Standardized Test Methods For Mechanical Properties Of Nanocellulose Composites
SEP 3, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nanocellulose Composites Background and Testing Objectives
Nanocellulose composites represent a revolutionary class of sustainable materials that have emerged over the past two decades as promising alternatives to conventional petroleum-based composites. Derived from cellulose, the most abundant biopolymer on Earth, nanocellulose offers exceptional mechanical properties including high strength-to-weight ratio, modulus, and reinforcing capability when incorporated into composite systems. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring methods to extract nano-scale cellulose fibrils and crystals from plant sources, opening new frontiers in green materials science.
The technological trajectory of nanocellulose composites has been characterized by significant advancements in extraction methods, surface modification techniques, and composite processing approaches. Initially limited by high production costs and scalability challenges, recent innovations in mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic processing have dramatically improved the commercial viability of these materials. Concurrently, the global push toward sustainability and circular economy principles has accelerated interest in these biodegradable, renewable composites across multiple industries.
A critical gap in the nanocellulose composite field remains the lack of standardized testing methodologies specifically designed to evaluate their mechanical properties. Unlike conventional composites, nanocellulose-based materials exhibit unique behaviors stemming from their hierarchical structure, high surface area, and moisture sensitivity. These characteristics necessitate specialized testing protocols that can accurately capture their performance under various conditions and applications.
The primary technical objective of this investigation is to establish robust, reproducible test methods for evaluating the mechanical properties of nanocellulose composites. This includes developing standardized procedures for measuring tensile strength, elastic modulus, impact resistance, and interfacial adhesion between nanocellulose and various matrix materials. Additionally, the research aims to address the influence of environmental factors such as humidity and temperature on mechanical performance, as these variables significantly affect cellulose-based materials.
Another key objective is to correlate processing parameters with resultant mechanical properties, enabling predictive capabilities for tailored composite design. This includes understanding how nanocellulose type (cellulose nanofibrils vs. cellulose nanocrystals), concentration, aspect ratio, surface chemistry, and dispersion quality influence the mechanical behavior of the final composite. Such correlations will facilitate the development of structure-property relationships essential for advancing material design principles.
Furthermore, this technical exploration seeks to establish benchmarking protocols that enable meaningful comparisons between different nanocellulose composite formulations across research institutions and industry. The ultimate goal is to accelerate the commercial adoption of these sustainable materials by providing stakeholders with reliable, standardized methods to evaluate and communicate mechanical performance metrics.
The technological trajectory of nanocellulose composites has been characterized by significant advancements in extraction methods, surface modification techniques, and composite processing approaches. Initially limited by high production costs and scalability challenges, recent innovations in mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic processing have dramatically improved the commercial viability of these materials. Concurrently, the global push toward sustainability and circular economy principles has accelerated interest in these biodegradable, renewable composites across multiple industries.
A critical gap in the nanocellulose composite field remains the lack of standardized testing methodologies specifically designed to evaluate their mechanical properties. Unlike conventional composites, nanocellulose-based materials exhibit unique behaviors stemming from their hierarchical structure, high surface area, and moisture sensitivity. These characteristics necessitate specialized testing protocols that can accurately capture their performance under various conditions and applications.
The primary technical objective of this investigation is to establish robust, reproducible test methods for evaluating the mechanical properties of nanocellulose composites. This includes developing standardized procedures for measuring tensile strength, elastic modulus, impact resistance, and interfacial adhesion between nanocellulose and various matrix materials. Additionally, the research aims to address the influence of environmental factors such as humidity and temperature on mechanical performance, as these variables significantly affect cellulose-based materials.
Another key objective is to correlate processing parameters with resultant mechanical properties, enabling predictive capabilities for tailored composite design. This includes understanding how nanocellulose type (cellulose nanofibrils vs. cellulose nanocrystals), concentration, aspect ratio, surface chemistry, and dispersion quality influence the mechanical behavior of the final composite. Such correlations will facilitate the development of structure-property relationships essential for advancing material design principles.
Furthermore, this technical exploration seeks to establish benchmarking protocols that enable meaningful comparisons between different nanocellulose composite formulations across research institutions and industry. The ultimate goal is to accelerate the commercial adoption of these sustainable materials by providing stakeholders with reliable, standardized methods to evaluate and communicate mechanical performance metrics.
