How Neopentane Optimizes Supply Chain Efficiency?
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neopentane Background and Objectives
Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, is a branched-chain alkane with the molecular formula C5H12. This colorless, flammable gas has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to optimize supply chain efficiency across various industries. The evolution of neopentane as a key component in supply chain management can be traced back to its unique physical and chemical properties, which make it an ideal candidate for numerous applications.
The development of neopentane technology has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and sustainable supply chain solutions. As global trade continues to expand and become more complex, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to streamline their operations and reduce costs. Neopentane has emerged as a promising solution to address these challenges, offering a range of benefits that can significantly improve supply chain performance.
One of the primary objectives of neopentane technology in supply chain optimization is to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it an excellent refrigerant and blowing agent, allowing for more efficient cooling and insulation processes in transportation and storage. This property has led to the development of advanced temperature-controlled logistics solutions, enabling the safe and efficient transport of temperature-sensitive goods across long distances.
Another key goal of neopentane technology is to improve the overall efficiency of material handling and transportation. Its low density and high compressibility allow for more compact storage and transportation of goods, potentially reducing the number of shipments required and minimizing fuel consumption. This aspect of neopentane technology aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly supply chain practices.
The evolution of neopentane in supply chain management has also been influenced by advancements in chemical engineering and materials science. Researchers and industry experts have been exploring novel applications of neopentane in areas such as packaging materials, fuel additives, and even as a potential energy storage medium. These ongoing developments aim to further expand the role of neopentane in optimizing various aspects of the supply chain, from production to final delivery.
As we look towards the future, the technological trajectory of neopentane in supply chain optimization is expected to focus on several key areas. These include the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods, the exploration of new applications in emerging industries, and the integration of neopentane-based solutions with advanced digital technologies such as IoT and AI to create smarter, more responsive supply chain systems.
The development of neopentane technology has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and sustainable supply chain solutions. As global trade continues to expand and become more complex, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to streamline their operations and reduce costs. Neopentane has emerged as a promising solution to address these challenges, offering a range of benefits that can significantly improve supply chain performance.
One of the primary objectives of neopentane technology in supply chain optimization is to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Its low boiling point and high vapor pressure make it an excellent refrigerant and blowing agent, allowing for more efficient cooling and insulation processes in transportation and storage. This property has led to the development of advanced temperature-controlled logistics solutions, enabling the safe and efficient transport of temperature-sensitive goods across long distances.
Another key goal of neopentane technology is to improve the overall efficiency of material handling and transportation. Its low density and high compressibility allow for more compact storage and transportation of goods, potentially reducing the number of shipments required and minimizing fuel consumption. This aspect of neopentane technology aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly supply chain practices.
The evolution of neopentane in supply chain management has also been influenced by advancements in chemical engineering and materials science. Researchers and industry experts have been exploring novel applications of neopentane in areas such as packaging materials, fuel additives, and even as a potential energy storage medium. These ongoing developments aim to further expand the role of neopentane in optimizing various aspects of the supply chain, from production to final delivery.
As we look towards the future, the technological trajectory of neopentane in supply chain optimization is expected to focus on several key areas. These include the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly production methods, the exploration of new applications in emerging industries, and the integration of neopentane-based solutions with advanced digital technologies such as IoT and AI to create smarter, more responsive supply chain systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Neopentane
The market demand for neopentane has been steadily growing due to its unique properties and versatile applications in various industries. As a key component in the optimization of supply chain efficiency, neopentane's market analysis reveals promising trends and opportunities.
In the chemical industry, neopentane serves as a crucial blowing agent for polyurethane foams, which are extensively used in insulation materials for construction and automotive sectors. The global construction industry's growth, particularly in emerging economies, has significantly boosted the demand for neopentane. Additionally, the automotive industry's shift towards lightweight materials and improved fuel efficiency has further increased the need for neopentane-based foam insulation.
The electronics sector represents another substantial market for neopentane. Its use as a heat transfer fluid in cooling systems for high-performance electronic devices has gained traction, especially with the rapid expansion of data centers and the increasing demand for efficient cooling solutions. The ongoing digital transformation across industries has indirectly contributed to the rising demand for neopentane in this application.
