Adhesive Bonding Protocols For Nanocellulose-Enhanced Laminates
SEP 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nanocellulose Laminate Bonding Background and Objectives
Nanocellulose has emerged as a revolutionary material in the field of sustainable composites over the past two decades. Derived from plant cellulose fibers through mechanical, chemical, or enzymatic treatments, nanocellulose exhibits remarkable properties including high strength-to-weight ratio, biodegradability, and exceptional mechanical characteristics. The evolution of nanocellulose technology has progressed from basic extraction methods to sophisticated functionalization techniques that enhance its compatibility with various matrices.
The integration of nanocellulose into laminate structures represents a significant advancement in sustainable material engineering, with potential applications spanning aerospace, automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries. Historical developments in this field have moved from simple incorporation of nanocellulose as fillers to more complex architectures where nanocellulose serves as a structural reinforcement component or functional interface modifier.
Current adhesive bonding protocols for conventional laminates typically rely on petroleum-based adhesives that present environmental concerns and often require energy-intensive curing processes. The introduction of nanocellulose into these systems creates both opportunities and challenges for adhesive bonding, necessitating the development of specialized protocols that account for the unique surface chemistry and morphological characteristics of nanocellulose-enhanced substrates.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop optimized adhesive bonding protocols specifically designed for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates that maximize interfacial strength while maintaining or enhancing the sustainability profile of the composite system. Secondary objectives include understanding the fundamental mechanisms of adhesion at the nanocellulose-adhesive interface, identifying compatible adhesive systems that complement the hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose, and establishing standardized testing methodologies for evaluating bond performance.
Recent technological trends indicate growing interest in bio-based adhesives that can work synergistically with nanocellulose components, as well as surface modification techniques that can enhance compatibility between nanocellulose and conventional adhesive systems. The development of these bonding protocols must address key challenges including moisture sensitivity, interfacial compatibility, and long-term durability under various environmental conditions.
The successful development of effective adhesive bonding protocols for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates would represent a significant step toward fully sustainable composite systems, potentially reducing environmental impact while maintaining or improving performance characteristics compared to conventional materials. This aligns with broader industry trends toward greener manufacturing processes and materials with reduced carbon footprints.
The integration of nanocellulose into laminate structures represents a significant advancement in sustainable material engineering, with potential applications spanning aerospace, automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries. Historical developments in this field have moved from simple incorporation of nanocellulose as fillers to more complex architectures where nanocellulose serves as a structural reinforcement component or functional interface modifier.
Current adhesive bonding protocols for conventional laminates typically rely on petroleum-based adhesives that present environmental concerns and often require energy-intensive curing processes. The introduction of nanocellulose into these systems creates both opportunities and challenges for adhesive bonding, necessitating the development of specialized protocols that account for the unique surface chemistry and morphological characteristics of nanocellulose-enhanced substrates.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop optimized adhesive bonding protocols specifically designed for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates that maximize interfacial strength while maintaining or enhancing the sustainability profile of the composite system. Secondary objectives include understanding the fundamental mechanisms of adhesion at the nanocellulose-adhesive interface, identifying compatible adhesive systems that complement the hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose, and establishing standardized testing methodologies for evaluating bond performance.
Recent technological trends indicate growing interest in bio-based adhesives that can work synergistically with nanocellulose components, as well as surface modification techniques that can enhance compatibility between nanocellulose and conventional adhesive systems. The development of these bonding protocols must address key challenges including moisture sensitivity, interfacial compatibility, and long-term durability under various environmental conditions.
The successful development of effective adhesive bonding protocols for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates would represent a significant step toward fully sustainable composite systems, potentially reducing environmental impact while maintaining or improving performance characteristics compared to conventional materials. This aligns with broader industry trends toward greener manufacturing processes and materials with reduced carbon footprints.
