Nanocellulose For Thermal Management: Composite Formulations For Heat Spreaders
SEP 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nanocellulose Thermal Management Background and Objectives
Thermal management has emerged as a critical challenge in modern electronics, aerospace, and energy systems due to increasing power densities and miniaturization trends. The evolution of thermal management technologies has progressed from traditional metallic heat spreaders to advanced composite materials, with recent focus on sustainable and high-performance alternatives. Nanocellulose, derived from abundant plant resources, represents a promising frontier in this technological evolution, combining exceptional thermal properties with environmental sustainability.
The development of nanocellulose-based thermal management materials has accelerated significantly over the past decade. Initially discovered in the early 2000s as a potential reinforcement material, nanocellulose has gradually revealed its remarkable thermal conductivity properties when properly engineered. Research has demonstrated that crystalline nanocellulose can exhibit thermal conductivity comparable to some metals while maintaining the lightweight characteristics of polymers.
Current technological trajectories indicate a growing interest in hybrid systems that combine nanocellulose with other thermally conductive materials such as graphene, boron nitride, and metallic nanoparticles. These composite formulations aim to leverage the unique properties of each component while addressing the inherent limitations of single-material approaches. The anisotropic nature of nanocellulose thermal conductivity presents both challenges and opportunities for directional heat management applications.
Market drivers for nanocellulose thermal management solutions include the increasing demand for sustainable materials, regulatory pressure to reduce environmental impact, and the technical requirements for more efficient thermal dissipation in next-generation electronics. The global push toward carbon neutrality has further accelerated interest in bio-based alternatives to traditional thermal management materials.
The primary technical objectives for nanocellulose-based heat spreaders include achieving thermal conductivity values exceeding 20 W/m·K, developing scalable manufacturing processes, ensuring long-term stability under operating conditions, and maintaining competitive cost structures. Secondary objectives focus on multifunctionality, incorporating features such as electromagnetic interference shielding, mechanical reinforcement, and fire resistance into thermal management solutions.
Research goals in this field aim to understand the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer in nanocellulose structures, optimize interface engineering between nanocellulose and other components, develop novel processing techniques for controlled orientation of nanocellulose fibrils, and establish standardized testing protocols for thermal performance evaluation. The ultimate objective is to create commercially viable, environmentally sustainable thermal management solutions that can compete with or surpass conventional materials in performance while offering additional benefits in terms of weight reduction and environmental impact.
The development of nanocellulose-based thermal management materials has accelerated significantly over the past decade. Initially discovered in the early 2000s as a potential reinforcement material, nanocellulose has gradually revealed its remarkable thermal conductivity properties when properly engineered. Research has demonstrated that crystalline nanocellulose can exhibit thermal conductivity comparable to some metals while maintaining the lightweight characteristics of polymers.
Current technological trajectories indicate a growing interest in hybrid systems that combine nanocellulose with other thermally conductive materials such as graphene, boron nitride, and metallic nanoparticles. These composite formulations aim to leverage the unique properties of each component while addressing the inherent limitations of single-material approaches. The anisotropic nature of nanocellulose thermal conductivity presents both challenges and opportunities for directional heat management applications.
Market drivers for nanocellulose thermal management solutions include the increasing demand for sustainable materials, regulatory pressure to reduce environmental impact, and the technical requirements for more efficient thermal dissipation in next-generation electronics. The global push toward carbon neutrality has further accelerated interest in bio-based alternatives to traditional thermal management materials.
The primary technical objectives for nanocellulose-based heat spreaders include achieving thermal conductivity values exceeding 20 W/m·K, developing scalable manufacturing processes, ensuring long-term stability under operating conditions, and maintaining competitive cost structures. Secondary objectives focus on multifunctionality, incorporating features such as electromagnetic interference shielding, mechanical reinforcement, and fire resistance into thermal management solutions.
Research goals in this field aim to understand the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer in nanocellulose structures, optimize interface engineering between nanocellulose and other components, develop novel processing techniques for controlled orientation of nanocellulose fibrils, and establish standardized testing protocols for thermal performance evaluation. The ultimate objective is to create commercially viable, environmentally sustainable thermal management solutions that can compete with or surpass conventional materials in performance while offering additional benefits in terms of weight reduction and environmental impact.