In the pharmaceutical industry, neopentane finds applications in the production of aerosol propellants and as a solvent in various processes. The growing pharmaceutical market, driven by an aging population and increased healthcare spending, has positively impacted the demand for neopentane.
The refrigeration and air conditioning industry also contributes to the market demand for neopentane. Its use as a refrigerant in certain applications, particularly where environmental regulations restrict the use of traditional refrigerants, has opened new avenues for market growth.
From a geographical perspective, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing market for neopentane, primarily due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by technological advancements and stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of more efficient and eco-friendly materials.
The market demand for neopentane is closely tied to global economic trends and industrial growth. Factors such as increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of energy efficiency are expected to drive the demand further. However, the market is not without challenges. Fluctuations in raw material prices, stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and the development of alternative materials pose potential risks to market growth.
In conclusion, the market demand analysis for neopentane indicates a positive outlook, with diverse applications across multiple industries driving growth. Its role in optimizing supply chain efficiency, particularly in sectors like construction, automotive, and electronics, positions neopentane as a valuable component in modern industrial processes. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the demand for neopentane is expected to maintain its upward trajectory in the foreseeable future.
In the chemical industry, neopentane serves as a crucial blowing agent for polyurethane foams, which are extensively used in insulation materials for construction and automotive sectors. The global construction industry's growth, particularly in emerging economies, has significantly boosted the demand for neopentane. Additionally, the automotive industry's shift towards lightweight materials and improved fuel efficiency has further increased the need for neopentane-based foam insulation.
The electronics sector represents another substantial market for neopentane. Its use as a heat transfer fluid in cooling systems for high-performance electronic devices has gained traction, especially with the rapid expansion of data centers and the increasing demand for efficient cooling solutions. The ongoing digital transformation across industries has indirectly contributed to the rising demand for neopentane in this application.
In the pharmaceutical industry, neopentane finds applications in the production of aerosol propellants and as a solvent in various processes. The growing pharmaceutical market, driven by an aging population and increased healthcare spending, has positively impacted the demand for neopentane.
The refrigeration and air conditioning industry also contributes to the market demand for neopentane. Its use as a refrigerant in certain applications, particularly where environmental regulations restrict the use of traditional refrigerants, has opened new avenues for market growth.
From a geographical perspective, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing market for neopentane, primarily due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by technological advancements and stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of more efficient and eco-friendly materials.
The market demand for neopentane is closely tied to global economic trends and industrial growth. Factors such as increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of energy efficiency are expected to drive the demand further. However, the market is not without challenges. Fluctuations in raw material prices, stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and the development of alternative materials pose potential risks to market growth.
In conclusion, the market demand analysis for neopentane indicates a positive outlook, with diverse applications across multiple industries driving growth. Its role in optimizing supply chain efficiency, particularly in sectors like construction, automotive, and electronics, positions neopentane as a valuable component in modern industrial processes. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the demand for neopentane is expected to maintain its upward trajectory in the foreseeable future.
Neopentane Supply Chain Challenges
The neopentane supply chain faces several significant challenges that impact its efficiency and effectiveness. One of the primary issues is the limited availability of neopentane, which is a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining. This scarcity can lead to supply shortages and price volatility, making it difficult for companies to maintain consistent production schedules and manage costs effectively.
Transportation and storage of neopentane present another set of challenges due to its highly flammable nature and low boiling point. Specialized equipment and safety measures are required for handling and transporting this substance, which increases operational costs and complexity throughout the supply chain. Additionally, strict regulatory compliance is necessary to ensure the safe handling of neopentane, further complicating logistics and distribution processes.
The global nature of the neopentane supply chain introduces geopolitical risks and trade barriers. Fluctuations in international relations, trade policies, and economic conditions can disrupt the flow of neopentane across borders, leading to supply chain instability and increased costs for manufacturers relying on this raw material.
Environmental concerns and sustainability pressures also pose challenges to the neopentane supply chain. As a hydrocarbon, neopentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and there is growing pressure to reduce its use or find more environmentally friendly alternatives. This shift towards sustainability may require significant investments in research and development, as well as potential restructuring of existing supply chain networks.