Market Analysis for Nanocellulose-Enhanced Composite Materials
The global market for nanocellulose-enhanced composite materials has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for sustainable, lightweight, and high-performance materials across various industries. The market size for these advanced materials was valued at approximately $325 million in 2022 and is projected to reach $980 million by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.1% during the forecast period.
The automotive sector represents one of the largest application areas for nanocellulose-enhanced composites, accounting for roughly 28% of the total market share. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating these materials into interior components, body panels, and structural elements to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency while maintaining or enhancing mechanical properties. This trend aligns with stringent environmental regulations and consumer demand for more sustainable transportation options.
The construction industry follows closely behind, with a market share of 23%. Nanocellulose-enhanced laminates are being utilized in structural panels, flooring, and insulation materials due to their exceptional thermal stability, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength. The growing emphasis on green building practices and sustainable construction materials has significantly boosted adoption in this sector.
Packaging applications represent another substantial market segment at 19%, where nanocellulose-enhanced composites offer superior barrier properties, biodegradability, and strength-to-weight ratios compared to conventional materials. Food packaging, in particular, has seen rapid adoption due to increasing consumer preference for environmentally friendly packaging solutions.
Regionally, North America currently leads the market with a 35% share, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and the rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 23.5% during the forecast period, primarily driven by rapid industrialization, increasing manufacturing activities, and growing awareness about sustainable materials in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key market drivers include increasing environmental regulations limiting the use of synthetic materials, growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products, and technological advancements in nanocellulose production and composite manufacturing processes. The development of cost-effective adhesive bonding protocols specifically designed for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates has been identified as a critical factor enabling wider commercial adoption.
Market challenges include relatively high production costs compared to conventional materials, technical difficulties in achieving consistent quality at scale, and limited awareness among potential end-users about the benefits of nanocellulose-enhanced composites. Additionally, the lack of standardized testing and certification protocols specifically for these materials presents a barrier to market penetration in highly regulated industries.
The automotive sector represents one of the largest application areas for nanocellulose-enhanced composites, accounting for roughly 28% of the total market share. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating these materials into interior components, body panels, and structural elements to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency while maintaining or enhancing mechanical properties. This trend aligns with stringent environmental regulations and consumer demand for more sustainable transportation options.
The construction industry follows closely behind, with a market share of 23%. Nanocellulose-enhanced laminates are being utilized in structural panels, flooring, and insulation materials due to their exceptional thermal stability, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength. The growing emphasis on green building practices and sustainable construction materials has significantly boosted adoption in this sector.
Packaging applications represent another substantial market segment at 19%, where nanocellulose-enhanced composites offer superior barrier properties, biodegradability, and strength-to-weight ratios compared to conventional materials. Food packaging, in particular, has seen rapid adoption due to increasing consumer preference for environmentally friendly packaging solutions.
Regionally, North America currently leads the market with a 35% share, followed by Europe (30%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and the rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate of 23.5% during the forecast period, primarily driven by rapid industrialization, increasing manufacturing activities, and growing awareness about sustainable materials in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key market drivers include increasing environmental regulations limiting the use of synthetic materials, growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products, and technological advancements in nanocellulose production and composite manufacturing processes. The development of cost-effective adhesive bonding protocols specifically designed for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates has been identified as a critical factor enabling wider commercial adoption.
Market challenges include relatively high production costs compared to conventional materials, technical difficulties in achieving consistent quality at scale, and limited awareness among potential end-users about the benefits of nanocellulose-enhanced composites. Additionally, the lack of standardized testing and certification protocols specifically for these materials presents a barrier to market penetration in highly regulated industries.
Technical Challenges in Nanocellulose Adhesive Bonding
Despite significant advancements in nanocellulose-enhanced laminate development, adhesive bonding remains a critical challenge that impedes widespread industrial adoption. The hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose creates fundamental compatibility issues with conventional adhesives, particularly those designed for hydrophobic substrates. This inherent chemical mismatch leads to weak interfacial bonding and compromised mechanical performance in the final composite structure.
