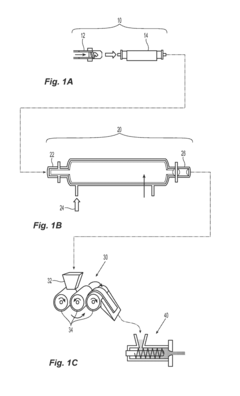
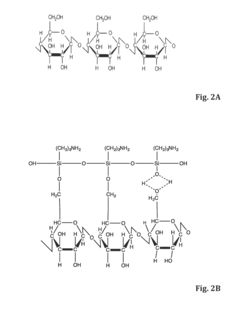
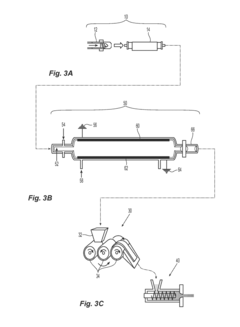
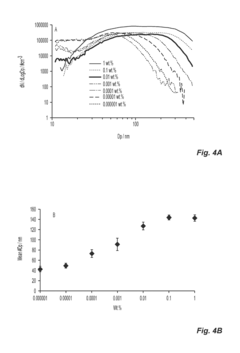
Surface Functionalization Of Nanocellulose For Improved Matrix Adhesion
SEP 3, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nanocellulose Functionalization Background and Objectives
Nanocellulose has emerged as a revolutionary biomaterial in the past two decades, gaining significant attention due to its exceptional mechanical properties, sustainability, and biodegradability. Derived from cellulose, the most abundant biopolymer on Earth, nanocellulose represents a class of nanomaterials with dimensions in the nanometer range, typically extracted from plant sources, agricultural residues, or produced through bacterial synthesis.
The evolution of nanocellulose technology has progressed through several distinct phases. Initially, research focused primarily on extraction and characterization methods, establishing fundamental understanding of nanocellulose structures including cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC). Subsequently, attention shifted toward potential applications, with early implementations in paper strengthening and packaging materials.
Despite nanocellulose's impressive intrinsic properties, including high specific strength, large surface area, and excellent barrier properties, its hydrophilic nature presents significant challenges for integration with hydrophobic polymer matrices. This fundamental incompatibility results in poor interfacial adhesion, leading to suboptimal mechanical performance in composite materials and limiting broader industrial adoption.
Surface functionalization has emerged as a critical approach to overcome these limitations. By modifying the surface chemistry of nanocellulose, researchers aim to enhance compatibility with various matrices while preserving or enhancing its inherent beneficial properties. The technological trajectory has evolved from simple physical treatments to sophisticated chemical modifications targeting specific functional groups and applications.
Current research objectives in nanocellulose functionalization center on developing scalable, environmentally friendly modification techniques that can be implemented in industrial settings. Key goals include enhancing matrix adhesion in polymer composites, improving dispersion stability, and tailoring surface properties for specific end applications ranging from packaging materials to biomedical devices.
The field is now moving toward precision functionalization, where surface modifications are designed at the molecular level to achieve specific interactions with target matrices. This represents a shift from generalized approaches to application-specific modifications that optimize performance for particular use cases.
Looking forward, the technological objectives include developing green functionalization methods that eliminate toxic reagents, reducing energy requirements for modification processes, and creating multifunctional nanocellulose derivatives capable of addressing multiple performance requirements simultaneously. These advancements aim to position nanocellulose as a viable alternative to synthetic materials in high-performance applications while maintaining its environmental advantages.
The evolution of nanocellulose technology has progressed through several distinct phases. Initially, research focused primarily on extraction and characterization methods, establishing fundamental understanding of nanocellulose structures including cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC). Subsequently, attention shifted toward potential applications, with early implementations in paper strengthening and packaging materials.
Despite nanocellulose's impressive intrinsic properties, including high specific strength, large surface area, and excellent barrier properties, its hydrophilic nature presents significant challenges for integration with hydrophobic polymer matrices. This fundamental incompatibility results in poor interfacial adhesion, leading to suboptimal mechanical performance in composite materials and limiting broader industrial adoption.
Surface functionalization has emerged as a critical approach to overcome these limitations. By modifying the surface chemistry of nanocellulose, researchers aim to enhance compatibility with various matrices while preserving or enhancing its inherent beneficial properties. The technological trajectory has evolved from simple physical treatments to sophisticated chemical modifications targeting specific functional groups and applications.