Market Demand Analysis for Sustainable Thermal Management Solutions
The global thermal management market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for efficient heat dissipation solutions across multiple industries. With the miniaturization of electronic devices and the rise in power densities, traditional thermal management materials are reaching their performance limits. This has created a substantial market opportunity for sustainable alternatives like nanocellulose-based heat spreaders, which offer comparable thermal conductivity to conventional materials while providing environmental benefits.
The electronics sector represents the largest market segment for thermal management solutions, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding industry averages. Data centers, in particular, are driving demand as they seek to reduce cooling costs which currently account for approximately 40% of their total energy consumption. The automotive industry, especially the electric vehicle segment, constitutes another rapidly expanding market as thermal management becomes critical for battery performance and longevity.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing sustainable materials in their supply chains, responding to regulatory pressures and consumer preferences. Market research indicates that companies with demonstrated sustainability credentials command premium pricing and enjoy stronger brand loyalty. This trend creates a favorable environment for nanocellulose-based thermal management solutions, which offer biodegradability and renewable sourcing advantages over traditional materials.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also emerging as significant potential markets for advanced thermal management materials. These industries require lightweight yet high-performance solutions that can withstand extreme operating conditions while meeting stringent reliability standards. Nanocellulose composites show promise in addressing these specific requirements.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the thermal management market, driven by its robust electronics manufacturing base. However, North America and Europe are showing accelerated adoption of sustainable thermal solutions due to stricter environmental regulations and corporate sustainability initiatives. These regions represent prime entry points for innovative nanocellulose-based heat spreaders.
Market forecasts suggest that sustainable thermal management materials will capture an increasing share of the overall market in the coming years. This growth is supported by the convergence of technological advancements in nanocellulose processing, increasing thermal performance requirements, and strengthening sustainability mandates across industries. The timing appears optimal for introducing nanocellulose-based heat spreaders as alternatives to conventional materials.
The electronics sector represents the largest market segment for thermal management solutions, with a compound annual growth rate exceeding industry averages. Data centers, in particular, are driving demand as they seek to reduce cooling costs which currently account for approximately 40% of their total energy consumption. The automotive industry, especially the electric vehicle segment, constitutes another rapidly expanding market as thermal management becomes critical for battery performance and longevity.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing sustainable materials in their supply chains, responding to regulatory pressures and consumer preferences. Market research indicates that companies with demonstrated sustainability credentials command premium pricing and enjoy stronger brand loyalty. This trend creates a favorable environment for nanocellulose-based thermal management solutions, which offer biodegradability and renewable sourcing advantages over traditional materials.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also emerging as significant potential markets for advanced thermal management materials. These industries require lightweight yet high-performance solutions that can withstand extreme operating conditions while meeting stringent reliability standards. Nanocellulose composites show promise in addressing these specific requirements.
Regional analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific dominates the thermal management market, driven by its robust electronics manufacturing base. However, North America and Europe are showing accelerated adoption of sustainable thermal solutions due to stricter environmental regulations and corporate sustainability initiatives. These regions represent prime entry points for innovative nanocellulose-based heat spreaders.
Market forecasts suggest that sustainable thermal management materials will capture an increasing share of the overall market in the coming years. This growth is supported by the convergence of technological advancements in nanocellulose processing, increasing thermal performance requirements, and strengthening sustainability mandates across industries. The timing appears optimal for introducing nanocellulose-based heat spreaders as alternatives to conventional materials.
Current State and Challenges in Nanocellulose Heat Spreader Technology
Nanocellulose-based heat spreaders represent an emerging frontier in thermal management technology, with significant research progress made globally over the past decade. Currently, the field has evolved from basic material characterization to functional composite development, with several research institutions and companies demonstrating promising prototypes. Laboratory-scale production has shown that nanocellulose composites can achieve thermal conductivity values ranging from 2-20 W/mK, depending on formulation and processing techniques, which positions them as viable alternatives to conventional materials in specific applications.
The global landscape of nanocellulose thermal management research shows concentration in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with Finland, Japan, and the United States leading in patent filings. Academic-industrial partnerships have accelerated in recent years, particularly in countries with strong forestry industries seeking to develop high-value applications for cellulose derivatives.