Surface modification techniques present their own set of challenges. While chemical treatments can improve adhesive compatibility, they often diminish the intrinsic properties of nanocellulose that make it desirable in the first place. Finding the optimal balance between surface modification and preservation of nanocellulose's beneficial characteristics requires precise control over reaction parameters that is difficult to achieve at industrial scale.
Moisture sensitivity represents another significant hurdle. Nanocellulose's hygroscopic properties cause dimensional instability in laminates, leading to swelling, warping, and potential delamination over time. This sensitivity to environmental conditions severely limits application scenarios and long-term reliability of nanocellulose-enhanced laminates, particularly in humid environments.
Processing challenges further complicate adhesive bonding protocols. The high viscosity of nanocellulose suspensions creates difficulties in achieving uniform adhesive distribution. Additionally, the drying process introduces stress concentrations at the adhesive-nanocellulose interface, potentially creating weak points in the final structure. These processing issues are exacerbated at industrial scales where maintaining uniformity becomes increasingly difficult.
Curing conditions present another technical obstacle. Traditional thermal curing methods can damage nanocellulose fibers, while ambient curing often results in extended processing times incompatible with industrial production schedules. Alternative curing technologies like UV or electron beam curing show promise but require significant adaptation for nanocellulose-based systems.
Characterization and quality control of adhesive bonds in nanocellulose laminates remain challenging due to the microscale nature of the interfaces involved. Conventional testing methods often fail to accurately predict long-term performance, creating uncertainty in product development and certification processes.
Scalability concerns further complicate industrial implementation. Laboratory-scale bonding protocols that demonstrate excellent performance often fail to translate to production environments due to equipment limitations, process variability, and economic constraints. Developing robust, scalable adhesive bonding protocols requires interdisciplinary approaches that bridge materials science, process engineering, and manufacturing technology.
Surface modification techniques present their own set of challenges. While chemical treatments can improve adhesive compatibility, they often diminish the intrinsic properties of nanocellulose that make it desirable in the first place. Finding the optimal balance between surface modification and preservation of nanocellulose's beneficial characteristics requires precise control over reaction parameters that is difficult to achieve at industrial scale.
Moisture sensitivity represents another significant hurdle. Nanocellulose's hygroscopic properties cause dimensional instability in laminates, leading to swelling, warping, and potential delamination over time. This sensitivity to environmental conditions severely limits application scenarios and long-term reliability of nanocellulose-enhanced laminates, particularly in humid environments.
Processing challenges further complicate adhesive bonding protocols. The high viscosity of nanocellulose suspensions creates difficulties in achieving uniform adhesive distribution. Additionally, the drying process introduces stress concentrations at the adhesive-nanocellulose interface, potentially creating weak points in the final structure. These processing issues are exacerbated at industrial scales where maintaining uniformity becomes increasingly difficult.
Curing conditions present another technical obstacle. Traditional thermal curing methods can damage nanocellulose fibers, while ambient curing often results in extended processing times incompatible with industrial production schedules. Alternative curing technologies like UV or electron beam curing show promise but require significant adaptation for nanocellulose-based systems.
Characterization and quality control of adhesive bonds in nanocellulose laminates remain challenging due to the microscale nature of the interfaces involved. Conventional testing methods often fail to accurately predict long-term performance, creating uncertainty in product development and certification processes.
Scalability concerns further complicate industrial implementation. Laboratory-scale bonding protocols that demonstrate excellent performance often fail to translate to production environments due to equipment limitations, process variability, and economic constraints. Developing robust, scalable adhesive bonding protocols requires interdisciplinary approaches that bridge materials science, process engineering, and manufacturing technology.