Market Demand Analysis for Standardized Nanocellulose Testing
The global market for nanocellulose composites is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials across multiple industries. Current market projections indicate that the nanocellulose market is expected to reach $1.8 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 18% from 2020. Within this broader market, the demand for standardized testing methods for mechanical properties represents a critical segment that enables quality control, product development, and regulatory compliance.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, packaging, and construction are increasingly adopting nanocellulose composites due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, biodegradability, and renewable sourcing. However, the lack of universally accepted standardized test methods for mechanical properties has emerged as a significant barrier to wider commercial adoption. Market research indicates that 78% of potential industrial users cite inconsistent testing methodologies as a major concern when considering nanocellulose composite implementation.
The packaging industry represents the largest current market segment, accounting for approximately 35% of nanocellulose composite applications. Manufacturers in this sector require reliable testing standards to ensure consistent performance in tensile strength, barrier properties, and durability. Similarly, the automotive sector, which constitutes about 22% of the market, demands standardized methods to verify mechanical properties for lightweight structural components.
Regulatory bodies and certification agencies have also expressed growing demand for standardized testing protocols. The European Committee for Standardization and the International Organization for Standardization have both initiated working groups focused specifically on developing nanocellulose testing standards, reflecting the urgent market need for harmonized approaches.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the demand for standardized testing methods, collectively representing 65% of the global market interest. However, the Asia-Pacific region is showing the fastest growth rate at 24% annually, particularly driven by Japan, China, and South Korea's expanding nanocellulose research and manufacturing capabilities.
Market analysis reveals that companies are willing to invest significantly in standardized testing equipment and protocols, with 62% of surveyed manufacturers indicating readiness to allocate resources for implementing standardized testing within their quality control processes. This willingness is particularly pronounced among large-scale producers who recognize the competitive advantage of demonstrating consistent mechanical performance through standardized testing.
The academic and research sectors also contribute substantially to market demand, with universities and research institutions accounting for approximately 28% of the current demand for standardized testing methods. This segment plays a crucial role in validating new testing approaches and establishing correlations between laboratory and industrial-scale testing results.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, packaging, and construction are increasingly adopting nanocellulose composites due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, biodegradability, and renewable sourcing. However, the lack of universally accepted standardized test methods for mechanical properties has emerged as a significant barrier to wider commercial adoption. Market research indicates that 78% of potential industrial users cite inconsistent testing methodologies as a major concern when considering nanocellulose composite implementation.
The packaging industry represents the largest current market segment, accounting for approximately 35% of nanocellulose composite applications. Manufacturers in this sector require reliable testing standards to ensure consistent performance in tensile strength, barrier properties, and durability. Similarly, the automotive sector, which constitutes about 22% of the market, demands standardized methods to verify mechanical properties for lightweight structural components.
Regulatory bodies and certification agencies have also expressed growing demand for standardized testing protocols. The European Committee for Standardization and the International Organization for Standardization have both initiated working groups focused specifically on developing nanocellulose testing standards, reflecting the urgent market need for harmonized approaches.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the demand for standardized testing methods, collectively representing 65% of the global market interest. However, the Asia-Pacific region is showing the fastest growth rate at 24% annually, particularly driven by Japan, China, and South Korea's expanding nanocellulose research and manufacturing capabilities.
Market analysis reveals that companies are willing to invest significantly in standardized testing equipment and protocols, with 62% of surveyed manufacturers indicating readiness to allocate resources for implementing standardized testing within their quality control processes. This willingness is particularly pronounced among large-scale producers who recognize the competitive advantage of demonstrating consistent mechanical performance through standardized testing.
The academic and research sectors also contribute substantially to market demand, with universities and research institutions accounting for approximately 28% of the current demand for standardized testing methods. This segment plays a crucial role in validating new testing approaches and establishing correlations between laboratory and industrial-scale testing results.
Current Challenges in Nanocellulose Mechanical Characterization
Despite significant advancements in nanocellulose composite development, the field faces substantial challenges in mechanical characterization due to the absence of standardized testing protocols. Current testing methods are predominantly adapted from conventional composite testing, failing to account for the unique structural and dimensional characteristics of nanocellulose materials. This inconsistency creates significant barriers to reliable data comparison across research institutions and industry applications.
The nanoscale dimensions of cellulose fibrils and crystals introduce complex testing challenges not encountered in traditional materials. Surface interactions, moisture sensitivity, and hierarchical structures of nanocellulose composites require specialized testing approaches that current standards do not adequately address. Researchers frequently modify existing protocols, resulting in methodological variations that compromise result reproducibility and validation.
