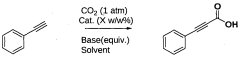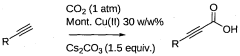How to Implement Carbonyl Processes for Sustainable Growth?
JUL 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carbonyl Process Evolution and Objectives
Carbonyl processes have played a pivotal role in the chemical industry for decades, serving as a cornerstone for the production of various essential compounds. The evolution of these processes has been driven by the need for more efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly manufacturing methods. Initially developed in the early 20th century, carbonyl processes have undergone significant transformations to meet the changing demands of industry and society.
The primary objective of implementing carbonyl processes for sustainable growth is to develop innovative approaches that minimize environmental impact while maximizing economic viability. This goal aligns with the broader global shift towards sustainable development and circular economy principles. By optimizing carbonyl processes, industries aim to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste generation, and decrease reliance on non-renewable resources.
One of the key evolutionary trends in carbonyl processes has been the transition from traditional fossil fuel-based feedstocks to renewable alternatives. This shift has been driven by the need to reduce carbon footprints and mitigate climate change impacts. Researchers and industry professionals have been exploring bio-based feedstocks and developing novel catalysts to enable more sustainable carbonyl reactions.
Another significant development in the field has been the integration of green chemistry principles into carbonyl processes. This approach focuses on designing chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. Innovations in this area include the development of solvent-free reactions, the use of recyclable catalysts, and the implementation of continuous flow processes to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
The advent of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, has also contributed to the evolution of carbonyl processes. These tools have enabled more precise process control, predictive modeling of reaction outcomes, and optimization of reaction conditions. By leveraging these technologies, researchers and engineers can accelerate the development of more sustainable carbonyl processes and improve overall process efficiency.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for carbonyl processes in sustainable growth are multifaceted. One primary goal is to achieve carbon neutrality in production processes, which will require innovative approaches to carbon capture and utilization. Additionally, there is a strong focus on developing closed-loop systems that maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste generation throughout the entire product lifecycle.
In conclusion, the evolution of carbonyl processes towards sustainable growth represents a critical area of research and development in the chemical industry. By addressing the challenges of environmental impact, resource depletion, and economic viability, these advancements pave the way for a more sustainable future in chemical manufacturing.
The primary objective of implementing carbonyl processes for sustainable growth is to develop innovative approaches that minimize environmental impact while maximizing economic viability. This goal aligns with the broader global shift towards sustainable development and circular economy principles. By optimizing carbonyl processes, industries aim to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste generation, and decrease reliance on non-renewable resources.
One of the key evolutionary trends in carbonyl processes has been the transition from traditional fossil fuel-based feedstocks to renewable alternatives. This shift has been driven by the need to reduce carbon footprints and mitigate climate change impacts. Researchers and industry professionals have been exploring bio-based feedstocks and developing novel catalysts to enable more sustainable carbonyl reactions.
Another significant development in the field has been the integration of green chemistry principles into carbonyl processes. This approach focuses on designing chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. Innovations in this area include the development of solvent-free reactions, the use of recyclable catalysts, and the implementation of continuous flow processes to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
The advent of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, has also contributed to the evolution of carbonyl processes. These tools have enabled more precise process control, predictive modeling of reaction outcomes, and optimization of reaction conditions. By leveraging these technologies, researchers and engineers can accelerate the development of more sustainable carbonyl processes and improve overall process efficiency.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for carbonyl processes in sustainable growth are multifaceted. One primary goal is to achieve carbon neutrality in production processes, which will require innovative approaches to carbon capture and utilization. Additionally, there is a strong focus on developing closed-loop systems that maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste generation throughout the entire product lifecycle.
In conclusion, the evolution of carbonyl processes towards sustainable growth represents a critical area of research and development in the chemical industry. By addressing the challenges of environmental impact, resource depletion, and economic viability, these advancements pave the way for a more sustainable future in chemical manufacturing.
Market Demand for Sustainable Carbonyl Products
The market demand for sustainable carbonyl products has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and stricter regulations on industrial processes. Carbonyl compounds, which include aldehydes and ketones, are essential building blocks in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The shift towards sustainable practices has created a significant opportunity for eco-friendly carbonyl production methods.
Consumer awareness and preference for environmentally responsible products have been key factors in driving this demand. Many end-users are now actively seeking products manufactured using sustainable processes, creating a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. This trend is particularly evident in the personal care and cosmetics industry, where natural and sustainably sourced ingredients are highly valued.
In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles, which has led to increased demand for sustainably produced carbonyl compounds. These compounds are crucial intermediates in the synthesis of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The industry's focus on reducing environmental impact while maintaining product quality has created a substantial market for sustainable carbonyl processes.
