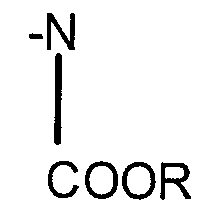Mastering Isocyanate Deployment for Strategic Implementations
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Technology Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have been a cornerstone in various industries since their discovery in the mid-20th century. The evolution of isocyanate technology has been marked by continuous advancements in synthesis, application techniques, and safety measures. Initially developed for polyurethane production, isocyanates have expanded their reach into diverse sectors, including automotive, construction, and electronics.
The primary objective in mastering isocyanate deployment is to optimize their performance while minimizing associated risks. This involves enhancing reaction control, improving product quality, and developing safer handling methods. Recent technological advancements have focused on creating more environmentally friendly isocyanates, addressing concerns about volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and potential health hazards.
One significant trend in isocyanate technology is the development of water-based systems, which reduce the need for organic solvents and lower VOC emissions. This aligns with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations. Another key area of focus is the creation of blocked isocyanates, which remain stable at room temperature and only become reactive under specific conditions, enhancing safety and ease of use.
The pursuit of bio-based isocyanates represents a promising frontier in the field. Researchers are exploring renewable resources as precursors for isocyanate production, aiming to decrease reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. This aligns with the broader trend towards sustainable chemistry and circular economy principles.
Advancements in catalysis have played a crucial role in isocyanate technology evolution. Novel catalysts have enabled more precise control over reaction kinetics, leading to improved product properties and reduced energy consumption. Additionally, the development of one-component systems has simplified application processes, opening up new possibilities for end-users.
The integration of nanotechnology with isocyanate chemistry is another area of significant potential. Nanocomposites incorporating isocyanates have shown enhanced mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties, expanding the range of possible applications. This convergence of technologies is expected to drive innovation in high-performance materials.
Looking ahead, the objectives for isocyanate technology include further improvements in safety profiles, increased use of renewable resources, and the development of smart, responsive materials. The industry aims to create isocyanate-based products with self-healing properties, adaptable characteristics, and enhanced durability. These advancements will likely reshape manufacturing processes and enable new product categories across multiple sectors.
The primary objective in mastering isocyanate deployment is to optimize their performance while minimizing associated risks. This involves enhancing reaction control, improving product quality, and developing safer handling methods. Recent technological advancements have focused on creating more environmentally friendly isocyanates, addressing concerns about volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and potential health hazards.
One significant trend in isocyanate technology is the development of water-based systems, which reduce the need for organic solvents and lower VOC emissions. This aligns with global sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations. Another key area of focus is the creation of blocked isocyanates, which remain stable at room temperature and only become reactive under specific conditions, enhancing safety and ease of use.
The pursuit of bio-based isocyanates represents a promising frontier in the field. Researchers are exploring renewable resources as precursors for isocyanate production, aiming to decrease reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. This aligns with the broader trend towards sustainable chemistry and circular economy principles.
Advancements in catalysis have played a crucial role in isocyanate technology evolution. Novel catalysts have enabled more precise control over reaction kinetics, leading to improved product properties and reduced energy consumption. Additionally, the development of one-component systems has simplified application processes, opening up new possibilities for end-users.
The integration of nanotechnology with isocyanate chemistry is another area of significant potential. Nanocomposites incorporating isocyanates have shown enhanced mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties, expanding the range of possible applications. This convergence of technologies is expected to drive innovation in high-performance materials.
Looking ahead, the objectives for isocyanate technology include further improvements in safety profiles, increased use of renewable resources, and the development of smart, responsive materials. The industry aims to create isocyanate-based products with self-healing properties, adaptable characteristics, and enhanced durability. These advancements will likely reshape manufacturing processes and enable new product categories across multiple sectors.
Market Demand Analysis for Isocyanate Applications
The global market for isocyanates has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The versatility of isocyanates, particularly in the production of polyurethanes, has led to their widespread adoption in construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics sectors.
In the construction industry, isocyanates are crucial components in the manufacture of insulation materials, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has boosted the demand for high-performance insulation products, directly impacting isocyanate consumption. Additionally, the automotive sector's shift towards lightweight materials for improved fuel efficiency has increased the use of polyurethane-based components, further driving isocyanate demand.
The furniture industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, with applications in flexible and rigid foams for cushioning and structural components. As consumer preferences evolve towards more durable and comfortable furniture, the demand for isocyanate-based materials continues to rise. Similarly, the electronics industry utilizes isocyanates in the production of protective coatings and encapsulants, contributing to the overall market growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of isocyanates, primarily due to rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India. The region's booming construction and automotive sectors have been key drivers of isocyanate demand. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets characterized by steady demand and a focus on innovative applications.