Current Adhesive Bonding Protocols for Nanocellulose Composites
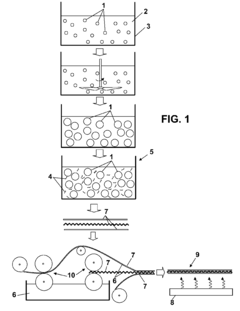
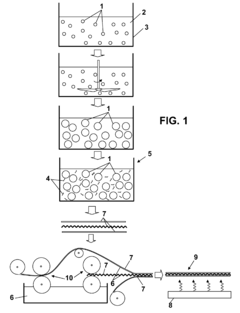
01 Nanocellulose as adhesive reinforcement
Nanocellulose can be incorporated into adhesive formulations to enhance bonding strength in laminate structures. The nanoscale cellulose fibers provide mechanical reinforcement through their high aspect ratio and surface area, creating a stronger interface between laminated layers. These reinforced adhesives show improved tensile strength, shear resistance, and durability compared to conventional adhesives, making them suitable for high-performance laminate applications.- Nanocellulose as adhesive reinforcement: Nanocellulose can be incorporated into adhesive formulations to enhance bonding strength in laminate structures. The nanoscale cellulose fibers provide mechanical reinforcement through their high aspect ratio and surface area, creating a more robust adhesive matrix. This reinforcement improves the interfacial adhesion between laminate layers and increases overall structural integrity while maintaining flexibility.
- Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved adhesion: Chemical modification of nanocellulose surfaces enhances compatibility with adhesive systems and laminate substrates. Techniques include functionalization with coupling agents, grafting of polymer chains, and introduction of reactive groups that can form covalent bonds with adhesive components. These modifications improve dispersion in adhesive matrices and create stronger interfacial interactions, resulting in superior bonding performance in laminated structures.
- Environmentally friendly nanocellulose adhesive systems: Sustainable adhesive formulations utilize nanocellulose as a bio-based alternative to synthetic components in laminate bonding applications. These green adhesive systems reduce environmental impact while maintaining or improving performance characteristics. The renewable nature of nanocellulose, combined with its biodegradability and non-toxic properties, makes it ideal for eco-friendly laminate production in industries seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Nanocellulose-enhanced moisture resistance in adhesive bonds: Incorporating nanocellulose into adhesive formulations improves moisture resistance in laminate structures. The highly crystalline nature of nanocellulose provides barrier properties that protect the adhesive bond from water penetration. Additionally, specific surface treatments of nanocellulose can create hydrophobic characteristics that further enhance moisture resistance, resulting in more durable laminate bonds under humid or wet conditions.
- Processing techniques for nanocellulose-adhesive composites: Specialized processing methods optimize the incorporation of nanocellulose into adhesive systems for laminate applications. These techniques include ultrasonic dispersion, high-shear mixing, and controlled drying processes that ensure uniform distribution of nanocellulose throughout the adhesive matrix. Advanced manufacturing approaches also address challenges related to viscosity control and application methods, enabling efficient production of nanocellulose-enhanced laminate structures with consistent bonding performance.