Demand fluctuations in industries that use neopentane, such as refrigeration, aerosols, and foam blowing, can create inventory management challenges. Balancing supply with varying demand requires sophisticated forecasting and inventory control systems, which may be difficult to implement across a complex, global supply chain.
Quality control is another critical challenge in the neopentane supply chain. Ensuring consistent purity and composition of neopentane is essential for its various applications, but maintaining quality standards across different suppliers and production facilities can be challenging. This necessitates rigorous testing and quality assurance processes throughout the supply chain.
Lastly, the neopentane supply chain faces technological challenges in terms of process optimization and digitalization. Implementing advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, blockchain for traceability, and AI-driven predictive maintenance can significantly improve efficiency but requires substantial investment and expertise to integrate these solutions effectively across the entire supply chain network.
Transportation and storage of neopentane present another set of challenges due to its highly flammable nature and low boiling point. Specialized equipment and safety measures are required for handling and transporting this substance, which increases operational costs and complexity throughout the supply chain. Additionally, strict regulatory compliance is necessary to ensure the safe handling of neopentane, further complicating logistics and distribution processes.
The global nature of the neopentane supply chain introduces geopolitical risks and trade barriers. Fluctuations in international relations, trade policies, and economic conditions can disrupt the flow of neopentane across borders, leading to supply chain instability and increased costs for manufacturers relying on this raw material.
Environmental concerns and sustainability pressures also pose challenges to the neopentane supply chain. As a hydrocarbon, neopentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and there is growing pressure to reduce its use or find more environmentally friendly alternatives. This shift towards sustainability may require significant investments in research and development, as well as potential restructuring of existing supply chain networks.
Demand fluctuations in industries that use neopentane, such as refrigeration, aerosols, and foam blowing, can create inventory management challenges. Balancing supply with varying demand requires sophisticated forecasting and inventory control systems, which may be difficult to implement across a complex, global supply chain.
Quality control is another critical challenge in the neopentane supply chain. Ensuring consistent purity and composition of neopentane is essential for its various applications, but maintaining quality standards across different suppliers and production facilities can be challenging. This necessitates rigorous testing and quality assurance processes throughout the supply chain.
Lastly, the neopentane supply chain faces technological challenges in terms of process optimization and digitalization. Implementing advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, blockchain for traceability, and AI-driven predictive maintenance can significantly improve efficiency but requires substantial investment and expertise to integrate these solutions effectively across the entire supply chain network.
Current Supply Chain Optimization Solutions
01 Supply chain optimization for neopentane production
Implementing advanced supply chain management techniques to optimize the production and distribution of neopentane. This includes improving inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics to reduce costs and increase efficiency in the neopentane supply chain.- Supply chain optimization for neopentane production: Implementing advanced supply chain management techniques to optimize the production and distribution of neopentane. This includes improving logistics, inventory management, and demand forecasting to enhance overall efficiency and reduce costs in the neopentane supply chain.
- Process improvements in neopentane manufacturing: Developing and implementing innovative manufacturing processes to increase the efficiency of neopentane production. This may involve optimizing reaction conditions, improving catalysts, or implementing new technologies to enhance yield and reduce energy consumption.
- Transportation and storage solutions for neopentane: Designing specialized transportation and storage solutions to ensure the safe and efficient handling of neopentane throughout the supply chain. This includes developing advanced containment systems, optimizing transportation routes, and implementing safety protocols to minimize risks associated with the volatile nature of neopentane.
- Digital technologies for neopentane supply chain management: Leveraging digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance the efficiency and transparency of the neopentane supply chain. These technologies can improve real-time tracking, automate processes, and facilitate better decision-making throughout the supply chain.
- Sustainable practices in neopentane production and distribution: Implementing sustainable practices in the neopentane supply chain to reduce environmental impact and improve long-term efficiency. This may include adopting green chemistry principles, optimizing energy use, and developing recycling or circular economy approaches for neopentane and its byproducts.