Current research objectives in nanocellulose functionalization center on developing scalable, environmentally friendly modification techniques that can be implemented in industrial settings. Key goals include enhancing matrix adhesion in polymer composites, improving dispersion stability, and tailoring surface properties for specific end applications ranging from packaging materials to biomedical devices.
The field is now moving toward precision functionalization, where surface modifications are designed at the molecular level to achieve specific interactions with target matrices. This represents a shift from generalized approaches to application-specific modifications that optimize performance for particular use cases.
Looking forward, the technological objectives include developing green functionalization methods that eliminate toxic reagents, reducing energy requirements for modification processes, and creating multifunctional nanocellulose derivatives capable of addressing multiple performance requirements simultaneously. These advancements aim to position nanocellulose as a viable alternative to synthetic materials in high-performance applications while maintaining its environmental advantages.
Market Analysis for Functionalized Nanocellulose Applications
The global market for functionalized nanocellulose is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials across multiple industries. Current market valuations indicate that the functionalized nanocellulose sector is growing at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 18-20%, with the global market expected to reach several billion dollars by 2030.
The adhesion-enhanced nanocellulose segment represents a particularly promising market opportunity, as industries seek to improve composite material performance while reducing environmental impact. Key market sectors showing strong demand include automotive manufacturing, aerospace, construction materials, and packaging industries, where lightweight yet strong materials can provide significant competitive advantages.
Consumer goods manufacturers are increasingly adopting functionalized nanocellulose for improved matrix adhesion in their products, responding to growing consumer preference for environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum-based materials. This shift is particularly evident in packaging applications, where enhanced barrier properties and mechanical strength achieved through better matrix adhesion translate to tangible performance benefits.
Regional market analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently lead in adoption of functionalized nanocellulose technologies, primarily due to stringent environmental regulations and strong research infrastructure. However, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, with significant investments in manufacturing capacity and research facilities, particularly in Japan, China, and South Korea.
Market demand analysis indicates that industries are willing to pay premium prices for functionalized nanocellulose that demonstrates superior matrix adhesion properties, as these translate directly to enhanced performance characteristics in final products. The price premium ranges widely depending on application, with high-tech industries showing willingness to pay substantially more for proven performance enhancements.
Supply chain considerations reveal potential bottlenecks in scaling production to meet growing demand. Current production capacity for high-quality functionalized nanocellulose remains limited, creating opportunities for companies that can efficiently scale manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality standards.
Market forecasts suggest that applications requiring enhanced matrix adhesion will drive significant growth in the functionalized nanocellulose market over the next decade. Industries with the highest growth potential include automotive composites, advanced construction materials, and specialized packaging solutions where mechanical performance is critical.
The adhesion-enhanced nanocellulose segment represents a particularly promising market opportunity, as industries seek to improve composite material performance while reducing environmental impact. Key market sectors showing strong demand include automotive manufacturing, aerospace, construction materials, and packaging industries, where lightweight yet strong materials can provide significant competitive advantages.
Consumer goods manufacturers are increasingly adopting functionalized nanocellulose for improved matrix adhesion in their products, responding to growing consumer preference for environmentally friendly alternatives to petroleum-based materials. This shift is particularly evident in packaging applications, where enhanced barrier properties and mechanical strength achieved through better matrix adhesion translate to tangible performance benefits.
Regional market analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently lead in adoption of functionalized nanocellulose technologies, primarily due to stringent environmental regulations and strong research infrastructure. However, Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, with significant investments in manufacturing capacity and research facilities, particularly in Japan, China, and South Korea.
Market demand analysis indicates that industries are willing to pay premium prices for functionalized nanocellulose that demonstrates superior matrix adhesion properties, as these translate directly to enhanced performance characteristics in final products. The price premium ranges widely depending on application, with high-tech industries showing willingness to pay substantially more for proven performance enhancements.
Supply chain considerations reveal potential bottlenecks in scaling production to meet growing demand. Current production capacity for high-quality functionalized nanocellulose remains limited, creating opportunities for companies that can efficiently scale manufacturing while maintaining consistent quality standards.
Market forecasts suggest that applications requiring enhanced matrix adhesion will drive significant growth in the functionalized nanocellulose market over the next decade. Industries with the highest growth potential include automotive composites, advanced construction materials, and specialized packaging solutions where mechanical performance is critical.
