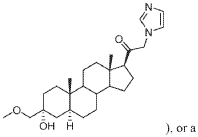
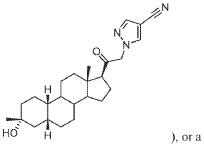
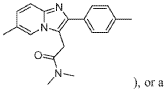
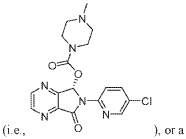
Muscimol Tolerance and Withdrawal: A Scientific Overview
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Muscimol Background and Research Objectives
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has been a subject of scientific interest for decades due to its unique pharmacological properties and potential therapeutic applications. Derived from the Amanita muscaria mushroom, this compound has played a significant role in both traditional practices and modern neuroscience research. The historical context of muscimol usage dates back centuries, with various cultures utilizing the mushroom for its psychoactive effects. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that scientists isolated and identified muscimol as the primary active compound responsible for these effects.
The evolution of muscimol research has been marked by significant milestones in our understanding of GABAergic neurotransmission. Initial studies focused on elucidating its mechanism of action, revealing its high affinity for GABA-A receptors and its potent inhibitory effects on neuronal activity. This discovery opened new avenues for investigating the role of GABAergic systems in various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards exploring muscimol's potential therapeutic applications. Studies have investigated its anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and sedative properties, highlighting its potential as a novel treatment for various neurological conditions. However, the development of tolerance and withdrawal symptoms associated with prolonged muscimol use has emerged as a critical area of concern, necessitating further investigation.
The current research objectives in muscimol studies are multifaceted, aiming to address several key aspects of its pharmacology and clinical potential. One primary goal is to elucidate the mechanisms underlying tolerance development to muscimol's effects. This involves investigating adaptive changes in GABA receptor expression, function, and signaling pathways that occur with chronic exposure. Understanding these processes is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate tolerance and maintain therapeutic efficacy over extended periods.
Another significant research objective is to characterize the withdrawal syndrome associated with muscimol discontinuation. This includes identifying the neurobiological substrates of withdrawal symptoms, their time course, and potential interventions to alleviate these effects. Such knowledge is essential for assessing the safety profile of muscimol-based therapies and developing appropriate protocols for their clinical use.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods to optimize muscimol's therapeutic potential while minimizing adverse effects. This includes investigating targeted delivery systems, controlled-release formulations, and combination therapies that may enhance efficacy and reduce the risk of tolerance and withdrawal.
In conclusion, the background and research objectives surrounding muscimol tolerance and withdrawal reflect a complex interplay of historical usage, scientific discovery, and ongoing clinical challenges. As we continue to unravel the intricacies of muscimol's effects on the brain, these research efforts hold promise for advancing our understanding of GABAergic neurotransmission and developing innovative therapeutic approaches for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The evolution of muscimol research has been marked by significant milestones in our understanding of GABAergic neurotransmission. Initial studies focused on elucidating its mechanism of action, revealing its high affinity for GABA-A receptors and its potent inhibitory effects on neuronal activity. This discovery opened new avenues for investigating the role of GABAergic systems in various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards exploring muscimol's potential therapeutic applications. Studies have investigated its anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and sedative properties, highlighting its potential as a novel treatment for various neurological conditions. However, the development of tolerance and withdrawal symptoms associated with prolonged muscimol use has emerged as a critical area of concern, necessitating further investigation.
The current research objectives in muscimol studies are multifaceted, aiming to address several key aspects of its pharmacology and clinical potential. One primary goal is to elucidate the mechanisms underlying tolerance development to muscimol's effects. This involves investigating adaptive changes in GABA receptor expression, function, and signaling pathways that occur with chronic exposure. Understanding these processes is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate tolerance and maintain therapeutic efficacy over extended periods.
Another significant research objective is to characterize the withdrawal syndrome associated with muscimol discontinuation. This includes identifying the neurobiological substrates of withdrawal symptoms, their time course, and potential interventions to alleviate these effects. Such knowledge is essential for assessing the safety profile of muscimol-based therapies and developing appropriate protocols for their clinical use.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods to optimize muscimol's therapeutic potential while minimizing adverse effects. This includes investigating targeted delivery systems, controlled-release formulations, and combination therapies that may enhance efficacy and reduce the risk of tolerance and withdrawal.
