How Isocyanates Streamline Global Material Resource Usage?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Technology Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have played a pivotal role in revolutionizing material science and resource utilization since their discovery in the early 20th century. The evolution of isocyanate technology has been driven by the increasing demand for versatile, high-performance materials across various industries. Initially developed for military applications during World War II, isocyanates quickly found their way into civilian use, marking the beginning of a new era in polymer chemistry.
The primary objective of isocyanate technology has been to enhance material properties while optimizing resource usage. This aligns perfectly with the global push for more sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes. Isocyanates' unique ability to form strong chemical bonds with a wide range of compounds has made them indispensable in the production of polyurethanes, a diverse family of polymers with applications ranging from flexible foams to rigid insulation materials.
As environmental concerns gained prominence, the focus of isocyanate technology shifted towards developing more eco-friendly formulations and production methods. This led to the exploration of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, aiming to reduce dependence on petrochemical feedstocks. Concurrently, efforts to improve the efficiency of isocyanate reactions have resulted in significant reductions in material waste and energy consumption during manufacturing processes.
The evolution of isocyanate technology has also been characterized by continuous improvements in safety and handling. Early challenges related to the toxicity and reactivity of isocyanates prompted the development of advanced containment systems, personal protective equipment, and safer production techniques. These advancements have not only enhanced worker safety but also expanded the potential applications of isocyanates in various industries.
Recent technological objectives in the field of isocyanates include the development of smart materials with self-healing properties, the integration of nanotechnology to enhance material performance, and the creation of isocyanate-based composites with unprecedented strength-to-weight ratios. These innovations are poised to further streamline global material resource usage by extending product lifespans, reducing maintenance requirements, and enabling the production of lighter, more durable goods.
Looking ahead, the future of isocyanate technology is closely tied to the principles of circular economy and sustainable development. Research is underway to develop fully recyclable isocyanate-based materials and to establish efficient recycling processes for existing polyurethane products. These efforts aim to minimize waste and maximize the utility of resources throughout the product lifecycle, aligning with global sustainability goals and resource conservation initiatives.
The primary objective of isocyanate technology has been to enhance material properties while optimizing resource usage. This aligns perfectly with the global push for more sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes. Isocyanates' unique ability to form strong chemical bonds with a wide range of compounds has made them indispensable in the production of polyurethanes, a diverse family of polymers with applications ranging from flexible foams to rigid insulation materials.
As environmental concerns gained prominence, the focus of isocyanate technology shifted towards developing more eco-friendly formulations and production methods. This led to the exploration of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, aiming to reduce dependence on petrochemical feedstocks. Concurrently, efforts to improve the efficiency of isocyanate reactions have resulted in significant reductions in material waste and energy consumption during manufacturing processes.
The evolution of isocyanate technology has also been characterized by continuous improvements in safety and handling. Early challenges related to the toxicity and reactivity of isocyanates prompted the development of advanced containment systems, personal protective equipment, and safer production techniques. These advancements have not only enhanced worker safety but also expanded the potential applications of isocyanates in various industries.
Recent technological objectives in the field of isocyanates include the development of smart materials with self-healing properties, the integration of nanotechnology to enhance material performance, and the creation of isocyanate-based composites with unprecedented strength-to-weight ratios. These innovations are poised to further streamline global material resource usage by extending product lifespans, reducing maintenance requirements, and enabling the production of lighter, more durable goods.
Looking ahead, the future of isocyanate technology is closely tied to the principles of circular economy and sustainable development. Research is underway to develop fully recyclable isocyanate-based materials and to establish efficient recycling processes for existing polyurethane products. These efforts aim to minimize waste and maximize the utility of resources throughout the product lifecycle, aligning with global sustainability goals and resource conservation initiatives.
Global Market Demand for Isocyanate-Based Materials
The global market demand for isocyanate-based materials has been experiencing significant growth, driven by their versatile applications across various industries. Polyurethanes, which are primarily derived from isocyanates, represent a major segment of this market. These materials find extensive use in construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics sectors, among others.
In the construction industry, isocyanate-based materials are widely utilized for insulation, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has led to increased adoption of polyurethane foams for thermal insulation. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing economies where rapid urbanization and infrastructure development are driving demand.
The automotive sector is another key consumer of isocyanate-based materials. Polyurethanes are used in vehicle interiors, seating, and under-the-hood applications. The push for lightweight vehicles to improve fuel efficiency has further boosted the demand for polyurethane components. Additionally, the growing electric vehicle market presents new opportunities for isocyanate-based materials in battery encapsulation and thermal management systems.
