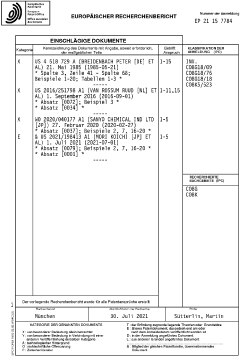
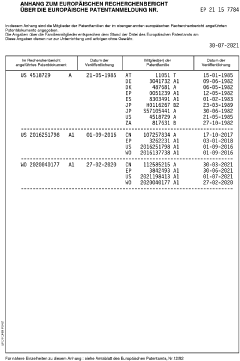
Next Steps in Isocyanate-Free Innovation
JUL 10, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate-Free Adhesives: Background and Objectives
Isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings have long been the industry standard due to their excellent performance characteristics, including high strength, durability, and versatility. However, growing concerns over the health and environmental impacts of isocyanates have driven a significant push towards developing isocyanate-free alternatives. This technological shift represents a critical juncture in the adhesives and coatings industry, with far-reaching implications for manufacturers, end-users, and regulatory bodies alike.
The evolution of adhesive and coating technologies has been marked by continuous innovation, with isocyanate-based products dominating the market for decades. These materials, particularly polyurethanes, have found widespread use across various industries, from construction and automotive to furniture and textiles. Their popularity stems from their ability to form strong, flexible bonds and create durable, protective coatings.
Despite their advantages, isocyanates pose significant health risks, including respiratory sensitization and potential carcinogenicity. These concerns have led to stricter regulations and a growing demand for safer alternatives. The challenge lies in developing isocyanate-free solutions that can match or exceed the performance of traditional formulations while addressing safety and environmental concerns.
Recent years have seen a surge in research and development efforts aimed at creating viable isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings. These initiatives focus on exploring alternative chemistries, such as silane-terminated polymers, epoxy-based systems, and bio-based materials. The objectives of this technological transition are multifaceted, encompassing improved worker safety, reduced environmental impact, and compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
The drive towards isocyanate-free innovation is not merely a response to regulatory pressures but also an opportunity for industry players to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Companies that successfully develop high-performance, environmentally friendly alternatives stand to gain significant market share and establish themselves as leaders in sustainable chemistry.
As the industry moves forward, the primary goals of isocyanate-free innovation include developing products that offer comparable or superior performance to traditional isocyanate-based systems, ensuring cost-effectiveness to facilitate widespread adoption, and creating formulations that are compatible with existing application methods and equipment. Additionally, there is a strong focus on improving the sustainability profile of these new materials, aligning with broader industry trends towards eco-friendly solutions.
The evolution of adhesive and coating technologies has been marked by continuous innovation, with isocyanate-based products dominating the market for decades. These materials, particularly polyurethanes, have found widespread use across various industries, from construction and automotive to furniture and textiles. Their popularity stems from their ability to form strong, flexible bonds and create durable, protective coatings.
Despite their advantages, isocyanates pose significant health risks, including respiratory sensitization and potential carcinogenicity. These concerns have led to stricter regulations and a growing demand for safer alternatives. The challenge lies in developing isocyanate-free solutions that can match or exceed the performance of traditional formulations while addressing safety and environmental concerns.
Recent years have seen a surge in research and development efforts aimed at creating viable isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings. These initiatives focus on exploring alternative chemistries, such as silane-terminated polymers, epoxy-based systems, and bio-based materials. The objectives of this technological transition are multifaceted, encompassing improved worker safety, reduced environmental impact, and compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
The drive towards isocyanate-free innovation is not merely a response to regulatory pressures but also an opportunity for industry players to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Companies that successfully develop high-performance, environmentally friendly alternatives stand to gain significant market share and establish themselves as leaders in sustainable chemistry.
As the industry moves forward, the primary goals of isocyanate-free innovation include developing products that offer comparable or superior performance to traditional isocyanate-based systems, ensuring cost-effectiveness to facilitate widespread adoption, and creating formulations that are compatible with existing application methods and equipment. Additionally, there is a strong focus on improving the sustainability profile of these new materials, aligning with broader industry trends towards eco-friendly solutions.
Market Demand Analysis for Eco-Friendly Adhesives
The market demand for eco-friendly adhesives and coatings has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness, stringent regulations, and consumer preferences for sustainable products. This shift towards isocyanate-free alternatives is particularly evident in industries such as construction, automotive, packaging, and consumer goods.
Environmental concerns have become a major factor influencing market dynamics. Traditional adhesives and coatings often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants, which contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. As a result, governments worldwide have implemented stricter regulations on VOC emissions, pushing manufacturers to develop and adopt eco-friendly alternatives.
Consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products have also played a crucial role in driving market growth. End-users are increasingly seeking products that are not only effective but also environmentally responsible. This trend has led to a surge in demand for bio-based and renewable raw materials in adhesive and coating formulations.
The construction industry has emerged as a key driver for eco-friendly adhesives and coatings. Green building certifications, such as LEED, have created a strong incentive for using sustainable materials. In this sector, water-based and solvent-free adhesives are gaining traction, particularly in applications like flooring, wall coverings, and insulation.
The automotive industry is another significant market for isocyanate-free innovations. With the push towards lightweight vehicles for improved fuel efficiency, manufacturers are seeking adhesives that can bond dissimilar materials while meeting stringent environmental standards. This has led to increased adoption of structural adhesives that are both high-performance and eco-friendly.
In the packaging industry, the demand for sustainable solutions has been driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer preferences. Food-safe, recyclable, and compostable adhesives are becoming increasingly important, especially in flexible packaging applications.
The consumer goods sector has also shown a growing interest in eco-friendly adhesives and coatings. From furniture to electronics, manufacturers are incorporating sustainable materials to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and comply with evolving regulations.
Market analysts project continued growth in the eco-friendly adhesives and coatings sector. The global green coatings market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with water-based coatings leading the way. Similarly, the bio-based adhesives market is forecasted to grow at a substantial rate, driven by applications in packaging, construction, and woodworking.
Environmental concerns have become a major factor influencing market dynamics. Traditional adhesives and coatings often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants, which contribute to air pollution and pose health risks. As a result, governments worldwide have implemented stricter regulations on VOC emissions, pushing manufacturers to develop and adopt eco-friendly alternatives.
Consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products have also played a crucial role in driving market growth. End-users are increasingly seeking products that are not only effective but also environmentally responsible. This trend has led to a surge in demand for bio-based and renewable raw materials in adhesive and coating formulations.
The construction industry has emerged as a key driver for eco-friendly adhesives and coatings. Green building certifications, such as LEED, have created a strong incentive for using sustainable materials. In this sector, water-based and solvent-free adhesives are gaining traction, particularly in applications like flooring, wall coverings, and insulation.
The automotive industry is another significant market for isocyanate-free innovations. With the push towards lightweight vehicles for improved fuel efficiency, manufacturers are seeking adhesives that can bond dissimilar materials while meeting stringent environmental standards. This has led to increased adoption of structural adhesives that are both high-performance and eco-friendly.
In the packaging industry, the demand for sustainable solutions has been driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer preferences. Food-safe, recyclable, and compostable adhesives are becoming increasingly important, especially in flexible packaging applications.
The consumer goods sector has also shown a growing interest in eco-friendly adhesives and coatings. From furniture to electronics, manufacturers are incorporating sustainable materials to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and comply with evolving regulations.
Market analysts project continued growth in the eco-friendly adhesives and coatings sector. The global green coatings market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with water-based coatings leading the way. Similarly, the bio-based adhesives market is forecasted to grow at a substantial rate, driven by applications in packaging, construction, and woodworking.
Current State of Isocyanate-Free Technology
The current state of isocyanate-free technology in adhesives and coatings has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by increasing environmental and health concerns associated with traditional isocyanate-based products. Manufacturers and researchers have been actively developing alternative solutions that offer comparable performance without the risks associated with isocyanates.
One of the primary approaches in isocyanate-free innovation has been the development of polyurethane dispersions (PUDs) that utilize alternative chemistries. These include waterborne systems based on polyurethane-acrylic hybrids, which combine the flexibility and adhesion of polyurethanes with the durability and weather resistance of acrylics. Such hybrid systems have shown promising results in both adhesive and coating applications, particularly in the automotive and construction industries.
Another significant area of development is in bio-based isocyanate-free technologies. Researchers have made progress in utilizing renewable resources such as vegetable oils, lignin, and cellulose to create sustainable alternatives. These bio-based systems not only address the isocyanate concern but also contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of adhesives and coatings.
Silane-terminated polymers (STPs) have emerged as a viable isocyanate-free option, especially in the construction adhesives sector. These moisture-curing systems offer excellent adhesion to a wide range of substrates and demonstrate good resistance to weathering and chemicals. Their ease of use and low VOC emissions make them increasingly popular in both professional and DIY markets.