In conclusion, the background and research objectives surrounding muscimol tolerance and withdrawal reflect a complex interplay of historical usage, scientific discovery, and ongoing clinical challenges. As we continue to unravel the intricacies of muscimol's effects on the brain, these research efforts hold promise for advancing our understanding of GABAergic neurotransmission and developing innovative therapeutic approaches for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Market Analysis of GABAergic Compounds
The market for GABAergic compounds, particularly those related to muscimol and its effects, has shown significant growth and potential in recent years. This segment of the pharmaceutical industry is driven by the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, anxiety, and sleep-related issues. The global GABAergic drugs market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period.
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic applications. While not widely used clinically due to its psychoactive properties, research into muscimol and related compounds has spurred interest in developing novel GABAergic drugs with improved safety profiles and reduced tolerance and withdrawal effects.
The market for GABAergic compounds is segmented based on drug class, including benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and others. Benzodiazepines currently dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of the total share. However, concerns over tolerance and withdrawal associated with long-term benzodiazepine use have created opportunities for new GABAergic compounds with improved pharmacological profiles.
Geographically, North America leads the GABAergic compounds market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds the largest market share due to high healthcare expenditure and a large patient population suffering from anxiety disorders and insomnia. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues and improving healthcare infrastructure.
Key players in the GABAergic compounds market include Pfizer, Novartis, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Merck & Co. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create novel GABAergic drugs with reduced tolerance and withdrawal effects. Additionally, several biotechnology startups are focusing on developing innovative GABAergic compounds, potentially disrupting the market landscape.
The growing interest in personalized medicine and the development of targeted therapies are expected to create new opportunities in the GABAergic compounds market. Research into the mechanisms of muscimol tolerance and withdrawal is likely to inform the development of next-generation GABAergic drugs with improved efficacy and safety profiles, potentially expanding the market further in the coming years.
Muscimol, a potent GABA receptor agonist, has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic applications. While not widely used clinically due to its psychoactive properties, research into muscimol and related compounds has spurred interest in developing novel GABAergic drugs with improved safety profiles and reduced tolerance and withdrawal effects.
The market for GABAergic compounds is segmented based on drug class, including benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and others. Benzodiazepines currently dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of the total share. However, concerns over tolerance and withdrawal associated with long-term benzodiazepine use have created opportunities for new GABAergic compounds with improved pharmacological profiles.
Geographically, North America leads the GABAergic compounds market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds the largest market share due to high healthcare expenditure and a large patient population suffering from anxiety disorders and insomnia. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing awareness of mental health issues and improving healthcare infrastructure.
Key players in the GABAergic compounds market include Pfizer, Novartis, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and Merck & Co. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to create novel GABAergic drugs with reduced tolerance and withdrawal effects. Additionally, several biotechnology startups are focusing on developing innovative GABAergic compounds, potentially disrupting the market landscape.
The growing interest in personalized medicine and the development of targeted therapies are expected to create new opportunities in the GABAergic compounds market. Research into the mechanisms of muscimol tolerance and withdrawal is likely to inform the development of next-generation GABAergic drugs with improved efficacy and safety profiles, potentially expanding the market further in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Muscimol Research
Despite significant advancements in muscimol research, several challenges persist in fully understanding its tolerance and withdrawal effects. One of the primary obstacles is the limited availability of long-term human studies, which hinders our ability to comprehensively assess the chronic effects of muscimol use. Animal models, while valuable, may not fully replicate human physiological responses, creating a gap in translational research.
Another challenge lies in the complex pharmacodynamics of muscimol. Its interaction with GABA-A receptors is well-established, but the precise mechanisms underlying tolerance development and withdrawal symptoms remain incompletely understood. This complexity is further compounded by individual variations in receptor sensitivity and metabolism, making it difficult to predict patient responses accurately.
The lack of standardized protocols for muscimol administration and withdrawal management presents an additional hurdle. Dosage regimens, duration of use, and tapering strategies vary widely across studies, complicating the comparison and integration of research findings. This inconsistency hampers the development of evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice.
