Optimizing Fiber Length And Aspect Ratio For Composite Performance
SEP 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Fiber Reinforcement Technology Background and Objectives
Fiber reinforcement technology has evolved significantly over the past century, transforming from simple applications in ancient civilizations to sophisticated engineered materials in modern industries. The concept of using fibers to strengthen materials dates back thousands of years, with examples including straw-reinforced clay bricks in ancient Egypt. However, the scientific understanding and industrial application of fiber reinforcement began in earnest during the mid-20th century with the development of glass fiber reinforced polymers (GFRP).
The evolution of fiber reinforcement technology has been characterized by continuous innovation in fiber materials, manufacturing processes, and design methodologies. From glass fibers in the 1930s to carbon fibers in the 1960s and aramid fibers in the 1970s, each advancement has expanded the performance envelope of composite materials. Recent decades have witnessed the emergence of natural fibers, nanofibers, and hybrid reinforcement systems, reflecting growing environmental concerns and specialized application requirements.
A critical aspect of fiber reinforcement technology is understanding the relationship between fiber characteristics and composite performance. Fiber length and aspect ratio (the ratio of length to diameter) have emerged as key parameters that significantly influence mechanical properties, processing capabilities, and overall performance of composite materials. These parameters affect critical properties including strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and long-term durability.
The current technological trajectory is focused on optimizing these fiber parameters for specific applications, moving beyond the traditional "longer is better" paradigm to a more nuanced understanding of application-specific requirements. This optimization process involves balancing competing factors such as mechanical performance, processability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability considerations.
The primary objectives of current research and development efforts in this field include: developing predictive models that accurately correlate fiber length and aspect ratio to composite performance; creating processing technologies that preserve fiber length during manufacturing; establishing design methodologies that leverage optimized fiber parameters for specific applications; and exploring sustainable approaches to fiber reinforcement that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Industry-specific optimization has become increasingly important, with aerospace demanding high-performance long fibers, automotive seeking balanced properties for mass production, and consumer products requiring cost-effective solutions with adequate performance. The convergence of computational modeling, advanced characterization techniques, and innovative manufacturing processes is enabling more precise control and optimization of fiber parameters.
The ultimate goal is to establish a comprehensive framework for fiber length and aspect ratio optimization that can be applied across industries, materials systems, and manufacturing processes, leading to more efficient material utilization, enhanced product performance, and accelerated innovation cycles in composite technology.
The evolution of fiber reinforcement technology has been characterized by continuous innovation in fiber materials, manufacturing processes, and design methodologies. From glass fibers in the 1930s to carbon fibers in the 1960s and aramid fibers in the 1970s, each advancement has expanded the performance envelope of composite materials. Recent decades have witnessed the emergence of natural fibers, nanofibers, and hybrid reinforcement systems, reflecting growing environmental concerns and specialized application requirements.
A critical aspect of fiber reinforcement technology is understanding the relationship between fiber characteristics and composite performance. Fiber length and aspect ratio (the ratio of length to diameter) have emerged as key parameters that significantly influence mechanical properties, processing capabilities, and overall performance of composite materials. These parameters affect critical properties including strength, stiffness, impact resistance, and long-term durability.
The current technological trajectory is focused on optimizing these fiber parameters for specific applications, moving beyond the traditional "longer is better" paradigm to a more nuanced understanding of application-specific requirements. This optimization process involves balancing competing factors such as mechanical performance, processability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability considerations.
The primary objectives of current research and development efforts in this field include: developing predictive models that accurately correlate fiber length and aspect ratio to composite performance; creating processing technologies that preserve fiber length during manufacturing; establishing design methodologies that leverage optimized fiber parameters for specific applications; and exploring sustainable approaches to fiber reinforcement that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Industry-specific optimization has become increasingly important, with aerospace demanding high-performance long fibers, automotive seeking balanced properties for mass production, and consumer products requiring cost-effective solutions with adequate performance. The convergence of computational modeling, advanced characterization techniques, and innovative manufacturing processes is enabling more precise control and optimization of fiber parameters.
