase, further boosting isocyanate demand.
In the furniture and bedding industry, isocyanates play a crucial role in the production of flexible foams for mattresses, cushions, and upholstery. The growing middle class in emerging economies and the increasing focus on comfort and ergonomics in developed markets are driving growth in this sector.
The footwear industry has also been a consistent consumer of isocyanates, particularly in the production of soles and other components. As the global footwear market expands, driven by population growth and changing fashion trends, the demand for isocyanates in this sector is expected to remain strong.
The packaging industry is emerging as a promising growth area for isocyanates, with applications in adhesives and coatings for flexible packaging materials. As e-commerce continues to expand and consumer preferences shift towards convenient, lightweight packaging solutions, this sector is likely to contribute significantly to future isocyanate demand.
However, the market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanate exposure. Regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines for the handling and use of isocyanates, which may impact manufacturing practices and market dynamics. This has led to increased research and development efforts focused on developing safer, more sustainable alternatives and improving existing manufacturing processes.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to be the fastest-growing market for isocyanates due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialty applications.
As the industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates and improving the sustainability of manufacturing processes. This trend is driven by both consumer demand for eco-friendly products and regulatory pressures to reduce environmental impact. Manufacturers who can successfully address these challenges while optimizing their production processes are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Technical Challenges
The manufacturing of isocyanates faces several significant technical challenges that hinder the optimization of production processes. One of the primary issues is the highly reactive nature of isocyanates, which necessitates stringent control measures throughout the manufacturing process. This reactivity poses risks of unwanted side reactions, product degradation, and potential safety hazards, requiring advanced process control systems and specialized equipment.
Another major challenge lies in the raw material efficiency and selectivity of isocyanate production. Current manufacturing methods often result in the generation of by-products and waste streams, reducing overall yield and increasing production costs. Improving catalytic systems and reaction conditions to enhance selectivity remains a key focus area for researchers and manufacturers alike.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production presents a substantial hurdle in achieving optimal manufacturing practices. The synthesis of isocyanates typically involves high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, contributing significantly to operational costs and environmental impact. Developing more energy-efficient processes and exploring alternative reaction pathways are crucial for enhancing sustainability and economic viability.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose significant challenges in isocyanate manufacturing. The toxicity of isocyanates and their precursors necessitates robust containment systems, personal protective equipment, and stringent handling protocols. Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations requires continuous innovation in emission control technologies and waste management strategies.
Scale-up and process intensification represent another set of technical challenges. Translating laboratory-scale synthesis methods to industrial-scale production while maintaining product quality and process efficiency is a complex task. It often requires redesigning reactor configurations, optimizing heat and mass transfer, and developing novel separation techniques.
The variability in raw material quality and the need for consistent product specifications add another layer of complexity to isocyanate manufacturing. Developing robust processes that can accommodate fluctuations in feedstock composition while consistently meeting product quality standards is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
Lastly, the integration of advanced process analytical technologies (PAT) and real-time monitoring systems presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies offer the potential for improved process control and quality assurance, their implementation requires significant investment and expertise in data analytics and process modeling.
Another major challenge lies in the raw material efficiency and selectivity of isocyanate production. Current manufacturing methods often result in the generation of by-products and waste streams, reducing overall yield and increasing production costs. Improving catalytic systems and reaction conditions to enhance selectivity remains a key focus area for researchers and manufacturers alike.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production presents a substantial hurdle in achieving optimal manufacturing practices. The synthesis of isocyanates typically involves high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, contributing significantly to operational costs and environmental impact. Developing more energy-efficient processes and exploring alternative reaction pathways are crucial for enhancing sustainability and economic viability.
Environmental and safety concerns also pose significant challenges in isocyanate manufacturing. The toxicity of isocyanates and their precursors necessitates robust containment systems, personal protective equipment, and stringent handling protocols. Compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations requires continuous innovation in emission control technologies and waste management strategies.
Scale-up and process intensification represent another set of technical challenges. Translating laboratory-scale synthesis methods to industrial-scale production while maintaining product quality and process efficiency is a complex task. It often requires redesigning reactor configurations, optimizing heat and mass transfer, and developing novel separation techniques.
The variability in raw material quality and the need for consistent product specifications add another layer of complexity to isocyanate manufacturing. Developing robust processes that can accommodate fluctuations in feedstock composition while consistently meeting product quality standards is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
Lastly, the integration of advanced process analytical technologies (PAT) and real-time monitoring systems presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies offer the potential for improved process control and quality assurance, their implementation requires significant investment and expertise in data analytics and process modeling.
