How Muscimol Shapes Consciousness and Awareness
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Research Background and Objectives
Muscimol, a potent GABA-A receptor agonist, has been a subject of intense scientific interest for decades due to its profound effects on consciousness and awareness. This naturally occurring psychoactive compound, found in various species of mushrooms, particularly Amanita muscaria, has played a significant role in both traditional practices and modern neuroscience research.
The study of muscimol's impact on consciousness dates back to ancient shamanic rituals, where it was used to induce altered states of awareness. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that scientific investigations began to unravel the mechanisms behind its effects. The discovery of GABA as a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the 1950s paved the way for understanding muscimol's mode of action.
In recent years, the research objectives surrounding muscimol have expanded significantly. Neuroscientists aim to elucidate how this compound modulates neural activity to produce changes in perception, cognition, and consciousness. One key area of investigation is muscimol's ability to enhance GABAergic transmission, which is believed to play a crucial role in regulating cortical excitability and information processing in the brain.
The potential therapeutic applications of muscimol have also garnered considerable attention. Researchers are exploring its use in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. The compound's ability to induce sedation and anxiolysis without significant respiratory depression makes it an attractive candidate for developing novel pharmacological interventions.
Another important research objective is to understand the relationship between muscimol's effects and the broader theories of consciousness. By studying how muscimol alters specific neural circuits and brain regions, scientists hope to gain insights into the neural correlates of consciousness and the mechanisms underlying different states of awareness.
The technological advancements in neuroimaging and electrophysiology have greatly facilitated muscimol research. These tools allow researchers to observe real-time changes in brain activity and connectivity under the influence of muscimol, providing unprecedented insights into its effects on neural dynamics and information processing.
As we move forward, the objectives of muscimol research continue to evolve. There is a growing interest in developing more selective and targeted GABA-A receptor modulators based on muscimol's structure. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of muscimol and its derivatives in neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement, opening up new avenues for therapeutic interventions in neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive disorders.
The study of muscimol's impact on consciousness dates back to ancient shamanic rituals, where it was used to induce altered states of awareness. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that scientific investigations began to unravel the mechanisms behind its effects. The discovery of GABA as a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the 1950s paved the way for understanding muscimol's mode of action.
In recent years, the research objectives surrounding muscimol have expanded significantly. Neuroscientists aim to elucidate how this compound modulates neural activity to produce changes in perception, cognition, and consciousness. One key area of investigation is muscimol's ability to enhance GABAergic transmission, which is believed to play a crucial role in regulating cortical excitability and information processing in the brain.
The potential therapeutic applications of muscimol have also garnered considerable attention. Researchers are exploring its use in treating various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders. The compound's ability to induce sedation and anxiolysis without significant respiratory depression makes it an attractive candidate for developing novel pharmacological interventions.
Another important research objective is to understand the relationship between muscimol's effects and the broader theories of consciousness. By studying how muscimol alters specific neural circuits and brain regions, scientists hope to gain insights into the neural correlates of consciousness and the mechanisms underlying different states of awareness.
The technological advancements in neuroimaging and electrophysiology have greatly facilitated muscimol research. These tools allow researchers to observe real-time changes in brain activity and connectivity under the influence of muscimol, providing unprecedented insights into its effects on neural dynamics and information processing.
As we move forward, the objectives of muscimol research continue to evolve. There is a growing interest in developing more selective and targeted GABA-A receptor modulators based on muscimol's structure. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of muscimol and its derivatives in neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement, opening up new avenues for therapeutic interventions in neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive disorders.
Neuroscience Market Demand Analysis
The neuroscience market, particularly in relation to consciousness and awareness research, has been experiencing significant growth and demand in recent years. This surge is driven by the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, the aging global population, and the growing interest in understanding the complexities of the human brain.