The ultimate goal is to establish a comprehensive framework for fiber length and aspect ratio optimization that can be applied across industries, materials systems, and manufacturing processes, leading to more efficient material utilization, enhanced product performance, and accelerated innovation cycles in composite technology.
Market Analysis of High-Performance Composite Materials
The global high-performance composite materials market has experienced robust growth, reaching approximately $26.5 billion in 2022 and projected to expand at a CAGR of 7.8% through 2028. This growth is primarily driven by increasing demand from aerospace, automotive, and wind energy sectors seeking lightweight yet strong materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
Fiber-reinforced composites represent the largest segment within this market, with carbon fiber composites accounting for nearly 40% of the total market value. The optimization of fiber length and aspect ratio has become a critical factor influencing market dynamics, as manufacturers seek to balance performance characteristics with production costs.
Aerospace applications currently dominate the market consumption, representing 31% of total demand, followed by automotive (24%) and wind energy (18%). The aerospace sector's preference for long continuous fibers with high aspect ratios has established premium pricing tiers, while automotive manufacturers increasingly adopt short and medium-length fibers for cost-effective mass production.
Regional analysis reveals North America leads the market with 38% share, followed by Europe (32%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest growth rate at 9.2% annually, driven by expanding manufacturing capabilities in China, Japan, and South Korea, particularly in optimizing fiber parameters for specific applications.
Market segmentation by fiber length shows long continuous fibers (>50mm) command premium pricing but represent only 35% of volume, while short fibers (<3mm) account for 45% of volume but generate only 30% of revenue. The medium-length fiber segment (3-50mm) is experiencing the fastest growth at 8.5% annually as it offers an attractive performance-to-cost ratio.
Customer demand patterns indicate a growing preference for tailored fiber aspect ratios optimized for specific applications rather than generic solutions. This trend has sparked increased R&D investment, with major industry players allocating 12-15% of revenue to research focused on fiber optimization technologies.
Competitive analysis reveals market consolidation among major suppliers, with the top five companies controlling approximately 65% of market share. These leaders have established significant intellectual property portfolios specifically addressing fiber length and aspect ratio optimization, creating substantial barriers to entry for new competitors.
Fiber-reinforced composites represent the largest segment within this market, with carbon fiber composites accounting for nearly 40% of the total market value. The optimization of fiber length and aspect ratio has become a critical factor influencing market dynamics, as manufacturers seek to balance performance characteristics with production costs.
Aerospace applications currently dominate the market consumption, representing 31% of total demand, followed by automotive (24%) and wind energy (18%). The aerospace sector's preference for long continuous fibers with high aspect ratios has established premium pricing tiers, while automotive manufacturers increasingly adopt short and medium-length fibers for cost-effective mass production.
Regional analysis reveals North America leads the market with 38% share, followed by Europe (32%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest growth rate at 9.2% annually, driven by expanding manufacturing capabilities in China, Japan, and South Korea, particularly in optimizing fiber parameters for specific applications.
Market segmentation by fiber length shows long continuous fibers (>50mm) command premium pricing but represent only 35% of volume, while short fibers (<3mm) account for 45% of volume but generate only 30% of revenue. The medium-length fiber segment (3-50mm) is experiencing the fastest growth at 8.5% annually as it offers an attractive performance-to-cost ratio.
Customer demand patterns indicate a growing preference for tailored fiber aspect ratios optimized for specific applications rather than generic solutions. This trend has sparked increased R&D investment, with major industry players allocating 12-15% of revenue to research focused on fiber optimization technologies.
Competitive analysis reveals market consolidation among major suppliers, with the top five companies controlling approximately 65% of market share. These leaders have established significant intellectual property portfolios specifically addressing fiber length and aspect ratio optimization, creating substantial barriers to entry for new competitors.