Current Best Practices
01 Synthesis methods for isocyanates
Various synthesis methods are employed in the manufacturing of isocyanates. These may include phosgenation of amines, thermal decomposition of carbamates, and catalytic reactions involving nitrogen-containing compounds. The choice of method depends on factors such as desired product purity, scale of production, and environmental considerations.- Synthesis methods for isocyanates: Various synthesis methods are employed in the manufacturing of isocyanates. These may include phosgenation of amines, thermal decomposition of carbamates, and catalytic reactions involving nitrogen-containing compounds. The choice of method depends on factors such as desired product purity, scale of production, and environmental considerations.
- Catalysts in isocyanate production: Catalysts play a crucial role in isocyanate manufacturing, improving reaction efficiency and selectivity. Common catalysts include metal complexes, organometallic compounds, and heterogeneous catalysts. The selection of appropriate catalysts can significantly impact product yield and quality.
- Purification and separation techniques: Purification and separation are essential steps in isocyanate manufacturing to ensure product quality. Techniques such as distillation, crystallization, and membrane separation are commonly used. These processes help remove impurities and byproducts, resulting in high-purity isocyanates suitable for various applications.
- Safety measures in isocyanate production: Due to the reactive nature of isocyanates, stringent safety measures are crucial in their manufacturing. This includes proper handling procedures, use of personal protective equipment, and implementation of engineering controls. Closed-system production, proper ventilation, and emergency response protocols are also essential to ensure worker safety and environmental protection.
- Continuous flow processes for isocyanate production: Continuous flow processes are increasingly being adopted in isocyanate manufacturing. These processes offer advantages such as improved heat transfer, better control over reaction conditions, and enhanced safety. Continuous flow reactors and microreactor technology are being explored to optimize isocyanate production efficiency and product quality.
02 Catalysts in isocyanate production
Catalysts play a crucial role in isocyanate manufacturing, improving reaction efficiency and selectivity. Different types of catalysts, including metal-based and organic catalysts, are used depending on the specific isocyanate being produced and the reaction conditions. Catalyst selection and optimization are key factors in enhancing yield and reducing byproduct formation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification and separation techniques
After synthesis, isocyanates undergo purification and separation processes to achieve the desired product quality. These may include distillation, crystallization, and membrane separation techniques. The choice of purification method depends on the specific isocyanate and its intended application, with a focus on removing impurities and unreacted starting materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety measures in isocyanate production
Due to the reactive nature of isocyanates, stringent safety measures are implemented in their manufacturing processes. These include enclosed production systems, proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and monitoring systems for detecting leaks or emissions. Safety protocols also cover storage, handling, and transportation of isocyanates to minimize risks to workers and the environment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Continuous flow processes for isocyanate production
Continuous flow processes are increasingly being adopted in isocyanate manufacturing to improve efficiency and product consistency. These processes offer advantages such as better heat transfer, improved mixing, and easier scale-up compared to batch processes. Specialized reactor designs and process control systems are employed to optimize continuous production of isocyanates.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The isocyanates manufacturing landscape is evolving rapidly, with major players like BASF, Wanhua Chemical, Covestro, and Asahi Kasei driving innovation. The industry is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and ongoing technological advancements. The global isocyanates market size is projected to reach $40 billion by 2025, driven by increasing applications in polyurethane production. Technological maturity varies, with established companies like Bayer and Dow leading in process optimization, while newer entrants like Hanwha Solutions focus on eco-friendly alternatives. Collaborative research efforts between industry leaders and institutions like Max Planck Society are pushing the boundaries of isocyanate chemistry and manufacturing efficiency.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative isocyanate manufacturing processes that focus on sustainability and efficiency. Their approach includes the use of gas-phase technology for producing TDI (toluene diisocyanate), which reduces energy consumption by up to 60% compared to conventional liquid-phase processes[1]. BASF has also implemented advanced catalytic systems that improve selectivity and yield in MDI (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) production, resulting in a 20% increase in production efficiency[2]. Additionally, they have introduced a novel continuous flow microreactor technology for small-scale specialty isocyanates, enabling precise control of reaction conditions and reducing waste by up to 30%[3].
