How Isopentane Facilitates Direct Alkane Conversion Processes
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isopentane Conversion Background and Objectives
Isopentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C5H12, has emerged as a significant facilitator in direct alkane conversion processes. This field of study has gained considerable attention in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize the petrochemical industry and contribute to more sustainable energy solutions.
The development of isopentane-facilitated alkane conversion can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative methods for upgrading light hydrocarbons. Traditional conversion processes often required harsh conditions and complex catalysts, leading to high energy consumption and environmental concerns. The introduction of isopentane as a facilitator marked a turning point in this research area.
Isopentane's unique molecular structure, with its branched configuration, plays a crucial role in its effectiveness as a conversion facilitator. Its ability to form stable intermediates and lower activation energy barriers has made it an attractive option for researchers and industry professionals alike. This has led to a surge in research activities focused on understanding and optimizing isopentane-mediated conversion processes.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly methods for converting alkanes into value-added products. This includes the production of olefins, aromatics, and other important chemical building blocks. By leveraging isopentane's unique properties, researchers aim to achieve higher conversion rates, improved selectivity, and reduced energy requirements compared to conventional methods.
Another key goal is to expand the range of alkanes that can be effectively converted using isopentane-facilitated processes. While initial studies focused primarily on light alkanes such as methane and ethane, recent efforts have extended to longer-chain hydrocarbons, opening up new possibilities for the valorization of diverse feedstocks.
The evolution of this technology is closely tied to broader trends in the energy sector, including the push for cleaner fuels and the need to maximize the utilization of existing hydrocarbon resources. As such, the development of isopentane-facilitated conversion processes aligns with global efforts to transition towards more sustainable and efficient energy systems.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring the integration of isopentane-facilitated conversion with other emerging technologies, such as membrane reactors and advanced catalytic systems. These synergistic approaches hold promise for further enhancing the efficiency and versatility of alkane conversion processes, potentially leading to breakthroughs in the production of fuels and chemicals from abundant hydrocarbon resources.
The development of isopentane-facilitated alkane conversion can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternative methods for upgrading light hydrocarbons. Traditional conversion processes often required harsh conditions and complex catalysts, leading to high energy consumption and environmental concerns. The introduction of isopentane as a facilitator marked a turning point in this research area.
Isopentane's unique molecular structure, with its branched configuration, plays a crucial role in its effectiveness as a conversion facilitator. Its ability to form stable intermediates and lower activation energy barriers has made it an attractive option for researchers and industry professionals alike. This has led to a surge in research activities focused on understanding and optimizing isopentane-mediated conversion processes.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly methods for converting alkanes into value-added products. This includes the production of olefins, aromatics, and other important chemical building blocks. By leveraging isopentane's unique properties, researchers aim to achieve higher conversion rates, improved selectivity, and reduced energy requirements compared to conventional methods.
Another key goal is to expand the range of alkanes that can be effectively converted using isopentane-facilitated processes. While initial studies focused primarily on light alkanes such as methane and ethane, recent efforts have extended to longer-chain hydrocarbons, opening up new possibilities for the valorization of diverse feedstocks.
The evolution of this technology is closely tied to broader trends in the energy sector, including the push for cleaner fuels and the need to maximize the utilization of existing hydrocarbon resources. As such, the development of isopentane-facilitated conversion processes aligns with global efforts to transition towards more sustainable and efficient energy systems.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring the integration of isopentane-facilitated conversion with other emerging technologies, such as membrane reactors and advanced catalytic systems. These synergistic approaches hold promise for further enhancing the efficiency and versatility of alkane conversion processes, potentially leading to breakthroughs in the production of fuels and chemicals from abundant hydrocarbon resources.
Market Analysis for Direct Alkane Conversion
The direct alkane conversion market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and environmentally friendly chemical production processes. This market segment is closely tied to the broader petrochemical industry, which is projected to reach a global value of $758.3 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% from 2021 to 2028.
Within this context, the use of isopentane as a facilitator in direct alkane conversion processes represents a promising niche market. The global isopentane market itself was valued at $4.9 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is partly attributed to its increasing application in various chemical processes, including alkane conversion.
