Constructing Effective Isocyanate Hiring and Training Protocols
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Safety Goals
Isocyanate safety goals are paramount in the construction of effective hiring and training protocols for industries dealing with these highly reactive chemicals. The primary objective is to establish a comprehensive framework that ensures the protection of workers, the environment, and the surrounding community from the potential hazards associated with isocyanate exposure.
A key safety goal is to minimize the risk of acute and chronic health effects among workers. This includes preventing respiratory sensitization, which can lead to occupational asthma, as well as skin irritation and allergic reactions. To achieve this, protocols must focus on proper personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, including respiratory protection, impermeable gloves, and protective clothing.
Another critical safety objective is to implement robust engineering controls to reduce isocyanate exposure. This involves designing and maintaining effective ventilation systems, enclosed processes, and automated handling systems to minimize direct contact with these chemicals. The goal is to create a work environment where exposure levels are consistently below permissible exposure limits (PELs) set by regulatory agencies.
Developing a culture of safety awareness is also a crucial aspect of isocyanate safety goals. This entails creating comprehensive training programs that educate workers about the properties of isocyanates, potential health risks, proper handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. The aim is to empower employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to work safely with these substances.
Environmental protection is another vital safety goal in isocyanate handling. Protocols should address proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods to prevent accidental releases or spills that could harm ecosystems or contaminate water sources. This includes implementing spill containment measures and establishing clear procedures for managing waste and byproducts.
Continuous monitoring and assessment of workplace conditions form an integral part of isocyanate safety goals. Regular air sampling, health surveillance of workers, and periodic review of safety procedures are essential to ensure that control measures remain effective over time. The objective is to create a dynamic safety system that can adapt to changing conditions and emerging risks.
Lastly, compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices is a fundamental safety goal. This involves staying up-to-date with the latest regulations from agencies such as OSHA, EPA, and relevant international bodies, and incorporating these requirements into hiring and training protocols. The aim is to not only meet legal obligations but to exceed them, fostering a proactive approach to isocyanate safety management.
A key safety goal is to minimize the risk of acute and chronic health effects among workers. This includes preventing respiratory sensitization, which can lead to occupational asthma, as well as skin irritation and allergic reactions. To achieve this, protocols must focus on proper personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, including respiratory protection, impermeable gloves, and protective clothing.
Another critical safety objective is to implement robust engineering controls to reduce isocyanate exposure. This involves designing and maintaining effective ventilation systems, enclosed processes, and automated handling systems to minimize direct contact with these chemicals. The goal is to create a work environment where exposure levels are consistently below permissible exposure limits (PELs) set by regulatory agencies.
Developing a culture of safety awareness is also a crucial aspect of isocyanate safety goals. This entails creating comprehensive training programs that educate workers about the properties of isocyanates, potential health risks, proper handling procedures, and emergency response protocols. The aim is to empower employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to work safely with these substances.
Environmental protection is another vital safety goal in isocyanate handling. Protocols should address proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods to prevent accidental releases or spills that could harm ecosystems or contaminate water sources. This includes implementing spill containment measures and establishing clear procedures for managing waste and byproducts.
Continuous monitoring and assessment of workplace conditions form an integral part of isocyanate safety goals. Regular air sampling, health surveillance of workers, and periodic review of safety procedures are essential to ensure that control measures remain effective over time. The objective is to create a dynamic safety system that can adapt to changing conditions and emerging risks.
Lastly, compliance with regulatory standards and industry best practices is a fundamental safety goal. This involves staying up-to-date with the latest regulations from agencies such as OSHA, EPA, and relevant international bodies, and incorporating these requirements into hiring and training protocols. The aim is to not only meet legal obligations but to exceed them, fostering a proactive approach to isocyanate safety management.
Industry Demand Analysis
The demand for effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols has been steadily increasing across various industries, particularly in manufacturing, construction, and automotive sectors. This surge is primarily driven by the growing awareness of workplace safety and the stringent regulations surrounding the handling of hazardous materials.
In the manufacturing sector, the use of isocyanates in the production of polyurethane foams, coatings, and adhesives has created a significant need for specialized training programs. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of having well-trained personnel to handle these potentially dangerous chemicals safely and efficiently. This has led to a rise in demand for comprehensive hiring protocols that can identify candidates with the necessary skills and knowledge to work with isocyanates.