The agrochemical industry is another significant driver of demand for sustainable carbonyl products. With increasing pressure to develop more environmentally friendly crop protection solutions, manufacturers are turning to greener synthesis methods for key intermediates, including carbonyl compounds. This shift is not only driven by regulatory requirements but also by the agricultural sector's own sustainability goals.
In the materials science and polymer industry, there is a rising interest in bio-based and biodegradable materials. Sustainable carbonyl compounds play a crucial role in the development of these materials, particularly in the production of biodegradable plastics and environmentally friendly coatings. This trend is expected to continue as more companies commit to reducing their carbon footprint and improving their overall sustainability profile.
The automotive and construction industries are also contributing to the demand for sustainable carbonyl products. As these sectors seek to reduce their environmental impact, they are increasingly looking for materials produced through greener processes. This includes adhesives, sealants, and coatings that incorporate sustainably produced carbonyl compounds.
Market analysts project that the global demand for sustainable carbonyl products will continue to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6-8% over the next five years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe and North America, as well as in rapidly developing economies that are prioritizing sustainable industrial development.
Consumer awareness and preference for environmentally responsible products have been key factors in driving this demand. Many end-users are now actively seeking products manufactured using sustainable processes, creating a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. This trend is particularly evident in the personal care and cosmetics industry, where natural and sustainably sourced ingredients are highly valued.
In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing emphasis on green chemistry principles, which has led to increased demand for sustainably produced carbonyl compounds. These compounds are crucial intermediates in the synthesis of many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The industry's focus on reducing environmental impact while maintaining product quality has created a substantial market for sustainable carbonyl processes.
The agrochemical industry is another significant driver of demand for sustainable carbonyl products. With increasing pressure to develop more environmentally friendly crop protection solutions, manufacturers are turning to greener synthesis methods for key intermediates, including carbonyl compounds. This shift is not only driven by regulatory requirements but also by the agricultural sector's own sustainability goals.
In the materials science and polymer industry, there is a rising interest in bio-based and biodegradable materials. Sustainable carbonyl compounds play a crucial role in the development of these materials, particularly in the production of biodegradable plastics and environmentally friendly coatings. This trend is expected to continue as more companies commit to reducing their carbon footprint and improving their overall sustainability profile.
The automotive and construction industries are also contributing to the demand for sustainable carbonyl products. As these sectors seek to reduce their environmental impact, they are increasingly looking for materials produced through greener processes. This includes adhesives, sealants, and coatings that incorporate sustainably produced carbonyl compounds.
Market analysts project that the global demand for sustainable carbonyl products will continue to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6-8% over the next five years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with stringent environmental regulations, such as Europe and North America, as well as in rapidly developing economies that are prioritizing sustainable industrial development.
Carbonyl Technology: Current State and Challenges
Carbonyl technology has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, yet it still faces numerous challenges in its quest for sustainable growth. The current state of carbonyl processes is characterized by a mix of traditional methods and innovative approaches, each with its own set of advantages and limitations.
One of the primary challenges in carbonyl technology is the optimization of reaction conditions to improve yield and selectivity. Many carbonyl processes still rely on harsh reaction environments, including high temperatures and pressures, which contribute to increased energy consumption and potential safety hazards. Researchers are actively exploring milder reaction conditions and catalytic systems to address these issues, but progress has been incremental.
Another significant challenge is the reliance on fossil fuel-derived feedstocks. The majority of carbonyl compounds are currently produced from petroleum-based starting materials, which raises sustainability concerns. The transition to bio-based or renewable feedstocks is a critical area of focus, but it requires overcoming hurdles related to cost-effectiveness, scalability, and product quality consistency.
The development of more efficient and selective catalysts remains a key challenge in carbonyl technology. While homogeneous catalysts often provide high selectivity, their separation and recycling pose difficulties in industrial applications. Heterogeneous catalysts offer easier separation but often suffer from lower activity and selectivity. Bridging this gap and designing catalysts that combine the best of both worlds is an ongoing research priority.
Environmental concerns also play a significant role in shaping the current state of carbonyl technology. The generation of waste products, particularly in the form of solvents and byproducts, necessitates the development of greener processes. Efforts are underway to implement solvent-free reactions, utilize green solvents, and design atom-economical processes that minimize waste generation.
The integration of continuous flow processes in carbonyl chemistry presents both opportunities and challenges. While continuous flow reactors offer benefits such as improved heat and mass transfer, precise control over reaction parameters, and potential for process intensification, their widespread adoption in the carbonyl industry is still limited. Overcoming scale-up issues and retrofitting existing batch processes are ongoing challenges in this area.
