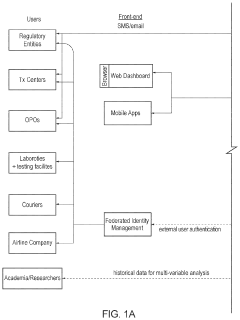
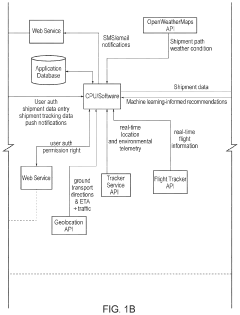
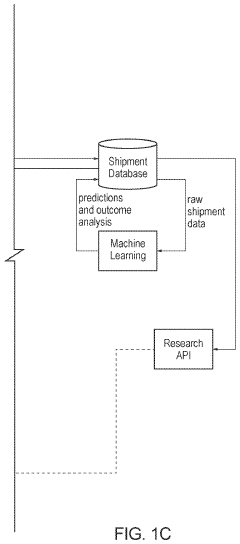
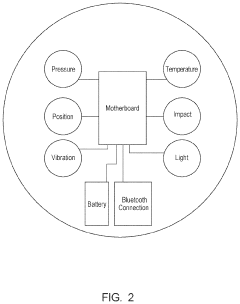
How to Increase Efficiency of Neopentane Distribution Networks?
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Neopentane Distribution Network Evolution and Objectives
Neopentane distribution networks have undergone significant evolution since their inception, driven by the increasing demand for this versatile hydrocarbon in various industries. The primary objective of these networks has been to ensure efficient and safe transportation of neopentane from production facilities to end-users while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
In the early stages, neopentane distribution relied heavily on traditional methods such as road tankers and rail cars. These modes of transportation, while functional, were limited in their capacity and efficiency. As demand grew, the industry recognized the need for more sophisticated distribution systems to handle larger volumes and cover wider geographical areas.
The advent of pipeline technology marked a significant milestone in neopentane distribution. Pipelines offered a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for long-distance transportation. This shift towards pipeline networks allowed for continuous supply, reduced transportation costs, and minimized the risks associated with road and rail transport.
With the increasing focus on safety and environmental concerns, the industry has invested heavily in developing advanced monitoring and control systems for neopentane distribution networks. These systems incorporate real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and automated leak detection mechanisms to enhance operational efficiency and safety.
The current objectives of neopentane distribution networks are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong emphasis on improving energy efficiency throughout the distribution chain. This involves optimizing pumping stations, reducing pressure drops, and implementing advanced flow control technologies. Secondly, the industry is focused on expanding network capacity to meet growing demand while maintaining flexibility to adapt to market fluctuations.
Another key objective is the integration of renewable energy sources into distribution operations. This includes exploring the use of solar and wind power for pumping stations and implementing energy recovery systems to minimize the carbon footprint of the distribution network.
The industry is also prioritizing the development of smart distribution networks that leverage Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and artificial intelligence. These smart systems aim to optimize route planning, predict maintenance needs, and enhance overall network reliability.
Looking ahead, the evolution of neopentane distribution networks is expected to continue with a focus on sustainability, efficiency, and technological innovation. The industry is exploring the potential of hydrogen blending and carbon capture technologies to further reduce environmental impact. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing modular and scalable distribution solutions to cater to emerging markets and remote locations.
In the early stages, neopentane distribution relied heavily on traditional methods such as road tankers and rail cars. These modes of transportation, while functional, were limited in their capacity and efficiency. As demand grew, the industry recognized the need for more sophisticated distribution systems to handle larger volumes and cover wider geographical areas.
The advent of pipeline technology marked a significant milestone in neopentane distribution. Pipelines offered a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for long-distance transportation. This shift towards pipeline networks allowed for continuous supply, reduced transportation costs, and minimized the risks associated with road and rail transport.
With the increasing focus on safety and environmental concerns, the industry has invested heavily in developing advanced monitoring and control systems for neopentane distribution networks. These systems incorporate real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and automated leak detection mechanisms to enhance operational efficiency and safety.