Ethical considerations also pose challenges in muscimol research. The potential for dependence and adverse effects limits the scope of human trials, particularly those investigating long-term use or high-dose regimens. This ethical constraint necessitates a heavy reliance on preclinical studies and retrospective analyses, which may not capture the full spectrum of human responses.
Furthermore, the molecular basis of muscimol tolerance remains elusive. While receptor downregulation and desensitization are implicated, the exact cellular adaptations and signaling pathways involved are not fully elucidated. This gap in knowledge impedes the development of targeted interventions to mitigate tolerance and withdrawal effects.
The heterogeneity of withdrawal symptoms presents another challenge. The manifestation and severity of withdrawal can vary significantly among individuals, making it difficult to establish a standardized approach to management. This variability also complicates the assessment of potential pharmacological interventions for withdrawal symptoms.
Lastly, the interaction of muscimol with other substances, particularly in polydrug use scenarios, remains understudied. The potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects with commonly co-administered drugs adds another layer of complexity to research efforts and clinical management strategies.
Another challenge lies in the complex pharmacodynamics of muscimol. Its interaction with GABA-A receptors is well-established, but the precise mechanisms underlying tolerance development and withdrawal symptoms remain incompletely understood. This complexity is further compounded by individual variations in receptor sensitivity and metabolism, making it difficult to predict patient responses accurately.
The lack of standardized protocols for muscimol administration and withdrawal management presents an additional hurdle. Dosage regimens, duration of use, and tapering strategies vary widely across studies, complicating the comparison and integration of research findings. This inconsistency hampers the development of evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice.
Ethical considerations also pose challenges in muscimol research. The potential for dependence and adverse effects limits the scope of human trials, particularly those investigating long-term use or high-dose regimens. This ethical constraint necessitates a heavy reliance on preclinical studies and retrospective analyses, which may not capture the full spectrum of human responses.
Furthermore, the molecular basis of muscimol tolerance remains elusive. While receptor downregulation and desensitization are implicated, the exact cellular adaptations and signaling pathways involved are not fully elucidated. This gap in knowledge impedes the development of targeted interventions to mitigate tolerance and withdrawal effects.
The heterogeneity of withdrawal symptoms presents another challenge. The manifestation and severity of withdrawal can vary significantly among individuals, making it difficult to establish a standardized approach to management. This variability also complicates the assessment of potential pharmacological interventions for withdrawal symptoms.
Lastly, the interaction of muscimol with other substances, particularly in polydrug use scenarios, remains understudied. The potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects with commonly co-administered drugs adds another layer of complexity to research efforts and clinical management strategies.
Existing Approaches to Muscimol Tolerance Management
01 Muscimol tolerance mechanisms
Research into the mechanisms of muscimol tolerance, focusing on GABA receptor adaptations and neuroplasticity. Studies explore how repeated exposure to muscimol affects receptor sensitivity and neurotransmitter systems, potentially leading to tolerance development.- Muscimol tolerance mechanisms: Research into the mechanisms of muscimol tolerance, focusing on GABA receptor adaptations and neuroplasticity. Studies explore how repeated exposure to muscimol affects receptor sensitivity and neurotransmitter systems, potentially leading to tolerance development.
- Withdrawal symptoms and management: Investigation of muscimol withdrawal symptoms and potential management strategies. This includes studying the physiological and psychological effects of discontinuing muscimol use, as well as developing interventions to mitigate withdrawal symptoms.
- Pharmacological interventions for muscimol dependence: Development of pharmacological treatments to address muscimol dependence and withdrawal. This involves researching potential medications that can help reduce cravings, alleviate withdrawal symptoms, or restore normal brain function after prolonged muscimol use.
- Neuroimaging studies on muscimol effects: Utilization of neuroimaging techniques to study the effects of muscimol on brain structure and function. These studies aim to understand how muscimol impacts various brain regions and neural circuits, potentially shedding light on tolerance and withdrawal mechanisms.
- Behavioral therapies for muscimol addiction: Exploration of behavioral interventions and therapies to address muscimol addiction and support recovery. This includes developing and evaluating cognitive-behavioral approaches, motivational enhancement techniques, and other psychosocial interventions tailored for muscimol dependence.