02 Process improvements in neopentane manufacturing
Developing and implementing innovative manufacturing processes to enhance the efficiency of neopentane production. This may involve optimizing reaction conditions, improving catalyst performance, and reducing energy consumption in the production process.Expand Specific Solutions03 Transportation and storage solutions for neopentane
Designing specialized transportation and storage solutions to ensure the safe and efficient handling of neopentane throughout the supply chain. This includes developing advanced containment systems and implementing safety protocols to minimize risks associated with the volatile nature of neopentane.Expand Specific Solutions04 Digital technologies for neopentane supply chain management
Leveraging digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance visibility, traceability, and decision-making in the neopentane supply chain. This includes implementing real-time monitoring systems and predictive analytics to optimize supply chain operations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable practices in neopentane production and distribution
Incorporating sustainable practices throughout the neopentane supply chain to reduce environmental impact and improve overall efficiency. This may include implementing green chemistry principles, optimizing energy use, and developing eco-friendly packaging and transportation methods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neopentane Industry
The neopentane supply chain optimization landscape is in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by demand for efficient petrochemical processes. The technology maturity varies among key players, with established companies like ExxonMobil Chemical Patents and Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij leading in innovation. Blue Yonder Group and SAP SE are advancing supply chain management solutions, while LG Chem and Wanhua Chemical Group focus on chemical production optimization. Academic institutions like Qingdao University contribute research, indicating a collaborative ecosystem. The market shows potential for further expansion as companies seek to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs in neopentane-related processes.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has developed advanced neopentane-based processes to optimize supply chain efficiency. Their approach involves using neopentane as a blowing agent in the production of expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, which is widely used in packaging and insulation. The company has implemented a closed-loop system that captures and recycles neopentane during the EPS manufacturing process, significantly reducing raw material costs and environmental impact[1]. Additionally, ExxonMobil has invested in state-of-the-art logistics systems that track neopentane shipments in real-time, allowing for just-in-time delivery and minimizing storage requirements at production facilities[3].
Strengths: Reduced raw material costs, improved environmental sustainability, and enhanced supply chain visibility. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs for implementing the closed-loop system and potential dependence on proprietary technology.
Blue Yonder Group, Inc.
Technical Solution: Blue Yonder has developed an AI-powered supply chain optimization platform that incorporates neopentane-specific parameters to enhance efficiency. The system utilizes machine learning algorithms to predict demand fluctuations for neopentane-based products, allowing manufacturers to adjust production schedules and inventory levels accordingly[2]. Blue Yonder's platform also integrates with IoT sensors to monitor neopentane storage conditions, ensuring optimal temperature and pressure are maintained throughout the supply chain. This reduces the risk of product degradation and improves overall quality control[4]. Furthermore, the platform provides advanced analytics capabilities that help identify bottlenecks in the neopentane supply chain, enabling companies to implement targeted improvements[5].
Strengths: Advanced predictive capabilities, improved inventory management, and enhanced quality control. Weaknesses: Reliance on high-quality data inputs and potential complexity in implementation for smaller organizations.
Innovative Neopentane Distribution Strategies
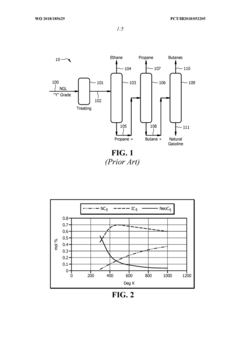
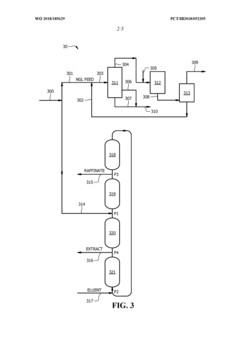
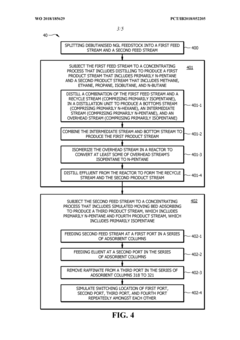
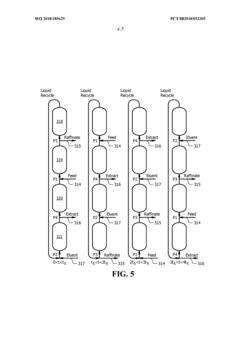
Process for npentanizing debutanized natural gasoline feedstock to thermal crackers
PatentWO2018185629A1
Innovation
- A method involving the splitting of n-pentane and isopentane streams into separate feed streams, followed by distillation and simulated moving bed adsorption processes to increase the concentration of n-pentane, utilizing catalysts like sulfated zirconia and platinum on alumina to isomerize isopentane to n-pentane, thereby enhancing the linear pentane to branched pentane ratio.