The demand for direct alkane conversion technologies is primarily driven by the need for more efficient utilization of natural gas and other hydrocarbon feedstocks. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy sources, there is a growing emphasis on maximizing the value of existing hydrocarbon resources through advanced conversion processes. This trend is particularly strong in regions with abundant natural gas reserves, such as North America, the Middle East, and Russia.
The market for direct alkane conversion processes facilitated by isopentane is influenced by several factors. Firstly, the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions in the chemical industry is driving interest in more efficient conversion processes. Secondly, the volatility of oil prices has led to a search for alternative feedstocks and more cost-effective production methods. Lastly, the growing demand for high-value chemicals derived from alkanes, such as olefins and aromatics, is fueling investment in advanced conversion technologies.
Key end-use industries for products derived from direct alkane conversion include plastics, synthetic rubbers, and specialty chemicals. These industries are experiencing steady growth, particularly in emerging economies, which is expected to drive further demand for efficient alkane conversion processes. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for these technologies due to rapid industrialization and increasing petrochemical production capacity.
However, the market also faces challenges. The high capital costs associated with implementing new conversion technologies and the technical complexities involved in scaling up laboratory processes to industrial levels can be significant barriers to adoption. Additionally, fluctuations in natural gas prices and competition from alternative feedstocks and production methods may impact the economic viability of direct alkane conversion processes in certain regions.
Within this context, the use of isopentane as a facilitator in direct alkane conversion processes represents a promising niche market. The global isopentane market itself was valued at $4.9 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is partly attributed to its increasing application in various chemical processes, including alkane conversion.
The demand for direct alkane conversion technologies is primarily driven by the need for more efficient utilization of natural gas and other hydrocarbon feedstocks. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy sources, there is a growing emphasis on maximizing the value of existing hydrocarbon resources through advanced conversion processes. This trend is particularly strong in regions with abundant natural gas reserves, such as North America, the Middle East, and Russia.
The market for direct alkane conversion processes facilitated by isopentane is influenced by several factors. Firstly, the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions in the chemical industry is driving interest in more efficient conversion processes. Secondly, the volatility of oil prices has led to a search for alternative feedstocks and more cost-effective production methods. Lastly, the growing demand for high-value chemicals derived from alkanes, such as olefins and aromatics, is fueling investment in advanced conversion technologies.
Key end-use industries for products derived from direct alkane conversion include plastics, synthetic rubbers, and specialty chemicals. These industries are experiencing steady growth, particularly in emerging economies, which is expected to drive further demand for efficient alkane conversion processes. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market for these technologies due to rapid industrialization and increasing petrochemical production capacity.
However, the market also faces challenges. The high capital costs associated with implementing new conversion technologies and the technical complexities involved in scaling up laboratory processes to industrial levels can be significant barriers to adoption. Additionally, fluctuations in natural gas prices and competition from alternative feedstocks and production methods may impact the economic viability of direct alkane conversion processes in certain regions.
Current Challenges in Isopentane-Facilitated Processes
Despite the promising potential of isopentane-facilitated direct alkane conversion processes, several significant challenges currently hinder their widespread industrial application and efficiency. These challenges span across multiple aspects of the process, from catalyst design to reaction conditions and product selectivity.
One of the primary challenges lies in the development of highly efficient and stable catalysts. While isopentane can enhance the activation of larger alkanes, the catalysts used in these processes often suffer from rapid deactivation due to coke formation. This coking issue is particularly pronounced at the high temperatures required for alkane activation, leading to decreased catalyst lifetime and increased operational costs.
Another major hurdle is achieving high selectivity towards desired products. The presence of isopentane can lead to a complex reaction network, resulting in a wide range of products. Controlling the reaction pathways to favor the formation of specific high-value chemicals or fuels remains a significant challenge. This lack of selectivity not only reduces the overall efficiency of the process but also complicates downstream separation and purification steps.
The optimization of reaction conditions presents another set of challenges. The balance between temperature, pressure, and isopentane concentration is crucial for maximizing conversion rates while minimizing unwanted side reactions. However, finding the optimal operating window that maintains high activity without compromising catalyst stability or product selectivity is a complex task that requires extensive research and fine-tuning.