Lastly, the application of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in carbonyl process development and optimization is gaining traction. These tools hold promise for accelerating reaction discovery, predicting optimal reaction conditions, and designing more efficient catalysts. However, the effective integration of these technologies into existing research and development frameworks remains a challenge that requires interdisciplinary collaboration and expertise.
One of the primary challenges in carbonyl technology is the optimization of reaction conditions to improve yield and selectivity. Many carbonyl processes still rely on harsh reaction environments, including high temperatures and pressures, which contribute to increased energy consumption and potential safety hazards. Researchers are actively exploring milder reaction conditions and catalytic systems to address these issues, but progress has been incremental.
Another significant challenge is the reliance on fossil fuel-derived feedstocks. The majority of carbonyl compounds are currently produced from petroleum-based starting materials, which raises sustainability concerns. The transition to bio-based or renewable feedstocks is a critical area of focus, but it requires overcoming hurdles related to cost-effectiveness, scalability, and product quality consistency.
The development of more efficient and selective catalysts remains a key challenge in carbonyl technology. While homogeneous catalysts often provide high selectivity, their separation and recycling pose difficulties in industrial applications. Heterogeneous catalysts offer easier separation but often suffer from lower activity and selectivity. Bridging this gap and designing catalysts that combine the best of both worlds is an ongoing research priority.
Environmental concerns also play a significant role in shaping the current state of carbonyl technology. The generation of waste products, particularly in the form of solvents and byproducts, necessitates the development of greener processes. Efforts are underway to implement solvent-free reactions, utilize green solvents, and design atom-economical processes that minimize waste generation.
The integration of continuous flow processes in carbonyl chemistry presents both opportunities and challenges. While continuous flow reactors offer benefits such as improved heat and mass transfer, precise control over reaction parameters, and potential for process intensification, their widespread adoption in the carbonyl industry is still limited. Overcoming scale-up issues and retrofitting existing batch processes are ongoing challenges in this area.