Methods for production of oxygenated terpenes
PatentActiveUS11807890B2
Innovation
- Engineered host cells, including E. coli and yeast, are used to produce oxygenated sesquiterpenes through the expression of Stevia rebaudiana Kaurene Oxidase (SrKO) enzymes, which catalyze the oxidation of sesquiterpene substrates like valencene to produce nootkatone and nootkatol, with modifications to enhance valencene oxidase activity and stability in bacterial systems.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact of neopentane in supply chain optimization is a critical consideration for sustainable business practices. Neopentane, a highly volatile organic compound, offers significant advantages in terms of supply chain efficiency but also poses potential environmental risks that must be carefully assessed and mitigated.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with neopentane is its contribution to air pollution. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), neopentane can readily evaporate into the atmosphere, potentially contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These air quality issues can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems, particularly in urban areas where supply chain activities are often concentrated.
Furthermore, neopentane has a high global warming potential, making it a potent greenhouse gas. Its release into the atmosphere can contribute to climate change, which has far-reaching consequences for the environment and society. As such, the use of neopentane in supply chain operations must be carefully managed to minimize emissions and prevent unintended releases.
Water pollution is another potential environmental risk associated with neopentane. In the event of spills or leaks during transportation or storage, neopentane can contaminate water sources, posing threats to aquatic ecosystems and potentially impacting drinking water supplies. This risk necessitates robust containment measures and emergency response protocols throughout the supply chain.
Despite these environmental concerns, the use of neopentane in supply chain optimization can also yield positive environmental outcomes. By improving logistics efficiency and reducing transportation requirements, neopentane-based solutions can lead to decreased fuel consumption and lower overall carbon emissions from supply chain activities. This reduction in transportation-related emissions can partially offset the direct environmental impacts of neopentane use.
To mitigate the environmental risks associated with neopentane, companies must implement comprehensive environmental management systems. These should include regular monitoring of emissions, leak detection and repair programs, and the use of best available technologies for containment and handling. Additionally, investing in research and development of more environmentally friendly alternatives or improved neopentane handling techniques can further reduce the environmental footprint of supply chain operations.
Regulatory compliance is a crucial aspect of environmental impact assessment for neopentane use. Companies must adhere to local, national, and international regulations governing the handling, storage, and transportation of volatile organic compounds. This includes obtaining necessary permits, conducting regular environmental audits, and reporting emissions data to relevant authorities.
In conclusion, while neopentane offers significant benefits for supply chain efficiency, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. A comprehensive approach that balances the economic advantages with environmental stewardship is essential for sustainable and responsible use of neopentane in supply chain optimization.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with neopentane is its contribution to air pollution. As a volatile organic compound (VOC), neopentane can readily evaporate into the atmosphere, potentially contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog. These air quality issues can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems, particularly in urban areas where supply chain activities are often concentrated.
Furthermore, neopentane has a high global warming potential, making it a potent greenhouse gas. Its release into the atmosphere can contribute to climate change, which has far-reaching consequences for the environment and society. As such, the use of neopentane in supply chain operations must be carefully managed to minimize emissions and prevent unintended releases.
Water pollution is another potential environmental risk associated with neopentane. In the event of spills or leaks during transportation or storage, neopentane can contaminate water sources, posing threats to aquatic ecosystems and potentially impacting drinking water supplies. This risk necessitates robust containment measures and emergency response protocols throughout the supply chain.
Despite these environmental concerns, the use of neopentane in supply chain optimization can also yield positive environmental outcomes. By improving logistics efficiency and reducing transportation requirements, neopentane-based solutions can lead to decreased fuel consumption and lower overall carbon emissions from supply chain activities. This reduction in transportation-related emissions can partially offset the direct environmental impacts of neopentane use.