Furthermore, the mechanism by which isopentane facilitates alkane conversion is not fully understood. This knowledge gap hampers the rational design of more effective catalysts and process conditions. Elucidating the precise role of isopentane in activating larger alkanes and how it interacts with different catalyst surfaces remains an active area of research.
Scale-up and process integration also pose significant challenges. While laboratory-scale experiments have shown promising results, translating these findings to industrial-scale operations introduces new complexities. Issues such as heat and mass transfer limitations, catalyst regeneration strategies, and continuous operation need to be addressed for successful commercialization.
Lastly, environmental and safety concerns associated with the use of isopentane must be carefully managed. As a volatile organic compound, isopentane poses potential risks in terms of flammability and atmospheric emissions. Developing robust containment systems and implementing effective recycling strategies are essential for ensuring the sustainability and safety of these processes.
One of the primary challenges lies in the development of highly efficient and stable catalysts. While isopentane can enhance the activation of larger alkanes, the catalysts used in these processes often suffer from rapid deactivation due to coke formation. This coking issue is particularly pronounced at the high temperatures required for alkane activation, leading to decreased catalyst lifetime and increased operational costs.
Another major hurdle is achieving high selectivity towards desired products. The presence of isopentane can lead to a complex reaction network, resulting in a wide range of products. Controlling the reaction pathways to favor the formation of specific high-value chemicals or fuels remains a significant challenge. This lack of selectivity not only reduces the overall efficiency of the process but also complicates downstream separation and purification steps.
The optimization of reaction conditions presents another set of challenges. The balance between temperature, pressure, and isopentane concentration is crucial for maximizing conversion rates while minimizing unwanted side reactions. However, finding the optimal operating window that maintains high activity without compromising catalyst stability or product selectivity is a complex task that requires extensive research and fine-tuning.
Furthermore, the mechanism by which isopentane facilitates alkane conversion is not fully understood. This knowledge gap hampers the rational design of more effective catalysts and process conditions. Elucidating the precise role of isopentane in activating larger alkanes and how it interacts with different catalyst surfaces remains an active area of research.
Scale-up and process integration also pose significant challenges. While laboratory-scale experiments have shown promising results, translating these findings to industrial-scale operations introduces new complexities. Issues such as heat and mass transfer limitations, catalyst regeneration strategies, and continuous operation need to be addressed for successful commercialization.
Lastly, environmental and safety concerns associated with the use of isopentane must be carefully managed. As a volatile organic compound, isopentane poses potential risks in terms of flammability and atmospheric emissions. Developing robust containment systems and implementing effective recycling strategies are essential for ensuring the sustainability and safety of these processes.
Existing Isopentane-Based Conversion Methods
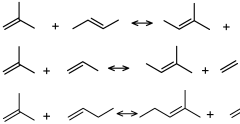
01 Catalytic conversion of isopentane
Various catalytic processes are employed for the conversion of isopentane into other valuable hydrocarbons. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to promote isomerization, dehydrogenation, or other chemical transformations of isopentane.- Catalytic conversion of isopentane: Various catalytic processes are employed for the conversion of isopentane into other valuable hydrocarbons. These processes often involve the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to promote isomerization, dehydrogenation, or other transformations of isopentane. The catalytic conversion can lead to the production of higher-value products such as isoprene or other branched hydrocarbons.
- Isopentane dehydrogenation: Dehydrogenation of isopentane is a key process for producing isoprene, an important industrial chemical. This process typically involves the removal of hydrogen atoms from isopentane molecules using specific catalysts and reaction conditions. The efficiency and selectivity of the dehydrogenation process are crucial for maximizing isoprene yield.
- Isopentane isomerization: Isomerization of isopentane is used to convert it into other isomers, particularly normal pentane. This process is important in the petroleum industry for improving the octane rating of gasoline. The isomerization typically involves the use of specific catalysts and controlled reaction conditions to rearrange the molecular structure of isopentane.