The global neuroscience market was valued at approximately $30 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach over $40 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5%. Within this market, the segment focusing on consciousness and awareness research, including studies on compounds like muscimol, is gaining traction due to its potential applications in treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The pharmaceutical industry has shown a keen interest in consciousness-altering substances, such as muscimol, for their potential therapeutic benefits. This has led to increased funding for research and development in this area. Major pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in neuroscience research, with some allocating up to 25% of their R&D budgets to neuroscience-related projects.
Academic institutions and research organizations are also contributing significantly to the market demand. The number of neuroscience-related publications has been growing at a rate of approximately 7% annually, indicating a robust research landscape. Specifically, studies on consciousness and awareness have seen a notable increase, with publications in this sub-field growing at a rate of about 10% per year.
The potential applications of muscimol and similar compounds in treating conditions such as anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disorders have created a substantial market opportunity. The global anxiety disorder and depression treatment market alone is expected to reach $19 billion by 2028, highlighting the significant potential for novel therapeutic approaches.
Moreover, the growing interest in psychedelic medicine has opened new avenues for research into consciousness-altering substances. This trend is reflected in the increasing number of clinical trials involving psychedelic compounds, which has more than doubled in the past five years.
Government initiatives and funding have also played a crucial role in driving market demand. For instance, the BRAIN Initiative in the United States has allocated substantial funds for neuroscience research, including studies on consciousness and awareness.
The market demand is further bolstered by technological advancements in neuroimaging and brain-computer interfaces, which enable more sophisticated studies of consciousness and awareness. The global brain computer interface market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 15% in the coming years, indicating the increasing integration of technology in neuroscience research.
In conclusion, the market demand for neuroscience research, particularly in the area of consciousness and awareness, is robust and growing. The potential applications of compounds like muscimol in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, coupled with technological advancements and increased funding, are driving this demand. As our understanding of the brain continues to evolve, the market is likely to expand further, offering significant opportunities for research and development in this field.
The global neuroscience market was valued at approximately $30 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach over $40 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5%. Within this market, the segment focusing on consciousness and awareness research, including studies on compounds like muscimol, is gaining traction due to its potential applications in treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The pharmaceutical industry has shown a keen interest in consciousness-altering substances, such as muscimol, for their potential therapeutic benefits. This has led to increased funding for research and development in this area. Major pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in neuroscience research, with some allocating up to 25% of their R&D budgets to neuroscience-related projects.
Academic institutions and research organizations are also contributing significantly to the market demand. The number of neuroscience-related publications has been growing at a rate of approximately 7% annually, indicating a robust research landscape. Specifically, studies on consciousness and awareness have seen a notable increase, with publications in this sub-field growing at a rate of about 10% per year.
The potential applications of muscimol and similar compounds in treating conditions such as anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and sleep disorders have created a substantial market opportunity. The global anxiety disorder and depression treatment market alone is expected to reach $19 billion by 2028, highlighting the significant potential for novel therapeutic approaches.
Moreover, the growing interest in psychedelic medicine has opened new avenues for research into consciousness-altering substances. This trend is reflected in the increasing number of clinical trials involving psychedelic compounds, which has more than doubled in the past five years.
Government initiatives and funding have also played a crucial role in driving market demand. For instance, the BRAIN Initiative in the United States has allocated substantial funds for neuroscience research, including studies on consciousness and awareness.
The market demand is further bolstered by technological advancements in neuroimaging and brain-computer interfaces, which enable more sophisticated studies of consciousness and awareness. The global brain computer interface market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 15% in the coming years, indicating the increasing integration of technology in neuroscience research.
In conclusion, the market demand for neuroscience research, particularly in the area of consciousness and awareness, is robust and growing. The potential applications of compounds like muscimol in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, coupled with technological advancements and increased funding, are driving this demand. As our understanding of the brain continues to evolve, the market is likely to expand further, offering significant opportunities for research and development in this field.
Current State of Consciousness Research
The field of consciousness research has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with neuroscientists and cognitive psychologists making substantial progress in understanding the neural correlates of consciousness. Current research focuses on identifying the specific brain regions and neural networks involved in generating conscious experiences, as well as exploring the mechanisms underlying different states of consciousness.