Lastly, the application of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in carbonyl process development and optimization is gaining traction. These tools hold promise for accelerating reaction discovery, predicting optimal reaction conditions, and designing more efficient catalysts. However, the effective integration of these technologies into existing research and development frameworks remains a challenge that requires interdisciplinary collaboration and expertise.
Current Sustainable Carbonyl Process Solutions
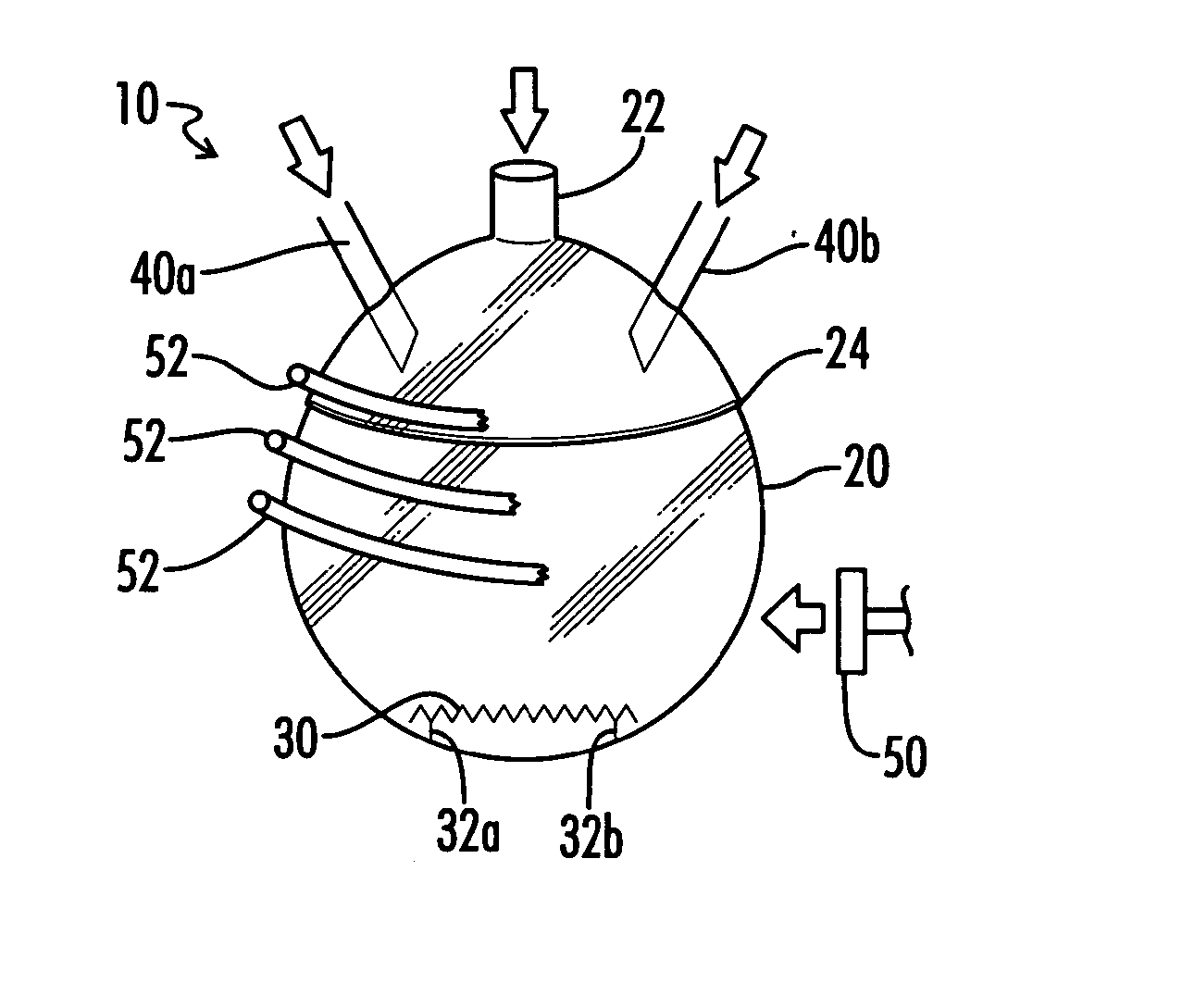
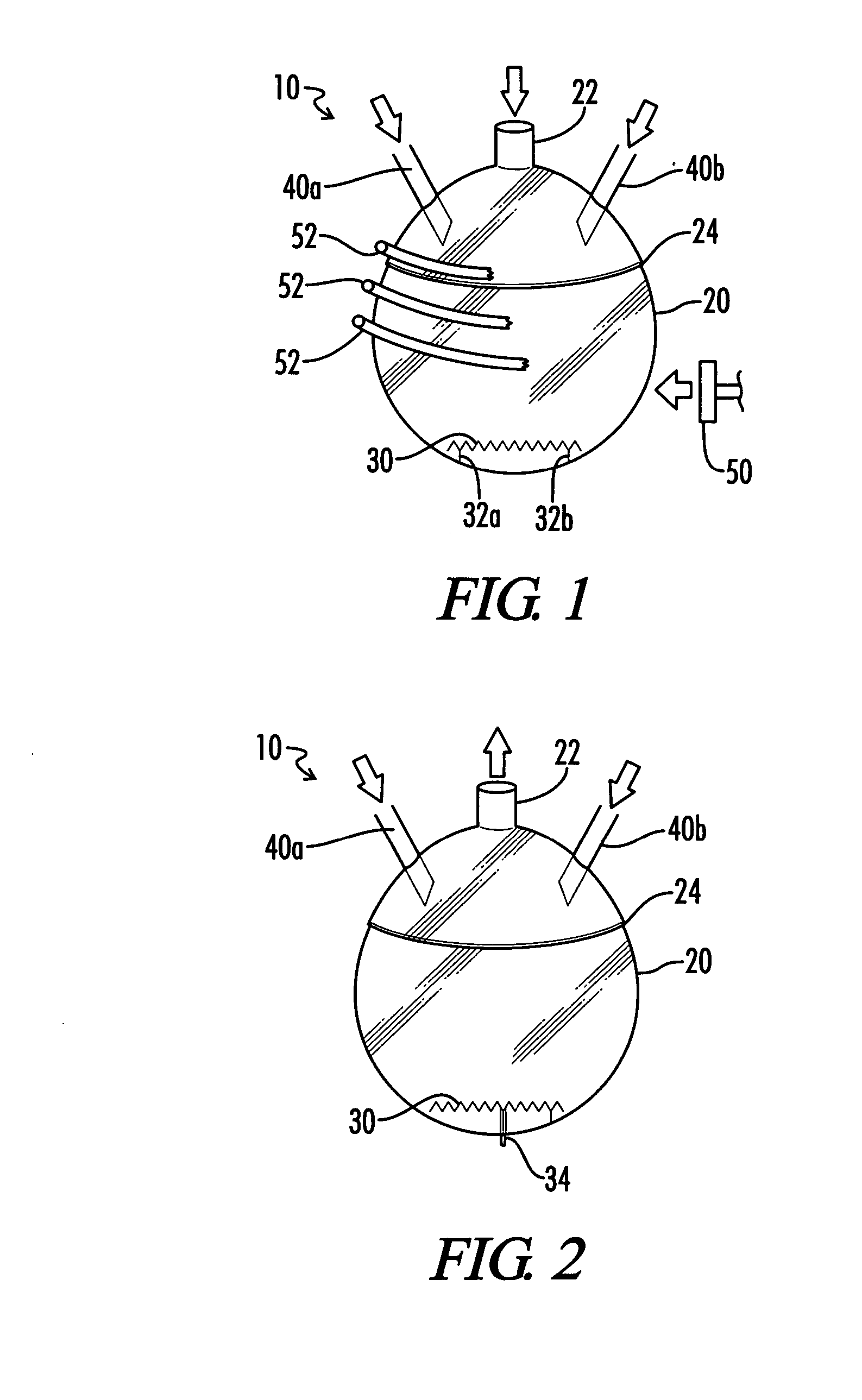
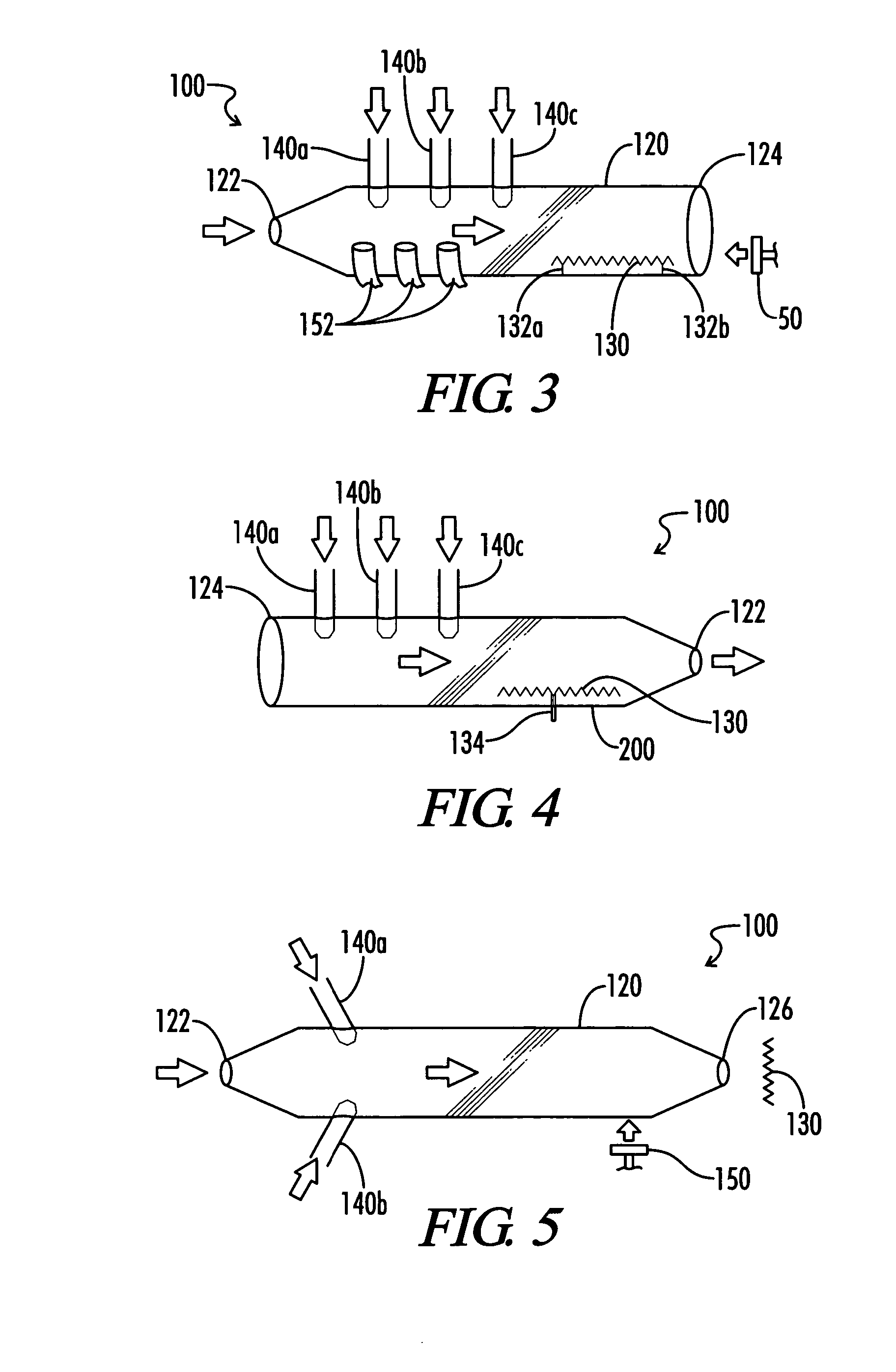
01 Carbonylation of organic compounds
Carbonylation processes involve the introduction of carbon monoxide into organic compounds to form carbonyl groups. These reactions are widely used in the production of various chemicals, including aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. The process often requires specific catalysts and reaction conditions to achieve high yields and selectivity.- Hydroformylation processes: Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis, is a key carbonyl process used to produce aldehydes from alkenes. This process typically involves the reaction of an olefin with carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst, often a rhodium or cobalt complex. The resulting aldehydes can be further processed into various valuable chemicals and materials.