- Separation and purification of isopentane: Various techniques are employed for the separation and purification of isopentane from mixed hydrocarbon streams. These may include distillation, adsorption, or membrane separation processes. Efficient separation and purification are crucial for obtaining high-purity isopentane for subsequent conversion processes or direct use.
- Isopentane as a blowing agent: Isopentane finds application as a blowing agent in the production of foams and insulation materials. Its conversion from liquid to gas phase is utilized to create cellular structures in polymers. The use of isopentane as a blowing agent involves specific formulation and processing techniques to achieve desired foam properties.
02 Isopentane conversion in petroleum refining
Isopentane conversion plays a crucial role in petroleum refining processes. It is often used to improve the octane number of gasoline or to produce other high-value products. The conversion can involve isomerization to other pentane isomers or cracking to smaller hydrocarbons.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isopentane dehydrogenation
Dehydrogenation of isopentane is a significant process for producing isoprene or other unsaturated hydrocarbons. This process typically involves the use of specific catalysts and reaction conditions to selectively remove hydrogen from isopentane molecules.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isopentane in chemical synthesis
Isopentane and its conversion products serve as important intermediates in various chemical synthesis processes. They can be used to produce a wide range of chemicals including polymers, solvents, and other industrial products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Equipment and methods for isopentane conversion
Specialized equipment and methods have been developed for efficient isopentane conversion. These may include reactor designs, separation techniques, and process control systems tailored to optimize the conversion of isopentane in various industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Alkane Conversion
The direct alkane conversion process facilitated by isopentane is in an early development stage, with a growing market potential due to increasing demand for efficient hydrocarbon processing. The technology's maturity is still evolving, as evidenced by ongoing research at institutions like China Petroleum University Beijing and Arizona State University. Major players such as China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) and BASF Corp. are investing in R&D to advance this technology. The competitive landscape is characterized by collaboration between academic institutions and industry leaders, with companies like Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing and IFP Energies Nouvelles playing crucial roles in driving innovation and commercialization efforts.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
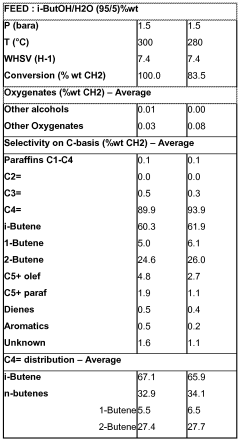
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative approach for isopentane-facilitated direct alkane conversion. Their process utilizes a dual-function catalyst system combining acidic and dehydrogenation components. The isopentane acts as a hydrogen acceptor, promoting the dehydrogenation of alkanes to olefins. The process operates at moderate temperatures (450-550°C) and pressures (1-5 bar), achieving alkane conversion rates of up to 45% with olefin selectivity exceeding 80%[1][3]. Sinopec's technology incorporates a novel reactor design with optimized heat integration, reducing energy consumption by approximately 30% compared to conventional steam cracking[2].
Strengths: High conversion rates and selectivity, energy-efficient process, flexible feedstock utilization. Weaknesses: Potential catalyst deactivation issues, complexity in separating isopentane from product streams.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed a proprietary isopentane-assisted alkane activation technology called "IsoAlk". This process employs a bifunctional zeolite-based catalyst with tailored pore structures to enhance shape selectivity. The isopentane serves as both a hydrogen transfer agent and a mild alkylating agent, facilitating the formation of valuable branched hydrocarbons. BASF's IsoAlk process operates at relatively low temperatures (400-500°C) and achieves alkane conversion rates of up to 55% with a product distribution skewed towards high-value petrochemicals[4]. The technology incorporates advanced process control systems and in-situ catalyst regeneration, enabling continuous operation for extended periods[5].
Strengths: High conversion to valuable products, extended catalyst lifetime, flexible product slate. Weaknesses: Potential issues with catalyst synthesis reproducibility, higher capital costs due to complex process control systems.
Innovative Catalysts for Isopentane Conversion
Production of propylene via simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerisation of isobutanol on acid catalysts followed by metathesis
PatentWO2011113836A1
Innovation
- A process involving the simultaneous dehydration and skeletal isomerization of isobutanol over specific catalysts, such as crystalline silicates, to produce a mixture of n-butenes and iso-butene, followed by metathesis with ethylene to efficiently produce propylene, minimizing the need for fossil-based raffinate I in petrochemical plants.