The construction industry has also seen a notable increase in the use of isocyanate-based products, especially in insulation and waterproofing applications. As a result, there is a growing market for training programs that focus on the proper application techniques and safety measures required when working with these materials. Construction firms are actively seeking employees who have undergone specialized isocyanate training to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to minimize the risk of workplace accidents.
In the automotive sector, the use of isocyanates in paints, coatings, and adhesives has created a demand for skilled workers who can handle these substances safely. Auto manufacturers and repair shops are investing in training programs to ensure their employees are well-versed in the proper handling and application of isocyanate-based products. This has led to an increased focus on developing effective hiring protocols that can identify candidates with the necessary expertise or potential to acquire these specialized skills.
The healthcare industry has also contributed to the growing demand for isocyanate training protocols. With the increasing use of medical devices and equipment that contain isocyanate-based materials, healthcare facilities are recognizing the need for staff training in proper handling and disposal procedures. This has created a niche market for training programs tailored specifically to healthcare professionals working with isocyanate-containing medical products.
As environmental concerns continue to gain prominence, there is a rising demand for training programs that focus on the safe disposal and environmental impact of isocyanates. Companies across various industries are seeking to implement protocols that not only ensure worker safety but also address the broader environmental implications of isocyanate use. This has led to an increased emphasis on developing hiring and training protocols that incorporate environmental awareness and sustainable practices.
The global nature of many industries has also contributed to the demand for standardized isocyanate training protocols. Multinational corporations are seeking to implement consistent safety standards across their operations worldwide, creating a need for comprehensive training programs that can be adapted to different regulatory environments while maintaining a core set of best practices.
In the manufacturing sector, the use of isocyanates in the production of polyurethane foams, coatings, and adhesives has created a significant need for specialized training programs. Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of having well-trained personnel to handle these potentially dangerous chemicals safely and efficiently. This has led to a rise in demand for comprehensive hiring protocols that can identify candidates with the necessary skills and knowledge to work with isocyanates.
The construction industry has also seen a notable increase in the use of isocyanate-based products, especially in insulation and waterproofing applications. As a result, there is a growing market for training programs that focus on the proper application techniques and safety measures required when working with these materials. Construction firms are actively seeking employees who have undergone specialized isocyanate training to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to minimize the risk of workplace accidents.
In the automotive sector, the use of isocyanates in paints, coatings, and adhesives has created a demand for skilled workers who can handle these substances safely. Auto manufacturers and repair shops are investing in training programs to ensure their employees are well-versed in the proper handling and application of isocyanate-based products. This has led to an increased focus on developing effective hiring protocols that can identify candidates with the necessary expertise or potential to acquire these specialized skills.
The healthcare industry has also contributed to the growing demand for isocyanate training protocols. With the increasing use of medical devices and equipment that contain isocyanate-based materials, healthcare facilities are recognizing the need for staff training in proper handling and disposal procedures. This has created a niche market for training programs tailored specifically to healthcare professionals working with isocyanate-containing medical products.
As environmental concerns continue to gain prominence, there is a rising demand for training programs that focus on the safe disposal and environmental impact of isocyanates. Companies across various industries are seeking to implement protocols that not only ensure worker safety but also address the broader environmental implications of isocyanate use. This has led to an increased emphasis on developing hiring and training protocols that incorporate environmental awareness and sustainable practices.
The global nature of many industries has also contributed to the demand for standardized isocyanate training protocols. Multinational corporations are seeking to implement consistent safety standards across their operations worldwide, creating a need for comprehensive training programs that can be adapted to different regulatory environments while maintaining a core set of best practices.
Current Challenges
The construction of effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized industry-wide guidelines for handling isocyanates safely. This absence of uniformity creates inconsistencies in training approaches across different organizations, potentially leading to gaps in worker knowledge and safety practices.
Another critical challenge is the rapidly evolving nature of isocyanate-related technologies and applications. As new formulations and uses for isocyanates emerge, training protocols must be continuously updated to address novel risks and safety considerations. This constant need for adaptation puts pressure on organizations to maintain up-to-date training materials and methodologies.
The complexity of isocyanate chemistry poses a significant hurdle in developing comprehensive training programs. Isocyanates encompass a wide range of compounds with varying properties and hazards, making it challenging to create training protocols that adequately cover all potential scenarios workers may encounter. This complexity also necessitates a high level of expertise among trainers, which can be difficult to source and maintain.