- Carbonylation of methanol: The carbonylation of methanol is an important industrial process for producing acetic acid. This process involves the reaction of methanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst, typically a rhodium or iridium complex. The reaction conditions and catalyst systems have been optimized over the years to improve yield, selectivity, and efficiency.
- Synthesis of aromatic aldehydes: Various carbonyl processes have been developed for the synthesis of aromatic aldehydes. These processes often involve the reaction of aromatic compounds with carbon monoxide and other reagents in the presence of catalysts. The resulting aromatic aldehydes are important intermediates in the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other fine chemicals.
- Carbonylation of olefins: The carbonylation of olefins is a versatile process for introducing carbonyl groups into organic molecules. This process can be used to produce a wide range of carbonyl compounds, including aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. Various catalysts and reaction conditions have been developed to control the selectivity and yield of these reactions.
- Catalytic systems for carbonyl processes: The development of novel catalytic systems is crucial for improving the efficiency and selectivity of carbonyl processes. Research in this area focuses on designing new ligands, exploring different metal centers, and optimizing reaction conditions. These advancements aim to enhance the performance of existing carbonyl processes and enable new transformations.
02 Synthesis of aldehydes and ketones
Carbonyl processes are employed in the synthesis of aldehydes and ketones from various starting materials. These reactions may involve the oxidation of alcohols, hydroformylation of alkenes, or the reduction of carboxylic acids and their derivatives. The choice of catalyst and reaction conditions plays a crucial role in determining the product distribution and yield.Expand Specific Solutions03 Production of carboxylic acids
Carbonyl processes are utilized in the production of carboxylic acids through various routes, such as the oxidation of aldehydes or the carbonylation of alcohols. These reactions often require specific catalysts, oxidizing agents, or high-pressure conditions to achieve efficient conversion. The development of selective and environmentally friendly processes is an ongoing area of research.Expand Specific Solutions04 Catalytic systems for carbonyl processes
The development of efficient catalytic systems is crucial for carbonyl processes. Various transition metal complexes, such as those based on rhodium, palladium, or cobalt, are employed as catalysts. Research focuses on improving catalyst activity, selectivity, and stability, as well as developing heterogeneous catalysts for easier separation and recycling.Expand Specific Solutions05 Green chemistry approaches in carbonyl processes
There is a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly carbonyl processes. This includes the use of renewable feedstocks, the development of solvent-free or aqueous reaction systems, and the application of continuous flow processes. These approaches aim to reduce waste generation, improve energy efficiency, and minimize the environmental impact of carbonyl chemistry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Carbonyl Industry
The implementation of carbonyl processes for sustainable growth is currently in a transitional phase, with the market showing significant potential for expansion. The global market size for carbonyl-based sustainable technologies is projected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Technologically, the field is rapidly evolving, with companies like BASF Corp., Umicore SA, and Wacker Chemie AG leading the way in research and development. These firms are investing heavily in innovative carbonyl processes that promise improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact. However, the technology is not yet fully mature, with challenges remaining in scalability and cost-effectiveness. Emerging players such as Novomer, Inc. are also making strides in developing novel carbonyl-based materials, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed an innovative carbonyl process for sustainable growth, focusing on the production of oxo-alcohols. Their approach utilizes syngas (CO and H2) in a hydroformylation reaction to convert olefins into aldehydes, which are then hydrogenated to alcohols[1]. This process is highly efficient, with a reported atom economy of over 99%[2]. BASF has also implemented a closed-loop system that recycles unreacted syngas, significantly reducing waste and improving overall sustainability[3]. Additionally, they have invested in catalytic technologies that operate at lower temperatures and pressures, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional methods[4].