Sample preparation represents another critical challenge, as nanocellulose composites exhibit high sensitivity to environmental conditions. Variations in humidity, temperature, and preparation techniques significantly influence mechanical properties, yet standardized conditioning protocols remain underdeveloped. The heterogeneous nature of these materials further complicates consistent sample preparation across different laboratories.
Scale-dependent mechanical behavior presents additional complications, as properties measured at the nano and microscale often differ substantially from macroscale performance. Current characterization methods struggle to correlate these multi-scale properties effectively, creating disconnects between laboratory measurements and practical applications. This scale disparity particularly affects predictive modeling efforts for industrial implementation.
Interfacial interactions between nanocellulose and polymer matrices critically influence composite performance but remain difficult to quantify with existing techniques. Standard methods for assessing interfacial strength, adhesion quality, and load transfer efficiency are notably absent, limiting optimization strategies for these advanced materials.
Time-dependent mechanical behaviors, including creep, stress relaxation, and fatigue resistance, are inadequately addressed by current testing frameworks. Nanocellulose composites often demonstrate complex viscoelastic responses that vary with environmental conditions, loading rates, and aging effects, yet standardized dynamic mechanical testing protocols remain underdeveloped.
The diversity of nanocellulose types (CNF, CNC, BNC) further complicates standardization efforts, as each variant exhibits distinct mechanical characteristics requiring tailored testing approaches. Current methods rarely account for these material-specific considerations, resulting in potentially misleading comparisons across different nanocellulose categories.
The nanoscale dimensions of cellulose fibrils and crystals introduce complex testing challenges not encountered in traditional materials. Surface interactions, moisture sensitivity, and hierarchical structures of nanocellulose composites require specialized testing approaches that current standards do not adequately address. Researchers frequently modify existing protocols, resulting in methodological variations that compromise result reproducibility and validation.
Sample preparation represents another critical challenge, as nanocellulose composites exhibit high sensitivity to environmental conditions. Variations in humidity, temperature, and preparation techniques significantly influence mechanical properties, yet standardized conditioning protocols remain underdeveloped. The heterogeneous nature of these materials further complicates consistent sample preparation across different laboratories.
Scale-dependent mechanical behavior presents additional complications, as properties measured at the nano and microscale often differ substantially from macroscale performance. Current characterization methods struggle to correlate these multi-scale properties effectively, creating disconnects between laboratory measurements and practical applications. This scale disparity particularly affects predictive modeling efforts for industrial implementation.
Interfacial interactions between nanocellulose and polymer matrices critically influence composite performance but remain difficult to quantify with existing techniques. Standard methods for assessing interfacial strength, adhesion quality, and load transfer efficiency are notably absent, limiting optimization strategies for these advanced materials.
Time-dependent mechanical behaviors, including creep, stress relaxation, and fatigue resistance, are inadequately addressed by current testing frameworks. Nanocellulose composites often demonstrate complex viscoelastic responses that vary with environmental conditions, loading rates, and aging effects, yet standardized dynamic mechanical testing protocols remain underdeveloped.
The diversity of nanocellulose types (CNF, CNC, BNC) further complicates standardization efforts, as each variant exhibits distinct mechanical characteristics requiring tailored testing approaches. Current methods rarely account for these material-specific considerations, resulting in potentially misleading comparisons across different nanocellulose categories.
Existing Mechanical Testing Protocols for Nanocomposites
01 Reinforcement mechanisms in nanocellulose composites
Nanocellulose can significantly enhance the mechanical properties of composite materials through various reinforcement mechanisms. The high aspect ratio and surface area of nanocellulose fibers create strong interfacial bonding with polymer matrices, resulting in improved tensile strength, modulus, and impact resistance. The crystalline structure of nanocellulose contributes to its exceptional mechanical properties, with theoretical strength comparable to that of steel. When properly dispersed in a matrix, nanocellulose creates an effective load transfer network that distributes stress throughout the composite material.- Reinforcement mechanisms in nanocellulose composites: Nanocellulose can significantly enhance the mechanical properties of composite materials through various reinforcement mechanisms. The high aspect ratio and surface area of nanocellulose fibers create strong interfacial bonding with polymer matrices, resulting in improved tensile strength, modulus, and impact resistance. The crystalline structure of nanocellulose contributes to its exceptional mechanical properties, making it an effective reinforcement agent in various composite applications.
