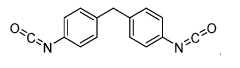
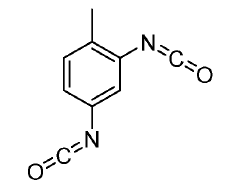
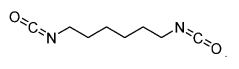
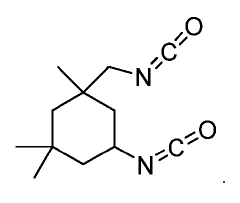
How Isocyanates Craft Novel Sustainable Innovations?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Technology Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have played a pivotal role in the development of polyurethane chemistry since their discovery in the 1930s. The evolution of isocyanate technology has been marked by continuous innovation, driven by the need for more sustainable and versatile materials across various industries. Initially, the focus was on developing basic polyurethane foams and coatings, but as environmental concerns grew, the trajectory shifted towards creating more eco-friendly and efficient isocyanate-based products.
The primary objective of current isocyanate technology is to harness its unique reactivity to craft novel sustainable innovations. This involves exploring new synthesis routes, developing bio-based isocyanates, and improving the overall environmental profile of isocyanate-derived materials. Researchers are actively pursuing ways to reduce the toxicity associated with traditional isocyanates while maintaining their desirable properties.
One significant trend in the field is the development of non-toxic alternatives to conventional isocyanates. This includes the exploration of blocked isocyanates, which release the reactive groups only under specific conditions, thereby enhancing safety and processability. Additionally, there is a growing interest in isocyanate-free chemistries that can mimic the performance of traditional polyurethanes.
The push for sustainability has led to increased efforts in creating bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. This aligns with the global shift towards reducing dependency on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprints. Researchers are investigating various plant-based feedstocks and biotechnological approaches to produce isocyanates with comparable or superior properties to their petrochemical counterparts.
Another key objective is to enhance the recyclability and biodegradability of isocyanate-based materials. This involves designing molecular structures that facilitate easier breakdown and reprocessing of polyurethanes at the end of their life cycle. Innovations in this area are crucial for addressing the growing concern of plastic waste and promoting a circular economy.
The integration of isocyanates with other advanced materials and technologies is also a significant focus. This includes their application in 3D printing, smart materials, and nanocomposites. By combining isocyanates with cutting-edge technologies, researchers aim to create multifunctional materials with enhanced properties and expanded applications.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing emphasis on developing more efficient and selective catalysts for isocyanate reactions. This not only improves the quality and consistency of the final products but also reduces energy consumption and waste generation in manufacturing processes. The ultimate goal is to establish isocyanate technology as a cornerstone of sustainable material science, capable of addressing global challenges in energy, environment, and resource utilization.
The primary objective of current isocyanate technology is to harness its unique reactivity to craft novel sustainable innovations. This involves exploring new synthesis routes, developing bio-based isocyanates, and improving the overall environmental profile of isocyanate-derived materials. Researchers are actively pursuing ways to reduce the toxicity associated with traditional isocyanates while maintaining their desirable properties.
One significant trend in the field is the development of non-toxic alternatives to conventional isocyanates. This includes the exploration of blocked isocyanates, which release the reactive groups only under specific conditions, thereby enhancing safety and processability. Additionally, there is a growing interest in isocyanate-free chemistries that can mimic the performance of traditional polyurethanes.
The push for sustainability has led to increased efforts in creating bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. This aligns with the global shift towards reducing dependency on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprints. Researchers are investigating various plant-based feedstocks and biotechnological approaches to produce isocyanates with comparable or superior properties to their petrochemical counterparts.
Another key objective is to enhance the recyclability and biodegradability of isocyanate-based materials. This involves designing molecular structures that facilitate easier breakdown and reprocessing of polyurethanes at the end of their life cycle. Innovations in this area are crucial for addressing the growing concern of plastic waste and promoting a circular economy.
The integration of isocyanates with other advanced materials and technologies is also a significant focus. This includes their application in 3D printing, smart materials, and nanocomposites. By combining isocyanates with cutting-edge technologies, researchers aim to create multifunctional materials with enhanced properties and expanded applications.
As the field progresses, there is an increasing emphasis on developing more efficient and selective catalysts for isocyanate reactions. This not only improves the quality and consistency of the final products but also reduces energy consumption and waste generation in manufacturing processes. The ultimate goal is to establish isocyanate technology as a cornerstone of sustainable material science, capable of addressing global challenges in energy, environment, and resource utilization.