Current Challenges in Fiber Length Optimization
Despite significant advancements in composite materials technology, optimizing fiber length and aspect ratio remains a complex challenge with multiple interrelated factors. Current manufacturing processes struggle to maintain consistent fiber length during production, particularly in injection molding where high shear forces cause significant fiber breakage. This results in unpredictable mechanical properties and performance variability across finished components, creating reliability concerns for critical applications.
The relationship between fiber orientation and length optimization presents another substantial challenge. Longer fibers tend to align differently than shorter ones during processing, creating complex orientation distributions that are difficult to predict and control. This orientation variability directly impacts mechanical properties, with different loading directions exhibiting significantly different strength and stiffness characteristics.
Scale-up issues further complicate fiber length optimization. Laboratory-scale successes often fail to translate to industrial production environments due to different flow dynamics, cooling rates, and processing parameters. The fiber length distribution that performs optimally in small-scale testing may be impossible to maintain in full-scale manufacturing operations.
Measurement and characterization of fiber length distributions in finished components remain technically challenging. Current methods are often destructive, time-consuming, and provide only statistical approximations rather than comprehensive spatial mapping of fiber length throughout a component. This limitation hinders the development of accurate predictive models.
The trade-off between processability and performance creates a fundamental optimization dilemma. While longer fibers generally provide superior mechanical properties, they significantly increase processing difficulties including higher viscosity, greater tool wear, and more challenging mold filling characteristics. This forces manufacturers to compromise between ideal mechanical properties and practical manufacturing considerations.
Cost considerations further constrain optimization efforts. Processes that preserve longer fiber lengths often require specialized equipment, slower production rates, or more expensive raw materials. The economic viability of these approaches varies significantly across different industry sectors and production volumes.
Recycling and sustainability concerns add another dimension to the challenge. Fiber length degradation during recycling processes significantly impacts the mechanical properties of recycled composites. Developing optimization strategies that account for multiple life cycles rather than just virgin material performance represents an emerging challenge in the field.
The relationship between fiber orientation and length optimization presents another substantial challenge. Longer fibers tend to align differently than shorter ones during processing, creating complex orientation distributions that are difficult to predict and control. This orientation variability directly impacts mechanical properties, with different loading directions exhibiting significantly different strength and stiffness characteristics.
Scale-up issues further complicate fiber length optimization. Laboratory-scale successes often fail to translate to industrial production environments due to different flow dynamics, cooling rates, and processing parameters. The fiber length distribution that performs optimally in small-scale testing may be impossible to maintain in full-scale manufacturing operations.
Measurement and characterization of fiber length distributions in finished components remain technically challenging. Current methods are often destructive, time-consuming, and provide only statistical approximations rather than comprehensive spatial mapping of fiber length throughout a component. This limitation hinders the development of accurate predictive models.
The trade-off between processability and performance creates a fundamental optimization dilemma. While longer fibers generally provide superior mechanical properties, they significantly increase processing difficulties including higher viscosity, greater tool wear, and more challenging mold filling characteristics. This forces manufacturers to compromise between ideal mechanical properties and practical manufacturing considerations.
Cost considerations further constrain optimization efforts. Processes that preserve longer fiber lengths often require specialized equipment, slower production rates, or more expensive raw materials. The economic viability of these approaches varies significantly across different industry sectors and production volumes.
Recycling and sustainability concerns add another dimension to the challenge. Fiber length degradation during recycling processes significantly impacts the mechanical properties of recycled composites. Developing optimization strategies that account for multiple life cycles rather than just virgin material performance represents an emerging challenge in the field.
Existing Methodologies for Fiber Length Determination
01 Mechanical performance enhancement of fiber composites
Various methods can be employed to enhance the mechanical properties of fiber composites, including strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. These methods involve optimizing fiber orientation, improving fiber-matrix interfacial bonding, and incorporating specific reinforcement materials. Enhanced mechanical performance is crucial for applications requiring high structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities.- Mechanical performance enhancement of fiber composites: Various methods can be employed to enhance the mechanical properties of fiber composites, including strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. These methods involve optimizing fiber orientation, improving fiber-matrix interfacial bonding, and incorporating specific reinforcement materials. Enhanced mechanical performance makes these composites suitable for structural applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries where high strength-to-weight ratios are required.