Regulatory compliance presents another layer of difficulty in constructing effective protocols. Different regions and countries may have varying regulations regarding isocyanate handling and worker safety, requiring organizations to navigate a complex web of legal requirements when developing their training programs. This regulatory landscape is often subject to change, further complicating the maintenance of compliant protocols.
The diverse workforce involved in isocyanate handling introduces additional challenges. Workers may have varying levels of education, language proficiency, and prior experience with hazardous materials. Designing training protocols that effectively communicate critical safety information to this diverse audience requires careful consideration of learning styles, cultural differences, and potential language barriers.
Furthermore, the high turnover rate in some industries that utilize isocyanates creates a continuous need for training new employees. This constant influx of new workers necessitates efficient onboarding processes that can quickly bring individuals up to speed on safety protocols without compromising thoroughness.
Lastly, the integration of new technologies in training methodologies presents both opportunities and challenges. While virtual reality simulations and interactive e-learning platforms offer innovative ways to enhance training effectiveness, their implementation requires significant investment and expertise. Organizations must carefully evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of adopting these technologies and ensure they align with the specific needs of isocyanate handling protocols.
Another critical challenge is the rapidly evolving nature of isocyanate-related technologies and applications. As new formulations and uses for isocyanates emerge, training protocols must be continuously updated to address novel risks and safety considerations. This constant need for adaptation puts pressure on organizations to maintain up-to-date training materials and methodologies.
The complexity of isocyanate chemistry poses a significant hurdle in developing comprehensive training programs. Isocyanates encompass a wide range of compounds with varying properties and hazards, making it challenging to create training protocols that adequately cover all potential scenarios workers may encounter. This complexity also necessitates a high level of expertise among trainers, which can be difficult to source and maintain.
Regulatory compliance presents another layer of difficulty in constructing effective protocols. Different regions and countries may have varying regulations regarding isocyanate handling and worker safety, requiring organizations to navigate a complex web of legal requirements when developing their training programs. This regulatory landscape is often subject to change, further complicating the maintenance of compliant protocols.
The diverse workforce involved in isocyanate handling introduces additional challenges. Workers may have varying levels of education, language proficiency, and prior experience with hazardous materials. Designing training protocols that effectively communicate critical safety information to this diverse audience requires careful consideration of learning styles, cultural differences, and potential language barriers.
Furthermore, the high turnover rate in some industries that utilize isocyanates creates a continuous need for training new employees. This constant influx of new workers necessitates efficient onboarding processes that can quickly bring individuals up to speed on safety protocols without compromising thoroughness.
Lastly, the integration of new technologies in training methodologies presents both opportunities and challenges. While virtual reality simulations and interactive e-learning platforms offer innovative ways to enhance training effectiveness, their implementation requires significant investment and expertise. Organizations must carefully evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of adopting these technologies and ensure they align with the specific needs of isocyanate handling protocols.
Existing Training Methods
01 Employee screening and selection for isocyanate handling
Implementing rigorous screening processes to identify suitable candidates for roles involving isocyanate handling. This includes assessing candidates' qualifications, experience, and understanding of safety protocols related to hazardous materials. The selection process may involve specialized tests and interviews to ensure candidates meet the necessary requirements for working with isocyanates.- Employee screening and selection for isocyanate handling: Implementing rigorous screening processes to identify suitable candidates for roles involving isocyanate handling. This includes assessing candidates' qualifications, experience, and understanding of safety protocols related to hazardous materials. The selection process may involve specialized tests and interviews to ensure candidates meet the required standards for working with isocyanates.
- Comprehensive training programs for isocyanate safety: Developing and implementing comprehensive training programs specifically focused on isocyanate safety. These programs cover topics such as proper handling techniques, personal protective equipment usage, emergency response procedures, and health hazards associated with isocyanate exposure. Regular refresher courses and assessments ensure employees maintain up-to-date knowledge and skills.
- Technology-assisted training and monitoring: Utilizing advanced technologies such as virtual reality simulations, e-learning platforms, and wearable devices to enhance isocyanate safety training and monitoring. These technologies provide immersive learning experiences, real-time feedback, and continuous monitoring of employee compliance with safety protocols.
- Certification and compliance management: Implementing systems to manage employee certifications and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements for isocyanate handling. This includes tracking training completion, maintaining certification records, and scheduling recertification processes. Automated systems may be used to alert management of upcoming certification expirations and compliance issues.