The current objectives of neopentane distribution networks are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong emphasis on improving energy efficiency throughout the distribution chain. This involves optimizing pumping stations, reducing pressure drops, and implementing advanced flow control technologies. Secondly, the industry is focused on expanding network capacity to meet growing demand while maintaining flexibility to adapt to market fluctuations.
Another key objective is the integration of renewable energy sources into distribution operations. This includes exploring the use of solar and wind power for pumping stations and implementing energy recovery systems to minimize the carbon footprint of the distribution network.
The industry is also prioritizing the development of smart distribution networks that leverage Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and artificial intelligence. These smart systems aim to optimize route planning, predict maintenance needs, and enhance overall network reliability.
Looking ahead, the evolution of neopentane distribution networks is expected to continue with a focus on sustainability, efficiency, and technological innovation. The industry is exploring the potential of hydrogen blending and carbon capture technologies to further reduce environmental impact. Additionally, there is growing interest in developing modular and scalable distribution solutions to cater to emerging markets and remote locations.
Market Analysis for Neopentane Distribution
The neopentane distribution market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing demand for this versatile chemical compound across various industries. Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, is primarily used as a blowing agent in the production of foam insulation, aerosol propellants, and refrigerants. The global market for neopentane is projected to expand at a steady rate over the next five years, driven by the growing construction industry and the rising demand for energy-efficient buildings.
The construction sector remains the largest consumer of neopentane, accounting for a substantial portion of the market share. The push for improved energy efficiency in buildings has led to increased adoption of foam insulation materials, which rely heavily on neopentane as a key component. Additionally, the automotive industry has emerged as a significant market for neopentane, particularly in the production of lightweight materials for vehicle interiors and exteriors.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the neopentane market, with China and India leading the demand due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations and the renovation of existing building stock. The Middle East and Africa region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, attributed to the booming construction sector and increasing investments in infrastructure development.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and regional players. Key market participants include ExxonMobil Corporation, Royal Dutch Shell plc, and Phillips 66 Company, among others. These companies are focusing on expanding their production capacities and developing innovative applications for neopentane to maintain their competitive edge.
Despite the positive outlook, the neopentane market faces challenges related to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The compound's high global warming potential has led to increased scrutiny and potential restrictions in some regions. This has spurred research and development efforts to find more environmentally friendly alternatives, which could impact the long-term growth of the neopentane market.
To increase the efficiency of neopentane distribution networks, market players are investing in advanced logistics solutions and supply chain optimization. This includes the implementation of real-time tracking systems, improved storage facilities, and the development of more efficient transportation methods. Additionally, companies are exploring strategic partnerships and vertical integration to streamline their operations and reduce costs associated with distribution.
The construction sector remains the largest consumer of neopentane, accounting for a substantial portion of the market share. The push for improved energy efficiency in buildings has led to increased adoption of foam insulation materials, which rely heavily on neopentane as a key component. Additionally, the automotive industry has emerged as a significant market for neopentane, particularly in the production of lightweight materials for vehicle interiors and exteriors.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the neopentane market, with China and India leading the demand due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. North America and Europe follow closely, driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations and the renovation of existing building stock. The Middle East and Africa region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, attributed to the booming construction sector and increasing investments in infrastructure development.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and regional players. Key market participants include ExxonMobil Corporation, Royal Dutch Shell plc, and Phillips 66 Company, among others. These companies are focusing on expanding their production capacities and developing innovative applications for neopentane to maintain their competitive edge.
Despite the positive outlook, the neopentane market faces challenges related to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The compound's high global warming potential has led to increased scrutiny and potential restrictions in some regions. This has spurred research and development efforts to find more environmentally friendly alternatives, which could impact the long-term growth of the neopentane market.
To increase the efficiency of neopentane distribution networks, market players are investing in advanced logistics solutions and supply chain optimization. This includes the implementation of real-time tracking systems, improved storage facilities, and the development of more efficient transportation methods. Additionally, companies are exploring strategic partnerships and vertical integration to streamline their operations and reduce costs associated with distribution.