02 Withdrawal management strategies
Development of strategies to manage muscimol withdrawal symptoms, including pharmacological interventions and supportive therapies. Approaches may involve tapering protocols, use of alternative GABA modulators, and addressing associated psychological symptoms.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biomarkers for tolerance and withdrawal
Identification and validation of biomarkers to assess muscimol tolerance and predict withdrawal severity. This may include neuroimaging techniques, genetic markers, or biochemical indicators that reflect changes in GABA system function.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel compounds to address tolerance
Development of new chemical entities or modified muscimol analogs designed to reduce tolerance development or mitigate withdrawal effects. These compounds may target specific GABA receptor subtypes or have improved pharmacokinetic profiles.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination therapies for withdrawal
Investigation of combination therapies that address multiple aspects of muscimol withdrawal. This may include combining GABA modulators with other classes of drugs, such as antidepressants or anxiolytics, to comprehensively manage withdrawal symptoms.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in GABAergic Drug Development
The research on muscimol tolerance and withdrawal is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions. Key players like Genentech, Roche, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals are leveraging their expertise in drug development to explore muscimol's potential. Universities such as Michigan and North Carolina at Chapel Hill are contributing valuable research. The technology is not yet fully mature, with ongoing studies focusing on understanding the mechanisms of tolerance and withdrawal. As the field progresses, collaborations between industry and academia are likely to drive innovation and market growth.
Theravance Biopharma R&D IP LLC
Technical Solution: Theravance Biopharma has been investigating novel approaches to modulating GABA-A receptors, including research on muscimol and related compounds. Their strategy involves developing allosteric modulators that can fine-tune receptor activity without causing significant receptor desensitization or downregulation [6]. This approach aims to minimize the development of tolerance and reduce withdrawal symptoms associated with chronic use. Theravance is also exploring the potential of combining muscimol-like compounds with other neuromodulators to create multi-modal therapies that could address complex neurological disorders while mitigating the risk of dependence [7].
Strengths: Innovative approach to receptor modulation; focus on reducing tolerance and withdrawal. Weaknesses: Early-stage research with limited clinical validation.
Psyched Wellness Ltd.
Technical Solution: Psyched Wellness Ltd. has developed a proprietary extraction and purification process for muscimol from Amanita muscaria mushrooms. Their approach focuses on creating a standardized, safe, and legal muscimol extract for potential therapeutic applications. The company has conducted preclinical studies to evaluate muscimol's effects on sleep, stress, and anxiety [1]. They are exploring the development of muscimol-based products for various wellness applications, including sleep aids and stress relief supplements. Psyched Wellness is also investigating the potential for muscimol in treating alcohol use disorder, leveraging its GABA-A receptor modulation properties [2].
Strengths: Specialized focus on muscimol research and product development; proprietary extraction process. Weaknesses: Limited clinical data on long-term effects and potential for tolerance or withdrawal.
Breakthrough Studies on Muscimol Withdrawal
Processes for extracting muscimol from amanita muscaria
PatentWO2022187974A1
Innovation
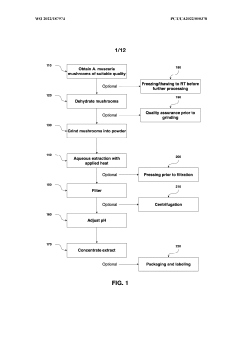
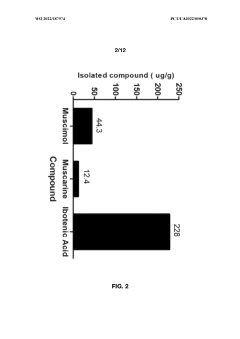
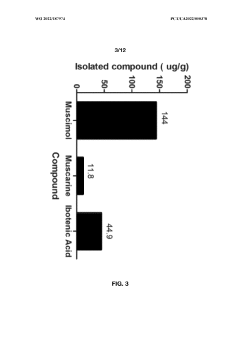
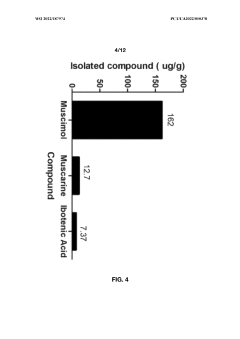
- Aqueous extraction methods involving heat, pH reduction, and concentration techniques such as distillation and refluxing are employed to decrease ibotenic acid content and increase muscimol content in the extract, including steps like grinding the mushroom biomass, filtering, and acidification to facilitate decarboxylation of ibotenic acid to muscimol.