Current Challenges in Nanocellulose Surface Modification
Despite the promising properties of nanocellulose, its inherent hydrophilicity presents significant challenges for effective matrix adhesion in composite applications. The hydroxyl-rich surface of nanocellulose creates compatibility issues with hydrophobic polymer matrices, resulting in poor interfacial bonding and suboptimal mechanical properties in the final composites. This fundamental mismatch in surface chemistry represents one of the most persistent obstacles in nanocellulose utilization.
Current surface modification techniques face several technical limitations. Chemical modification methods, while effective at altering surface properties, often compromise the intrinsic mechanical strength of nanocellulose fibrils through structural degradation. The high surface area of nanocellulose requires substantial quantities of modification reagents, raising concerns about process economics and environmental sustainability. Additionally, achieving uniform surface modification across all nanocellulose particles remains challenging due to accessibility issues within the hierarchical structure.
Scalability presents another significant hurdle. Laboratory-scale modification protocols frequently fail to translate effectively to industrial production environments. The complex separation and purification steps required after modification add considerable cost and complexity to manufacturing processes. Many current approaches also utilize environmentally problematic solvents and reagents, contradicting the eco-friendly premise of nanocellulose-based materials.
Characterization of modified nanocellulose surfaces poses analytical challenges. Quantifying the degree of surface substitution accurately requires sophisticated analytical techniques not readily available in production settings. The heterogeneity of nanocellulose sources further complicates standardization efforts, as modification protocols must be adapted for different nanocellulose types and morphologies.
The stability of functionalized surfaces represents an ongoing concern. Many surface modifications demonstrate limited durability under processing conditions or during the service life of the composite. Thermal degradation during high-temperature composite processing can reverse surface modifications, while moisture exposure may trigger hydrolysis of certain functional groups, compromising long-term performance.
Balancing the degree of modification presents a complex optimization problem. Excessive surface functionalization can diminish the beneficial properties of nanocellulose, while insufficient modification fails to adequately improve matrix compatibility. This delicate balance varies depending on the target matrix and desired composite properties, necessitating customized approaches rather than universal solutions.
Regulatory and safety considerations add another layer of complexity, particularly for applications in food packaging, biomedical devices, or other sensitive sectors. Novel surface modification agents must undergo rigorous safety assessments before commercial implementation, creating significant barriers to innovation and market entry.
Current surface modification techniques face several technical limitations. Chemical modification methods, while effective at altering surface properties, often compromise the intrinsic mechanical strength of nanocellulose fibrils through structural degradation. The high surface area of nanocellulose requires substantial quantities of modification reagents, raising concerns about process economics and environmental sustainability. Additionally, achieving uniform surface modification across all nanocellulose particles remains challenging due to accessibility issues within the hierarchical structure.
Scalability presents another significant hurdle. Laboratory-scale modification protocols frequently fail to translate effectively to industrial production environments. The complex separation and purification steps required after modification add considerable cost and complexity to manufacturing processes. Many current approaches also utilize environmentally problematic solvents and reagents, contradicting the eco-friendly premise of nanocellulose-based materials.
Characterization of modified nanocellulose surfaces poses analytical challenges. Quantifying the degree of surface substitution accurately requires sophisticated analytical techniques not readily available in production settings. The heterogeneity of nanocellulose sources further complicates standardization efforts, as modification protocols must be adapted for different nanocellulose types and morphologies.
The stability of functionalized surfaces represents an ongoing concern. Many surface modifications demonstrate limited durability under processing conditions or during the service life of the composite. Thermal degradation during high-temperature composite processing can reverse surface modifications, while moisture exposure may trigger hydrolysis of certain functional groups, compromising long-term performance.
Balancing the degree of modification presents a complex optimization problem. Excessive surface functionalization can diminish the beneficial properties of nanocellulose, while insufficient modification fails to adequately improve matrix compatibility. This delicate balance varies depending on the target matrix and desired composite properties, necessitating customized approaches rather than universal solutions.
Regulatory and safety considerations add another layer of complexity, particularly for applications in food packaging, biomedical devices, or other sensitive sectors. Novel surface modification agents must undergo rigorous safety assessments before commercial implementation, creating significant barriers to innovation and market entry.