Strengths: High atom economy, efficient use of resources, reduced energy consumption. Weaknesses: Dependence on fossil-based feedstocks for syngas production, potential for catalyst deactivation in long-term operations.
Celanese International Corp.
Technical Solution: Celanese has pioneered a carbonyl process for sustainable acetic acid production, leveraging their proprietary AO Plus technology. This process utilizes methanol carbonylation with a rhodium-based catalyst, achieving conversion rates of over 99%[5]. The company has further enhanced sustainability by implementing a methanol recycling system, reducing raw material consumption by up to 20%[6]. Celanese has also developed a novel purification technique that reduces energy usage in the separation process by approximately 15%[7]. Their integrated approach includes the use of cogeneration plants to maximize energy efficiency, resulting in a 25% reduction in overall carbon footprint compared to conventional acetic acid production methods[8].
Strengths: High conversion rates, efficient methanol recycling, reduced energy consumption in purification. Weaknesses: Reliance on precious metal catalysts, potential for catalyst poisoning by impurities in the feedstock.
Innovative Carbonyl Process Patents and Literature
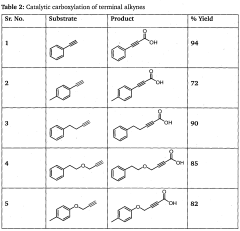
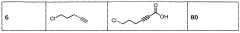
A process for preparation of alkynyl carboxylic acids
PatentWO2013110998A1
Innovation
- A single-step heterogeneous catalytic process using metal-exchanged montmorillonite K-10 clay catalysts, specifically copper-exchanged montmorillonite K-10, in the presence of a base and solvent at mild conditions (50-60°C and 1 atm) for the carboxylation of terminal alkynes to produce alkynyl carboxylic acids with high yield and selectivity.
Continuous process for the use of metal carbonyls for the production of nano-scale metal particles formed of non-noble metals
PatentInactiveUS20070283784A1
Innovation
- A continuous process using metal carbonyls to produce non-noble metal nano-scale particles by decomposing them in a reactor vessel with controlled energy sources, allowing for deposition on a support or collection without the need for extreme conditions, utilizing a reactor system that can operate at atmospheric pressure and moderate temperatures.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The implementation of carbonyl processes for sustainable growth necessitates a comprehensive environmental impact assessment to ensure responsible and eco-friendly industrial practices. This assessment begins with an evaluation of the carbon footprint associated with carbonyl processes, considering both direct emissions from production facilities and indirect emissions from energy consumption and transportation.
A key focus of the environmental impact assessment is the analysis of potential air pollution resulting from carbonyl processes. This includes the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous air pollutants that may contribute to smog formation and pose health risks to nearby communities. The assessment also examines the potential for water pollution, particularly the discharge of process wastewater containing organic compounds and heavy metals.
Waste management is another critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment for carbonyl processes. This involves evaluating the generation, handling, and disposal of solid and liquid waste products, including spent catalysts, byproducts, and contaminated materials. The assessment considers the potential for soil contamination and the long-term effects on local ecosystems.
Energy consumption and resource efficiency are also scrutinized in the environmental impact assessment. This includes an analysis of the energy intensity of carbonyl processes and the potential for implementing energy-saving technologies and renewable energy sources. The assessment also examines the use of raw materials and explores opportunities for circular economy practices, such as recycling and reuse of byproducts.
The environmental impact assessment extends to the broader ecological consequences of carbonyl processes. This involves evaluating the potential effects on local biodiversity, including impacts on flora and fauna in surrounding habitats. The assessment also considers the cumulative environmental impacts of multiple industrial facilities in the region, taking into account potential synergistic effects and long-term ecological changes.
Climate change implications are a crucial component of the environmental impact assessment for carbonyl processes. This includes an analysis of greenhouse gas emissions and their contribution to global warming. The assessment explores strategies for reducing carbon emissions through process optimization, carbon capture technologies, and the use of alternative, low-carbon feedstocks.
Finally, the environmental impact assessment addresses the potential for accidental releases and environmental emergencies associated with carbonyl processes. This involves evaluating the risks of chemical spills, explosions, and other industrial accidents, as well as the preparedness and response measures in place to mitigate environmental damage in such events.
A key focus of the environmental impact assessment is the analysis of potential air pollution resulting from carbonyl processes. This includes the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous air pollutants that may contribute to smog formation and pose health risks to nearby communities. The assessment also examines the potential for water pollution, particularly the discharge of process wastewater containing organic compounds and heavy metals.