- Thermal and environmental resistance properties: Fiber composites can be formulated to exhibit superior thermal stability and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. This involves selecting appropriate fiber types, matrix materials, and incorporating additives that enhance thermal conductivity or insulation properties. These improvements extend the service life and application range of fiber composites in extreme environments and outdoor applications.
- Manufacturing processes for performance optimization: Advanced manufacturing techniques significantly impact the performance characteristics of fiber composites. Processes such as pultrusion, resin transfer molding, compression molding, and automated fiber placement allow for precise control over fiber content, orientation, and void formation. Optimized manufacturing processes result in composites with consistent quality, reduced defects, and enhanced overall performance properties.
- Sustainable and bio-based fiber composites: Development of environmentally friendly fiber composites using natural fibers (such as flax, hemp, jute) and bio-based resins addresses sustainability concerns while maintaining performance requirements. These materials offer reduced environmental impact, biodegradability options, and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional composites. Research focuses on improving the inherent limitations of natural fibers such as moisture sensitivity and variable properties to match conventional composite performance.
- Multifunctional and smart fiber composites: Integration of additional functionalities into fiber composites creates materials with capabilities beyond mechanical performance. These include self-healing properties, electrical conductivity, sensing capabilities, and energy harvesting functions. By incorporating nanomaterials, conductive fillers, or specialized coatings, these composites can monitor their own structural health, respond to environmental stimuli, or serve multiple purposes simultaneously in advanced applications.
02 Thermal and environmental resistance properties
Fiber composites can be formulated to exhibit superior thermal stability and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. This involves selecting appropriate fiber types, matrix materials, and protective additives. Improved thermal and environmental resistance extends the service life of composite materials in harsh operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lightweight design and structural efficiency
Fiber composites can be engineered for optimal strength-to-weight ratios, enabling lightweight designs without compromising structural integrity. This involves strategic placement of fibers, core materials selection, and innovative manufacturing techniques. Lightweight composite structures offer significant advantages in transportation, aerospace, and portable applications where weight reduction is critical.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functional and smart composite materials
Advanced fiber composites can be designed with additional functional properties beyond mechanical performance, including electrical conductivity, thermal management capabilities, and self-sensing or self-healing characteristics. These smart composites incorporate specialized fibers, nanofillers, or responsive elements that enable multifunctional performance for specialized applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable and bio-based fiber composites
Environmentally friendly fiber composites utilize natural fibers, bio-based resins, and sustainable manufacturing processes to reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance requirements. These materials offer biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and renewable resource utilization. Research focuses on optimizing the performance of natural fiber composites to match or exceed that of traditional synthetic composites.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Composites
The fiber composite industry is currently in a growth phase, with the market for optimized fiber length and aspect ratio technologies expanding rapidly due to increasing demand in aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. The global market size is estimated to exceed $10 billion, driven by lightweight material requirements for fuel efficiency and performance. Leading companies like Northrop Grumman, Boeing, and Toray Industries have achieved significant technological maturity in fiber optimization, while emerging players such as Arris Composites are advancing additive manufacturing techniques for continuous fiber composites. Safran and Airbus are focusing on aerospace applications, developing proprietary methods to balance fiber length with mechanical properties. Research institutions including Kyoto University and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute are contributing fundamental advances in understanding aspect ratio effects on composite performance.
Arris Composites, Inc.
Technical Solution: Arris Composites has developed a revolutionary approach to fiber length and aspect ratio optimization through their Additive Molding™ technology. This process allows for precise control of continuous fiber alignment and orientation in three dimensions, effectively optimizing the aspect ratio contribution to mechanical performance. Their technology enables the creation of complex composite structures with fiber continuity maintained throughout the part, eliminating the performance compromises typically associated with chopped fiber composites. Arris's process can create parts with localized fiber reinforcement precisely where needed, with their research showing up to 60% weight reduction compared to traditional composites while maintaining equivalent strength. Their manufacturing approach allows for fiber aspect ratio optimization on a zone-by-zone basis within a single part, enabling performance tuning for specific load paths and stress concentrations. The company has demonstrated that their optimized fiber placement can improve impact resistance by up to 50% compared to conventional composites with random fiber orientation.