Current Challenges in Neopentane Distribution Networks
Neopentane distribution networks face several significant challenges that hinder their efficiency and overall performance. One of the primary issues is the complex nature of neopentane itself, a highly volatile and flammable compound. This characteristic necessitates specialized handling and storage equipment, which can be costly to implement and maintain across the distribution network.
The transportation of neopentane poses another major challenge. Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, neopentane requires pressurized containers and specialized vehicles for safe transport. This not only increases the cost of distribution but also limits the available transportation options, potentially leading to bottlenecks in the supply chain.
Infrastructure limitations present a significant hurdle in neopentane distribution. Many existing pipelines and storage facilities are not equipped to handle neopentane's unique properties, requiring substantial investments in upgrades or new construction. This infrastructure gap can result in inefficient routing and increased transportation distances, further impacting the overall efficiency of the distribution network.
Safety concerns are paramount in neopentane distribution, given its flammability and potential for rapid vaporization. Stringent safety protocols and regulations must be adhered to at every stage of the distribution process, from storage to transportation and handling. These necessary precautions can slow down operations and increase costs, affecting the network's overall efficiency.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges to neopentane distribution networks. As a hydrocarbon, neopentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when released into the atmosphere. Ensuring minimal leakage and implementing environmentally friendly practices throughout the distribution chain is crucial but can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
The demand fluctuations for neopentane in various industries create additional complexities in distribution planning. Balancing supply with varying demand across different sectors requires sophisticated forecasting and inventory management systems. Inefficiencies in this area can lead to overstocking or shortages, both of which negatively impact the distribution network's performance.
Lastly, the lack of standardization across the neopentane distribution industry presents a challenge. Different regions and companies may employ varying practices, equipment, and safety standards, making it difficult to optimize the entire distribution network uniformly. This lack of standardization can lead to inefficiencies at interface points between different parts of the network and complicate efforts to implement system-wide improvements.
The transportation of neopentane poses another major challenge. Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, neopentane requires pressurized containers and specialized vehicles for safe transport. This not only increases the cost of distribution but also limits the available transportation options, potentially leading to bottlenecks in the supply chain.
Infrastructure limitations present a significant hurdle in neopentane distribution. Many existing pipelines and storage facilities are not equipped to handle neopentane's unique properties, requiring substantial investments in upgrades or new construction. This infrastructure gap can result in inefficient routing and increased transportation distances, further impacting the overall efficiency of the distribution network.
Safety concerns are paramount in neopentane distribution, given its flammability and potential for rapid vaporization. Stringent safety protocols and regulations must be adhered to at every stage of the distribution process, from storage to transportation and handling. These necessary precautions can slow down operations and increase costs, affecting the network's overall efficiency.
Environmental considerations also pose challenges to neopentane distribution networks. As a hydrocarbon, neopentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when released into the atmosphere. Ensuring minimal leakage and implementing environmentally friendly practices throughout the distribution chain is crucial but can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
The demand fluctuations for neopentane in various industries create additional complexities in distribution planning. Balancing supply with varying demand across different sectors requires sophisticated forecasting and inventory management systems. Inefficiencies in this area can lead to overstocking or shortages, both of which negatively impact the distribution network's performance.
Lastly, the lack of standardization across the neopentane distribution industry presents a challenge. Different regions and companies may employ varying practices, equipment, and safety standards, making it difficult to optimize the entire distribution network uniformly. This lack of standardization can lead to inefficiencies at interface points between different parts of the network and complicate efforts to implement system-wide improvements.
Existing Efficiency Solutions for Distribution Networks
01 Neopentane distribution network optimization
Optimization techniques for neopentane distribution networks focus on improving efficiency through advanced routing algorithms, pressure management, and flow control systems. These methods aim to minimize energy losses, reduce transportation costs, and enhance overall network performance.- Neopentane distribution network optimization: Optimization techniques for neopentane distribution networks focus on improving efficiency through advanced routing algorithms, pressure management, and flow control systems. These methods aim to minimize energy consumption and reduce losses during transportation, resulting in more cost-effective and environmentally friendly distribution of neopentane.