Market Demand for Sustainable Isocyanate Applications
The market demand for sustainable isocyanate applications has been steadily growing in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations. Isocyanates, traditionally associated with polyurethane production, are now finding novel applications in sustainable innovations across various industries.
In the construction sector, there is a rising demand for eco-friendly insulation materials. Isocyanate-based foam insulations offer superior thermal performance while reducing energy consumption in buildings. This market segment is expected to expand significantly as governments worldwide implement stricter energy efficiency standards for new and existing structures.
The automotive industry is another key driver for sustainable isocyanate applications. Lightweight materials are crucial for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Isocyanate-based composites and coatings are being developed to replace heavier traditional materials, meeting both performance and sustainability requirements. The shift towards electric vehicles further amplifies this demand, as weight reduction becomes even more critical for extending battery range.
In the packaging industry, there is a growing need for biodegradable and recyclable materials. Isocyanate-modified biopolymers are emerging as promising alternatives to conventional plastics. These materials offer improved barrier properties and mechanical strength while being more environmentally friendly. The food and beverage sector, in particular, is showing increased interest in these sustainable packaging solutions.
The textile industry is also exploring sustainable isocyanate applications. Water-based polyurethane coatings derived from bio-based isocyanates are gaining traction as alternatives to solvent-based systems. These coatings provide durability and weather resistance to fabrics while reducing environmental impact and improving worker safety.
In the medical field, there is a rising demand for biocompatible materials. Isocyanate-based hydrogels and tissue scaffolds are being developed for wound healing and tissue engineering applications. These materials offer tunable properties and biodegradability, addressing the need for advanced, sustainable healthcare solutions.
The adhesives and sealants market is another area where sustainable isocyanate applications are in high demand. Low-VOC and solvent-free formulations are being developed to meet stringent environmental regulations while maintaining performance. These products find applications in various industries, from construction to electronics.
As sustainability becomes a core focus for businesses and consumers alike, the market for innovative, eco-friendly isocyanate applications is poised for substantial growth. Companies investing in research and development of these sustainable technologies are likely to gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
In the construction sector, there is a rising demand for eco-friendly insulation materials. Isocyanate-based foam insulations offer superior thermal performance while reducing energy consumption in buildings. This market segment is expected to expand significantly as governments worldwide implement stricter energy efficiency standards for new and existing structures.
The automotive industry is another key driver for sustainable isocyanate applications. Lightweight materials are crucial for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Isocyanate-based composites and coatings are being developed to replace heavier traditional materials, meeting both performance and sustainability requirements. The shift towards electric vehicles further amplifies this demand, as weight reduction becomes even more critical for extending battery range.
In the packaging industry, there is a growing need for biodegradable and recyclable materials. Isocyanate-modified biopolymers are emerging as promising alternatives to conventional plastics. These materials offer improved barrier properties and mechanical strength while being more environmentally friendly. The food and beverage sector, in particular, is showing increased interest in these sustainable packaging solutions.
The textile industry is also exploring sustainable isocyanate applications. Water-based polyurethane coatings derived from bio-based isocyanates are gaining traction as alternatives to solvent-based systems. These coatings provide durability and weather resistance to fabrics while reducing environmental impact and improving worker safety.
In the medical field, there is a rising demand for biocompatible materials. Isocyanate-based hydrogels and tissue scaffolds are being developed for wound healing and tissue engineering applications. These materials offer tunable properties and biodegradability, addressing the need for advanced, sustainable healthcare solutions.
The adhesives and sealants market is another area where sustainable isocyanate applications are in high demand. Low-VOC and solvent-free formulations are being developed to meet stringent environmental regulations while maintaining performance. These products find applications in various industries, from construction to electronics.
As sustainability becomes a core focus for businesses and consumers alike, the market for innovative, eco-friendly isocyanate applications is poised for substantial growth. Companies investing in research and development of these sustainable technologies are likely to gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate-Based Sustainability
The development of sustainable innovations based on isocyanates faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent toxicity of isocyanates, which poses risks to both human health and the environment. This toxicity necessitates stringent safety measures during production, handling, and application processes, increasing operational costs and complexity.
Another major challenge lies in the sourcing of raw materials for isocyanate production. Traditionally, isocyanates are derived from fossil fuels, which contradicts the principles of sustainability. The transition to bio-based or renewable sources for isocyanate production is still in its infancy, presenting technical and economic hurdles that need to be overcome.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production also presents a sustainability challenge. The synthesis of isocyanates typically requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in significant energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Developing more energy-efficient production methods remains a key area of focus for researchers and industry professionals.