Current Surface Functionalization Methodologies
01 Nanocellulose as adhesive matrix enhancer
Nanocellulose can be incorporated into adhesive formulations to enhance matrix properties. The unique fibrillar structure of nanocellulose provides reinforcement to adhesive matrices, improving mechanical strength and stability. When properly dispersed, nanocellulose creates a network within the adhesive that enhances cohesion while maintaining flexibility. These enhanced properties make nanocellulose-modified adhesives suitable for applications requiring strong bonding under various environmental conditions.- Nanocellulose as adhesive matrix enhancer: Nanocellulose can be incorporated into adhesive formulations to enhance matrix properties. The unique fibrillar structure of nanocellulose provides reinforcement to adhesive matrices, improving mechanical strength and stability. When properly dispersed, nanocellulose creates a network within the adhesive that enhances cohesion while maintaining flexibility. This approach results in stronger adhesive bonds with improved durability under various environmental conditions.
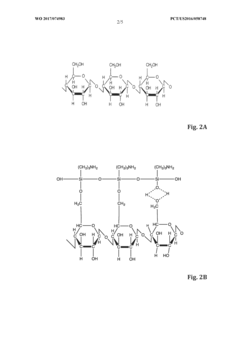
- Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved adhesion: Chemical modification of nanocellulose surfaces can significantly improve its compatibility and adhesion with various matrices. Techniques such as silylation, acetylation, or grafting of functional groups onto nanocellulose surfaces reduce hydrophilicity and enhance interfacial bonding with hydrophobic matrices. These modifications create stronger chemical interactions between the nanocellulose and surrounding matrix, resulting in improved mechanical properties and reduced moisture sensitivity in the final composite materials.
- Nanocellulose-based adhesives for biomedical applications: Nanocellulose can be formulated into biocompatible adhesives for medical and healthcare applications. These adhesives leverage nanocellulose's biocompatibility, non-toxicity, and ability to form strong hydrogel networks. When combined with other biocompatible polymers, nanocellulose creates adhesive matrices suitable for wound dressings, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery systems. The resulting adhesives provide strong tissue adhesion while supporting cellular growth and tissue regeneration.
- Nanocellulose composites with enhanced interfacial adhesion: Incorporating nanocellulose into composite materials can significantly improve interfacial adhesion between different components. The high surface area and numerous hydroxyl groups of nanocellulose facilitate strong interactions with both organic and inorganic materials. Various techniques including physical blending, in-situ polymerization, and layer-by-layer assembly can be used to optimize the distribution of nanocellulose within composite matrices, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and structural integrity.
- Processing techniques for nanocellulose matrix adhesion: Specific processing techniques can optimize nanocellulose dispersion and adhesion within various matrices. Methods such as high-pressure homogenization, ultrasonication, and specialized drying processes help prevent nanocellulose aggregation and ensure uniform distribution throughout the matrix. Additionally, controlling the pH, temperature, and ionic strength during processing can significantly impact the interfacial interactions between nanocellulose and the surrounding matrix, leading to improved adhesion properties and overall performance of the final material.
02 Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved adhesion
Chemical modification of nanocellulose surfaces can significantly improve its compatibility and adhesion with various matrix materials. Techniques such as silylation, esterification, and grafting of functional groups onto nanocellulose surfaces alter its hydrophilic nature, enhancing interfacial bonding with hydrophobic matrices. These modifications reduce aggregation tendencies and improve dispersion, resulting in stronger adhesion between nanocellulose and the surrounding matrix material.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanocellulose-based adhesives for biomedical applications
Nanocellulose matrices show excellent potential as biocompatible adhesives for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Their natural origin, biocompatibility, and tunable adhesion properties make them suitable for tissue engineering, wound dressings, and drug delivery systems. The porous structure of nanocellulose matrices allows for controlled release of active ingredients while providing adhesion to biological tissues. These adhesives can be formulated to have varying degrees of strength and degradability depending on the specific biomedical application.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanocellulose composite adhesives with enhanced properties
Combining nanocellulose with other materials creates composite adhesives with synergistic properties. Nanocellulose can be incorporated with synthetic polymers, natural resins, or inorganic particles to develop adhesives with enhanced strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance. These composite formulations often demonstrate improved thermal stability, moisture resistance, and adhesion strength compared to conventional adhesives. The versatility of these composites allows for customization to meet specific application requirements across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing techniques for optimizing nanocellulose matrix adhesion
Various processing methods can optimize the adhesion properties of nanocellulose matrices. Techniques such as freeze-drying, solvent exchange, and mechanical dispersion affect the morphology and surface characteristics of nanocellulose, directly influencing its adhesion behavior. Controlling the drying conditions and dispersion state of nanocellulose suspensions is crucial for developing adhesives with consistent performance. Advanced processing approaches can create hierarchical structures within nanocellulose matrices that enhance mechanical interlocking with substrate surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Nanocellulose Research and Development
Surface functionalization of nanocellulose for improved matrix adhesion is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding as sustainable materials gain prominence. The global market is projected to reach significant scale as industries seek eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic reinforcements. Technologically, this field is advancing rapidly with varying degrees of maturity across applications. Leading research institutions like Donghua University, Brown University, and North Carolina State University are pioneering fundamental research, while companies such as UPM-Kymmene, Valmet Technologies, and VTT are developing commercial applications. Empa and Max Planck Society are advancing characterization techniques, while industrial players like Kao Corp. are exploring consumer product applications, creating a diverse competitive landscape spanning academic research to commercial implementation.