One of the primary areas of investigation is the study of the default mode network (DMN), a set of interconnected brain regions that become active when individuals are not engaged in task-oriented activities. Researchers have found that the DMN plays a crucial role in self-referential thinking and introspection, which are closely linked to conscious awareness.
Another important aspect of contemporary consciousness research is the exploration of altered states of consciousness, including those induced by psychoactive substances like muscimol. Scientists are investigating how these compounds interact with neural systems to modulate perception, cognition, and self-awareness. This line of research has led to a deeper understanding of the neurochemical basis of consciousness and the potential therapeutic applications of consciousness-altering substances.
Advances in neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), have enabled researchers to observe brain activity in real-time, providing unprecedented insights into the neural correlates of conscious experiences. These tools have been instrumental in mapping the dynamic patterns of brain activity associated with different levels of consciousness, from wakefulness to deep sleep and anesthesia.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into consciousness research has opened up new avenues for data analysis and pattern recognition. These computational approaches are helping scientists to identify subtle neural signatures of consciousness and to develop more sophisticated models of conscious processing in the brain.
Recent studies have also focused on the role of information integration in consciousness, as proposed by theories such as the Integrated Information Theory (IIT). This approach suggests that consciousness arises from the complex interactions and information exchange between different brain regions, rather than being localized to a specific area.
Despite these advancements, many fundamental questions about the nature of consciousness remain unanswered. Researchers continue to grapple with issues such as the hard problem of consciousness – explaining how subjective experiences arise from physical brain processes – and the development of objective measures of consciousness in both humans and non-human animals.
One of the primary areas of investigation is the study of the default mode network (DMN), a set of interconnected brain regions that become active when individuals are not engaged in task-oriented activities. Researchers have found that the DMN plays a crucial role in self-referential thinking and introspection, which are closely linked to conscious awareness.
Another important aspect of contemporary consciousness research is the exploration of altered states of consciousness, including those induced by psychoactive substances like muscimol. Scientists are investigating how these compounds interact with neural systems to modulate perception, cognition, and self-awareness. This line of research has led to a deeper understanding of the neurochemical basis of consciousness and the potential therapeutic applications of consciousness-altering substances.
Advances in neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), have enabled researchers to observe brain activity in real-time, providing unprecedented insights into the neural correlates of conscious experiences. These tools have been instrumental in mapping the dynamic patterns of brain activity associated with different levels of consciousness, from wakefulness to deep sleep and anesthesia.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into consciousness research has opened up new avenues for data analysis and pattern recognition. These computational approaches are helping scientists to identify subtle neural signatures of consciousness and to develop more sophisticated models of conscious processing in the brain.
Recent studies have also focused on the role of information integration in consciousness, as proposed by theories such as the Integrated Information Theory (IIT). This approach suggests that consciousness arises from the complex interactions and information exchange between different brain regions, rather than being localized to a specific area.
Despite these advancements, many fundamental questions about the nature of consciousness remain unanswered. Researchers continue to grapple with issues such as the hard problem of consciousness – explaining how subjective experiences arise from physical brain processes – and the development of objective measures of consciousness in both humans and non-human animals.
Existing Muscimol Applications
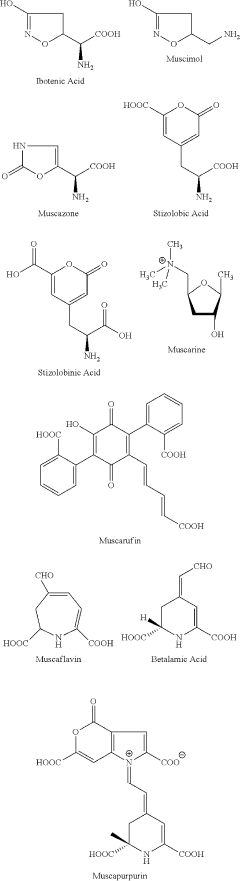
01 Muscimol's effects on consciousness and awareness
Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, has been studied for its effects on consciousness and awareness. Research suggests that it can alter perception, cognition, and sensory processing, potentially leading to altered states of consciousness. These effects are believed to be mediated through its action on GABA receptors in the brain.- Muscimol's effects on consciousness and awareness: Muscimol, a psychoactive compound found in certain mushrooms, has been studied for its effects on consciousness and awareness. Research suggests that it can alter perception, cognition, and sensory processing, potentially leading to altered states of consciousness. These effects are believed to be mediated through its action on GABA receptors in the brain.