Recyclability and end-of-life management of isocyanate-based products pose additional challenges. Many products containing isocyanates, such as polyurethane foams and coatings, are difficult to recycle or dispose of in an environmentally friendly manner. This issue is particularly pressing given the growing emphasis on circular economy principles and extended producer responsibility.
Furthermore, regulatory pressures and evolving environmental standards present ongoing challenges for isocyanate-based innovations. Stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other emissions are driving the need for low-VOC or VOC-free isocyanate formulations, which can be technically challenging to develop without compromising performance.
The development of safer alternatives to traditional isocyanates is another area of focus. While some progress has been made in creating non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs), these alternatives often fall short in terms of performance, cost-effectiveness, or scalability compared to their isocyanate-based counterparts.
Lastly, the challenge of public perception and consumer awareness cannot be overlooked. The negative associations with isocyanates due to their potential health risks can impact market acceptance of isocyanate-based sustainable innovations, necessitating extensive education and communication efforts to highlight the benefits and safety measures implemented in modern applications.
Another major challenge lies in the sourcing of raw materials for isocyanate production. Traditionally, isocyanates are derived from fossil fuels, which contradicts the principles of sustainability. The transition to bio-based or renewable sources for isocyanate production is still in its infancy, presenting technical and economic hurdles that need to be overcome.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production also presents a sustainability challenge. The synthesis of isocyanates typically requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in significant energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Developing more energy-efficient production methods remains a key area of focus for researchers and industry professionals.
Recyclability and end-of-life management of isocyanate-based products pose additional challenges. Many products containing isocyanates, such as polyurethane foams and coatings, are difficult to recycle or dispose of in an environmentally friendly manner. This issue is particularly pressing given the growing emphasis on circular economy principles and extended producer responsibility.
Furthermore, regulatory pressures and evolving environmental standards present ongoing challenges for isocyanate-based innovations. Stricter regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other emissions are driving the need for low-VOC or VOC-free isocyanate formulations, which can be technically challenging to develop without compromising performance.
The development of safer alternatives to traditional isocyanates is another area of focus. While some progress has been made in creating non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs), these alternatives often fall short in terms of performance, cost-effectiveness, or scalability compared to their isocyanate-based counterparts.
Lastly, the challenge of public perception and consumer awareness cannot be overlooked. The negative associations with isocyanates due to their potential health risks can impact market acceptance of isocyanate-based sustainable innovations, necessitating extensive education and communication efforts to highlight the benefits and safety measures implemented in modern applications.
Existing Sustainable Isocyanate Solutions
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various formulations, curing methods, and applications of isocyanate-based polymers in coatings, adhesives, and other materials.
- Isocyanate-based foams and insulation materials: Several patents focus on the development of isocyanate-based foams and insulation materials. These include improvements in foam formulations, blowing agents, and processing techniques to enhance thermal insulation properties and structural integrity.
- Isocyanate modifications and derivatives: Patents in this category describe various modifications and derivatives of isocyanates, including blocked isocyanates, isocyanate prepolymers, and novel isocyanate compounds with enhanced properties or specific functionalities.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, several patents address safety concerns and improved handling methods. These include storage techniques, exposure prevention, and the development of less hazardous isocyanate formulations or alternatives.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various formulations, curing methods, and applications of isocyanate-based polymers in coatings, adhesives, and foams.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes
Research into isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes is presented, addressing health and environmental concerns associated with traditional isocyanates. These alternatives aim to provide similar performance characteristics while reducing potential hazards.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of isocyanates
Techniques for modifying and functionalizing isocyanates to enhance their properties or create new derivatives are described. These modifications can improve reactivity, stability, or introduce new functional groups for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Patents related to the safe handling, storage, and use of isocyanates are included. These cover protective equipment, exposure prevention methods, and techniques for neutralizing or disposing of isocyanate-containing materials safely.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Isocyanate Industry
The isocyanates market is in a mature growth phase, with a global market size estimated to exceed $30 billion by 2025. The technology's maturity is evident in the diverse applications across industries, from polyurethanes to coatings. Key players like Wanhua Chemical, BASF, and Covestro are driving innovation in sustainable isocyanate solutions. Wanhua Chemical Group, a market leader, is focusing on eco-friendly alternatives and bio-based isocyanates. BASF is developing low-emission isocyanates for automotive applications, while Covestro is pioneering isocyanate-free technologies. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing R&D efforts to address environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, with a growing emphasis on green chemistry and circular economy principles.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed innovative isocyanate-based solutions for sustainable applications. They have pioneered the use of bio-based polyols in combination with isocyanates to create more environmentally friendly polyurethane products[1]. Their research focuses on improving the efficiency of isocyanate production processes, reducing energy consumption and waste generation. Wanhua has also developed novel catalysts that enhance the reactivity of isocyanates, allowing for lower processing temperatures and reduced environmental impact[2]. Additionally, they are exploring the use of CO2 as a raw material in isocyanate production, potentially reducing the carbon footprint of their products[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, vertically integrated production, and a wide range of isocyanate products. Weaknesses: Dependence on petrochemical feedstocks and potential regulatory challenges related to isocyanate handling and use.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has made significant strides in developing sustainable innovations using isocyanates. They have introduced a range of bio-based polyurethanes using isocyanates derived from renewable resources[4]. BASF's research focuses on improving the durability and performance of isocyanate-based coatings, adhesives, and sealants, extending product lifespans and reducing waste. They have also developed water-based polyurethane dispersions that significantly reduce VOC emissions[5]. BASF's commitment to sustainability is further demonstrated by their efforts to optimize isocyanate production processes, reducing energy consumption and improving atom efficiency[6].