Method for treating sleep fragmentation disorders using neurosteroid positive allosteric modulators of the GABA a receptor
PatentWO2020185710A1
Innovation
- The use of neurosteroid GABAA positive allosteric modulators, such as CCD-3693, Co-13-4444, ganaxolone, pregnanolone, Sage-217, and brexanolone, or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, administered to alleviate symptoms, treat, or prevent sleep disorders by enhancing sleep consolidation and reducing arousals.
Regulatory Framework for GABAergic Substances
The regulatory framework for GABAergic substances, including muscimol, is complex and multifaceted, involving various international and national agencies. At the global level, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) plays a crucial role in coordinating drug control policies and monitoring the implementation of international drug control conventions.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is responsible for enforcing controlled substance laws and regulations. Muscimol, as a GABAergic compound, falls under the purview of the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). While muscimol itself is not specifically scheduled, its parent compound, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, is subject to varying degrees of regulation across different states.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of GABAergic substances used as pharmaceutical products. This includes evaluating their safety, efficacy, and potential for abuse. The FDA's role extends to monitoring adverse effects and implementing risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) for certain GABAergic medications.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for the scientific evaluation, supervision, and safety monitoring of medicines, including those with GABAergic properties. The EMA works in conjunction with national regulatory authorities to ensure consistent standards across the European Union.
The World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines and recommendations on the use and control of psychoactive substances, including GABAergic compounds. Their Expert Committee on Drug Dependence (ECDD) regularly reviews substances for potential scheduling under international drug control conventions.
Research involving GABAergic substances is subject to strict ethical guidelines and regulatory oversight. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or Ethics Committees play a crucial role in approving and monitoring research protocols involving human subjects. These bodies ensure that studies adhere to principles of informed consent, minimization of risk, and protection of vulnerable populations.
The pharmaceutical industry must navigate this complex regulatory landscape when developing and marketing GABAergic drugs. This includes conducting extensive clinical trials, submitting comprehensive data packages to regulatory agencies, and implementing post-marketing surveillance programs to monitor long-term safety and efficacy.
As scientific understanding of GABAergic mechanisms evolves, regulatory frameworks continue to adapt. This includes ongoing discussions about the classification of novel GABAergic compounds, the potential therapeutic applications of substances like muscimol, and the need for balanced policies that facilitate research while mitigating risks of misuse or abuse.
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is responsible for enforcing controlled substance laws and regulations. Muscimol, as a GABAergic compound, falls under the purview of the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). While muscimol itself is not specifically scheduled, its parent compound, Amanita muscaria mushrooms, is subject to varying degrees of regulation across different states.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of GABAergic substances used as pharmaceutical products. This includes evaluating their safety, efficacy, and potential for abuse. The FDA's role extends to monitoring adverse effects and implementing risk evaluation and mitigation strategies (REMS) for certain GABAergic medications.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for the scientific evaluation, supervision, and safety monitoring of medicines, including those with GABAergic properties. The EMA works in conjunction with national regulatory authorities to ensure consistent standards across the European Union.
The World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines and recommendations on the use and control of psychoactive substances, including GABAergic compounds. Their Expert Committee on Drug Dependence (ECDD) regularly reviews substances for potential scheduling under international drug control conventions.
Research involving GABAergic substances is subject to strict ethical guidelines and regulatory oversight. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or Ethics Committees play a crucial role in approving and monitoring research protocols involving human subjects. These bodies ensure that studies adhere to principles of informed consent, minimization of risk, and protection of vulnerable populations.
The pharmaceutical industry must navigate this complex regulatory landscape when developing and marketing GABAergic drugs. This includes conducting extensive clinical trials, submitting comprehensive data packages to regulatory agencies, and implementing post-marketing surveillance programs to monitor long-term safety and efficacy.