Furniture and bedding industries continue to be significant consumers of isocyanate-based flexible foams. The rising middle-class population in emerging markets, coupled with changing lifestyles and increased disposable incomes, has led to higher demand for comfortable and durable furniture products.
The electronics industry utilizes isocyanate-based materials in the production of coatings, adhesives, and potting compounds. With the rapid growth of consumer electronics and the expansion of 5G networks, the demand for these materials in electronic applications is expected to rise.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest and fastest-growing market for isocyanate-based materials. China, in particular, is a major consumer and producer, driven by its robust manufacturing sector and construction activities. North America and Europe also represent significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and sustainable applications.
The global shift towards sustainability has led to increased research and development efforts in bio-based isocyanates and recyclable polyurethanes. This trend is likely to shape the future market demand, as industries seek more environmentally friendly alternatives without compromising on performance.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. The industry is responding by investing in more efficient production processes and developing innovative products that meet evolving regulatory standards and consumer preferences.
In the construction industry, isocyanate-based materials are widely utilized for insulation, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has led to increased adoption of polyurethane foams for thermal insulation. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing economies where rapid urbanization and infrastructure development are driving demand.
The automotive sector is another key consumer of isocyanate-based materials. Polyurethanes are used in vehicle interiors, seating, and under-the-hood applications. The push for lightweight vehicles to improve fuel efficiency has further boosted the demand for polyurethane components. Additionally, the growing electric vehicle market presents new opportunities for isocyanate-based materials in battery encapsulation and thermal management systems.
Furniture and bedding industries continue to be significant consumers of isocyanate-based flexible foams. The rising middle-class population in emerging markets, coupled with changing lifestyles and increased disposable incomes, has led to higher demand for comfortable and durable furniture products.
The electronics industry utilizes isocyanate-based materials in the production of coatings, adhesives, and potting compounds. With the rapid growth of consumer electronics and the expansion of 5G networks, the demand for these materials in electronic applications is expected to rise.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific remains the largest and fastest-growing market for isocyanate-based materials. China, in particular, is a major consumer and producer, driven by its robust manufacturing sector and construction activities. North America and Europe also represent significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and sustainable applications.
The global shift towards sustainability has led to increased research and development efforts in bio-based isocyanates and recyclable polyurethanes. This trend is likely to shape the future market demand, as industries seek more environmentally friendly alternatives without compromising on performance.
Despite the positive growth outlook, the market faces challenges such as volatile raw material prices and stringent environmental regulations. The industry is responding by investing in more efficient production processes and developing innovative products that meet evolving regulatory standards and consumer preferences.
Current Isocyanate Applications and Challenges
Isocyanates have become integral components in various industries, revolutionizing material resource usage globally. Their versatility and reactivity make them indispensable in the production of polyurethanes, which find applications in diverse sectors such as construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics. However, the widespread use of isocyanates also presents significant challenges that need to be addressed.
In the construction industry, isocyanates are extensively used in the manufacture of rigid foam insulation, sealants, and adhesives. These materials contribute to energy efficiency in buildings by providing superior thermal insulation properties. The automotive sector relies heavily on isocyanate-based polyurethanes for producing lightweight components, enhancing fuel efficiency, and improving vehicle safety through the use of energy-absorbing materials.
The furniture industry utilizes isocyanates in the production of flexible foams for cushions and mattresses, offering comfort and durability. In electronics, isocyanates play a crucial role in the development of protective coatings and encapsulants, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic components.
Despite their widespread applications, isocyanates face several challenges. One of the primary concerns is their potential health hazards. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory irritation, allergic reactions, and in some cases, occupational asthma. This necessitates stringent safety measures and personal protective equipment in manufacturing and application processes.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the isocyanate industry. The production and disposal of isocyanate-based materials can have negative environmental impacts, including the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the generation of non-biodegradable waste. This has led to increased pressure for the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives and improved recycling technologies.
Another significant challenge is the dependence on fossil fuel-derived raw materials for isocyanate production. As global efforts to reduce carbon footprints intensify, the industry faces the task of finding sustainable feedstock alternatives and developing bio-based isocyanates.
Regulatory compliance presents an ongoing challenge for isocyanate manufacturers and users. Stringent regulations regarding the production, handling, and use of isocyanates require continuous adaptation and investment in compliance measures. This includes implementing advanced emission control technologies and developing safer formulations to meet evolving environmental and health standards.