Strengths: Extensive R&D resources, global presence, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: High capital investment requirements for new sustainable technologies and potential market resistance to higher-priced eco-friendly alternatives.
Innovative Isocyanate Sustainability Patents
Sustainable preparation of organic amino compounds for the production of organic isocyanates
PatentWO2024017890A2
Innovation
- A process using green hydrogen and green ammonia to produce organic amino compounds, which are then used to synthesize isocyanates, incorporating renewable energy sources and reducing waste through closed-loop recycling of materials.
Flow chemistry synthesis of isocyanates
PatentWO2021119606A1
Innovation
- A continuous flow process involving the mixing of acyl hydrazides with nitrous acid to form acyl azides, followed by heating in the presence of an organic solvent to produce isocyanates through Curtius rearrangement, offering a safer and more scalable method for isocyanate synthesis.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate Technologies
Isocyanate technologies have a complex relationship with environmental sustainability. While these compounds have enabled significant advancements in various industries, their production and use have raised concerns about potential environmental impacts.
The manufacturing process of isocyanates often involves the use of fossil fuel-derived raw materials, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, recent innovations in bio-based isocyanates are showing promise in reducing the reliance on petrochemicals. These sustainable alternatives utilize renewable resources such as plant oils or agricultural waste, potentially lowering the overall carbon footprint of isocyanate production.
In terms of air quality, the volatile nature of some isocyanates poses risks of atmospheric pollution. Emissions during production and application can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and other air pollutants. To address this, advanced emission control technologies and improved manufacturing processes are being developed to minimize the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Water pollution is another area of concern, particularly in regions where isocyanate production facilities are located near water bodies. Proper waste management and water treatment systems are crucial to prevent contamination of aquatic ecosystems. Industry leaders are investing in closed-loop systems and advanced filtration technologies to reduce water consumption and improve the quality of discharged effluents.
The persistence of isocyanate-based products in the environment is a topic of ongoing research. While many polyurethane materials derived from isocyanates are durable and long-lasting, this characteristic can also lead to challenges in waste management and biodegradation. Efforts are underway to develop more easily recyclable or biodegradable isocyanate-based materials, aligning with circular economy principles.
On the positive side, isocyanate technologies have contributed to energy efficiency in various applications. For instance, polyurethane insulation materials, which often contain isocyanates, play a significant role in reducing energy consumption in buildings. This indirect environmental benefit helps offset some of the negative impacts associated with isocyanate production.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, life cycle assessments are becoming increasingly important. These comprehensive analyses help identify areas for improvement across the entire value chain of isocyanate-based products, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Such assessments are driving innovation in green chemistry approaches and circular economy strategies within the isocyanate sector.
The manufacturing process of isocyanates often involves the use of fossil fuel-derived raw materials, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. However, recent innovations in bio-based isocyanates are showing promise in reducing the reliance on petrochemicals. These sustainable alternatives utilize renewable resources such as plant oils or agricultural waste, potentially lowering the overall carbon footprint of isocyanate production.
In terms of air quality, the volatile nature of some isocyanates poses risks of atmospheric pollution. Emissions during production and application can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone and other air pollutants. To address this, advanced emission control technologies and improved manufacturing processes are being developed to minimize the release of harmful substances into the environment.