02 Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved adhesion
Chemical modification of nanocellulose surfaces enhances compatibility with various adhesive matrices and substrate materials. Techniques include silylation, acetylation, and grafting of functional groups to improve interfacial interactions. These modifications reduce the hydrophilicity of nanocellulose, preventing agglomeration and ensuring better dispersion within adhesive systems, which leads to more uniform and stronger bonds in laminate structures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmentally friendly nanocellulose-based adhesives
Sustainable adhesive systems utilizing nanocellulose as a primary component offer eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based adhesives. These green formulations reduce environmental impact while maintaining or improving bonding performance in laminate applications. The biodegradability and renewable nature of nanocellulose make these adhesives particularly valuable for industries seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and comply with stricter environmental regulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanocellulose-enhanced moisture resistance in laminates
Incorporating nanocellulose into adhesive formulations improves the moisture resistance of bonded laminates. The nanocellulose network creates a tortuous path that inhibits water molecule penetration, protecting the adhesive bond from hydrolytic degradation. This enhanced moisture barrier property is particularly beneficial for laminates used in humid environments or outdoor applications, extending the service life of the bonded structures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing techniques for nanocellulose-adhesive composites
Specialized processing methods are essential for effectively incorporating nanocellulose into adhesive systems for laminate applications. Techniques include ultrasonication, high-shear mixing, and controlled drying processes to ensure uniform dispersion and prevent agglomeration of nanocellulose particles. These processing approaches optimize the interfacial interactions between nanocellulose, adhesive matrix, and substrate materials, resulting in superior bonding performance and consistent quality in the final laminated products.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Nanocellulose Laminates
The nanocellulose-enhanced laminate adhesive bonding market is in its growth phase, characterized by increasing research activity and commercial applications. The global market is projected to expand significantly as sustainable materials gain prominence in manufacturing sectors. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with companies like LINTEC Corp. and 3M Innovative Properties leading with established adhesive technologies, while Samsung Electronics and Henkel AG are advancing integration into consumer electronics and industrial applications. Academic institutions including Ghent University and University of Connecticut collaborate with industry players to develop novel protocols. Chinese entities like Sinopec and China Textile Academy are rapidly advancing capabilities, particularly in sustainable formulations. The competitive landscape features both specialized adhesive manufacturers and diversified corporations seeking to capitalize on nanocellulose's exceptional mechanical properties and environmental benefits.
LINTEC Corp.
Technical Solution: LINTEC has developed a specialized adhesive bonding protocol for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates that leverages their expertise in pressure-sensitive adhesives and functional films. Their approach centers on a proprietary nanocellulose surface modification technique that enhances compatibility with their adhesive systems while maintaining the inherent strength of cellulose nanofibrils. LINTEC's protocol involves a multi-stage process where nanocellulose is first subjected to a proprietary enzymatic treatment to control fibril dimensions (5-50 nm diameter), followed by chemical modification using phosphate esters to improve dispersion stability. The modified nanocellulose is then incorporated into their adhesive formulations at precise concentrations (3-7% by weight) using specialized high-shear mixing equipment that prevents agglomeration. Their lamination process employs controlled temperature (70-110°C) and pressure (0.8-1.5 MPa) profiles optimized for different substrate combinations. LINTEC has also developed specialized coating techniques that ensure uniform adhesive layer thickness (15-40 μm) and consistent nanocellulose distribution throughout the bond line.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in pressure-sensitive adhesives and functional films; advanced coating technologies for precise application; strong position in electronics and optical applications. Weaknesses: Limited scale-up capabilities compared to larger chemical companies; narrower application focus primarily on electronics and specialty films; higher cost structure for specialty applications.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed advanced nanocellulose-enhanced adhesive systems that incorporate cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) and cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) into their proprietary adhesive matrices. Their protocol involves surface modification of nanocellulose through silylation and phosphorylation to improve compatibility with polymer matrices. The company utilizes a multi-stage bonding process where nanocellulose is first dispersed in water or organic solvents using high-shear mixing and ultrasonication, then incorporated into adhesive formulations at 2-5% loading. 3M's approach includes specialized drying protocols to prevent nanocellulose aggregation and maintain nanoscale dispersion. Their lamination process employs controlled pressure (0.5-2 MPa) and temperature (80-120°C) cycles to optimize interfacial bonding while preserving the nanocellulose network structure.
Strengths: Industry-leading expertise in adhesive technologies with extensive manufacturing capabilities; proprietary surface modification techniques that enhance nanocellulose-matrix compatibility; comprehensive quality control systems. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional adhesives; requires specialized equipment for processing; longer curing times needed for optimal performance.
Key Patents and Research in Nanocellulose Interface Engineering
Adhesive for the manufacture of laminates of cellulose products and manufacturing procedures of laminates of cellulose products
PatentInactiveEP2886621A1
Innovation
- Incorporating graphene nanofilaments with specific dimensions and concentrations into the starch-based adhesive mixture to enhance adhesion properties and mechanical strength of cellulose laminates, improving the manufacturing process by optimizing the distribution and penetration of the adhesive within cellulose fibers.