The isocyanate industry also grapples with supply chain vulnerabilities. Recent global events have highlighted the need for more resilient supply chains, as disruptions in raw material availability can significantly impact production and downstream industries. This challenge necessitates the exploration of alternative sourcing strategies and the development of more localized production capabilities.
In the construction industry, isocyanates are extensively used in the manufacture of rigid foam insulation, sealants, and adhesives. These materials contribute to energy efficiency in buildings by providing superior thermal insulation properties. The automotive sector relies heavily on isocyanate-based polyurethanes for producing lightweight components, enhancing fuel efficiency, and improving vehicle safety through the use of energy-absorbing materials.
The furniture industry utilizes isocyanates in the production of flexible foams for cushions and mattresses, offering comfort and durability. In electronics, isocyanates play a crucial role in the development of protective coatings and encapsulants, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic components.
Despite their widespread applications, isocyanates face several challenges. One of the primary concerns is their potential health hazards. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory irritation, allergic reactions, and in some cases, occupational asthma. This necessitates stringent safety measures and personal protective equipment in manufacturing and application processes.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the isocyanate industry. The production and disposal of isocyanate-based materials can have negative environmental impacts, including the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the generation of non-biodegradable waste. This has led to increased pressure for the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives and improved recycling technologies.
Another significant challenge is the dependence on fossil fuel-derived raw materials for isocyanate production. As global efforts to reduce carbon footprints intensify, the industry faces the task of finding sustainable feedstock alternatives and developing bio-based isocyanates.
Regulatory compliance presents an ongoing challenge for isocyanate manufacturers and users. Stringent regulations regarding the production, handling, and use of isocyanates require continuous adaptation and investment in compliance measures. This includes implementing advanced emission control technologies and developing safer formulations to meet evolving environmental and health standards.
The isocyanate industry also grapples with supply chain vulnerabilities. Recent global events have highlighted the need for more resilient supply chains, as disruptions in raw material availability can significantly impact production and downstream industries. This challenge necessitates the exploration of alternative sourcing strategies and the development of more localized production capabilities.
Existing Isocyanate Resource Optimization Strategies
01 Resource allocation in virtualized environments
This point focuses on the efficient allocation and management of resources in virtualized computing environments. It involves techniques for dynamically assigning and optimizing resources such as CPU, memory, and storage across virtual machines or containers to ensure optimal performance and utilization.- Resource allocation in virtualized environments: This point focuses on the efficient allocation and management of resources in virtualized computing environments. It involves techniques for dynamically assigning and optimizing resources such as CPU, memory, and storage across virtual machines or containers to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization.
- Workload scheduling and load balancing: This aspect deals with intelligent scheduling of tasks and workloads across distributed computing resources. It includes methods for balancing loads across multiple nodes or servers to maximize efficiency, minimize response times, and ensure optimal resource usage in complex computing environments.
- Resource monitoring and management in cloud environments: This point covers techniques for monitoring, analyzing, and managing resources in cloud computing environments. It includes methods for real-time resource tracking, predictive analytics for resource needs, and automated management systems to optimize resource allocation and usage in large-scale cloud infrastructures.
- Energy-efficient resource utilization: This aspect focuses on strategies and technologies for minimizing energy consumption in computing environments while maintaining performance. It includes techniques for power-aware resource allocation, dynamic voltage and frequency scaling, and intelligent workload placement to reduce overall energy usage in data centers and distributed systems.
- Container-based resource management: This point addresses resource management specifically in containerized environments. It covers methods for efficient allocation, isolation, and scaling of resources for containers, as well as orchestration techniques to manage container lifecycles and resource usage across clusters of machines.
02 Workload scheduling and load balancing
This aspect deals with the intelligent distribution of tasks and workloads across available resources. It includes algorithms and methods for scheduling jobs, balancing loads, and optimizing resource usage to improve overall system performance and efficiency in distributed computing environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Resource monitoring and management systems
This point covers systems and methods for monitoring resource usage, tracking performance metrics, and managing resource allocation in real-time. It includes tools and techniques for analyzing resource consumption patterns, identifying bottlenecks, and making informed decisions about resource allocation and optimization.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cloud-based resource management
This category focuses on managing and optimizing resources in cloud computing environments. It includes techniques for provisioning, scaling, and orchestrating cloud resources, as well as methods for efficient utilization of shared resources across multiple tenants or applications in cloud platforms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Resource usage prediction and optimization
This point addresses predictive analytics and machine learning techniques used to forecast resource usage patterns and optimize resource allocation. It includes methods for anticipating future resource demands, proactively adjusting resource allocations, and implementing intelligent resource management strategies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Isocyanate Producers and Market Dynamics
The isocyanates market is in a mature growth stage, with a global market size estimated to exceed $30 billion by 2025. Major players like BASF, Covestro, and Wanhua Chemical dominate the industry, leveraging their advanced R&D capabilities and extensive product portfolios. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread application across various sectors, including automotive, construction, and electronics. However, companies are increasingly focusing on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving production efficiency to address environmental concerns and streamline resource usage. Emerging players like Momentive Performance Materials and Mitsui Chemicals are also making significant strides in specialized applications, contributing to the market's ongoing evolution and competitiveness.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative isocyanate-based solutions to optimize material resource usage globally. Their approach includes the use of aliphatic isocyanates for high-performance coatings with improved durability and weather resistance[1]. BASF's isocyanate technology enables the production of lightweight polyurethane foams, reducing material consumption in automotive and construction industries[2]. They have also introduced bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain[3]. BASF's isocyanate products feature enhanced reactivity and crosslinking properties, allowing for more efficient manufacturing processes and reduced waste[4].