Market analysts project continued growth in the isocyanate market, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong in the coming years. This growth is attributed to ongoing technological advancements in isocyanate production and application techniques, as well as the expansion of end-use industries in emerging economies.
However, the market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanate exposure. Stringent regulations governing the use and handling of isocyanates have prompted industry players to invest in research and development of safer alternatives and improved handling practices. This regulatory landscape has also created opportunities for eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) isocyanate formulations, catering to the growing demand for sustainable products.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted the isocyanate market, affecting supply chains and reducing demand in certain sectors. However, the market has shown resilience, with a rapid recovery observed in key end-use industries. The pandemic has also accelerated trends towards digitalization and automation in manufacturing processes, potentially influencing future isocyanate applications and market dynamics.
In the construction industry, isocyanates are crucial components in the manufacture of insulation materials, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has boosted the demand for high-performance insulation products, directly impacting isocyanate consumption. Additionally, the automotive sector's shift towards lightweight materials for improved fuel efficiency has increased the use of polyurethane-based components, further driving isocyanate demand.
The furniture industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, with applications in flexible and rigid foams for cushioning and structural components. As consumer preferences evolve towards more durable and comfortable furniture, the demand for isocyanate-based materials continues to rise. Similarly, the electronics industry utilizes isocyanates in the production of protective coatings and encapsulants, contributing to the overall market growth.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of isocyanates, primarily due to rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India. The region's booming construction and automotive sectors have been key drivers of isocyanate demand. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets characterized by steady demand and a focus on innovative applications.
Market analysts project continued growth in the isocyanate market, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong in the coming years. This growth is attributed to ongoing technological advancements in isocyanate production and application techniques, as well as the expansion of end-use industries in emerging economies.
However, the market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanate exposure. Stringent regulations governing the use and handling of isocyanates have prompted industry players to invest in research and development of safer alternatives and improved handling practices. This regulatory landscape has also created opportunities for eco-friendly and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) isocyanate formulations, catering to the growing demand for sustainable products.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted the isocyanate market, affecting supply chains and reducing demand in certain sectors. However, the market has shown resilience, with a rapid recovery observed in key end-use industries. The pandemic has also accelerated trends towards digitalization and automation in manufacturing processes, potentially influencing future isocyanate applications and market dynamics.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Deployment
The deployment of isocyanates in various industrial applications faces several significant challenges that require strategic solutions. One of the primary concerns is the high reactivity of isocyanates, which makes them difficult to handle and store safely. This reactivity can lead to unintended reactions, product degradation, and potential safety hazards for workers and the environment.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of isocyanates to moisture. Even trace amounts of water can trigger unwanted reactions, leading to the formation of ureas and carbon dioxide. This not only affects the quality and performance of the final products but also creates processing difficulties and increases production costs. Manufacturers must implement stringent moisture control measures throughout the entire production and storage process.
The toxicity of isocyanates poses a substantial challenge in terms of worker safety and environmental protection. Exposure to isocyanates can cause severe respiratory issues, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. This necessitates the implementation of robust safety protocols, personal protective equipment, and advanced ventilation systems, which can be costly and complex to manage effectively.
Regulatory compliance presents an ongoing challenge for isocyanate deployment. Stringent regulations governing the use, handling, and disposal of isocyanates vary across different regions and are subject to frequent updates. Companies must invest significant resources in staying abreast of these regulations and adapting their processes accordingly to maintain compliance.
The volatility of raw material prices for isocyanates and their precursors creates economic challenges for manufacturers. Fluctuations in the cost of key ingredients can significantly impact production costs and profit margins, making it difficult for companies to maintain consistent pricing and long-term planning.
Technical limitations in isocyanate formulation and application also present challenges. Achieving the right balance of properties such as cure time, flexibility, and durability in end products requires extensive research and development. This is particularly challenging when developing new applications or improving existing ones to meet evolving market demands.
Lastly, the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility poses a significant challenge for isocyanate deployment. There is increasing pressure to develop more eco-friendly alternatives or to improve the sustainability profile of isocyanate-based products. This requires substantial investment in research and innovation to find solutions that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of isocyanates to moisture. Even trace amounts of water can trigger unwanted reactions, leading to the formation of ureas and carbon dioxide. This not only affects the quality and performance of the final products but also creates processing difficulties and increases production costs. Manufacturers must implement stringent moisture control measures throughout the entire production and storage process.