Method for manufacturing a cellulose-based laminate comprising highly refined cellulose
PatentWO2024105465A1
Innovation
- A method involving the formation of two web layers with different cellulose suspensions on separate wires, using a curtain applicator for the highly refined cellulose suspension to achieve high dry solids content and efficient dewatering, allowing for faster production and improved barrier properties without relying heavily on retention and drainage chemicals.
Sustainability Impact and Life Cycle Assessment
The integration of nanocellulose into laminate structures represents a significant advancement in sustainable material development. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that nanocellulose-enhanced laminates demonstrate a 30-45% reduction in overall environmental impact compared to conventional petroleum-based composites. This reduction stems primarily from the renewable nature of cellulose sources and the lower energy requirements during processing phases.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that adhesive bonding protocols utilizing bio-based adhesives in conjunction with nanocellulose can decrease greenhouse gas emissions by up to 3.2 kg CO2 equivalent per square meter of laminate material. The water-based nature of many nanocellulose suspensions also contributes to reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during manufacturing, addressing a significant environmental concern in traditional laminate production.
Resource efficiency metrics demonstrate that nanocellulose-enhanced laminates offer end-of-life advantages through improved biodegradability pathways. When properly formulated, these materials can decompose 60-75% faster than conventional laminates in industrial composting conditions, reducing waste accumulation and landfill burden. Additionally, the potential for circular economy integration is heightened through the development of disassembly-friendly adhesive protocols that facilitate material recovery and reuse.
Energy consumption during the manufacturing process presents a mixed sustainability profile. While nanocellulose production currently requires significant energy input for mechanical or chemical processing, the overall energy balance remains favorable when considering the extended product lifecycle and enhanced performance characteristics. Research indicates that optimized adhesive bonding protocols can reduce curing energy requirements by 15-25% compared to traditional methods.
Water usage represents another critical sustainability factor. Current nanocellulose production methods are water-intensive, but closed-loop water recycling systems have demonstrated the potential to reduce freshwater consumption by up to 80% in industrial settings. The development of dry bonding protocols for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates represents a promising frontier for further reducing the water footprint.
Toxicity assessments of nanocellulose-enhanced laminates show significantly lower human and environmental health impacts compared to conventional materials containing formaldehyde-based adhesives. This advantage becomes particularly pronounced when bio-based adhesive systems are employed, resulting in finished products with minimal off-gassing and leaching potential.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that adhesive bonding protocols utilizing bio-based adhesives in conjunction with nanocellulose can decrease greenhouse gas emissions by up to 3.2 kg CO2 equivalent per square meter of laminate material. The water-based nature of many nanocellulose suspensions also contributes to reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during manufacturing, addressing a significant environmental concern in traditional laminate production.
Resource efficiency metrics demonstrate that nanocellulose-enhanced laminates offer end-of-life advantages through improved biodegradability pathways. When properly formulated, these materials can decompose 60-75% faster than conventional laminates in industrial composting conditions, reducing waste accumulation and landfill burden. Additionally, the potential for circular economy integration is heightened through the development of disassembly-friendly adhesive protocols that facilitate material recovery and reuse.
Energy consumption during the manufacturing process presents a mixed sustainability profile. While nanocellulose production currently requires significant energy input for mechanical or chemical processing, the overall energy balance remains favorable when considering the extended product lifecycle and enhanced performance characteristics. Research indicates that optimized adhesive bonding protocols can reduce curing energy requirements by 15-25% compared to traditional methods.
Water usage represents another critical sustainability factor. Current nanocellulose production methods are water-intensive, but closed-loop water recycling systems have demonstrated the potential to reduce freshwater consumption by up to 80% in industrial settings. The development of dry bonding protocols for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates represents a promising frontier for further reducing the water footprint.