UPM-Kymmene Oyj
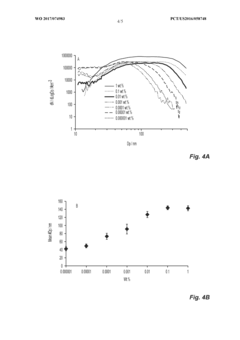
Technical Solution: UPM has developed proprietary GrowDex® and FibDex® technologies based on functionalized nanocellulose for biomedical and composite applications. Their surface functionalization approach focuses on controlled esterification and silylation processes that modify the hydroxyl groups on nanocellulose surfaces to create strong covalent bonds with matrix materials. UPM's technology enables precise control over the degree of surface substitution, allowing customization of hydrophobicity and reactivity for specific matrix compatibility requirements. Their industrial-scale production methods incorporate environmentally friendly reagents and processes that maintain the structural integrity of nanocellulose while introducing functional groups. UPM has demonstrated that their functionalized nanocellulose can improve interfacial adhesion in polylactic acid (PLA) composites by up to 60%, resulting in significantly enhanced mechanical properties and reduced moisture sensitivity in the final products.
Strengths: Vertically integrated production from forest resources to functionalized nanocellulose products; established commercial-scale manufacturing capabilities with consistent quality control. Weaknesses: Their functionalization technologies may be optimized primarily for their own product lines, potentially limiting versatility across diverse application fields.
Eidgenössische Materialprüfungs & Forschungsanstalt Empa
Technical Solution: Empa has pioneered innovative approaches to nanocellulose surface functionalization focusing on sustainable chemistry principles. Their research has developed plasma-assisted surface modification techniques that create reactive sites on nanocellulose surfaces without using wet chemistry, significantly reducing environmental impact. Empa's scientists have successfully implemented click chemistry approaches for nanocellulose functionalization, enabling precise attachment of functional molecules that enhance matrix compatibility. Their work demonstrates that controlled surface charge modification through polyelectrolyte adsorption can improve dispersion stability and interfacial adhesion in various polymer matrices. Empa has also developed bio-inspired functionalization strategies that mimic natural adhesion mechanisms, such as incorporating catechol groups inspired by mussel adhesive proteins, which have shown exceptional bonding strength at the nanocellulose-matrix interface even under wet conditions. Their research indicates that these functionalized nanocellulose materials can improve composite strength by 30-50% compared to conventional reinforcement approaches.
Strengths: Cutting-edge research combining fundamental science with practical applications; strong focus on environmentally friendly functionalization methods with reduced chemical usage. Weaknesses: Some of their more advanced techniques may face challenges in scaling to industrial production volumes cost-effectively.
Critical Patents and Literature on Nanocellulose-Matrix Interfaces
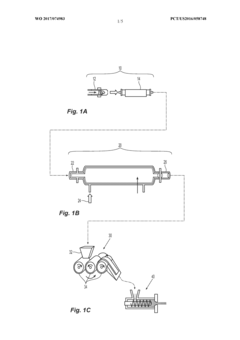
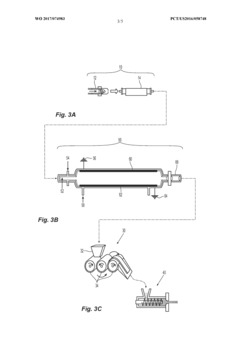
Method for preparing modified nanocrystalline cellulose
PatentActiveUS20190055324A1
Innovation
- A method involving the aerosolization of cellulose nanoparticles and their functionalization with silanes or reactive gas radicals in flow reactors to produce compatible and environmentally friendly nanocomposites, which can be combined with various polymers to form high-performance composites.