Strengths: Wide range of applications, sustainability focus, and high-performance products. Weaknesses: Potential health and safety concerns associated with isocyanate handling.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed a comprehensive isocyanate portfolio to address global material resource optimization. Their MDI (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) technology enables the production of high-quality polyurethane materials with improved insulation properties, reducing energy consumption in buildings[1]. Wanhua's innovative HMDI (hexamethylene diisocyanate) products offer superior weatherability and chemical resistance for coatings applications, extending product lifespans[2]. The company has also introduced water-based polyurethane dispersions using novel isocyanate chemistries, reducing VOC emissions and improving environmental sustainability[3].
Strengths: Diverse product range, strong R&D capabilities, and focus on sustainable solutions. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges in different global markets.
Key Innovations in Isocyanate Synthesis and Usage
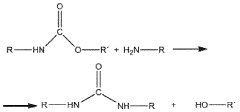
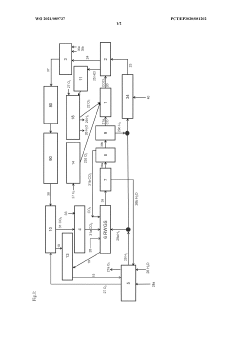
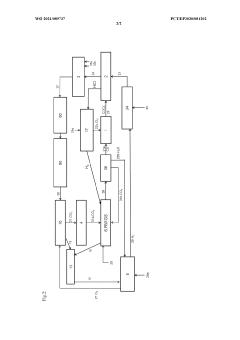
Sustainable preparation of organic amino compounds for the production of organic isocyanates
PatentWO2024017890A2
Innovation
- A process using green hydrogen and green ammonia to produce organic amino compounds, which are then used to synthesize isocyanates, incorporating renewable energy sources and reducing waste through closed-loop recycling of materials.
Method for isocyanate and polyurethane production with improved sustainability
PatentWO2021089737A1
Innovation
- A process that recycles polyurethane waste through pyrolysis and reverse water gas shift reaction, utilizing renewable energy for hydrogen and oxygen production, and closed-loop carbon dioxide recycling to produce isocyanates and polyurethanes, reducing fossil raw material use and carbon emissions.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate Manufacturing
The manufacturing of isocyanates, while essential for various industries, has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The production process involves several stages, each with potential environmental impacts. One of the primary concerns is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during synthesis and handling. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog.
Water pollution is another critical issue associated with isocyanate manufacturing. The process often generates wastewater containing various chemical compounds, including unreacted raw materials and byproducts. If not properly treated, these effluents can contaminate local water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the human water supply.
Energy consumption in isocyanate production is substantial, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The high-temperature reactions and distillation processes required for synthesis demand significant energy inputs, often derived from fossil fuels. This reliance on non-renewable energy sources exacerbates the carbon footprint of isocyanate manufacturing.
Solid waste generation is an additional environmental concern. Catalysts, solvents, and other materials used in the production process may result in hazardous waste that requires specialized disposal methods. Improper handling or disposal of these wastes can lead to soil contamination and long-term environmental degradation.
The transportation of raw materials and finished isocyanate products also contributes to the overall environmental impact. The global nature of the isocyanate supply chain often involves long-distance shipping, resulting in increased fuel consumption and associated emissions.
However, it's important to note that the isocyanate industry has made significant strides in recent years to mitigate these environmental impacts. Many manufacturers have implemented cleaner production technologies, such as closed-loop systems and advanced emission control devices. These innovations help reduce VOC emissions and improve energy efficiency.