Strengths: Unique additive manufacturing approach enables previously impossible fiber architectures; rapid prototyping capabilities accelerate optimization cycles. Weaknesses: Relatively new technology with limited long-term performance data; current production volumes may not meet demands of large-scale industrial applications.
Safran SA
Technical Solution: Safran has developed sophisticated fiber optimization technologies specifically for aerospace composite applications. Their approach focuses on tailoring fiber length and aspect ratio to achieve optimal balance between mechanical performance and manufacturing efficiency. Safran's research has established correlations between fiber aspect ratios and critical aerospace performance metrics like fatigue resistance and damage tolerance. Their proprietary simulation tools can predict how fiber dimensions affect composite behavior under extreme temperature and pressure conditions typical in aerospace applications. Safran employs a hybrid approach combining continuous and discontinuous fibers with optimized aspect ratios to create structures with directionally-tuned properties. Their manufacturing processes include specialized fiber handling techniques that preserve fiber length during high-volume production, addressing a common challenge in industrial composite manufacturing. Safran's testing has demonstrated that optimized fiber aspect ratios can improve composite toughness by up to 35% while reducing weight by 15-20% compared to traditional aerospace materials.
Strengths: Deep expertise in high-performance aerospace applications; extensive testing capabilities for validating fiber optimization models under extreme conditions. Weaknesses: Solutions primarily focused on aerospace certification requirements may limit applicability in other industries; high development costs reflected in premium pricing.
Critical Patents in Fiber Aspect Ratio Engineering
Composite fiber, composite mixed-filament fiber including same, woven/knitted fabric, and garment
PatentPendingUS20240060217A1
Innovation
- A composite fiber comprising polyester-based thermoplastic resins A and B, with specific molecular weight differences, thickness ratios, and structural configurations, which provides a puffy soft texture, high resilience, and a delicate worsted-wool feeling, while maintaining excellent stretchability and wear resistance.
Composite fiber, fiber aggregate, skin material and interior material
PatentInactiveJP2022014513A
Innovation
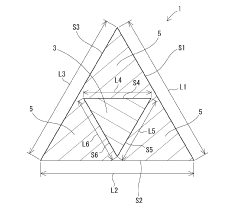
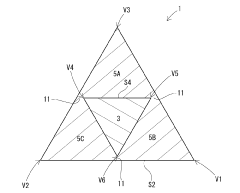
- A composite fiber with a substantially triangular cross-sectional shape, comprising a core and sheath made of different materials, where the core and sheath have specific side lengths and materials (polyamide 6/66 for the core and polyethylene terephthalate/polybutylene terephthalate/polytrimethylene terephthalate for the sheath) to enhance near-infrared reflection and dyeability.
Manufacturing Process Considerations for Optimal Fiber Integration
The manufacturing process for fiber-reinforced composites significantly impacts the final performance characteristics of the material. Optimizing fiber integration requires careful consideration of processing parameters that directly affect fiber length preservation and aspect ratio maintenance throughout production.
Fiber damage during processing represents a critical challenge in composite manufacturing. Conventional methods such as extrusion, injection molding, and compression molding subject fibers to intense shear forces that can lead to fiber breakage and length reduction. Studies indicate that initial fiber lengths can decrease by 30-70% during processing, with the most severe reductions occurring in high-shear processes like injection molding.
Temperature control during processing plays a dual role in fiber integration. Excessive processing temperatures can degrade fiber-matrix interfaces, while insufficient temperatures may result in inadequate fiber wetting and poor matrix flow. The optimal processing temperature window must be established based on both matrix polymer characteristics and fiber type to maintain fiber integrity while ensuring proper consolidation.