Waste management is another critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment for carbonyl processes. This involves evaluating the generation, handling, and disposal of solid and liquid waste products, including spent catalysts, byproducts, and contaminated materials. The assessment considers the potential for soil contamination and the long-term effects on local ecosystems.
Energy consumption and resource efficiency are also scrutinized in the environmental impact assessment. This includes an analysis of the energy intensity of carbonyl processes and the potential for implementing energy-saving technologies and renewable energy sources. The assessment also examines the use of raw materials and explores opportunities for circular economy practices, such as recycling and reuse of byproducts.
The environmental impact assessment extends to the broader ecological consequences of carbonyl processes. This involves evaluating the potential effects on local biodiversity, including impacts on flora and fauna in surrounding habitats. The assessment also considers the cumulative environmental impacts of multiple industrial facilities in the region, taking into account potential synergistic effects and long-term ecological changes.
Climate change implications are a crucial component of the environmental impact assessment for carbonyl processes. This includes an analysis of greenhouse gas emissions and their contribution to global warming. The assessment explores strategies for reducing carbon emissions through process optimization, carbon capture technologies, and the use of alternative, low-carbon feedstocks.
Finally, the environmental impact assessment addresses the potential for accidental releases and environmental emergencies associated with carbonyl processes. This involves evaluating the risks of chemical spills, explosions, and other industrial accidents, as well as the preparedness and response measures in place to mitigate environmental damage in such events.
Regulatory Framework for Carbonyl Processes
The regulatory framework for carbonyl processes plays a crucial role in ensuring sustainable growth and environmental protection. Governments worldwide have implemented stringent regulations to control emissions, waste management, and safety standards associated with these processes. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established comprehensive guidelines under the Clean Air Act, specifically targeting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) often produced in carbonyl processes.
In the European Union, the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) sets strict limits on emissions from industrial activities, including those involving carbonyl compounds. This directive emphasizes the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) to minimize environmental impact. Additionally, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with substances used in carbonyl processes.
Many countries have adopted similar regulatory frameworks, often tailored to their specific industrial landscapes. For instance, China's Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law includes provisions for controlling emissions from chemical processes, including those involving carbonyls. Japan's Air Pollution Control Act also addresses these concerns, with a focus on reducing volatile organic compound emissions.
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement and the Montreal Protocol, indirectly influence carbonyl process regulations by setting broader environmental goals. These agreements drive the development of more sustainable practices and technologies in industrial processes, including those involving carbonyl compounds.
Regulatory bodies often require companies to implement robust monitoring and reporting systems to ensure compliance. This includes regular emissions testing, waste management audits, and detailed record-keeping of chemical usage and disposal. Many jurisdictions also mandate the use of specific control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers or scrubbers, to reduce emissions from carbonyl processes.
Worker safety regulations form another critical component of the regulatory framework. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries set exposure limits for carbonyl compounds and require appropriate personal protective equipment and safety protocols in workplaces handling these substances.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to encourage the development and adoption of greener carbonyl processes. This includes incentives for using renewable feedstocks, implementing closed-loop systems, and improving energy efficiency. Some jurisdictions are also exploring the concept of extended producer responsibility, holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including those derived from carbonyl processes.
In the European Union, the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) sets strict limits on emissions from industrial activities, including those involving carbonyl compounds. This directive emphasizes the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) to minimize environmental impact. Additionally, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with substances used in carbonyl processes.
Many countries have adopted similar regulatory frameworks, often tailored to their specific industrial landscapes. For instance, China's Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law includes provisions for controlling emissions from chemical processes, including those involving carbonyls. Japan's Air Pollution Control Act also addresses these concerns, with a focus on reducing volatile organic compound emissions.
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement and the Montreal Protocol, indirectly influence carbonyl process regulations by setting broader environmental goals. These agreements drive the development of more sustainable practices and technologies in industrial processes, including those involving carbonyl compounds.
Regulatory bodies often require companies to implement robust monitoring and reporting systems to ensure compliance. This includes regular emissions testing, waste management audits, and detailed record-keeping of chemical usage and disposal. Many jurisdictions also mandate the use of specific control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers or scrubbers, to reduce emissions from carbonyl processes.
Worker safety regulations form another critical component of the regulatory framework. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries set exposure limits for carbonyl compounds and require appropriate personal protective equipment and safety protocols in workplaces handling these substances.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations are evolving to encourage the development and adoption of greener carbonyl processes. This includes incentives for using renewable feedstocks, implementing closed-loop systems, and improving energy efficiency. Some jurisdictions are also exploring the concept of extended producer responsibility, holding manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including those derived from carbonyl processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!