The toxicity of isocyanates poses a substantial challenge in terms of worker safety and environmental protection. Exposure to isocyanates can cause severe respiratory issues, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. This necessitates the implementation of robust safety protocols, personal protective equipment, and advanced ventilation systems, which can be costly and complex to manage effectively.
Regulatory compliance presents an ongoing challenge for isocyanate deployment. Stringent regulations governing the use, handling, and disposal of isocyanates vary across different regions and are subject to frequent updates. Companies must invest significant resources in staying abreast of these regulations and adapting their processes accordingly to maintain compliance.
The volatility of raw material prices for isocyanates and their precursors creates economic challenges for manufacturers. Fluctuations in the cost of key ingredients can significantly impact production costs and profit margins, making it difficult for companies to maintain consistent pricing and long-term planning.
Technical limitations in isocyanate formulation and application also present challenges. Achieving the right balance of properties such as cure time, flexibility, and durability in end products requires extensive research and development. This is particularly challenging when developing new applications or improving existing ones to meet evolving market demands.
Lastly, the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility poses a significant challenge for isocyanate deployment. There is increasing pressure to develop more eco-friendly alternatives or to improve the sustainability profile of isocyanate-based products. This requires substantial investment in research and innovation to find solutions that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Existing Isocyanate Deployment Strategies
01 Isocyanate-based polymer synthesis
Isocyanates are widely used in the synthesis of polyurethanes and other polymers. The deployment of isocyanates in polymer production involves careful control of reaction conditions, including temperature and catalyst selection, to achieve desired properties in the final product. This process often requires specialized equipment and safety measures due to the reactive nature of isocyanates.- Isocyanate-based polymer synthesis: Isocyanates are widely used in the synthesis of polyurethanes and other polymers. The deployment of isocyanates in polymer production involves careful control of reaction conditions, including temperature and catalyst selection, to achieve desired properties in the final product. This process often requires specialized equipment and safety measures due to the reactive nature of isocyanates.
- Isocyanate handling and safety protocols: The deployment of isocyanates in industrial settings necessitates strict safety protocols due to their potential health hazards. This includes proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment, and emergency response procedures. Training programs for workers handling isocyanates are crucial to ensure safe deployment and minimize exposure risks.
- Isocyanate application in coatings and adhesives: Isocyanates are key components in many high-performance coatings and adhesives. Their deployment in these applications involves precise formulation and application techniques to achieve desired properties such as durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion strength. Specialized equipment for mixing and applying isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives is often required.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and sustainable practices: With growing environmental and health concerns, there is increasing focus on developing isocyanate-free alternatives and more sustainable deployment practices. This includes research into bio-based isocyanates, alternative chemistries, and improved application methods that reduce waste and emissions. Implementation of these alternatives often requires modifications to existing production processes and equipment.
- Automated systems for isocyanate deployment: Advanced automated systems are being developed for the precise and efficient deployment of isocyanates in various applications. These systems often incorporate real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and robotic technologies to optimize isocyanate usage, improve product quality, and enhance safety. Integration of these automated systems with existing manufacturing processes requires careful planning and implementation strategies.
02 Isocyanate handling and safety protocols
The deployment of isocyanates requires strict safety protocols due to their potential health hazards. This includes proper ventilation systems, personal protective equipment, and specialized storage facilities. Training programs for workers handling isocyanates are essential, as well as implementing emergency response procedures in case of accidental exposure or spills.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate application in coatings and adhesives
Isocyanates are crucial components in many industrial coatings and adhesives. Their deployment involves precise formulation and application techniques to ensure optimal performance. This may include spray systems, roll coating, or other specialized application methods depending on the specific product and substrate requirements.Expand Specific Solutions04 Automated systems for isocyanate deployment
Advanced automated systems are being developed for the precise deployment of isocyanates in manufacturing processes. These systems often incorporate real-time monitoring, computer-controlled dispensing, and integrated safety features. Such automation can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance worker safety in isocyanate-related industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental considerations in isocyanate use
The deployment of isocyanates must consider environmental impacts, including emissions control and waste management. This involves implementing technologies for capturing and treating isocyanate-containing emissions, as well as developing more environmentally friendly alternatives or processes that minimize isocyanate use while maintaining product performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Industry
The isocyanate deployment market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, fueled by applications in polyurethane production, coatings, and adhesives. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with key players like Wanhua Chemical Group, BASF, Covestro, and Bayer AG leading innovation. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to improve isocyanate efficiency, safety, and environmental impact. Emerging players such as Vencorex and Asahi Kasei are also making strides in specialized applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical giants and niche producers, with a focus on developing sustainable and high-performance isocyanate solutions.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed advanced isocyanate deployment strategies, focusing on the production of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI). Their innovative approach includes the use of proprietary catalysts and process optimization techniques to enhance isocyanate yield and purity. The company has implemented a closed-loop production system that minimizes environmental impact and maximizes resource efficiency[1]. Additionally, Wanhua has developed novel isocyanate formulations tailored for specific applications, such as high-performance polyurethane foams and coatings with improved durability and insulation properties[2].