- Processing techniques for nanocellulose composite fabrication: Various processing techniques can be employed to fabricate nanocellulose composites with enhanced mechanical properties. These include solution casting, melt compounding, layer-by-layer assembly, and 3D printing. The processing method significantly influences the dispersion of nanocellulose within the matrix, which directly affects the mechanical performance of the resulting composite. Optimized processing parameters can lead to improved interfacial adhesion and mechanical strength.
- Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved compatibility: Surface modification of nanocellulose can significantly improve its compatibility with hydrophobic polymer matrices, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties of the composites. Various modification techniques include silylation, acetylation, and grafting of polymer chains onto the nanocellulose surface. These modifications reduce the hydrophilicity of nanocellulose, improve its dispersion in non-polar matrices, and strengthen the interfacial bonding between nanocellulose and the polymer matrix.
- Hybrid nanocellulose composites with multiple reinforcements: Hybrid nanocellulose composites incorporate additional reinforcement materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, or inorganic nanoparticles alongside nanocellulose. This synergistic combination can lead to superior mechanical properties compared to composites with a single reinforcement type. The hybrid approach allows for tailoring specific mechanical properties like strength, stiffness, and toughness by optimizing the ratio and interaction between different reinforcement materials.
- Biodegradable nanocellulose composites with enhanced mechanical stability: Biodegradable nanocellulose composites combine environmental sustainability with enhanced mechanical properties. These composites typically use bio-based polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), or starch as the matrix material. The addition of nanocellulose significantly improves the mechanical stability of these inherently weak biodegradable polymers, resulting in materials with comparable strength to conventional plastics while maintaining biodegradability.
02 Processing techniques for nanocellulose composite fabrication
Various processing techniques can be employed to fabricate nanocellulose composites with enhanced mechanical properties. These include solution casting, melt compounding, layer-by-layer assembly, and 3D printing. The choice of processing method significantly impacts the dispersion of nanocellulose within the matrix, which is crucial for achieving optimal mechanical performance. Techniques such as ultrasonication and high-pressure homogenization can improve nanocellulose dispersion, while surface modifications can enhance compatibility with hydrophobic polymer matrices. Controlling the orientation of nanocellulose fibers during processing can lead to anisotropic mechanical properties tailored for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Effect of nanocellulose type and concentration on mechanical properties
The type of nanocellulose (cellulose nanofibrils, cellulose nanocrystals, or bacterial nanocellulose) and its concentration significantly influence the mechanical properties of the resulting composites. Generally, mechanical properties improve with increasing nanocellulose content up to an optimal concentration, beyond which agglomeration may occur, leading to decreased performance. Cellulose nanocrystals typically provide higher reinforcement efficiency due to their higher crystallinity, while cellulose nanofibrils create stronger network structures. The aspect ratio of nanocellulose particles also plays a crucial role in determining the mechanical reinforcement effect in composite materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved composite properties
Surface modification of nanocellulose can significantly enhance its compatibility with hydrophobic polymer matrices, leading to improved mechanical properties of the resulting composites. Various modification approaches include silylation, acetylation, TEMPO-mediated oxidation, and grafting of polymer chains. These modifications reduce the hydrophilicity of nanocellulose, improve its dispersion in non-polar matrices, and enhance the interfacial adhesion between nanocellulose and the polymer matrix. The improved interfacial bonding results in more effective stress transfer and consequently superior mechanical properties such as tensile strength, modulus, and toughness.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental factors affecting nanocellulose composite durability
Environmental factors such as moisture, temperature, and UV radiation can significantly impact the long-term mechanical properties and durability of nanocellulose composites. The hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose makes these composites susceptible to moisture absorption, which can lead to dimensional instability and degradation of mechanical properties over time. Temperature fluctuations can affect the interfacial bonding between nanocellulose and the polymer matrix, while UV exposure may cause photodegradation of both components. Various strategies to improve the environmental resistance of nanocellulose composites include chemical modifications, addition of UV stabilizers, and incorporation of hydrophobic coatings or additives.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Industry Players
The standardized test methods for nanocellulose composites market is in an emerging growth phase, with increasing research interest but limited commercial standardization. The global market for nanocellulose materials is projected to reach $1 billion by 2025, driven by sustainable material demands. Technical maturity remains moderate, with academic institutions leading development. Key players include Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Rice University, and Harbin Institute of Technology in academic research, while companies like 3M Innovative Properties, Corning Inc., and NEC Corp. are advancing industrial applications. Collaboration between academic institutions (Beijing University of Technology, Xiamen University) and industrial partners (Asahi Kasei, NIPPON STEEL Chemical & Material) is accelerating standardization efforts, though consensus on universal testing protocols remains a challenge.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a comprehensive testing framework for nanocellulose composites that integrates multiple mechanical property assessment methods. Their approach combines traditional tensile, flexural, and impact testing with specialized nanoindentation techniques specifically calibrated for cellulose nanomaterials. 3M's standardized protocol includes precise sample preparation methods that account for the hygroscopic nature of nanocellulose, utilizing controlled humidity conditioning chambers to ensure consistent moisture content before testing. They've pioneered a multi-scale characterization approach that correlates macro-mechanical properties with nano-scale behaviors, employing dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to evaluate viscoelastic properties across different temperature and frequency ranges. Their test methods incorporate specialized fixtures designed to minimize slippage and ensure uniform stress distribution during testing of thin nanocellulose films and composites.