Furthermore, there is a growing trend towards the development of bio-based isocyanates, which aim to reduce reliance on petroleum-derived raw materials. These alternative production methods have the potential to lower the overall environmental footprint of isocyanate manufacturing, although they are still in the early stages of development and implementation.
Water pollution is another critical issue associated with isocyanate manufacturing. The process often generates wastewater containing various chemical compounds, including unreacted raw materials and byproducts. If not properly treated, these effluents can contaminate local water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the human water supply.
Energy consumption in isocyanate production is substantial, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The high-temperature reactions and distillation processes required for synthesis demand significant energy inputs, often derived from fossil fuels. This reliance on non-renewable energy sources exacerbates the carbon footprint of isocyanate manufacturing.
Solid waste generation is an additional environmental concern. Catalysts, solvents, and other materials used in the production process may result in hazardous waste that requires specialized disposal methods. Improper handling or disposal of these wastes can lead to soil contamination and long-term environmental degradation.
The transportation of raw materials and finished isocyanate products also contributes to the overall environmental impact. The global nature of the isocyanate supply chain often involves long-distance shipping, resulting in increased fuel consumption and associated emissions.
However, it's important to note that the isocyanate industry has made significant strides in recent years to mitigate these environmental impacts. Many manufacturers have implemented cleaner production technologies, such as closed-loop systems and advanced emission control devices. These innovations help reduce VOC emissions and improve energy efficiency.
Furthermore, there is a growing trend towards the development of bio-based isocyanates, which aim to reduce reliance on petroleum-derived raw materials. These alternative production methods have the potential to lower the overall environmental footprint of isocyanate manufacturing, although they are still in the early stages of development and implementation.
Regulatory Framework for Isocyanate Use and Disposal
The regulatory framework for isocyanate use and disposal plays a crucial role in streamlining global material resource usage. Governments and international organizations have established comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safe handling, application, and disposal of isocyanates, recognizing their significant impact on various industries and the environment.
At the global level, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach for communicating chemical hazards, including those associated with isocyanates. This system facilitates international trade and promotes consistent safety standards across borders, contributing to more efficient resource utilization.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has implemented stringent regulations for isocyanate exposure in the workplace. These guidelines mandate proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and regular health monitoring for workers handling isocyanates. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanate emissions and disposal under the Clean Air Act and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
The European Union has adopted the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with isocyanates. This comprehensive approach ensures that isocyanates are used responsibly throughout their lifecycle, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have developed their own regulatory frameworks for isocyanate management. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both address the registration, evaluation, and control of isocyanates and their derivatives.
Proper disposal of isocyanate-containing materials is a critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Many countries have implemented specific guidelines for the treatment and disposal of isocyanate waste, often requiring specialized facilities and processes to prevent environmental contamination.
The regulatory landscape also encourages innovation in isocyanate alternatives and more sustainable production methods. This drive for improvement has led to the development of bio-based isocyanates and water-based polyurethane systems, which offer reduced environmental impact and improved resource efficiency.
Compliance with these regulations often necessitates significant investments in technology and processes. However, these investments ultimately contribute to more efficient resource usage by minimizing waste, improving worker safety, and reducing environmental impact. The regulatory framework thus serves as a catalyst for optimizing isocyanate use across industries, aligning with global sustainability goals.
At the global level, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach for communicating chemical hazards, including those associated with isocyanates. This system facilitates international trade and promotes consistent safety standards across borders, contributing to more efficient resource utilization.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has implemented stringent regulations for isocyanate exposure in the workplace. These guidelines mandate proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and regular health monitoring for workers handling isocyanates. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanate emissions and disposal under the Clean Air Act and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
The European Union has adopted the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with isocyanates. This comprehensive approach ensures that isocyanates are used responsibly throughout their lifecycle, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have developed their own regulatory frameworks for isocyanate management. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both address the registration, evaluation, and control of isocyanates and their derivatives.
Proper disposal of isocyanate-containing materials is a critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Many countries have implemented specific guidelines for the treatment and disposal of isocyanate waste, often requiring specialized facilities and processes to prevent environmental contamination.
The regulatory landscape also encourages innovation in isocyanate alternatives and more sustainable production methods. This drive for improvement has led to the development of bio-based isocyanates and water-based polyurethane systems, which offer reduced environmental impact and improved resource efficiency.
Compliance with these regulations often necessitates significant investments in technology and processes. However, these investments ultimately contribute to more efficient resource usage by minimizing waste, improving worker safety, and reducing environmental impact. The regulatory framework thus serves as a catalyst for optimizing isocyanate use across industries, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!