Water pollution is another area of concern, particularly in regions where isocyanate production facilities are located near water bodies. Proper waste management and water treatment systems are crucial to prevent contamination of aquatic ecosystems. Industry leaders are investing in closed-loop systems and advanced filtration technologies to reduce water consumption and improve the quality of discharged effluents.
The persistence of isocyanate-based products in the environment is a topic of ongoing research. While many polyurethane materials derived from isocyanates are durable and long-lasting, this characteristic can also lead to challenges in waste management and biodegradation. Efforts are underway to develop more easily recyclable or biodegradable isocyanate-based materials, aligning with circular economy principles.
On the positive side, isocyanate technologies have contributed to energy efficiency in various applications. For instance, polyurethane insulation materials, which often contain isocyanates, play a significant role in reducing energy consumption in buildings. This indirect environmental benefit helps offset some of the negative impacts associated with isocyanate production.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, life cycle assessments are becoming increasingly important. These comprehensive analyses help identify areas for improvement across the entire value chain of isocyanate-based products, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Such assessments are driving innovation in green chemistry approaches and circular economy strategies within the isocyanate sector.
Regulatory Framework for Sustainable Isocyanates
The regulatory framework for sustainable isocyanates is a critical aspect of ensuring the responsible development and use of these versatile chemicals in environmentally friendly applications. As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, governments and international organizations have been implementing stricter regulations to govern the production, handling, and disposal of isocyanates.
At the forefront of these regulatory efforts is the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register their substances and provide detailed information on their properties, hazards, and safe use. For isocyanates, this has led to increased scrutiny and the need for comprehensive safety data sheets and exposure scenarios.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established guidelines under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) for the use of isocyanates in various applications. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has also set permissible exposure limits and mandates proper handling procedures to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with isocyanate exposure.
The regulatory landscape is evolving to address the specific challenges of sustainable isocyanate use. This includes promoting the development of bio-based isocyanates and encouraging the use of recycled or renewable raw materials in their production. Regulations are also focusing on the end-of-life management of isocyanate-containing products, with an emphasis on recyclability and biodegradability.
Several countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs that require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal or recycling. This approach is particularly relevant for isocyanate-based materials used in construction and automotive industries, where proper disposal and recycling are crucial for reducing environmental impact.
Certification schemes and eco-labels are emerging as important tools in the regulatory framework. These voluntary programs, such as the GreenGuard Certification for low-emitting materials, provide incentives for manufacturers to develop more sustainable isocyanate-based products. They also offer consumers and businesses a way to identify environmentally preferable options.
International collaboration is key to establishing a cohesive regulatory framework for sustainable isocyanates. Organizations like the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) are working to harmonize global standards and promote best practices in the sustainable use of chemicals, including isocyanates. This collaborative approach aims to create a level playing field for industry while ensuring consistent environmental protection across borders.
As research into novel sustainable innovations continues, regulators are tasked with staying ahead of technological advancements. This requires a flexible regulatory approach that can adapt to new developments in isocyanate chemistry and applications, while maintaining rigorous safety and environmental standards.
At the forefront of these regulatory efforts is the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register their substances and provide detailed information on their properties, hazards, and safe use. For isocyanates, this has led to increased scrutiny and the need for comprehensive safety data sheets and exposure scenarios.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established guidelines under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) for the use of isocyanates in various applications. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has also set permissible exposure limits and mandates proper handling procedures to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with isocyanate exposure.
The regulatory landscape is evolving to address the specific challenges of sustainable isocyanate use. This includes promoting the development of bio-based isocyanates and encouraging the use of recycled or renewable raw materials in their production. Regulations are also focusing on the end-of-life management of isocyanate-containing products, with an emphasis on recyclability and biodegradability.
Several countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs that require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal or recycling. This approach is particularly relevant for isocyanate-based materials used in construction and automotive industries, where proper disposal and recycling are crucial for reducing environmental impact.
Certification schemes and eco-labels are emerging as important tools in the regulatory framework. These voluntary programs, such as the GreenGuard Certification for low-emitting materials, provide incentives for manufacturers to develop more sustainable isocyanate-based products. They also offer consumers and businesses a way to identify environmentally preferable options.
International collaboration is key to establishing a cohesive regulatory framework for sustainable isocyanates. Organizations like the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) are working to harmonize global standards and promote best practices in the sustainable use of chemicals, including isocyanates. This collaborative approach aims to create a level playing field for industry while ensuring consistent environmental protection across borders.
As research into novel sustainable innovations continues, regulators are tasked with staying ahead of technological advancements. This requires a flexible regulatory approach that can adapt to new developments in isocyanate chemistry and applications, while maintaining rigorous safety and environmental standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!