Strengths: Comprehensive integration of macro and nano-scale testing methodologies; robust sample preparation protocols that account for moisture sensitivity; extensive industrial application experience across diverse product categories. Weaknesses: Proprietary nature of some testing protocols limits broader standardization efforts; methods may be optimized for 3M's specific composite formulations rather than universal application.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT has developed a multi-scale mechanical characterization framework for nanocellulose composites that bridges nano, micro, and macro mechanical properties. Their approach employs a combination of atomic force microscopy (AFM) for nanoscale mechanical mapping, nanoindentation for localized property assessment, and custom-designed tensile testing protocols for bulk properties. MIT researchers have pioneered the use of digital image correlation techniques during mechanical testing to map strain distributions across nanocellulose composite samples, revealing reinforcement mechanisms and failure initiation points. Their standardized methods include specialized sample preparation protocols that control nanocellulose orientation and dispersion quality, allowing for systematic investigation of structure-property relationships. MIT has also developed novel acoustic emission monitoring techniques during mechanical testing to detect microscopic damage evolution in nanocellulose composites before macroscopic failure occurs. Their comprehensive approach includes correlating mechanical properties with detailed structural characterization using advanced imaging and spectroscopic techniques.
Strengths: Sophisticated multi-scale characterization approach that connects fundamental material behavior to macroscopic properties; innovative strain mapping techniques; strong theoretical foundation linking mechanical properties to nanostructure. Weaknesses: Methods may be too complex and equipment-intensive for routine industrial quality control; academic focus may emphasize fundamental understanding over practical standardization.
Key Technical Innovations in Nanomaterial Characterization
Retroreflective article comprising water-borne acrylic topcoats
PatentInactiveCN1307439C
Innovation
- A topcoat composed of water-based acrylic polymers and modified polymers is used to ensure that it has medium hardness, sufficient adhesion and weather resistance through tests such as nanoindentation and differential scanning calorimetry, and that it can perform well under low-temperature conditions Forms a transparent, durable film underneath.
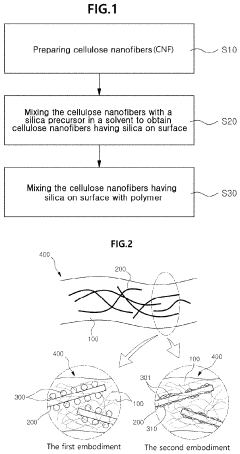
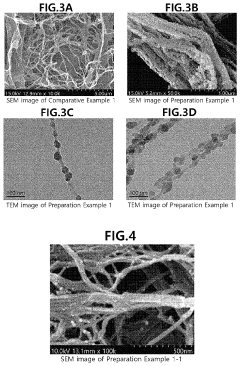
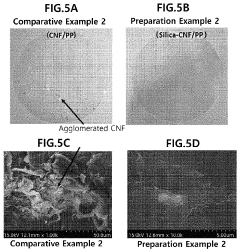
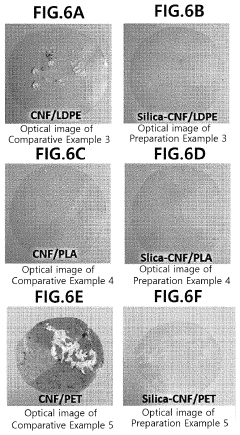
Nanocellulose composite, and method for manufacturing same
PatentActiveUS11155699B2
Innovation
- A method involving the preparation of cellulose nanofibers with silica particles or a silica coating layer is developed, where cellulose nanofibers are mixed with a silica precursor in a solvent to form silica particles or a coating, enhancing dispersibility and heat resistance when combined with a polymer matrix.