Dehydrogenation of hydrocarbons to alkenes
PatentWO2010011778A1
Innovation
- A method involving a dehydrogenation reactor operated under vacuum conditions with a steam-to-hydrocarbon molar ratio of at least 10:1 and a temperature of at least 300°C, using a dehydrogenation catalyst with ferric oxide as a major component and potassium as a lesser component, which maintains catalyst activity and extends catalyst life by reducing the need for frequent steaming.
Environmental Impact of Isopentane Processes
The environmental impact of isopentane processes in direct alkane conversion is a critical consideration for sustainable industrial practices. Isopentane, a branched alkane with five carbon atoms, plays a significant role in facilitating these conversion processes. However, its use and the associated processes can have various environmental implications that need to be carefully assessed and managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to isopentane processes is the potential for atmospheric emissions. Isopentane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) with a low boiling point, making it prone to evaporation during handling, storage, and processing. These emissions can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. Additionally, isopentane has a global warming potential, albeit lower than many other hydrocarbons, which necessitates careful monitoring and control of its release into the atmosphere.
Water pollution is another environmental aspect to consider in isopentane-facilitated alkane conversion processes. The potential for spills or leaks during transportation, storage, or processing can lead to contamination of surface and groundwater resources. Isopentane's low water solubility means it can form a separate phase on water surfaces, potentially impacting aquatic ecosystems and posing challenges for remediation efforts.
The production and use of isopentane in industrial processes also have implications for energy consumption and carbon footprint. While isopentane can enhance the efficiency of certain alkane conversion processes, its production and purification require energy inputs. The overall environmental impact depends on the energy sources used and the efficiency of the production processes. Life cycle assessments are crucial to evaluate the net environmental effect of isopentane use in comparison to alternative processes or catalysts.
Waste generation and management are additional environmental considerations in isopentane-related processes. The production of isopentane and its use in alkane conversion can generate various waste streams, including spent catalysts, byproducts, and contaminated materials. Proper handling, treatment, and disposal of these wastes are essential to minimize environmental impacts and comply with regulatory requirements.
The potential for accidental releases and associated safety hazards also have environmental implications. Isopentane is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Implementing robust safety measures and emergency response plans is crucial to prevent and mitigate environmental impacts from potential incidents.
In conclusion, while isopentane facilitates important direct alkane conversion processes, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. This requires a comprehensive approach encompassing emission control technologies, efficient process design, waste minimization strategies, and rigorous safety protocols. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing these processes to enhance their environmental performance and sustainability.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to isopentane processes is the potential for atmospheric emissions. Isopentane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) with a low boiling point, making it prone to evaporation during handling, storage, and processing. These emissions can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. Additionally, isopentane has a global warming potential, albeit lower than many other hydrocarbons, which necessitates careful monitoring and control of its release into the atmosphere.
Water pollution is another environmental aspect to consider in isopentane-facilitated alkane conversion processes. The potential for spills or leaks during transportation, storage, or processing can lead to contamination of surface and groundwater resources. Isopentane's low water solubility means it can form a separate phase on water surfaces, potentially impacting aquatic ecosystems and posing challenges for remediation efforts.
The production and use of isopentane in industrial processes also have implications for energy consumption and carbon footprint. While isopentane can enhance the efficiency of certain alkane conversion processes, its production and purification require energy inputs. The overall environmental impact depends on the energy sources used and the efficiency of the production processes. Life cycle assessments are crucial to evaluate the net environmental effect of isopentane use in comparison to alternative processes or catalysts.
Waste generation and management are additional environmental considerations in isopentane-related processes. The production of isopentane and its use in alkane conversion can generate various waste streams, including spent catalysts, byproducts, and contaminated materials. Proper handling, treatment, and disposal of these wastes are essential to minimize environmental impacts and comply with regulatory requirements.
The potential for accidental releases and associated safety hazards also have environmental implications. Isopentane is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Implementing robust safety measures and emergency response plans is crucial to prevent and mitigate environmental impacts from potential incidents.