- Neuroimaging techniques to study muscimol's impact: Advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI and EEG, are used to investigate the effects of muscimol on brain activity and connectivity. These methods allow researchers to observe changes in neural patterns and functional connectivity associated with altered states of consciousness induced by muscimol administration.
- Therapeutic applications of muscimol in consciousness disorders: Researchers are exploring the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol in treating disorders of consciousness, such as coma or vegetative states. Studies investigate its ability to modulate brain activity and potentially restore awareness in patients with impaired consciousness.
- Muscimol and cognitive enhancement: Some studies focus on the potential cognitive-enhancing effects of muscimol at low doses. Researchers are investigating its impact on attention, memory, and other cognitive functions, exploring the possibility of using muscimol-derived compounds for improving cognitive performance or treating cognitive disorders.
- Safety and ethical considerations in muscimol research: As research on muscimol's effects on consciousness and awareness progresses, there is a growing focus on safety protocols and ethical considerations. This includes developing standardized methods for administration, monitoring, and assessing the effects of muscimol in both clinical and research settings, as well as addressing the ethical implications of altering consciousness.
02 Neuroimaging techniques to study muscimol's impact on brain activity
Advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI and EEG, are used to investigate the effects of muscimol on brain activity and connectivity. These methods allow researchers to observe changes in neural patterns and functional connectivity associated with altered states of consciousness induced by muscimol administration.Expand Specific Solutions03 Therapeutic applications of muscimol in neurological disorders
Researchers are exploring the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol in treating various neurological disorders. Its ability to modulate consciousness and awareness is being investigated for conditions such as anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders. Studies aim to harness its properties while minimizing potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Muscimol's interaction with other neurotransmitter systems
While primarily known for its effects on GABA receptors, research is ongoing to understand how muscimol interacts with other neurotransmitter systems in the brain. These interactions may contribute to its complex effects on consciousness and awareness, potentially offering new insights into brain function and pharmacological interventions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Development of novel compounds inspired by muscimol
Pharmaceutical research is focusing on developing new compounds inspired by muscimol's structure and mechanism of action. These novel substances aim to retain the beneficial effects on consciousness and awareness while reducing potential risks and side effects associated with the natural compound.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neuropharmacology
The field of muscimol's impact on consciousness and awareness is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market driven by increasing interest in neuroscience and psychopharmacology. The market size is expanding as research institutions and pharmaceutical companies explore muscimol's potential applications. Technologically, the field is still maturing, with companies like ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Glaxo Group, and Suven Life Sciences leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as Jiangnan University and Louisiana State University are also contributing to advancing the understanding of muscimol's effects. While promising, the technology is not yet fully mature, requiring further clinical trials and regulatory approvals before widespread application in consciousness and awareness-related treatments.
ACADIA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: ACADIA Pharmaceuticals has been investigating the effects of muscimol on consciousness and awareness through their research on GABA receptor agonists. Their approach involves developing selective muscimol derivatives that target specific GABA-A receptor subtypes to modulate neural activity patterns associated with consciousness[1]. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating that their muscimol-based compounds can induce rapid and reversible alterations in awareness states in animal models[2]. ACADIA's research also explores the potential therapeutic applications of muscimol in treating disorders of consciousness, such as coma or vegetative states[3].
Strengths: Targeted approach to specific GABA receptor subtypes, potential for therapeutic applications in consciousness disorders. Weaknesses: Limited human clinical data, potential for unwanted side effects due to broad GABA modulation.