- Continuous improvement and feedback mechanisms: Establishing processes for continuous improvement of isocyanate safety protocols and training programs. This involves gathering feedback from employees, analyzing incident reports, and incorporating lessons learned into updated training materials and procedures. Regular safety audits and performance evaluations help identify areas for improvement in hiring and training practices.
02 Comprehensive isocyanate safety training programs
Developing and implementing comprehensive training programs specifically focused on isocyanate safety. These programs cover topics such as proper handling techniques, personal protective equipment usage, emergency response procedures, and health hazards associated with isocyanate exposure. Regular refresher courses and assessments are conducted to ensure ongoing compliance and knowledge retention.Expand Specific Solutions03 Digital learning platforms for isocyanate training
Utilizing digital learning platforms and technologies to deliver isocyanate safety training. This includes e-learning modules, virtual reality simulations, and interactive online courses that allow employees to learn and practice isocyanate handling procedures in a safe, controlled environment. These platforms also enable tracking of training completion and performance metrics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Compliance management systems for isocyanate protocols
Implementing compliance management systems to ensure adherence to isocyanate handling protocols and regulations. These systems track employee certifications, training schedules, and safety audits. They also facilitate documentation of incidents, near-misses, and corrective actions related to isocyanate handling, helping organizations maintain regulatory compliance and improve safety practices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Personalized training and career development for isocyanate handlers
Creating personalized training and career development plans for employees working with isocyanates. This approach takes into account individual skill levels, learning styles, and career aspirations to provide targeted training and growth opportunities. It may include mentorship programs, advanced certifications, and cross-training in related areas to enhance overall competence and job satisfaction among isocyanate handlers.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for constructing effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols is in a growth phase, driven by increasing safety regulations and industry awareness. The global market size for isocyanate-related safety solutions is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 5-7% over the next five years. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations in training methodologies and safety equipment. Key players like Covestro Deutschland AG, BASF Corp., and Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. are investing in advanced training programs and safety protocols. Companies such as 3M Innovative Properties Co. and Dow Global Technologies LLC are developing new technologies to enhance isocyanate handling safety, while Breakthrough Performancetech LLC is focusing on innovative simulation-based training solutions for skill development in this specialized area.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has developed a comprehensive isocyanate safety program that includes advanced training protocols and hiring practices. Their approach focuses on a multi-tiered training system, starting with basic safety awareness for all employees and progressing to specialized training for those directly handling isocyanates. The company utilizes virtual reality simulations to provide realistic, hands-on training scenarios without exposure risks[1]. Additionally, Covestro has implemented a rigorous pre-employment screening process that includes medical evaluations and aptitude tests specifically designed to assess candidates' suitability for working with hazardous materials[2]. Their hiring protocol also incorporates a probationary period with close supervision and regular assessments to ensure new employees can safely handle isocyanates in real-world conditions[3].
Strengths: Innovative use of technology in training, comprehensive screening process. Weaknesses: Potentially high implementation costs, may limit the pool of eligible candidates.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has implemented a robust isocyanate safety program that integrates advanced hiring and training protocols. Their approach includes a detailed pre-employment assessment that evaluates candidates' understanding of chemical safety principles and their ability to follow complex procedures[1]. BASF's training program is modular and tailored to specific roles, ensuring that employees receive relevant, in-depth instruction on isocyanate handling. The company has also developed a proprietary online learning management system that tracks employee progress and automatically schedules refresher courses[2]. BASF's protocol emphasizes hands-on training in controlled environments, using state-of-the-art personal protective equipment (PPE) and handling techniques. Additionally, they have implemented a mentor system where experienced employees guide new hires through a structured on-the-job training program[3].
Strengths: Tailored, role-specific training, continuous learning approach. Weaknesses: Potentially time-consuming implementation, may require significant resources for smaller operations.