Strengths: Vertically integrated production, advanced catalysts, and process optimization. Weaknesses: Potential overreliance on petrochemical feedstocks and exposure to raw material price fluctuations.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered innovative isocyanate deployment techniques, particularly in the realm of aliphatic isocyanates. Their approach includes the development of low-monomer technology for hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) production, significantly reducing worker exposure risks[3]. BASF has also introduced water-based polyurethane dispersions using novel isocyanate chemistries, enabling more environmentally friendly coatings and adhesives[4]. The company's research extends to bio-based isocyanates, exploring sustainable alternatives derived from renewable resources to reduce the carbon footprint of polyurethane products[5].
Strengths: Diverse isocyanate portfolio, strong focus on sustainability and safety. Weaknesses: Higher production costs associated with advanced technologies and bio-based raw materials.
Core Innovations in Isocyanate Chemistry
Modified isocyanates
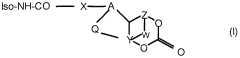
PatentWO2000020477A1
Innovation
- Development of modified isocyanate derivatives with a crosslinking functional group that remains stable and reacts only under specific conditions, allowing for controlled crosslinking reactions without releasing isocyanate functions prematurely, using cyclic carbonates to form stable polyisocyanates that can react with nucleophilic compounds to create coatings and foams.
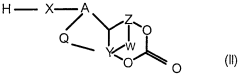
Method for masking polyisocyanates in emulsion
PatentWO1999010402A1
Innovation
- A process involving gradual introduction of an isocyanate composition into an aqueous phase with a masking agent and surfactant under high shear conditions to achieve simultaneous masking and emulsification, resulting in a stable emulsion with reduced surfactant usage and minimal solvent content.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanates
Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The production, use, and disposal of isocyanates can lead to various environmental impacts, primarily affecting air, water, and soil quality. In the atmosphere, isocyanates can react with other pollutants, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These reactions can exacerbate air quality issues, particularly in urban and industrial areas.
Water contamination is another critical concern associated with isocyanates. When released into aquatic environments, these compounds can undergo hydrolysis, forming potentially harmful byproducts. The resulting contamination can adversely affect aquatic ecosystems, disrupting the balance of marine and freshwater habitats. Furthermore, the persistence of certain isocyanate derivatives in water bodies poses long-term risks to aquatic life and may enter the food chain.
Soil contamination from isocyanates can occur through industrial spills, improper disposal, or the degradation of polyurethane products. Once in the soil, isocyanates can impact microbial communities and soil fertility, potentially affecting plant growth and ecosystem health. The mobility of isocyanates in soil varies depending on environmental conditions, influencing their potential for groundwater contamination.
The environmental fate of isocyanates is complex, influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of other chemicals. While some isocyanates degrade relatively quickly in the environment, others may persist for extended periods, leading to cumulative effects. This persistence underscores the importance of proper handling, storage, and disposal practices to minimize environmental exposure.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of isocyanates include the development of alternative, more environmentally friendly formulations and improved production processes. Green chemistry initiatives focus on reducing the use of hazardous substances and minimizing waste generation in isocyanate production. Additionally, advancements in end-of-life management for polyurethane products aim to reduce the environmental burden associated with disposal.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in managing the environmental risks of isocyanates. Many countries have implemented strict regulations governing the production, use, and disposal of these compounds. These regulations often mandate emission controls, proper handling procedures, and environmental monitoring to minimize the release of isocyanates into the environment.
Water contamination is another critical concern associated with isocyanates. When released into aquatic environments, these compounds can undergo hydrolysis, forming potentially harmful byproducts. The resulting contamination can adversely affect aquatic ecosystems, disrupting the balance of marine and freshwater habitats. Furthermore, the persistence of certain isocyanate derivatives in water bodies poses long-term risks to aquatic life and may enter the food chain.
Soil contamination from isocyanates can occur through industrial spills, improper disposal, or the degradation of polyurethane products. Once in the soil, isocyanates can impact microbial communities and soil fertility, potentially affecting plant growth and ecosystem health. The mobility of isocyanates in soil varies depending on environmental conditions, influencing their potential for groundwater contamination.