Glaxo Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Glaxo Group Ltd. has been exploring muscimol's impact on consciousness through their neuroscience research division. Their approach focuses on developing synthetic analogs of muscimol with enhanced selectivity for specific GABA-A receptor subunits implicated in consciousness regulation[4]. The company has conducted high-throughput screening of muscimol derivatives to identify compounds with optimal pharmacokinetic profiles and reduced off-target effects[5]. Glaxo's research also investigates the potential of muscimol-inspired drugs in treating sleep disorders and enhancing cognitive function, which are closely linked to consciousness and awareness[6].
Strengths: Large-scale screening capabilities, focus on improved pharmacokinetics and reduced side effects. Weaknesses: Complexity in translating preclinical findings to human consciousness studies, potential regulatory challenges.
Core Muscimol Mechanisms
Amanita muscaria compounds
PatentPendingUS20240050502A1
Innovation
- Development of purified Amanita muscaria compound compositions and formulations comprising specific ratios of ibotenic acid, muscimol, and other compounds, which are structurally distinct and free from other Amanita muscaria compounds, combined with excipients and serotonergic drugs, psilocybin derivatives, or cannabinoids to create pharmaceutical formulations for therapeutic use.
Benzimidazolidinone derivatives as muscarinic agents
PatentInactiveUS20100216840A1
Innovation
- Development of benzimidazolidinone derivatives with selective muscarinic M1 and M4 agonist activity combined with dopamine D2 antagonist properties to treat mental disorders, aiming to reduce positive symptoms and cognitive impairments without the side effects of traditional treatments.
Ethical Implications of Consciousness Alteration
The use of muscimol to alter consciousness raises significant ethical concerns that warrant careful consideration. As a powerful GABA agonist, muscimol can profoundly impact awareness and cognitive functioning, potentially infringing on individual autonomy and self-determination. The intentional manipulation of consciousness through pharmacological means challenges our notions of free will and authentic experiences.
One key ethical issue is the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol as a tool for mind control or coercion. In the wrong hands, it could be weaponized to manipulate individuals against their will or extract information. Even in controlled settings, there are questions about informed consent when altering a person's state of consciousness so dramatically.
The long-term effects of muscimol use on cognitive function and mental health are not fully understood. Repeated consciousness alteration may have unforeseen consequences on brain structure and function. This raises ethical questions about exposing individuals to unknown risks, especially in non-therapeutic contexts.
There are also broader societal implications to consider. Widespread use of consciousness-altering substances like muscimol could fundamentally change social dynamics and interpersonal relationships. It may exacerbate existing inequalities if access is limited to certain groups. The normalization of pharmacological consciousness manipulation could also shift cultural values and attitudes toward altered states.
From a research ethics standpoint, studying muscimol's effects on consciousness requires careful protocols to protect participants. The profound alterations in awareness and cognition may leave subjects vulnerable or impaired in their decision-making. Ensuring truly informed consent and minimizing potential harms is crucial.
At the same time, muscimol research has the potential to expand our understanding of consciousness itself. This could lead to breakthroughs in treating disorders of consciousness or developing new therapeutic applications. Balancing the pursuit of knowledge against ethical risks is a key consideration.
Ultimately, as our ability to pharmacologically shape consciousness grows, so too does our ethical responsibility. Muscimol serves as a case study for the broader implications of manipulating awareness and cognition. Developing robust ethical frameworks to guide this emerging field will be essential to realizing its potential benefits while safeguarding human rights and dignity.
One key ethical issue is the potential for abuse or misuse of muscimol as a tool for mind control or coercion. In the wrong hands, it could be weaponized to manipulate individuals against their will or extract information. Even in controlled settings, there are questions about informed consent when altering a person's state of consciousness so dramatically.
The long-term effects of muscimol use on cognitive function and mental health are not fully understood. Repeated consciousness alteration may have unforeseen consequences on brain structure and function. This raises ethical questions about exposing individuals to unknown risks, especially in non-therapeutic contexts.