In the field of high-performance coatings, epoxy-based systems have been refined to match or exceed the properties of isocyanate-containing counterparts. Advanced epoxy formulations, often incorporating nano-materials or hybrid technologies, have shown improved durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion properties, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Recent innovations in UV-curable systems have also contributed to the isocyanate-free landscape. These fast-curing, energy-efficient technologies have found applications in both adhesives and coatings, particularly in industries requiring rapid processing times, such as electronics and packaging.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain in achieving the full spectrum of properties offered by isocyanate-based systems, particularly in terms of heat resistance and flexibility. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing formulations and exploring novel chemistries to bridge these performance gaps.
One of the primary approaches in isocyanate-free innovation has been the development of polyurethane dispersions (PUDs) that utilize alternative chemistries. These include waterborne systems based on polyurethane-acrylic hybrids, which combine the flexibility and adhesion of polyurethanes with the durability and weather resistance of acrylics. Such hybrid systems have shown promising results in both adhesive and coating applications, particularly in the automotive and construction industries.
Another significant area of development is in bio-based isocyanate-free technologies. Researchers have made progress in utilizing renewable resources such as vegetable oils, lignin, and cellulose to create sustainable alternatives. These bio-based systems not only address the isocyanate concern but also contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of adhesives and coatings.
Silane-terminated polymers (STPs) have emerged as a viable isocyanate-free option, especially in the construction adhesives sector. These moisture-curing systems offer excellent adhesion to a wide range of substrates and demonstrate good resistance to weathering and chemicals. Their ease of use and low VOC emissions make them increasingly popular in both professional and DIY markets.
In the field of high-performance coatings, epoxy-based systems have been refined to match or exceed the properties of isocyanate-containing counterparts. Advanced epoxy formulations, often incorporating nano-materials or hybrid technologies, have shown improved durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion properties, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Recent innovations in UV-curable systems have also contributed to the isocyanate-free landscape. These fast-curing, energy-efficient technologies have found applications in both adhesives and coatings, particularly in industries requiring rapid processing times, such as electronics and packaging.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain in achieving the full spectrum of properties offered by isocyanate-based systems, particularly in terms of heat resistance and flexibility. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing formulations and exploring novel chemistries to bridge these performance gaps.
Existing Isocyanate-Free Solutions
01 Use of polyurethane dispersions
Isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings can be formulated using polyurethane dispersions. These dispersions are typically water-based and offer excellent adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance. They can be used in various applications, including textile coatings, automotive coatings, and wood adhesives.- Epoxy-based adhesives and coatings: Epoxy-based formulations are used as alternatives to isocyanate-containing adhesives and coatings. These systems typically involve epoxy resins cured with various hardeners, offering good adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability without the use of isocyanates.
- Silane-modified polymer systems: Silane-modified polymers are employed in isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings. These moisture-curable systems provide excellent adhesion to various substrates and offer good flexibility and weather resistance, making them suitable for construction and automotive applications.
- Bio-based adhesives and coatings: Environmentally friendly adhesives and coatings derived from renewable resources are developed as isocyanate-free alternatives. These formulations often utilize plant-based oils, starches, or proteins, offering sustainable solutions with reduced environmental impact.
- Acrylic-based adhesive systems: Acrylic-based adhesives and coatings are formulated without isocyanates, providing fast curing, good adhesion to various substrates, and excellent weathering resistance. These systems are often used in automotive, construction, and industrial applications.
- Polyurethane dispersions without free isocyanates: Water-based polyurethane dispersions are developed without free isocyanates, offering improved safety and environmental benefits. These systems provide good film formation, adhesion, and chemical resistance, suitable for various coating applications.
02 Epoxy-based formulations
Epoxy-based systems are widely used as alternatives to isocyanate-containing adhesives and coatings. These formulations typically consist of epoxy resins and hardeners, providing excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability. They are commonly used in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Silane-modified polymers
Silane-modified polymers offer an isocyanate-free alternative for adhesives and coatings. These polymers combine the flexibility of organic materials with the durability of silicones, resulting in products with excellent adhesion, weatherability, and UV resistance. They are particularly useful in construction sealants and industrial coatings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bio-based adhesives and coatings
Bio-based materials derived from renewable resources are increasingly used in isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings. These formulations often incorporate plant-based oils, starches, or proteins, offering environmentally friendly alternatives with good performance characteristics. They find applications in packaging, wood products, and construction materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Acrylic-based systems
Acrylic-based adhesives and coatings provide isocyanate-free alternatives with excellent weatherability, UV resistance, and adhesion properties. These systems can be formulated as water-based or solvent-based products, offering versatility in application methods and curing mechanisms. They are widely used in architectural coatings, pressure-sensitive adhesives, and automotive applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate-Free Innovation
The isocyanate-free innovation for adhesives and coatings is in a transitional phase, with the market showing significant growth potential. The global push for sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions is driving this trend. Major players like Covestro, Dow, LANXESS, and Henkel are investing heavily in R&D to develop viable alternatives. The technology is maturing rapidly, with companies such as Bayer and Evonik making substantial progress in formulating high-performance, isocyanate-free products. However, challenges remain in matching the performance of traditional isocyanate-based systems across all applications, indicating that the technology is not yet fully mature and there is room for further innovation and market expansion.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has developed a range of isocyanate-free polyurethane dispersions (PUDs) for adhesives and coatings applications. Their innovative approach utilizes bio-based raw materials and incorporates carbodiimide crosslinking technology[1]. This technology enables the formation of strong chemical bonds without the use of isocyanates, resulting in high-performance, environmentally friendly products. Covestro's PUDs offer excellent adhesion to various substrates, high flexibility, and good chemical resistance[2]. The company has also introduced waterborne polyurethane coatings that are free from isocyanates, providing a sustainable alternative for industries such as automotive and furniture[3].