Despite promising advances, several significant technical challenges persist. The inherent hydrophilicity of nanocellulose creates moisture sensitivity issues that can compromise long-term thermal performance stability. Current manufacturing processes face scalability limitations, with difficulties in achieving consistent dispersion of nanocellulose and conductive fillers at industrial scales. The interfacial thermal resistance between nanocellulose and conductive additives remains a critical bottleneck, limiting the maximum achievable thermal conductivity.
Anisotropic thermal properties present another challenge, as nanocellulose-based composites typically exhibit directional heat transfer characteristics that must be carefully engineered for specific applications. This anisotropy, while potentially advantageous in certain designs, complicates integration into conventional thermal management systems.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Current production methods for high-purity nanocellulose are energy-intensive and expensive, with estimates suggesting production costs 5-10 times higher than conventional materials with similar thermal performance. The economic viability of these materials depends on achieving manufacturing breakthroughs that reduce energy consumption and processing complexity.
Environmental stability represents another unresolved challenge, as nanocellulose composites must maintain consistent thermal performance across varying humidity conditions and temperature cycles. Research indicates performance degradation of 15-30% after extended environmental exposure, necessitating effective encapsulation or chemical modification strategies.
Standardization gaps further complicate industrial adoption, with inconsistent testing methodologies and performance metrics across the research community making direct comparisons between different formulations difficult. Industry-wide standards for characterizing nanocellulose-based thermal materials are still in early development stages, hampering technology transfer from laboratory to commercial applications.
The global landscape of nanocellulose thermal management research shows concentration in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with Finland, Japan, and the United States leading in patent filings. Academic-industrial partnerships have accelerated in recent years, particularly in countries with strong forestry industries seeking to develop high-value applications for cellulose derivatives.
Despite promising advances, several significant technical challenges persist. The inherent hydrophilicity of nanocellulose creates moisture sensitivity issues that can compromise long-term thermal performance stability. Current manufacturing processes face scalability limitations, with difficulties in achieving consistent dispersion of nanocellulose and conductive fillers at industrial scales. The interfacial thermal resistance between nanocellulose and conductive additives remains a critical bottleneck, limiting the maximum achievable thermal conductivity.
Anisotropic thermal properties present another challenge, as nanocellulose-based composites typically exhibit directional heat transfer characteristics that must be carefully engineered for specific applications. This anisotropy, while potentially advantageous in certain designs, complicates integration into conventional thermal management systems.
Cost-effectiveness remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Current production methods for high-purity nanocellulose are energy-intensive and expensive, with estimates suggesting production costs 5-10 times higher than conventional materials with similar thermal performance. The economic viability of these materials depends on achieving manufacturing breakthroughs that reduce energy consumption and processing complexity.
Environmental stability represents another unresolved challenge, as nanocellulose composites must maintain consistent thermal performance across varying humidity conditions and temperature cycles. Research indicates performance degradation of 15-30% after extended environmental exposure, necessitating effective encapsulation or chemical modification strategies.
Standardization gaps further complicate industrial adoption, with inconsistent testing methodologies and performance metrics across the research community making direct comparisons between different formulations difficult. Industry-wide standards for characterizing nanocellulose-based thermal materials are still in early development stages, hampering technology transfer from laboratory to commercial applications.
Current Formulation Approaches for Nanocellulose Heat Spreaders
01 Nanocellulose-based thermal insulation materials
Nanocellulose can be used to create highly effective thermal insulation materials due to its low thermal conductivity and porous structure. These composites can be formulated as aerogels, foams, or films that trap air within their structure, significantly reducing heat transfer. The incorporation of nanocellulose into insulation materials provides advantages such as lightweight properties, biodegradability, and sustainability while maintaining excellent thermal management capabilities for applications in buildings, packaging, and protective equipment.- Nanocellulose-based thermal insulation materials: Nanocellulose can be used to create highly effective thermal insulation materials due to its low thermal conductivity and porous structure. These composites can be formulated as aerogels, foams, or films that trap air within their structure, significantly reducing heat transfer. The incorporation of nanocellulose into insulation materials provides advantages such as lightweight properties, biodegradability, and sustainability while maintaining excellent thermal management capabilities for applications in buildings, packaging, and protective equipment.