Core Safety Innovations
Worker specific health and safety training
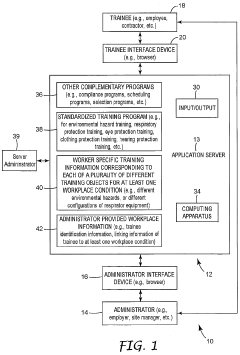
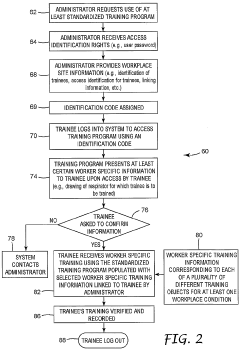
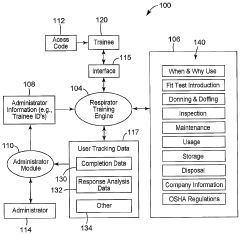
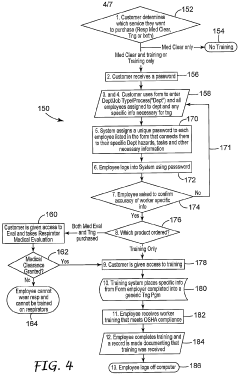
PatentWO2004102314A2
Innovation
- A system that provides worker-specific training information by linking each trainee with the appropriate training objects based on their unique workplace conditions and equipment, using a standardized training program and unique identification codes to ensure each employee receives tailored training relevant to their specific respirator or safety equipment.
System, apparatus, and method of accelerated training for performance under stress
PatentInactiveUS20210275094A1
Innovation
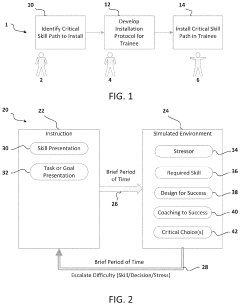
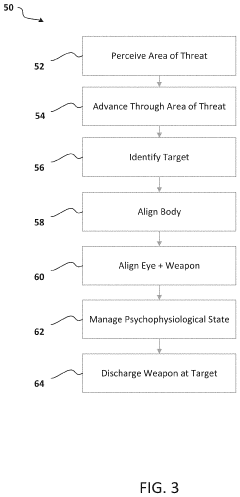
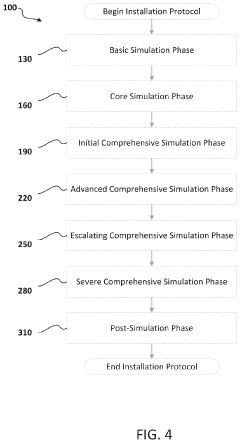
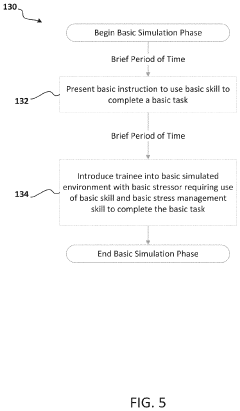
- A method and system for training that integrates accelerated learning with psychophysiological state management and stress inoculation, using simulated environments to rapidly install critical skills subconsciously, enhancing situational awareness and reducing training time by monitoring and adjusting the training protocol based on internal and external markers of learning under stress.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of constructing effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols. The use of isocyanates in various industries is subject to stringent regulations due to their potential health hazards. Organizations must adhere to these regulations to ensure worker safety and avoid legal repercussions.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific standards for isocyanate exposure in the workplace. These standards include permissible exposure limits (PELs) and requirements for personal protective equipment (PPE). Employers must ensure that their hiring and training protocols align with OSHA's guidelines, including proper hazard communication and medical surveillance programs.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Companies must comply with reporting and recordkeeping requirements, as well as implement measures to prevent environmental contamination. This includes proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures for isocyanate-containing materials.
Internationally, regulations vary by country, but many follow guidelines set by organizations such as the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the International Labour Organization (ILO). The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes strict requirements on the use and import of isocyanates.
Effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols must incorporate these regulatory requirements. This includes developing comprehensive training programs that cover hazard identification, safe handling procedures, emergency response, and proper use of PPE. Employers should also implement regular assessments to ensure ongoing compliance and update their protocols as regulations evolve.
Documentation plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Organizations must maintain detailed records of employee training, exposure monitoring, and medical examinations. These records serve as evidence of compliance during inspections and audits by regulatory agencies.
To stay current with regulatory changes, companies should establish a system for monitoring updates from relevant agencies. This may involve designating a compliance officer or team responsible for tracking and implementing new requirements. Regular internal audits can help identify areas for improvement and ensure continued adherence to regulations.
Collaboration with industry associations and participation in regulatory forums can provide valuable insights into best practices and upcoming regulatory changes. This proactive approach allows organizations to anticipate and prepare for new compliance requirements, ensuring their isocyanate hiring and training protocols remain effective and compliant.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific standards for isocyanate exposure in the workplace. These standards include permissible exposure limits (PELs) and requirements for personal protective equipment (PPE). Employers must ensure that their hiring and training protocols align with OSHA's guidelines, including proper hazard communication and medical surveillance programs.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Companies must comply with reporting and recordkeeping requirements, as well as implement measures to prevent environmental contamination. This includes proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures for isocyanate-containing materials.