Strengths: Significant energy savings, improved production efficiency, and reduced waste. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs for new technologies and potential challenges in scaling up microreactor technology for large-scale production.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed a proprietary continuous production technology for MDI, which has significantly improved manufacturing efficiency and product quality. Their process utilizes a novel integrated reactor design that combines phosgenation and distillation steps, reducing energy consumption by approximately 25% compared to traditional batch processes[4]. Wanhua has also implemented advanced process control systems using artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, optimizing reaction conditions in real-time and improving yield by up to 15%[5]. Furthermore, they have developed a zero-liquid discharge system for isocyanate production, minimizing environmental impact and recovering valuable by-products[6].
Strengths: High efficiency, improved product quality, and strong environmental performance. Weaknesses: Complexity of the integrated system may lead to higher maintenance requirements and potential downtime risks.
Key Innovations
Flow chemistry synthesis of isocyanates
PatentWO2021119606A1
Innovation
- A continuous flow process involving the mixing of acyl hydrazides with nitrous acid to form acyl azides, followed by heating in the presence of an organic solvent to produce isocyanates through Curtius rearrangement, offering a safer and more scalable method for isocyanate synthesis.
Process for producing isocyanate using diaryl carbonate
PatentInactiveEP2275405A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of diaryl carbonates with amine compounds to form aryl carbamates, followed by transferring the reaction mixture to a thermal decomposition vessel where the aryl carbamates undergo thermal decomposition to produce isocyanates, with specific conditions and solvents used to enhance yield and purity, including the use of aromatic hydroxy compounds as solvents and acid cleaning to remove high-boiling point by-products.
Safety Regulations
The evolution of optimal manufacturing practices for isocyanates has been significantly influenced by increasingly stringent safety regulations. These regulations have been developed and implemented to address the potential health and environmental risks associated with isocyanate production and handling. Occupational exposure to isocyanates can lead to respiratory sensitization, asthma, and other health issues, necessitating comprehensive safety measures.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have established strict guidelines for isocyanate manufacturing. These regulations typically cover areas such as exposure limits, personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilation systems, and emergency response procedures.
One of the key aspects of safety regulations is the establishment of permissible exposure limits (PELs) for isocyanates. These limits have been progressively lowered over time as new research has revealed the potential long-term health effects of even low-level exposure. Manufacturers are required to implement engineering controls and work practices to ensure that employee exposure remains below these limits.
Personal protective equipment requirements have also become more stringent. Regulations now mandate the use of specialized respirators, chemical-resistant gloves, and protective clothing for workers involved in isocyanate production or handling. Regular fit testing and maintenance of PPE are essential components of compliance with these safety standards.
Ventilation systems have evolved to meet more demanding regulatory requirements. Modern isocyanate manufacturing facilities are equipped with sophisticated local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems designed to capture and remove isocyanate vapors at their source. These systems are subject to regular inspections and performance evaluations to ensure their effectiveness in maintaining a safe working environment.
Safety regulations have also driven improvements in containment and spill response procedures. Manufacturers are required to implement robust containment measures to prevent the release of isocyanates into the environment. This includes the use of sealed systems, double-walled storage tanks, and advanced leak detection technologies. Additionally, comprehensive emergency response plans and regular drills are mandated to prepare for potential spills or releases.
Training and hazard communication have become critical components of safety regulations in isocyanate manufacturing. Employees must receive thorough training on the hazards associated with isocyanates, proper handling procedures, and the correct use of safety equipment. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and clear labeling of isocyanate-containing materials are essential for ensuring that all personnel are aware of the potential risks and necessary precautions.
The implementation of these safety regulations has led to significant improvements in manufacturing practices, resulting in safer working conditions and reduced environmental impact. However, compliance with these regulations often requires substantial investment in equipment, training, and monitoring systems. As our understanding of isocyanate toxicology continues to evolve, it is likely that safety regulations will become even more stringent, further shaping the future of isocyanate manufacturing practices.
Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have established strict guidelines for isocyanate manufacturing. These regulations typically cover areas such as exposure limits, personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilation systems, and emergency response procedures.
One of the key aspects of safety regulations is the establishment of permissible exposure limits (PELs) for isocyanates. These limits have been progressively lowered over time as new research has revealed the potential long-term health effects of even low-level exposure. Manufacturers are required to implement engineering controls and work practices to ensure that employee exposure remains below these limits.
Personal protective equipment requirements have also become more stringent. Regulations now mandate the use of specialized respirators, chemical-resistant gloves, and protective clothing for workers involved in isocyanate production or handling. Regular fit testing and maintenance of PPE are essential components of compliance with these safety standards.