The environmental fate of isocyanates is complex, influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of other chemicals. While some isocyanates degrade relatively quickly in the environment, others may persist for extended periods, leading to cumulative effects. This persistence underscores the importance of proper handling, storage, and disposal practices to minimize environmental exposure.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of isocyanates include the development of alternative, more environmentally friendly formulations and improved production processes. Green chemistry initiatives focus on reducing the use of hazardous substances and minimizing waste generation in isocyanate production. Additionally, advancements in end-of-life management for polyurethane products aim to reduce the environmental burden associated with disposal.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in managing the environmental risks of isocyanates. Many countries have implemented strict regulations governing the production, use, and disposal of these compounds. These regulations often mandate emission controls, proper handling procedures, and environmental monitoring to minimize the release of isocyanates into the environment.
Safety Protocols for Isocyanate Handling
Isocyanate handling requires stringent safety protocols due to the compound's high reactivity and potential health hazards. Proper safety measures are crucial for protecting workers and ensuring the integrity of manufacturing processes. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is the first line of defense, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, face shields, and respiratory protection. Impermeable protective clothing should cover all exposed skin areas. Respiratory protection may range from air-purifying respirators to supplied-air systems, depending on exposure levels and work conditions.
Workplace engineering controls are essential for minimizing exposure risks. These include proper ventilation systems with local exhaust ventilation to capture and remove isocyanate vapors at the source. Enclosed processes and automated handling systems can significantly reduce worker exposure. Regular air monitoring should be conducted to ensure that isocyanate concentrations remain below permissible exposure limits.
Emergency response procedures must be well-established and regularly practiced. This includes having readily accessible eyewash stations and safety showers, as well as spill containment and cleanup equipment. Workers should be trained in proper spill response techniques and the use of neutralizing agents specific to isocyanates.
Storage and handling protocols are critical for preventing accidents. Isocyanates should be stored in tightly sealed containers in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from incompatible materials. Temperature control is crucial, as excessive heat can lead to polymerization or decomposition. Proper labeling and segregation of different isocyanate types are necessary to prevent mixing errors.
Worker education and training form the foundation of a comprehensive safety program. Employees must understand the hazards associated with isocyanates, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher training and updates on new safety protocols or equipment are essential for maintaining a safety-conscious work environment.
Health monitoring programs should be implemented for workers regularly exposed to isocyanates. This includes baseline and periodic medical examinations, with particular attention to respiratory function. Early detection of sensitization or other health effects can prevent more serious long-term health consequences.
Waste management and disposal procedures must comply with local and national regulations. Proper decontamination of equipment and disposal of contaminated materials are necessary to prevent environmental contamination and protect waste handling personnel.
By implementing these comprehensive safety protocols, organizations can effectively manage the risks associated with isocyanate handling, ensuring worker safety and regulatory compliance while optimizing their strategic use of these versatile compounds.
Workplace engineering controls are essential for minimizing exposure risks. These include proper ventilation systems with local exhaust ventilation to capture and remove isocyanate vapors at the source. Enclosed processes and automated handling systems can significantly reduce worker exposure. Regular air monitoring should be conducted to ensure that isocyanate concentrations remain below permissible exposure limits.
Emergency response procedures must be well-established and regularly practiced. This includes having readily accessible eyewash stations and safety showers, as well as spill containment and cleanup equipment. Workers should be trained in proper spill response techniques and the use of neutralizing agents specific to isocyanates.
Storage and handling protocols are critical for preventing accidents. Isocyanates should be stored in tightly sealed containers in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from incompatible materials. Temperature control is crucial, as excessive heat can lead to polymerization or decomposition. Proper labeling and segregation of different isocyanate types are necessary to prevent mixing errors.
Worker education and training form the foundation of a comprehensive safety program. Employees must understand the hazards associated with isocyanates, proper handling techniques, and emergency procedures. Regular refresher training and updates on new safety protocols or equipment are essential for maintaining a safety-conscious work environment.
Health monitoring programs should be implemented for workers regularly exposed to isocyanates. This includes baseline and periodic medical examinations, with particular attention to respiratory function. Early detection of sensitization or other health effects can prevent more serious long-term health consequences.
Waste management and disposal procedures must comply with local and national regulations. Proper decontamination of equipment and disposal of contaminated materials are necessary to prevent environmental contamination and protect waste handling personnel.
By implementing these comprehensive safety protocols, organizations can effectively manage the risks associated with isocyanate handling, ensuring worker safety and regulatory compliance while optimizing their strategic use of these versatile compounds.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!