Feed rate and screw design in extrusion-based processes directly influence fiber attrition. Lower screw speeds and specialized gentle-mixing screw designs have demonstrated significant improvements in preserving fiber length. Research shows that optimized screw configurations can maintain up to 40% longer average fiber lengths compared to conventional designs, particularly for high-aspect-ratio fibers.
Fiber orientation control represents another manufacturing consideration that interacts with length and aspect ratio optimization. Flow patterns during molding processes tend to align fibers in the flow direction, which can create anisotropic mechanical properties. Techniques such as flow manipulation, strategic gating in injection molding, and specialized tooling can help achieve desired fiber orientation distributions while minimizing fiber damage.
Pre-processing fiber treatments significantly impact manufacturing outcomes. Surface treatments that enhance fiber-matrix compatibility not only improve interfacial adhesion but also affect how fibers respond to processing forces. Silane coupling agents and plasma treatments have shown particular promise in allowing higher aspect ratio fibers to survive manufacturing processes with less damage.
Post-processing considerations include annealing and controlled cooling rates, which can relieve internal stresses that might otherwise lead to fiber-matrix debonding or microcracking. These steps are particularly important for composites containing high-aspect-ratio fibers, as residual stresses can concentrate at fiber ends and initiate failure.
Advanced manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing and automated fiber placement offer new paradigms for fiber integration that can potentially preserve fiber length and aspect ratio more effectively than traditional methods. These emerging techniques allow for more precise control over fiber placement and orientation while subjecting fibers to lower mechanical stresses during processing.
Fiber damage during processing represents a critical challenge in composite manufacturing. Conventional methods such as extrusion, injection molding, and compression molding subject fibers to intense shear forces that can lead to fiber breakage and length reduction. Studies indicate that initial fiber lengths can decrease by 30-70% during processing, with the most severe reductions occurring in high-shear processes like injection molding.
Temperature control during processing plays a dual role in fiber integration. Excessive processing temperatures can degrade fiber-matrix interfaces, while insufficient temperatures may result in inadequate fiber wetting and poor matrix flow. The optimal processing temperature window must be established based on both matrix polymer characteristics and fiber type to maintain fiber integrity while ensuring proper consolidation.
Feed rate and screw design in extrusion-based processes directly influence fiber attrition. Lower screw speeds and specialized gentle-mixing screw designs have demonstrated significant improvements in preserving fiber length. Research shows that optimized screw configurations can maintain up to 40% longer average fiber lengths compared to conventional designs, particularly for high-aspect-ratio fibers.
Fiber orientation control represents another manufacturing consideration that interacts with length and aspect ratio optimization. Flow patterns during molding processes tend to align fibers in the flow direction, which can create anisotropic mechanical properties. Techniques such as flow manipulation, strategic gating in injection molding, and specialized tooling can help achieve desired fiber orientation distributions while minimizing fiber damage.
Pre-processing fiber treatments significantly impact manufacturing outcomes. Surface treatments that enhance fiber-matrix compatibility not only improve interfacial adhesion but also affect how fibers respond to processing forces. Silane coupling agents and plasma treatments have shown particular promise in allowing higher aspect ratio fibers to survive manufacturing processes with less damage.
Post-processing considerations include annealing and controlled cooling rates, which can relieve internal stresses that might otherwise lead to fiber-matrix debonding or microcracking. These steps are particularly important for composites containing high-aspect-ratio fibers, as residual stresses can concentrate at fiber ends and initiate failure.
Advanced manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing and automated fiber placement offer new paradigms for fiber integration that can potentially preserve fiber length and aspect ratio more effectively than traditional methods. These emerging techniques allow for more precise control over fiber placement and orientation while subjecting fibers to lower mechanical stresses during processing.
Sustainability Aspects of Advanced Composite Development
The sustainability of composite materials is becoming increasingly critical as industries strive to reduce environmental impacts while maintaining performance advantages. When optimizing fiber length and aspect ratio for composite performance, sustainability considerations must be integrated into the development process to ensure long-term viability and environmental compatibility.