- Nanocellulose composites with phase change materials: Combining nanocellulose with phase change materials (PCMs) creates advanced thermal management composites that can absorb, store, and release thermal energy. The nanocellulose provides structural support and encapsulation for the PCMs, preventing leakage during phase transitions. These hybrid composites offer controlled thermal regulation capabilities, making them suitable for applications in smart textiles, building materials, and electronic device cooling where temperature stabilization is critical.
- Electrically conductive nanocellulose composites for thermal management: Nanocellulose can be combined with conductive materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, or metallic nanoparticles to create electrically conductive composites with enhanced thermal management properties. These composites facilitate efficient heat dissipation through improved thermal conductivity while maintaining the lightweight and sustainable characteristics of nanocellulose. Applications include flexible electronics, electromagnetic interference shielding, and thermal interface materials where both electrical conductivity and heat management are required.
- Nanocellulose-reinforced polymer composites for thermal applications: Incorporating nanocellulose into polymer matrices creates reinforced composites with improved thermal stability and management properties. The nanocellulose fibers or crystals enhance the mechanical strength while also modifying the thermal behavior of the polymer. These composites can be engineered to have specific thermal expansion coefficients, heat deflection temperatures, and flame-retardant properties, making them suitable for automotive components, aerospace materials, and consumer products requiring dimensional stability under thermal stress.
- Nanocellulose-based films and coatings for thermal barrier applications: Nanocellulose can be processed into thin films and coatings that provide effective thermal barriers. These films exhibit low thermal diffusivity while maintaining optical transparency and flexibility. By controlling the nanocellulose orientation, density, and potential additives, the thermal barrier properties can be tailored for specific applications. These materials are particularly valuable in packaging, window films, and protective coatings where heat transfer needs to be minimized while maintaining other functional properties such as transparency or gas barrier capabilities.
02 Nanocellulose composites with phase change materials
Combining nanocellulose with phase change materials (PCMs) creates advanced thermal management composites that can absorb, store, and release thermal energy. The nanocellulose provides structural support and encapsulation for the PCMs, preventing leakage during phase transitions while enhancing thermal energy storage capacity. These composites can maintain stable temperatures by absorbing excess heat when temperatures rise and releasing it when temperatures fall, making them suitable for applications in smart textiles, building materials, and electronic device cooling systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrically conductive nanocellulose composites for thermal management
Nanocellulose can be combined with conductive materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, or metallic nanoparticles to create electrically conductive composites with enhanced thermal management properties. These composites facilitate efficient heat dissipation through both conductive and radiative mechanisms. The unique network structure of nanocellulose allows for effective dispersion of conductive fillers, creating continuous pathways for heat transfer while maintaining mechanical integrity. These materials are particularly valuable in electronic packaging, flexible electronics, and thermal interface materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanocellulose-reinforced polymer composites for thermal applications
Incorporating nanocellulose into polymer matrices creates composites with improved thermal stability and heat resistance. The high aspect ratio and crystallinity of nanocellulose fibers enhance the thermal properties of the base polymer by creating tortuous paths for heat flow and increasing the overall thermal decomposition temperature. These reinforced composites exhibit reduced thermal expansion, improved flame retardancy, and enhanced dimensional stability under thermal stress, making them suitable for automotive components, aerospace applications, and high-temperature industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Functionalized nanocellulose for advanced thermal management systems
Chemical modification and functionalization of nanocellulose surfaces can tailor its thermal properties for specific applications. Techniques such as silylation, acetylation, or grafting with thermal-responsive polymers can enhance hydrophobicity, thermal stability, and compatibility with various matrices. Functionalized nanocellulose can be engineered to respond to thermal stimuli, creating smart materials that actively manage heat flow based on environmental conditions. These advanced materials find applications in wearable electronics, biomedical devices, and next-generation thermal management systems that require precise temperature control.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Nanocellulose Composite Development
The nanocellulose thermal management market is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activity but limited commercial deployment. Market size remains modest but is projected to expand significantly as thermal management challenges intensify in electronics and automotive sectors. Technologically, nanocellulose heat spreader composites are transitioning from laboratory to early commercial applications, with varying maturity levels across players. Research institutions like University of Maine, FPInnovations, and Chinese Academy of Sciences lead fundamental research, while companies including DIC Corp., Asahi Kasei, and Siemens are advancing application-specific formulations. Collaboration between academic institutions (Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Kyoto University) and industrial partners is accelerating development of commercially viable solutions with enhanced thermal conductivity and sustainability benefits.