To mitigate the environmental risks associated with neopentane, companies must implement comprehensive environmental management systems. These should include regular monitoring of emissions, leak detection and repair programs, and the use of best available technologies for containment and handling. Additionally, investing in research and development of more environmentally friendly alternatives or improved neopentane handling techniques can further reduce the environmental footprint of supply chain operations.
Regulatory compliance is a crucial aspect of environmental impact assessment for neopentane use. Companies must adhere to local, national, and international regulations governing the handling, storage, and transportation of volatile organic compounds. This includes obtaining necessary permits, conducting regular environmental audits, and reporting emissions data to relevant authorities.
In conclusion, while neopentane offers significant benefits for supply chain efficiency, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. A comprehensive approach that balances the economic advantages with environmental stewardship is essential for sustainable and responsible use of neopentane in supply chain optimization.
Regulatory Compliance in Neopentane Handling
Regulatory compliance in neopentane handling is a critical aspect of supply chain optimization, given the unique properties and potential hazards associated with this hydrocarbon. Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, is a highly volatile and flammable substance, necessitating strict adherence to safety regulations and environmental standards throughout its lifecycle.
In the United States, the handling and transportation of neopentane fall under the purview of multiple regulatory bodies. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace safety, including proper storage, handling, and personal protective equipment requirements. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates emissions and potential environmental impacts, while the Department of Transportation (DOT) oversees the safe transport of neopentane as a hazardous material.
Internationally, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Companies dealing with neopentane must ensure proper labeling, safety data sheets, and training for personnel in accordance with GHS guidelines.
Storage and handling of neopentane require specialized equipment and facilities. Tanks and containers must be designed to withstand high pressures and prevent leaks. Proper ventilation systems and grounding procedures are essential to mitigate the risk of fire or explosion. Regular inspections and maintenance of storage and handling equipment are mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
Transportation of neopentane is subject to strict regulations due to its classification as a flammable gas. Carriers must comply with specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Route planning and risk assessments are crucial to minimize potential hazards during transit. Emergency response plans must be in place, and drivers transporting neopentane require specialized training and certifications.
Compliance with these regulations not only ensures safety but also contributes to supply chain efficiency. Proper handling and storage reduce the risk of accidents and product loss, while standardized transportation procedures facilitate smoother logistics operations. Companies that invest in robust compliance programs often find they can optimize their supply chains by reducing delays, minimizing fines, and improving overall operational reliability.
To maintain regulatory compliance, companies must implement comprehensive management systems that track and document all aspects of neopentane handling. This includes maintaining detailed records of inventory, safety inspections, employee training, and incident reports. Regular audits and reviews of these systems help identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing adherence to evolving regulations.
In the United States, the handling and transportation of neopentane fall under the purview of multiple regulatory bodies. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for workplace safety, including proper storage, handling, and personal protective equipment requirements. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates emissions and potential environmental impacts, while the Department of Transportation (DOT) oversees the safe transport of neopentane as a hazardous material.
Internationally, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. Companies dealing with neopentane must ensure proper labeling, safety data sheets, and training for personnel in accordance with GHS guidelines.
Storage and handling of neopentane require specialized equipment and facilities. Tanks and containers must be designed to withstand high pressures and prevent leaks. Proper ventilation systems and grounding procedures are essential to mitigate the risk of fire or explosion. Regular inspections and maintenance of storage and handling equipment are mandated to ensure ongoing compliance and safety.
Transportation of neopentane is subject to strict regulations due to its classification as a flammable gas. Carriers must comply with specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Route planning and risk assessments are crucial to minimize potential hazards during transit. Emergency response plans must be in place, and drivers transporting neopentane require specialized training and certifications.
Compliance with these regulations not only ensures safety but also contributes to supply chain efficiency. Proper handling and storage reduce the risk of accidents and product loss, while standardized transportation procedures facilitate smoother logistics operations. Companies that invest in robust compliance programs often find they can optimize their supply chains by reducing delays, minimizing fines, and improving overall operational reliability.
To maintain regulatory compliance, companies must implement comprehensive management systems that track and document all aspects of neopentane handling. This includes maintaining detailed records of inventory, safety inspections, employee training, and incident reports. Regular audits and reviews of these systems help identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing adherence to evolving regulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!