Strengths: Eco-friendly formulations, reduced VOC emissions, improved worker safety. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, may require modifications to existing manufacturing processes.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has pioneered the development of VORASURF™ polyurethane additives, which are designed to work in isocyanate-free foam systems[4]. These additives enable the production of flexible foams with improved physical properties and processing characteristics without the use of isocyanates. Additionally, Dow has introduced VORALAST™ H2Foam, a novel polyurethane foam system that utilizes hydrogen as a blowing agent, eliminating the need for isocyanates in certain applications[5]. The company is also exploring bio-based alternatives and hybrid technologies that combine different polymer chemistries to achieve isocyanate-free solutions for adhesives and coatings[6].
Strengths: Versatile product range, compatibility with existing manufacturing equipment. Weaknesses: Limited application in high-performance coatings, ongoing research needed for broader adoption.
Core Innovations in Alternative Chemistries
Novel phthalate-free isocyanurate composition
PatentInactiveEP3909994A1
Innovation
- Compositions containing isocyanurates with isocyanate groups and alkyl diphenyl phosphate, where the weight ratio of these components ranges from 1:1 to 1:8, with a preferred embodiment of 20-35% isocyanurates and 65-80% 2-ethylhexyl diphenyl phosphate, trimerized in the presence of a catalyst to achieve low viscosity and stability.
Low-modulus silylated polyurethanes
PatentActiveUS20150284610A1
Innovation
- A method for producing silylated polyurethanes by reacting a polyether polyol with a polyisocyanate in the presence of a solvent, followed by a silane of specific formula, which allows for the formation of a hydroxy-terminated prepolymer that can cure in the presence of atmospheric moisture, creating a polymer with excellent extensibility and restoring force.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of isocyanate-free innovations for adhesives and coatings reveals significant potential for reducing ecological footprints across various industries. These novel formulations aim to address the environmental concerns associated with traditional isocyanate-based products, which have been linked to health hazards and ecological damage.
One of the primary environmental benefits of isocyanate-free alternatives is the reduction in volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Many new formulations utilize water-based or high-solids technologies, dramatically lowering the release of harmful vapors during application and curing processes. This improvement not only enhances air quality but also contributes to the mitigation of smog formation and greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the shift towards bio-based raw materials in isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings presents an opportunity to decrease reliance on fossil fuel-derived resources. By incorporating renewable feedstocks, such as plant-based oils or recycled polymers, these innovations support the circular economy and reduce overall carbon footprints. Life cycle assessments have shown promising results, with some bio-based alternatives demonstrating up to 30% lower environmental impact compared to their petroleum-based counterparts.
Water consumption and wastewater generation are also critical factors in environmental impact assessments. Isocyanate-free technologies often require less water for production and cleanup, leading to reduced strain on water resources and decreased wastewater treatment needs. This aspect is particularly crucial in water-stressed regions and industries with high water usage.
The end-of-life considerations for isocyanate-free products show improved recyclability and biodegradability compared to traditional formulations. Many new adhesives and coatings are designed with easier separation and recycling in mind, facilitating the recovery of materials at the end of product lifecycles. Some biodegradable options even offer the potential for composting, further reducing landfill waste.
However, it is important to note that the environmental benefits of isocyanate-free innovations can vary depending on specific formulations and applications. Comprehensive life cycle analyses are necessary to accurately compare the environmental impacts of new technologies with existing solutions across different use cases and geographical regions.