Method for preparing modified nanocrystalline cellulose
PatentWO2017074983A1
Innovation
- A method for producing modified nanocrystalline cellulose by aerosolizing cellulose nanoparticles and functionalizing them with silanes or reactive gas radicals in flow reactors, allowing for scalable and environmentally friendly surface modification, enabling compatibility with various polymer matrices.
Sustainability Aspects of Nanocellulose Functionalization
The sustainability aspects of nanocellulose functionalization represent a critical dimension in the advancement of this technology for improved matrix adhesion applications. Nanocellulose, derived from renewable biomass sources, inherently possesses environmental advantages over petroleum-based alternatives. However, the sustainability profile becomes more complex when considering the various functionalization methods employed to enhance matrix compatibility.
Chemical modification processes often involve solvents, reagents, and catalysts that may present environmental concerns. Traditional functionalization approaches utilizing chlorinated compounds, strong acids, or toxic coupling agents can generate hazardous waste streams and consume significant energy resources. Recent research has pivoted toward greener functionalization pathways, including enzyme-mediated modifications, aqueous-based reactions, and solvent-free mechanochemical processes that substantially reduce environmental impact.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing functionalized nanocellulose composites with conventional materials demonstrate significant reductions in carbon footprint, particularly when bio-based functionalization agents are employed. The cradle-to-grave analysis reveals that properly designed functionalization protocols can maintain the inherent sustainability benefits of nanocellulose while achieving the desired matrix adhesion properties.
Energy consumption during functionalization represents another sustainability consideration. Conventional chemical treatments often require elevated temperatures and extended reaction times, whereas emerging technologies like microwave-assisted or ultrasound-enhanced functionalization can reduce energy requirements by up to 60%. These energy-efficient approaches not only improve the environmental profile but also enhance economic viability for industrial-scale implementation.
Water usage and effluent management constitute important sustainability metrics for nanocellulose functionalization. Surface modification techniques that minimize water consumption or enable water recycling are gaining prominence. Closed-loop systems that recover and reuse process chemicals further enhance sustainability credentials while reducing operational costs.
Biodegradability and end-of-life considerations must also be evaluated when assessing functionalized nanocellulose sustainability. Certain functionalization approaches may introduce non-biodegradable elements or impede natural decomposition pathways. Research indicates that carefully selected bio-based coupling agents and environmentally benign surface treatments can preserve the biodegradability of nanocellulose while achieving the desired interfacial adhesion properties.
The economic dimension of sustainability cannot be overlooked. Cost-effective functionalization methods that reduce energy inputs, minimize waste generation, and utilize renewable reagents contribute to both environmental and economic sustainability. This holistic approach ensures that functionalized nanocellulose solutions remain commercially viable while delivering environmental benefits across their entire lifecycle.
Chemical modification processes often involve solvents, reagents, and catalysts that may present environmental concerns. Traditional functionalization approaches utilizing chlorinated compounds, strong acids, or toxic coupling agents can generate hazardous waste streams and consume significant energy resources. Recent research has pivoted toward greener functionalization pathways, including enzyme-mediated modifications, aqueous-based reactions, and solvent-free mechanochemical processes that substantially reduce environmental impact.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing functionalized nanocellulose composites with conventional materials demonstrate significant reductions in carbon footprint, particularly when bio-based functionalization agents are employed. The cradle-to-grave analysis reveals that properly designed functionalization protocols can maintain the inherent sustainability benefits of nanocellulose while achieving the desired matrix adhesion properties.
Energy consumption during functionalization represents another sustainability consideration. Conventional chemical treatments often require elevated temperatures and extended reaction times, whereas emerging technologies like microwave-assisted or ultrasound-enhanced functionalization can reduce energy requirements by up to 60%. These energy-efficient approaches not only improve the environmental profile but also enhance economic viability for industrial-scale implementation.
Water usage and effluent management constitute important sustainability metrics for nanocellulose functionalization. Surface modification techniques that minimize water consumption or enable water recycling are gaining prominence. Closed-loop systems that recover and reuse process chemicals further enhance sustainability credentials while reducing operational costs.