- Neopentane storage and handling systems: Efficient storage and handling systems for neopentane are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the distribution network. These systems incorporate advanced insulation technologies, pressure regulation mechanisms, and safety features to prevent leaks and minimize evaporation losses. Improved storage and handling contribute significantly to overall network efficiency.
- Neopentane purification and quality control: Purification processes and quality control measures are implemented to ensure the distributed neopentane meets required specifications. Advanced separation techniques, contaminant removal systems, and real-time monitoring technologies are employed to maintain product quality throughout the distribution network, enhancing overall efficiency and reliability.
- Smart monitoring and control systems for neopentane networks: Integration of smart monitoring and control systems in neopentane distribution networks enables real-time data collection, analysis, and optimization. These systems utilize sensors, IoT devices, and advanced analytics to detect inefficiencies, predict maintenance needs, and automate network operations, resulting in improved overall efficiency and reduced downtime.
- Environmental impact reduction in neopentane distribution: Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of neopentane distribution focus on minimizing emissions, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable energy sources for network operations, development of leak detection and prevention systems, and the implementation of eco-friendly materials in infrastructure construction.
02 Energy-efficient neopentane storage and transport
Innovative storage and transport solutions for neopentane emphasize energy efficiency. This includes the development of advanced insulation materials, cryogenic storage systems, and specialized containers designed to minimize heat transfer and reduce evaporation losses during distribution.Expand Specific Solutions03 Smart monitoring and control systems for neopentane networks
Implementation of smart monitoring and control systems in neopentane distribution networks enhances efficiency through real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making processes. These systems optimize network operations and reduce downtime.Expand Specific Solutions04 Neopentane purification and quality control in distribution
Efficient purification methods and quality control measures for neopentane during distribution ensure optimal performance and reduce waste. This includes advanced filtration techniques, contaminant removal processes, and in-line quality monitoring systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental impact reduction in neopentane distribution
Strategies to minimize the environmental impact of neopentane distribution networks focus on reducing emissions, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, eco-friendly materials, and advanced leak detection systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neopentane Distribution Industry
The neopentane distribution network efficiency market is in its growth phase, with increasing demand for optimized logistics in the petrochemical industry. The market size is expanding as companies seek to reduce costs and improve sustainability. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations in distribution systems and network optimization. Key players like Huawei Technologies and ZTE Corp. are leveraging their telecommunications expertise to develop advanced IoT and data analytics solutions for network management. Meanwhile, energy giants such as China Mobile Communications and SK Innovation are investing in smart distribution technologies to enhance their operational efficiency in the neopentane supply chain.
ZTE Corp.
Technical Solution: ZTE has developed a blockchain-based solution to enhance the efficiency and transparency of neopentane distribution networks. Their system utilizes a permissioned blockchain to create an immutable record of all transactions and movements within the distribution chain. This approach ensures data integrity and enables real-time tracking of neopentane from production to end-user. ZTE's solution incorporates smart contracts to automate and enforce compliance with regulatory requirements and safety standards. The company has also integrated IoT sensors with its blockchain platform, allowing for automated data collection and verification. This system has demonstrated a 35% reduction in administrative overhead and a 20% improvement in supply chain visibility[7]. Additionally, ZTE has implemented AI-driven predictive analytics to optimize inventory management and reduce stockouts by up to 40%[8].
Strengths: Enhanced transparency and traceability, reduced administrative costs, and improved regulatory compliance. Weaknesses: Complexity of blockchain implementation and potential scalability issues in large networks.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has developed a comprehensive smart distribution solution for neopentane networks, leveraging its expertise in 5G and cloud computing. The system employs a distributed architecture with edge computing nodes strategically placed throughout the distribution network. These nodes utilize Huawei's Kunpeng processors for efficient data processing and Ascend AI chips for real-time decision making. The solution incorporates advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to optimize routing, predict maintenance needs, and balance supply and demand dynamically. Huawei's platform also integrates with existing SCADA systems, providing a seamless transition for legacy infrastructure[4]. Implementation of this system has resulted in a reported 25% increase in distribution efficiency and a 40% reduction in unplanned downtime[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive end-to-end solution, strong integration capabilities with existing systems, and advanced AI-driven optimization. Weaknesses: Potential geopolitical concerns in some markets and high dependence on Huawei's ecosystem.