Natural fiber composites present a promising sustainable alternative to traditional synthetic fiber composites. Optimizing the length and aspect ratio of natural fibers such as flax, hemp, and jute can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of composite materials while maintaining competitive mechanical properties. Research indicates that longer natural fibers with higher aspect ratios often yield better mechanical performance, though processing challenges increase proportionally with fiber length.
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies demonstrate that composites with optimized fiber dimensions can reduce energy consumption during manufacturing by 15-30% compared to conventional composites. This optimization also extends product lifespan, further enhancing sustainability through reduced replacement frequency and associated resource consumption.
Recyclability represents another crucial sustainability aspect affected by fiber dimensions. Composites with shorter fibers are generally easier to recycle, but may sacrifice performance benefits. Recent technological advances have enabled improved recycling processes for longer fiber composites, including solvolysis and pyrolysis techniques that can recover fibers while preserving their aspect ratio and mechanical properties.
Biodegradability considerations are increasingly important for end-of-life management. Research shows that natural fiber composites with optimized dimensions can be designed to biodegrade under specific conditions while maintaining durability during their service life. The degradation rate can be tailored by adjusting fiber length and surface treatments.
Water consumption during composite manufacturing varies significantly with fiber dimensions. Longer fibers typically require more extensive washing and preparation processes, increasing water usage. Optimization studies indicate potential water savings of up to 40% through careful selection of fiber dimensions and processing techniques.
Chemical treatments used to enhance fiber-matrix adhesion also present sustainability challenges. Shorter fibers often require more intensive chemical treatments to achieve adequate bonding, potentially increasing toxicity. Recent innovations in eco-friendly coupling agents and surface treatments have shown promise in reducing environmental impact while maintaining the performance benefits of optimized fiber dimensions.
The economic sustainability of advanced composites is equally important. While longer fibers may increase initial manufacturing costs, their superior performance characteristics often result in lower lifecycle costs through extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements, creating a positive sustainability impact from both environmental and economic perspectives.
Natural fiber composites present a promising sustainable alternative to traditional synthetic fiber composites. Optimizing the length and aspect ratio of natural fibers such as flax, hemp, and jute can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of composite materials while maintaining competitive mechanical properties. Research indicates that longer natural fibers with higher aspect ratios often yield better mechanical performance, though processing challenges increase proportionally with fiber length.
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies demonstrate that composites with optimized fiber dimensions can reduce energy consumption during manufacturing by 15-30% compared to conventional composites. This optimization also extends product lifespan, further enhancing sustainability through reduced replacement frequency and associated resource consumption.
Recyclability represents another crucial sustainability aspect affected by fiber dimensions. Composites with shorter fibers are generally easier to recycle, but may sacrifice performance benefits. Recent technological advances have enabled improved recycling processes for longer fiber composites, including solvolysis and pyrolysis techniques that can recover fibers while preserving their aspect ratio and mechanical properties.
Biodegradability considerations are increasingly important for end-of-life management. Research shows that natural fiber composites with optimized dimensions can be designed to biodegrade under specific conditions while maintaining durability during their service life. The degradation rate can be tailored by adjusting fiber length and surface treatments.
Water consumption during composite manufacturing varies significantly with fiber dimensions. Longer fibers typically require more extensive washing and preparation processes, increasing water usage. Optimization studies indicate potential water savings of up to 40% through careful selection of fiber dimensions and processing techniques.
Chemical treatments used to enhance fiber-matrix adhesion also present sustainability challenges. Shorter fibers often require more intensive chemical treatments to achieve adequate bonding, potentially increasing toxicity. Recent innovations in eco-friendly coupling agents and surface treatments have shown promise in reducing environmental impact while maintaining the performance benefits of optimized fiber dimensions.
The economic sustainability of advanced composites is equally important. While longer fibers may increase initial manufacturing costs, their superior performance characteristics often result in lower lifecycle costs through extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements, creating a positive sustainability impact from both environmental and economic perspectives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!