There are also broader societal implications to consider. Widespread use of consciousness-altering substances like muscimol could fundamentally change social dynamics and interpersonal relationships. It may exacerbate existing inequalities if access is limited to certain groups. The normalization of pharmacological consciousness manipulation could also shift cultural values and attitudes toward altered states.
From a research ethics standpoint, studying muscimol's effects on consciousness requires careful protocols to protect participants. The profound alterations in awareness and cognition may leave subjects vulnerable or impaired in their decision-making. Ensuring truly informed consent and minimizing potential harms is crucial.
At the same time, muscimol research has the potential to expand our understanding of consciousness itself. This could lead to breakthroughs in treating disorders of consciousness or developing new therapeutic applications. Balancing the pursuit of knowledge against ethical risks is a key consideration.
Ultimately, as our ability to pharmacologically shape consciousness grows, so too does our ethical responsibility. Muscimol serves as a case study for the broader implications of manipulating awareness and cognition. Developing robust ethical frameworks to guide this emerging field will be essential to realizing its potential benefits while safeguarding human rights and dignity.
Regulatory Framework for Psychoactive Research
The regulatory framework for psychoactive research involving muscimol and other consciousness-altering substances is complex and multifaceted. At the international level, the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 classifies many psychoactive compounds, including muscimol, and establishes guidelines for their control and research use. However, individual countries have significant latitude in implementing these regulations.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies muscimol as a Schedule III controlled substance, allowing for its use in research with appropriate licensing and oversight. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in approving clinical trials involving muscimol and similar compounds. Researchers must obtain an Investigational New Drug (IND) application before conducting human studies, which requires extensive preclinical data and safety information.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) provide funding and guidelines for psychoactive research, including studies on consciousness and awareness. These agencies have specific protocols for handling and storing controlled substances, as well as reporting requirements for research outcomes.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the approval process for clinical trials involving psychoactive substances. The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) provides data and analysis on drug use and research trends, informing policy decisions across the European Union.
Many countries have established ethics committees or institutional review boards (IRBs) that must approve research protocols involving human subjects and psychoactive substances. These bodies ensure that studies adhere to ethical standards and protect participant safety.
Recent years have seen a growing interest in psychedelic research, leading to some regulatory changes. For instance, some jurisdictions have begun to relax restrictions on certain psychoactive compounds for research purposes. However, muscimol research remains tightly controlled due to its potent effects on consciousness and potential for misuse.
Researchers working with muscimol must navigate a complex landscape of regulations, including strict security measures for storage and handling, detailed record-keeping requirements, and regular audits by regulatory bodies. Additionally, there are often restrictions on the publication and dissemination of research findings related to controlled substances, which can impact the scientific community's ability to share and build upon new discoveries in consciousness research.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies muscimol as a Schedule III controlled substance, allowing for its use in research with appropriate licensing and oversight. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in approving clinical trials involving muscimol and similar compounds. Researchers must obtain an Investigational New Drug (IND) application before conducting human studies, which requires extensive preclinical data and safety information.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) provide funding and guidelines for psychoactive research, including studies on consciousness and awareness. These agencies have specific protocols for handling and storing controlled substances, as well as reporting requirements for research outcomes.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the approval process for clinical trials involving psychoactive substances. The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) provides data and analysis on drug use and research trends, informing policy decisions across the European Union.
Many countries have established ethics committees or institutional review boards (IRBs) that must approve research protocols involving human subjects and psychoactive substances. These bodies ensure that studies adhere to ethical standards and protect participant safety.
Recent years have seen a growing interest in psychedelic research, leading to some regulatory changes. For instance, some jurisdictions have begun to relax restrictions on certain psychoactive compounds for research purposes. However, muscimol research remains tightly controlled due to its potent effects on consciousness and potential for misuse.
Researchers working with muscimol must navigate a complex landscape of regulations, including strict security measures for storage and handling, detailed record-keeping requirements, and regular audits by regulatory bodies. Additionally, there are often restrictions on the publication and dissemination of research findings related to controlled substances, which can impact the scientific community's ability to share and build upon new discoveries in consciousness research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!