As research and development in this field progress, continuous improvement in environmental performance is expected. Future innovations may focus on enhancing the durability and longevity of isocyanate-free products, which could further reduce resource consumption and waste generation over extended product lifespans.
One of the primary environmental benefits of isocyanate-free alternatives is the reduction in volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Many new formulations utilize water-based or high-solids technologies, dramatically lowering the release of harmful vapors during application and curing processes. This improvement not only enhances air quality but also contributes to the mitigation of smog formation and greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the shift towards bio-based raw materials in isocyanate-free adhesives and coatings presents an opportunity to decrease reliance on fossil fuel-derived resources. By incorporating renewable feedstocks, such as plant-based oils or recycled polymers, these innovations support the circular economy and reduce overall carbon footprints. Life cycle assessments have shown promising results, with some bio-based alternatives demonstrating up to 30% lower environmental impact compared to their petroleum-based counterparts.
Water consumption and wastewater generation are also critical factors in environmental impact assessments. Isocyanate-free technologies often require less water for production and cleanup, leading to reduced strain on water resources and decreased wastewater treatment needs. This aspect is particularly crucial in water-stressed regions and industries with high water usage.
The end-of-life considerations for isocyanate-free products show improved recyclability and biodegradability compared to traditional formulations. Many new adhesives and coatings are designed with easier separation and recycling in mind, facilitating the recovery of materials at the end of product lifecycles. Some biodegradable options even offer the potential for composting, further reducing landfill waste.
However, it is important to note that the environmental benefits of isocyanate-free innovations can vary depending on specific formulations and applications. Comprehensive life cycle analyses are necessary to accurately compare the environmental impacts of new technologies with existing solutions across different use cases and geographical regions.
As research and development in this field progress, continuous improvement in environmental performance is expected. Future innovations may focus on enhancing the durability and longevity of isocyanate-free products, which could further reduce resource consumption and waste generation over extended product lifespans.
Regulatory Landscape for Adhesives and Coatings
The regulatory landscape for adhesives and coatings is undergoing significant changes, driven by increasing environmental and health concerns. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to reduce the use of harmful chemicals, particularly isocyanates, in these products.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has been a key driver for change. It requires manufacturers to register chemicals and provide safety data, with a focus on reducing the use of substances of very high concern (SVHCs). Isocyanates, commonly used in adhesives and coatings, are under scrutiny due to their potential health risks.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also been active in regulating adhesives and coatings. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), the EPA has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances. Recent amendments to TSCA have strengthened the EPA's ability to evaluate and regulate chemicals, including those used in adhesives and coatings.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have been updating their chemical regulations to align more closely with international standards. China's new chemical substance notification system and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both aim to enhance the management of chemical substances, including those used in adhesives and coatings.
Industry-specific regulations are also evolving. For instance, in the automotive sector, there is a growing push for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) adhesives and coatings to improve air quality in vehicle interiors. Similarly, the construction industry is seeing increased demand for green building materials, including eco-friendly adhesives and coatings.
The food packaging industry faces particularly stringent regulations. Both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have strict guidelines for materials that come into contact with food, including adhesives used in packaging.
As regulations tighten, manufacturers are increasingly investing in research and development of isocyanate-free alternatives. This shift is not only driven by regulatory compliance but also by market demand for safer, more sustainable products. Companies that can innovate and adapt to this changing regulatory landscape are likely to gain a competitive edge in the adhesives and coatings market.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has been a key driver for change. It requires manufacturers to register chemicals and provide safety data, with a focus on reducing the use of substances of very high concern (SVHCs). Isocyanates, commonly used in adhesives and coatings, are under scrutiny due to their potential health risks.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also been active in regulating adhesives and coatings. Under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), the EPA has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances. Recent amendments to TSCA have strengthened the EPA's ability to evaluate and regulate chemicals, including those used in adhesives and coatings.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have been updating their chemical regulations to align more closely with international standards. China's new chemical substance notification system and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both aim to enhance the management of chemical substances, including those used in adhesives and coatings.
Industry-specific regulations are also evolving. For instance, in the automotive sector, there is a growing push for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) adhesives and coatings to improve air quality in vehicle interiors. Similarly, the construction industry is seeing increased demand for green building materials, including eco-friendly adhesives and coatings.
The food packaging industry faces particularly stringent regulations. Both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have strict guidelines for materials that come into contact with food, including adhesives used in packaging.
As regulations tighten, manufacturers are increasingly investing in research and development of isocyanate-free alternatives. This shift is not only driven by regulatory compliance but also by market demand for safer, more sustainable products. Companies that can innovate and adapt to this changing regulatory landscape are likely to gain a competitive edge in the adhesives and coatings market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!