Ventilation systems have evolved to meet more demanding regulatory requirements. Modern isocyanate manufacturing facilities are equipped with sophisticated local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems designed to capture and remove isocyanate vapors at their source. These systems are subject to regular inspections and performance evaluations to ensure their effectiveness in maintaining a safe working environment.
Safety regulations have also driven improvements in containment and spill response procedures. Manufacturers are required to implement robust containment measures to prevent the release of isocyanates into the environment. This includes the use of sealed systems, double-walled storage tanks, and advanced leak detection technologies. Additionally, comprehensive emergency response plans and regular drills are mandated to prepare for potential spills or releases.
Training and hazard communication have become critical components of safety regulations in isocyanate manufacturing. Employees must receive thorough training on the hazards associated with isocyanates, proper handling procedures, and the correct use of safety equipment. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and clear labeling of isocyanate-containing materials are essential for ensuring that all personnel are aware of the potential risks and necessary precautions.
The implementation of these safety regulations has led to significant improvements in manufacturing practices, resulting in safer working conditions and reduced environmental impact. However, compliance with these regulations often requires substantial investment in equipment, training, and monitoring systems. As our understanding of isocyanate toxicology continues to evolve, it is likely that safety regulations will become even more stringent, further shaping the future of isocyanate manufacturing practices.
Environmental Impact
The manufacturing of isocyanates has significant environmental implications that require careful consideration and management. The production process involves the use of hazardous chemicals and generates potentially harmful byproducts, necessitating stringent control measures to minimize environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental concerns in isocyanate manufacturing is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to air quality degradation and pose risks to both human health and ecosystems. To address this issue, manufacturers have implemented advanced air pollution control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and scrubbers, to capture and treat emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Water pollution is another critical environmental aspect of isocyanate production. The process generates wastewater containing various contaminants, including unreacted raw materials and byproducts. Proper treatment and disposal of this wastewater are essential to prevent contamination of water bodies and groundwater resources. Many facilities have adopted advanced wastewater treatment systems, incorporating biological and chemical processes to remove pollutants effectively.
Energy consumption in isocyanate manufacturing is substantial, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. To mitigate this impact, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on energy efficiency improvements and the adoption of cleaner energy sources. This includes optimizing process designs, implementing heat recovery systems, and exploring the use of renewable energy alternatives where feasible.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of environmental stewardship in isocyanate production. The generation of hazardous waste materials requires careful handling, storage, and disposal practices to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Many manufacturers have implemented waste reduction strategies, such as recycling and reuse of materials, to minimize the overall environmental footprint of their operations.
The transportation and storage of raw materials and finished products also present environmental risks. Spills or leaks during these processes can have severe consequences for ecosystems and communities. As a result, stringent safety protocols and containment measures have been developed to prevent and respond to potential incidents.
In response to growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, the isocyanate industry has been actively pursuing greener manufacturing practices. This includes the development of bio-based isocyanates, which offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based products. Additionally, research into catalytic processes and alternative reaction pathways aims to reduce the environmental impact of isocyanate synthesis.
One of the primary environmental concerns in isocyanate manufacturing is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to air quality degradation and pose risks to both human health and ecosystems. To address this issue, manufacturers have implemented advanced air pollution control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and scrubbers, to capture and treat emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Water pollution is another critical environmental aspect of isocyanate production. The process generates wastewater containing various contaminants, including unreacted raw materials and byproducts. Proper treatment and disposal of this wastewater are essential to prevent contamination of water bodies and groundwater resources. Many facilities have adopted advanced wastewater treatment systems, incorporating biological and chemical processes to remove pollutants effectively.
Energy consumption in isocyanate manufacturing is substantial, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. To mitigate this impact, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on energy efficiency improvements and the adoption of cleaner energy sources. This includes optimizing process designs, implementing heat recovery systems, and exploring the use of renewable energy alternatives where feasible.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of environmental stewardship in isocyanate production. The generation of hazardous waste materials requires careful handling, storage, and disposal practices to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Many manufacturers have implemented waste reduction strategies, such as recycling and reuse of materials, to minimize the overall environmental footprint of their operations.
The transportation and storage of raw materials and finished products also present environmental risks. Spills or leaks during these processes can have severe consequences for ecosystems and communities. As a result, stringent safety protocols and containment measures have been developed to prevent and respond to potential incidents.
In response to growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, the isocyanate industry has been actively pursuing greener manufacturing practices. This includes the development of bio-based isocyanates, which offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based products. Additionally, research into catalytic processes and alternative reaction pathways aims to reduce the environmental impact of isocyanate synthesis.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!