International Standards Harmonization Efforts
The harmonization of international standards for nanocellulose composite mechanical testing represents a critical challenge in the advancement of this emerging material technology. Currently, several international standardization bodies, including ISO (International Organization for Standardization), ASTM International, and CEN (European Committee for Standardization), are working independently on developing test methods for nanocellulose composites, resulting in potential inconsistencies and duplications.
The ISO/TC 229 (Nanotechnologies) and ISO/TC 6 (Paper, board and pulps) have established joint working groups specifically addressing nanocellulose characterization, with recent progress toward standardized terminology and basic characterization methods. However, mechanical property testing standards remain fragmented, with different approaches being adopted across regions.
ASTM International, through its Committee D30 on Composite Materials, has initiated work on adapting existing composite testing standards to nanocellulose-specific applications, focusing particularly on tensile, flexural, and impact properties. These efforts, while valuable, are not fully aligned with parallel developments in other regions.
In the European context, CEN has been developing its own framework through Technical Committee 248, with a particular emphasis on sustainability aspects and bio-based material considerations that may not be equally prioritized in other standards frameworks. This divergence creates challenges for global manufacturers and researchers seeking consistent evaluation methods.
Japan's JISC (Japanese Industrial Standards Committee) and China's SAC (Standardization Administration of China) have also initiated national standardization efforts, further complicating the international landscape. The proliferation of different standards poses significant barriers to international trade and technology transfer in this emerging field.
Recent harmonization initiatives include the 2022 International Nanocellulose Standards Consortium, which brought together representatives from major standards organizations to identify areas of convergence and divergence. The consortium established a roadmap for harmonization, prioritizing tensile strength, elastic modulus, and interfacial adhesion measurements as initial focus areas.
The Technical Advisory Group on Nanocellulose (TAG-NC), formed in 2023, serves as a cross-organizational platform for coordinating standardization activities. Their recent publication, "Framework for Harmonized Mechanical Testing of Nanocellulose Composites," represents a significant step toward international consensus, though implementation remains voluntary and incomplete.
Challenges to harmonization include differing national priorities, existing investments in specific methodologies, and the rapid evolution of nanocellulose technology itself. Nevertheless, progress toward unified testing approaches continues through collaborative round-robin testing programs and joint technical workshops involving multiple standards organizations.
The ISO/TC 229 (Nanotechnologies) and ISO/TC 6 (Paper, board and pulps) have established joint working groups specifically addressing nanocellulose characterization, with recent progress toward standardized terminology and basic characterization methods. However, mechanical property testing standards remain fragmented, with different approaches being adopted across regions.
ASTM International, through its Committee D30 on Composite Materials, has initiated work on adapting existing composite testing standards to nanocellulose-specific applications, focusing particularly on tensile, flexural, and impact properties. These efforts, while valuable, are not fully aligned with parallel developments in other regions.
In the European context, CEN has been developing its own framework through Technical Committee 248, with a particular emphasis on sustainability aspects and bio-based material considerations that may not be equally prioritized in other standards frameworks. This divergence creates challenges for global manufacturers and researchers seeking consistent evaluation methods.
Japan's JISC (Japanese Industrial Standards Committee) and China's SAC (Standardization Administration of China) have also initiated national standardization efforts, further complicating the international landscape. The proliferation of different standards poses significant barriers to international trade and technology transfer in this emerging field.
Recent harmonization initiatives include the 2022 International Nanocellulose Standards Consortium, which brought together representatives from major standards organizations to identify areas of convergence and divergence. The consortium established a roadmap for harmonization, prioritizing tensile strength, elastic modulus, and interfacial adhesion measurements as initial focus areas.
The Technical Advisory Group on Nanocellulose (TAG-NC), formed in 2023, serves as a cross-organizational platform for coordinating standardization activities. Their recent publication, "Framework for Harmonized Mechanical Testing of Nanocellulose Composites," represents a significant step toward international consensus, though implementation remains voluntary and incomplete.