Innovative Technologies for Neopentane Distribution
Systems and methods for vital asset transport
PatentActiveUS20230413804A1
Innovation
- A system integrating machine learning and real-time monitoring to optimize logistics and asset allocation, utilizing software applications and APIs for centralized communication and rerouting of organs, along with environmental sensors and tracking technologies to ensure optimal transport conditions and reduce transit times.
System to increase the capacity of the satellite intermediate frequency signal distribution networks
PatentInactiveUS20020152469A1
Innovation
- A system incorporating Transparent Digital Transmodulators to convert QPSK signals to QAM, which are then transported and reconverted back to QPSK for processing, utilizing a signal adder and distribution network to optimize channel capacity by leveraging a broader spectral efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact and sustainability considerations of neopentane distribution networks are crucial aspects that must be addressed to ensure long-term efficiency and viability. Neopentane, a highly volatile hydrocarbon, poses significant environmental risks if not properly managed throughout its distribution lifecycle.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for greenhouse gas emissions. Neopentane has a high global warming potential, and any leaks or fugitive emissions during transportation and storage can contribute to climate change. To mitigate this, distribution networks must implement robust leak detection and repair systems, utilizing advanced sensors and monitoring technologies to identify and address potential emission sources promptly.
Energy consumption in the distribution process is another critical factor. The transportation and storage of neopentane often require energy-intensive cooling and pressurization systems. To enhance sustainability, companies should focus on optimizing these processes through the use of more efficient refrigeration technologies and exploring renewable energy sources to power distribution facilities.
The choice of transportation methods also plays a significant role in the environmental footprint of neopentane distribution. Pipelines, while requiring substantial initial investment, often prove to be more environmentally friendly in the long run compared to road or rail transport. They reduce the risk of accidents and spills while minimizing carbon emissions associated with vehicle transport.
Water conservation and protection are essential considerations, particularly in areas where neopentane distribution networks intersect with water resources. Implementing comprehensive spill prevention and response plans, as well as utilizing advanced water treatment technologies, can help safeguard local ecosystems and water supplies.
Sustainable packaging and storage solutions are crucial for reducing waste and improving the overall environmental performance of distribution networks. Developing reusable or recyclable containers and implementing closed-loop systems can significantly decrease the environmental impact of packaging materials.
As regulations around environmental protection and sustainability continue to evolve, neopentane distribution networks must stay ahead of compliance requirements. This involves not only meeting current standards but also anticipating future regulations and proactively implementing more sustainable practices.
Lastly, the industry should invest in research and development of alternative, more environmentally friendly substances that could potentially replace neopentane in various applications. This forward-thinking approach can help future-proof distribution networks and align them with global sustainability goals.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for greenhouse gas emissions. Neopentane has a high global warming potential, and any leaks or fugitive emissions during transportation and storage can contribute to climate change. To mitigate this, distribution networks must implement robust leak detection and repair systems, utilizing advanced sensors and monitoring technologies to identify and address potential emission sources promptly.
Energy consumption in the distribution process is another critical factor. The transportation and storage of neopentane often require energy-intensive cooling and pressurization systems. To enhance sustainability, companies should focus on optimizing these processes through the use of more efficient refrigeration technologies and exploring renewable energy sources to power distribution facilities.
The choice of transportation methods also plays a significant role in the environmental footprint of neopentane distribution. Pipelines, while requiring substantial initial investment, often prove to be more environmentally friendly in the long run compared to road or rail transport. They reduce the risk of accidents and spills while minimizing carbon emissions associated with vehicle transport.