As scientific understanding of GABAergic mechanisms evolves, regulatory frameworks continue to adapt. This includes ongoing discussions about the classification of novel GABAergic compounds, the potential therapeutic applications of substances like muscimol, and the need for balanced policies that facilitate research while mitigating risks of misuse or abuse.
Ethical Considerations in Muscimol Studies
The ethical considerations surrounding muscimol studies are multifaceted and require careful attention from researchers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare professionals. One primary concern is the potential for abuse and addiction, given muscimol's psychoactive properties. Researchers must implement stringent protocols to prevent misuse and ensure participant safety throughout clinical trials and experimental studies.
Another critical ethical issue is informed consent. Participants in muscimol studies must be fully aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with the compound. This includes possible short-term cognitive impairment, altered perception, and the risk of developing tolerance or experiencing withdrawal symptoms. Clear communication and comprehensive documentation are essential to maintain ethical standards in this regard.
The long-term effects of muscimol use remain largely unknown, raising ethical questions about the duration and intensity of human trials. Researchers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of prolonged exposure, particularly when studying tolerance and withdrawal. This necessitates robust monitoring systems and the establishment of clear endpoints for studies to minimize potential harm to participants.
Animal studies involving muscimol also present ethical challenges. While these studies are crucial for understanding the compound's effects and developing potential therapeutic applications, researchers must adhere to strict animal welfare guidelines. This includes minimizing animal suffering, using the minimum number of animals necessary for valid results, and exploring alternative research methods where possible.
The potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, particularly in treating neurological disorders, introduce additional ethical considerations. Balancing the urgency of developing new treatments with the need for thorough safety evaluations is crucial. Researchers and regulatory bodies must collaborate to establish clear guidelines for the progression from preclinical to clinical studies, ensuring that potential benefits to patients are not overshadowed by undue risks.
Confidentiality and data protection are also paramount in muscimol studies. Given the sensitive nature of information collected during trials, including personal medical histories and potential substance use, researchers must implement robust data security measures. This protects participants' privacy and maintains the integrity of the research process.
Lastly, there is an ethical imperative to publish all results from muscimol studies, including negative findings. This transparency is crucial for advancing scientific knowledge, preventing unnecessary duplication of studies, and ensuring that the full spectrum of muscimol's effects is understood by the scientific community and the public.
Another critical ethical issue is informed consent. Participants in muscimol studies must be fully aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with the compound. This includes possible short-term cognitive impairment, altered perception, and the risk of developing tolerance or experiencing withdrawal symptoms. Clear communication and comprehensive documentation are essential to maintain ethical standards in this regard.
The long-term effects of muscimol use remain largely unknown, raising ethical questions about the duration and intensity of human trials. Researchers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of prolonged exposure, particularly when studying tolerance and withdrawal. This necessitates robust monitoring systems and the establishment of clear endpoints for studies to minimize potential harm to participants.
Animal studies involving muscimol also present ethical challenges. While these studies are crucial for understanding the compound's effects and developing potential therapeutic applications, researchers must adhere to strict animal welfare guidelines. This includes minimizing animal suffering, using the minimum number of animals necessary for valid results, and exploring alternative research methods where possible.
The potential therapeutic applications of muscimol, particularly in treating neurological disorders, introduce additional ethical considerations. Balancing the urgency of developing new treatments with the need for thorough safety evaluations is crucial. Researchers and regulatory bodies must collaborate to establish clear guidelines for the progression from preclinical to clinical studies, ensuring that potential benefits to patients are not overshadowed by undue risks.
Confidentiality and data protection are also paramount in muscimol studies. Given the sensitive nature of information collected during trials, including personal medical histories and potential substance use, researchers must implement robust data security measures. This protects participants' privacy and maintains the integrity of the research process.
Lastly, there is an ethical imperative to publish all results from muscimol studies, including negative findings. This transparency is crucial for advancing scientific knowledge, preventing unnecessary duplication of studies, and ensuring that the full spectrum of muscimol's effects is understood by the scientific community and the public.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!