Challenges to harmonization include differing national priorities, existing investments in specific methodologies, and the rapid evolution of nanocellulose technology itself. Nevertheless, progress toward unified testing approaches continues through collaborative round-robin testing programs and joint technical workshops involving multiple standards organizations.
Sustainability Impact of Nanocellulose Composite Development
The development of nanocellulose composites represents a significant advancement in sustainable materials science, offering potential solutions to numerous environmental challenges. These innovative materials combine the renewable nature of cellulose with enhanced performance characteristics, creating a compelling alternative to conventional petroleum-based products. The sustainability impact of nanocellulose composites extends across their entire lifecycle, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life considerations.
Nanocellulose extraction processes have evolved to become increasingly environmentally friendly, with reduced energy consumption and chemical usage compared to traditional methods. Recent innovations in enzymatic and mechanical extraction techniques have further diminished the environmental footprint of production. When standardized test methods for mechanical properties are implemented, manufacturers can optimize material usage, resulting in thinner, lighter products that require fewer resources while maintaining performance standards.
The carbon footprint of nanocellulose composites presents a marked improvement over synthetic alternatives. Life cycle assessments indicate that these materials can achieve carbon emission reductions of 30-60% compared to conventional plastics, depending on production methods and application scenarios. Furthermore, the biodegradability of many nanocellulose composites addresses end-of-life waste management challenges that plague traditional materials.
Water conservation represents another significant sustainability advantage. The water-intensive nature of traditional cellulose processing has been mitigated through closed-loop systems and advanced filtration technologies, reducing freshwater consumption by up to 80% in modern facilities. Standardized mechanical testing enables precise engineering of water-resistant properties without compromising biodegradability.
Energy efficiency in manufacturing processes continues to improve as technologies mature. Current production methods require approximately 25-40% less energy than conventional plastic manufacturing when evaluated on a functional unit basis. The establishment of standardized mechanical property testing facilitates process optimization, further reducing energy requirements.
The agricultural impact of sourcing raw materials for nanocellulose production must be carefully managed. Sustainable forestry practices and agricultural waste utilization have emerged as preferred sourcing strategies. The diversification of cellulose sources, including agricultural residues and invasive species, reduces pressure on forest resources while creating value from waste streams.
Economic sustainability aspects are equally compelling. The development of nanocellulose composite industries creates opportunities for rural economies and agricultural communities. As standardized testing methods become more widely adopted, market barriers decrease, enabling broader commercialization and economic benefits across diverse geographic regions.
Nanocellulose extraction processes have evolved to become increasingly environmentally friendly, with reduced energy consumption and chemical usage compared to traditional methods. Recent innovations in enzymatic and mechanical extraction techniques have further diminished the environmental footprint of production. When standardized test methods for mechanical properties are implemented, manufacturers can optimize material usage, resulting in thinner, lighter products that require fewer resources while maintaining performance standards.
The carbon footprint of nanocellulose composites presents a marked improvement over synthetic alternatives. Life cycle assessments indicate that these materials can achieve carbon emission reductions of 30-60% compared to conventional plastics, depending on production methods and application scenarios. Furthermore, the biodegradability of many nanocellulose composites addresses end-of-life waste management challenges that plague traditional materials.
Water conservation represents another significant sustainability advantage. The water-intensive nature of traditional cellulose processing has been mitigated through closed-loop systems and advanced filtration technologies, reducing freshwater consumption by up to 80% in modern facilities. Standardized mechanical testing enables precise engineering of water-resistant properties without compromising biodegradability.
Energy efficiency in manufacturing processes continues to improve as technologies mature. Current production methods require approximately 25-40% less energy than conventional plastic manufacturing when evaluated on a functional unit basis. The establishment of standardized mechanical property testing facilitates process optimization, further reducing energy requirements.
The agricultural impact of sourcing raw materials for nanocellulose production must be carefully managed. Sustainable forestry practices and agricultural waste utilization have emerged as preferred sourcing strategies. The diversification of cellulose sources, including agricultural residues and invasive species, reduces pressure on forest resources while creating value from waste streams.
Economic sustainability aspects are equally compelling. The development of nanocellulose composite industries creates opportunities for rural economies and agricultural communities. As standardized testing methods become more widely adopted, market barriers decrease, enabling broader commercialization and economic benefits across diverse geographic regions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!