Internationally, regulations vary by country, but many follow guidelines set by organizations such as the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the International Labour Organization (ILO). The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes strict requirements on the use and import of isocyanates.
Effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols must incorporate these regulatory requirements. This includes developing comprehensive training programs that cover hazard identification, safe handling procedures, emergency response, and proper use of PPE. Employers should also implement regular assessments to ensure ongoing compliance and update their protocols as regulations evolve.
Documentation plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Organizations must maintain detailed records of employee training, exposure monitoring, and medical examinations. These records serve as evidence of compliance during inspections and audits by regulatory agencies.
To stay current with regulatory changes, companies should establish a system for monitoring updates from relevant agencies. This may involve designating a compliance officer or team responsible for tracking and implementing new requirements. Regular internal audits can help identify areas for improvement and ensure continued adherence to regulations.
Collaboration with industry associations and participation in regulatory forums can provide valuable insights into best practices and upcoming regulatory changes. This proactive approach allows organizations to anticipate and prepare for new compliance requirements, ensuring their isocyanate hiring and training protocols remain effective and compliant.
Health Impact Assessment
The implementation of effective isocyanate hiring and training protocols necessitates a comprehensive health impact assessment to ensure the safety and well-being of workers and the surrounding community. This assessment begins with identifying potential exposure routes, including inhalation, skin contact, and ingestion. Isocyanates, known for their high reactivity and potential to cause respiratory sensitization, require careful evaluation of both acute and chronic health effects.
Short-term exposure to isocyanates can lead to irritation of the eyes, nose, throat, and skin, while long-term exposure may result in occupational asthma, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, and other respiratory disorders. The health impact assessment should consider the varying susceptibility among individuals, as some may develop sensitization even at low exposure levels.
A crucial aspect of the assessment involves evaluating the effectiveness of personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls in mitigating health risks. This includes analyzing the efficacy of respirators, gloves, and protective clothing, as well as ventilation systems and containment measures. The assessment should also address the potential for off-site migration of isocyanates and its impact on community health.
Monitoring strategies play a vital role in the health impact assessment. This includes establishing protocols for air sampling, biological monitoring, and medical surveillance. Regular health screenings, including pulmonary function tests and skin examinations, should be incorporated to detect early signs of isocyanate-related health effects.
The assessment should also consider the psychological impact of working with hazardous materials on employees. This includes evaluating stress levels, risk perception, and the effectiveness of risk communication strategies. Additionally, the potential for accidents and spills should be assessed, with emergency response procedures evaluated for their ability to minimize health impacts during incidents.
Lastly, the health impact assessment should address the long-term sustainability of isocyanate use, considering alternatives and emerging technologies that may reduce health risks. This forward-looking approach ensures that the hiring and training protocols remain relevant and effective in protecting worker health as industry practices evolve.
Short-term exposure to isocyanates can lead to irritation of the eyes, nose, throat, and skin, while long-term exposure may result in occupational asthma, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, and other respiratory disorders. The health impact assessment should consider the varying susceptibility among individuals, as some may develop sensitization even at low exposure levels.
A crucial aspect of the assessment involves evaluating the effectiveness of personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls in mitigating health risks. This includes analyzing the efficacy of respirators, gloves, and protective clothing, as well as ventilation systems and containment measures. The assessment should also address the potential for off-site migration of isocyanates and its impact on community health.
Monitoring strategies play a vital role in the health impact assessment. This includes establishing protocols for air sampling, biological monitoring, and medical surveillance. Regular health screenings, including pulmonary function tests and skin examinations, should be incorporated to detect early signs of isocyanate-related health effects.
The assessment should also consider the psychological impact of working with hazardous materials on employees. This includes evaluating stress levels, risk perception, and the effectiveness of risk communication strategies. Additionally, the potential for accidents and spills should be assessed, with emergency response procedures evaluated for their ability to minimize health impacts during incidents.
Lastly, the health impact assessment should address the long-term sustainability of isocyanate use, considering alternatives and emerging technologies that may reduce health risks. This forward-looking approach ensures that the hiring and training protocols remain relevant and effective in protecting worker health as industry practices evolve.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!