Toxicity assessments of nanocellulose-enhanced laminates show significantly lower human and environmental health impacts compared to conventional materials containing formaldehyde-based adhesives. This advantage becomes particularly pronounced when bio-based adhesive systems are employed, resulting in finished products with minimal off-gassing and leaching potential.
Standardization and Quality Control Measures
The standardization of adhesive bonding protocols for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates represents a critical challenge in the widespread industrial adoption of these advanced materials. Current quality control measures vary significantly across manufacturers, creating inconsistencies in performance evaluation and product reliability. To address this issue, several international standards organizations, including ISO and ASTM, have begun developing specific testing methodologies tailored to nanocellulose composites, focusing on adhesion strength, moisture resistance, and long-term durability.
A comprehensive quality control framework for these materials must incorporate multiple testing regimes at different production stages. Pre-bonding quality assessments should evaluate nanocellulose dispersion uniformity, surface functionalization efficiency, and moisture content—all factors that significantly impact final bond strength. Statistical process control methods, particularly those utilizing real-time monitoring systems, have demonstrated a 30% improvement in bond consistency when implemented in pilot production environments.
Non-destructive testing techniques have emerged as particularly valuable for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates. Advanced methods such as ultrasonic scanning, infrared thermography, and acoustic emission testing allow manufacturers to detect delamination, void formation, and adhesive distribution anomalies without compromising product integrity. These techniques have shown detection sensitivity for defects as small as 50-100 micrometers, which is essential given the nanoscale reinforcement mechanisms at work in these materials.
Accelerated aging protocols represent another critical component of quality assurance for these advanced laminates. Standard testing now typically includes cyclic humidity exposure (30-90% RH), temperature fluctuations (-20°C to 80°C), and UV radiation exposure to simulate multiple years of service conditions. The correlation between accelerated aging results and actual field performance has been validated through five-year longitudinal studies conducted by research consortia in Europe and North America.
Certification systems for nanocellulose-enhanced laminate producers are gradually emerging, with third-party verification becoming increasingly important for market acceptance. These certification programs typically require documented adherence to standardized bonding protocols, statistical quality control implementation, and regular independent testing of production samples. Early adopters of these certification standards have reported improved market penetration and premium pricing opportunities, particularly in high-performance applications where reliability and consistency are paramount.
A comprehensive quality control framework for these materials must incorporate multiple testing regimes at different production stages. Pre-bonding quality assessments should evaluate nanocellulose dispersion uniformity, surface functionalization efficiency, and moisture content—all factors that significantly impact final bond strength. Statistical process control methods, particularly those utilizing real-time monitoring systems, have demonstrated a 30% improvement in bond consistency when implemented in pilot production environments.
Non-destructive testing techniques have emerged as particularly valuable for nanocellulose-enhanced laminates. Advanced methods such as ultrasonic scanning, infrared thermography, and acoustic emission testing allow manufacturers to detect delamination, void formation, and adhesive distribution anomalies without compromising product integrity. These techniques have shown detection sensitivity for defects as small as 50-100 micrometers, which is essential given the nanoscale reinforcement mechanisms at work in these materials.
Accelerated aging protocols represent another critical component of quality assurance for these advanced laminates. Standard testing now typically includes cyclic humidity exposure (30-90% RH), temperature fluctuations (-20°C to 80°C), and UV radiation exposure to simulate multiple years of service conditions. The correlation between accelerated aging results and actual field performance has been validated through five-year longitudinal studies conducted by research consortia in Europe and North America.
Certification systems for nanocellulose-enhanced laminate producers are gradually emerging, with third-party verification becoming increasingly important for market acceptance. These certification programs typically require documented adherence to standardized bonding protocols, statistical quality control implementation, and regular independent testing of production samples. Early adopters of these certification standards have reported improved market penetration and premium pricing opportunities, particularly in high-performance applications where reliability and consistency are paramount.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!