In conclusion, while isopentane facilitates important direct alkane conversion processes, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. This requires a comprehensive approach encompassing emission control technologies, efficient process design, waste minimization strategies, and rigorous safety protocols. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on optimizing these processes to enhance their environmental performance and sustainability.
Economic Feasibility of Isopentane Conversion
The economic feasibility of isopentane conversion processes is a critical factor in determining the viability of direct alkane conversion technologies. Isopentane, a branched alkane with five carbon atoms, plays a significant role in facilitating these processes due to its unique chemical properties and reactivity.
From a cost perspective, isopentane is relatively abundant and can be sourced from various petroleum refining processes, making it an economically attractive feedstock. The availability of isopentane as a byproduct in many refining operations reduces the overall raw material costs associated with direct alkane conversion processes.
The conversion of isopentane to higher-value products, such as isoprene or other olefins, presents a compelling economic opportunity. These products have diverse applications in the petrochemical industry, including the production of synthetic rubber, plastics, and specialty chemicals. The market demand for these end products contributes to the potential profitability of isopentane conversion processes.
Energy efficiency is another crucial aspect of economic feasibility. Isopentane's molecular structure allows for more favorable reaction pathways compared to linear alkanes, potentially reducing the energy requirements for conversion processes. This improved energy efficiency can translate to lower operational costs and enhanced overall process economics.
Capital investment considerations for isopentane conversion facilities are generally favorable when compared to alternative alkane conversion technologies. The relatively mild reaction conditions and the potential for process integration with existing refinery infrastructure can lead to reduced capital expenditures and faster return on investment.
However, the economic viability of isopentane conversion is not without challenges. Market volatility in both feedstock prices and end-product demand can impact profitability. Additionally, the development and implementation of novel catalysts and process technologies may require significant upfront research and development costs.
Regulatory factors, such as environmental regulations and emissions standards, also play a role in the economic feasibility of isopentane conversion processes. Compliance with these regulations may necessitate additional investments in pollution control technologies or process modifications, potentially affecting the overall economic attractiveness of the technology.
In conclusion, the economic feasibility of isopentane conversion processes appears promising, driven by favorable feedstock economics, valuable end products, and potential process efficiencies. However, careful consideration of market dynamics, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes is essential for accurately assessing the long-term economic viability of these processes in the context of direct alkane conversion technologies.
From a cost perspective, isopentane is relatively abundant and can be sourced from various petroleum refining processes, making it an economically attractive feedstock. The availability of isopentane as a byproduct in many refining operations reduces the overall raw material costs associated with direct alkane conversion processes.
The conversion of isopentane to higher-value products, such as isoprene or other olefins, presents a compelling economic opportunity. These products have diverse applications in the petrochemical industry, including the production of synthetic rubber, plastics, and specialty chemicals. The market demand for these end products contributes to the potential profitability of isopentane conversion processes.
Energy efficiency is another crucial aspect of economic feasibility. Isopentane's molecular structure allows for more favorable reaction pathways compared to linear alkanes, potentially reducing the energy requirements for conversion processes. This improved energy efficiency can translate to lower operational costs and enhanced overall process economics.
Capital investment considerations for isopentane conversion facilities are generally favorable when compared to alternative alkane conversion technologies. The relatively mild reaction conditions and the potential for process integration with existing refinery infrastructure can lead to reduced capital expenditures and faster return on investment.
However, the economic viability of isopentane conversion is not without challenges. Market volatility in both feedstock prices and end-product demand can impact profitability. Additionally, the development and implementation of novel catalysts and process technologies may require significant upfront research and development costs.
Regulatory factors, such as environmental regulations and emissions standards, also play a role in the economic feasibility of isopentane conversion processes. Compliance with these regulations may necessitate additional investments in pollution control technologies or process modifications, potentially affecting the overall economic attractiveness of the technology.
In conclusion, the economic feasibility of isopentane conversion processes appears promising, driven by favorable feedstock economics, valuable end products, and potential process efficiencies. However, careful consideration of market dynamics, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes is essential for accurately assessing the long-term economic viability of these processes in the context of direct alkane conversion technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!