Biodegradability and end-of-life considerations must also be evaluated when assessing functionalized nanocellulose sustainability. Certain functionalization approaches may introduce non-biodegradable elements or impede natural decomposition pathways. Research indicates that carefully selected bio-based coupling agents and environmentally benign surface treatments can preserve the biodegradability of nanocellulose while achieving the desired interfacial adhesion properties.
The economic dimension of sustainability cannot be overlooked. Cost-effective functionalization methods that reduce energy inputs, minimize waste generation, and utilize renewable reagents contribute to both environmental and economic sustainability. This holistic approach ensures that functionalized nanocellulose solutions remain commercially viable while delivering environmental benefits across their entire lifecycle.
Scalability and Industrial Implementation Challenges
The transition from laboratory-scale surface functionalization of nanocellulose to industrial implementation presents significant challenges that must be addressed for commercial viability. Current laboratory methods typically involve batch processing with small quantities, utilizing precise control over reaction conditions and extensive purification steps. These approaches, while effective for research purposes, face substantial hurdles when scaled to industrial volumes where cost-efficiency, consistency, and throughput become paramount considerations.
One primary challenge is the development of continuous processing methods that can handle large volumes of nanocellulose while maintaining uniform surface modification. Traditional batch reactors used in laboratories cannot efficiently process the quantities required for commercial applications. Continuous flow reactors and specialized mixing technologies need further development to ensure homogeneous functionalization across all nanocellulose particles without agglomeration or inconsistent treatment.
Chemical consumption represents another critical barrier to industrial implementation. Laboratory-scale functionalization often employs excess reagents to ensure complete surface coverage, a practice economically unsustainable at industrial scale. Optimization of reagent usage, recycling of chemicals, and development of more efficient coupling agents are essential for cost-effective production. Additionally, the environmental impact of chemical waste streams must be minimized through closed-loop systems and green chemistry approaches.
Energy requirements for processing present further complications, particularly for water removal and drying steps that are energy-intensive yet crucial for certain functionalization pathways. Innovative drying technologies and process intensification methods are needed to reduce energy consumption while maintaining product quality. Alternative approaches that can operate in high-consistency conditions could significantly improve energy efficiency.
Quality control and characterization at industrial scale pose unique challenges compared to laboratory settings. Rapid, inline analytical methods must be developed to monitor functionalization degree, surface coverage uniformity, and product consistency during continuous production. Current analytical techniques often require specialized equipment and significant sample preparation, making them impractical for real-time industrial monitoring.
Regulatory considerations and standardization also impact industrial implementation. The lack of established standards for functionalized nanocellulose products creates uncertainty for manufacturers and end-users. Development of industry-wide specifications and testing protocols is necessary to facilitate market acceptance and ensure consistent performance across different production batches and suppliers.
One primary challenge is the development of continuous processing methods that can handle large volumes of nanocellulose while maintaining uniform surface modification. Traditional batch reactors used in laboratories cannot efficiently process the quantities required for commercial applications. Continuous flow reactors and specialized mixing technologies need further development to ensure homogeneous functionalization across all nanocellulose particles without agglomeration or inconsistent treatment.
Chemical consumption represents another critical barrier to industrial implementation. Laboratory-scale functionalization often employs excess reagents to ensure complete surface coverage, a practice economically unsustainable at industrial scale. Optimization of reagent usage, recycling of chemicals, and development of more efficient coupling agents are essential for cost-effective production. Additionally, the environmental impact of chemical waste streams must be minimized through closed-loop systems and green chemistry approaches.
Energy requirements for processing present further complications, particularly for water removal and drying steps that are energy-intensive yet crucial for certain functionalization pathways. Innovative drying technologies and process intensification methods are needed to reduce energy consumption while maintaining product quality. Alternative approaches that can operate in high-consistency conditions could significantly improve energy efficiency.
Quality control and characterization at industrial scale pose unique challenges compared to laboratory settings. Rapid, inline analytical methods must be developed to monitor functionalization degree, surface coverage uniformity, and product consistency during continuous production. Current analytical techniques often require specialized equipment and significant sample preparation, making them impractical for real-time industrial monitoring.
Regulatory considerations and standardization also impact industrial implementation. The lack of established standards for functionalized nanocellulose products creates uncertainty for manufacturers and end-users. Development of industry-wide specifications and testing protocols is necessary to facilitate market acceptance and ensure consistent performance across different production batches and suppliers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!