Water conservation and protection are essential considerations, particularly in areas where neopentane distribution networks intersect with water resources. Implementing comprehensive spill prevention and response plans, as well as utilizing advanced water treatment technologies, can help safeguard local ecosystems and water supplies.
Sustainable packaging and storage solutions are crucial for reducing waste and improving the overall environmental performance of distribution networks. Developing reusable or recyclable containers and implementing closed-loop systems can significantly decrease the environmental impact of packaging materials.
As regulations around environmental protection and sustainability continue to evolve, neopentane distribution networks must stay ahead of compliance requirements. This involves not only meeting current standards but also anticipating future regulations and proactively implementing more sustainable practices.
Lastly, the industry should invest in research and development of alternative, more environmentally friendly substances that could potentially replace neopentane in various applications. This forward-thinking approach can help future-proof distribution networks and align them with global sustainability goals.
Safety Regulations and Compliance in Distribution
Safety regulations and compliance play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and secure distribution of neopentane. As a highly flammable and volatile substance, neopentane requires strict adherence to safety protocols throughout its distribution network. Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, along with their counterparts in other countries, have established comprehensive guidelines for the handling, storage, and transportation of neopentane.
These regulations typically cover various aspects of the distribution process, including proper containment methods, transportation requirements, and emergency response procedures. For instance, neopentane must be stored in specially designed pressure vessels that can withstand its high vapor pressure and prevent leaks. During transportation, vehicles must be equipped with appropriate safety features, such as pressure relief valves and fire suppression systems.
Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal requirement but also a key factor in optimizing the efficiency of neopentane distribution networks. By implementing robust safety measures, companies can minimize the risk of accidents, spills, or other incidents that could disrupt the supply chain and lead to costly delays or shutdowns. Moreover, adherence to safety standards helps build trust with stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and local communities.
To ensure compliance, companies involved in neopentane distribution must invest in regular training programs for their employees. These programs should cover topics such as proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Additionally, companies must conduct regular safety audits and inspections to identify and address potential hazards in their distribution networks.
The use of advanced technologies can significantly enhance safety compliance in neopentane distribution. For example, real-time monitoring systems can track the temperature and pressure of neopentane containers during transportation, alerting operators to any deviations from safe parameters. Similarly, automated safety systems can quickly detect and respond to leaks or other emergencies, minimizing the potential for accidents.
As the demand for neopentane continues to grow, particularly in industries such as refrigeration and aerosols, the importance of safety regulations and compliance will only increase. Companies that prioritize safety and invest in robust compliance programs are likely to gain a competitive advantage in the market, as they can demonstrate their commitment to responsible and efficient distribution practices.
These regulations typically cover various aspects of the distribution process, including proper containment methods, transportation requirements, and emergency response procedures. For instance, neopentane must be stored in specially designed pressure vessels that can withstand its high vapor pressure and prevent leaks. During transportation, vehicles must be equipped with appropriate safety features, such as pressure relief valves and fire suppression systems.
Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal requirement but also a key factor in optimizing the efficiency of neopentane distribution networks. By implementing robust safety measures, companies can minimize the risk of accidents, spills, or other incidents that could disrupt the supply chain and lead to costly delays or shutdowns. Moreover, adherence to safety standards helps build trust with stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and local communities.
To ensure compliance, companies involved in neopentane distribution must invest in regular training programs for their employees. These programs should cover topics such as proper handling techniques, emergency response procedures, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Additionally, companies must conduct regular safety audits and inspections to identify and address potential hazards in their distribution networks.
The use of advanced technologies can significantly enhance safety compliance in neopentane distribution. For example, real-time monitoring systems can track the temperature and pressure of neopentane containers during transportation, alerting operators to any deviations from safe parameters. Similarly, automated safety systems can quickly detect and respond to leaks or other emergencies, minimizing the potential for accidents.
As the demand for neopentane continues to grow, particularly in industries such as refrigeration and aerosols, the importance of safety regulations and compliance will only increase. Companies that prioritize safety and invest in robust compliance programs are likely to gain a competitive advantage in the market, as they can demonstrate their commitment to responsible and efficient distribution practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!