Soane Materials LLC
Technical Solution: Soane Materials has developed innovative nanocellulose-based thermal management solutions utilizing their expertise in surface chemistry and materials science. Their proprietary NanoCool™ technology combines chemically modified nanocellulose with specialized thermal fillers in a hierarchical structure that maximizes heat spreading efficiency. The company's approach involves creating anisotropic structures where heat preferentially flows along engineered pathways, achieving in-plane thermal conductivity values of 15-20 W/mK. Soane's materials feature proprietary cross-linking chemistry that enhances mechanical stability and moisture resistance while maintaining flexibility. Their manufacturing process allows for precise control of porosity and density, enabling customization for specific thermal management requirements. The company has also developed specialized coating technologies that improve interfacial thermal conductance when these materials are integrated into electronic assemblies.
Strengths: Advanced surface chemistry expertise; highly engineered material structures; excellent thermal performance while maintaining flexibility. Weaknesses: Relatively new to commercial-scale production; higher cost compared to conventional materials; limited long-term performance data in field applications.
Granbio Intellectual Property Holdings LLC
Technical Solution: Granbio has developed proprietary BioPlus™ nanocellulose technology specifically engineered for thermal management applications. Their approach leverages bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) with its inherently high crystallinity and purity to create thermal interface materials with superior performance. Granbio's process involves in-situ growth of thermally conductive nanoparticles within the nanocellulose network, creating intimate contact between components that minimizes thermal boundary resistance. Their composites achieve thermal conductivity values of 8-12 W/mK while maintaining flexibility and low density. The company has developed specialized surface chemistry modifications that enhance compatibility with electronic components and improve long-term stability. Granbio's materials feature tunable thickness (25-500 μm) and can be manufactured in continuous rolls suitable for high-volume electronics applications.
Strengths: Proprietary bacterial nanocellulose production technology; highly pure starting material; established commercial-scale production capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to plant-derived nanocellulose; limited customization options for specific thermal profiles; potential challenges with integration into existing manufacturing processes.
Critical Patents and Research in Nanocellulose Thermal Conductivity
Nano cellulose/expanded graphite composite film and preparation method thereof
PatentActiveCN114181413A
Innovation
- By self-assembly of nanocellulose and expanded graphite, the expanded graphite is dispersed in nanocellulose using stirring and ultrasonic treatment, followed by suction filtration and hot pressing to prepare a composite film, and the mass proportion and processing conditions of expanded graphite are controlled to achieve Improve performance.
Nanocellulose composite, and method for manufacturing same
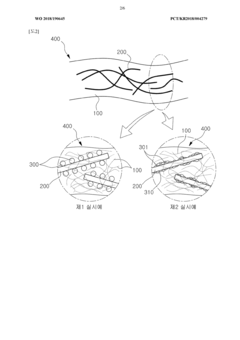
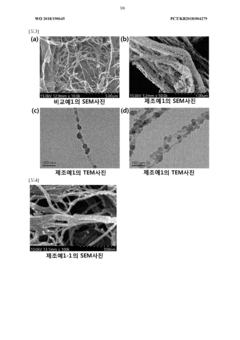
PatentWO2018190645A1
Innovation
- A method involving the preparation of cellulose nanofibers with a silica coating or silica particles attached to their surface, which are then mixed with a polymer to form a composite, enhancing dispersibility and heat resistance through surface vitrification and uneven silica coating.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of nanocellulose-based thermal management solutions represents a significant advantage over conventional materials. Nanocellulose is derived from renewable biomass sources, primarily wood pulp and agricultural residues, offering a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based polymers and metal-based heat spreaders. The production process of nanocellulose has a substantially lower carbon footprint compared to traditional materials used in thermal management applications, with studies indicating up to 65% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions throughout the lifecycle.
Water consumption during nanocellulose production remains a concern, as the extraction and purification processes are water-intensive. However, closed-loop water recycling systems have been implemented in modern production facilities, reducing freshwater requirements by approximately 80%. Energy consumption during nanocellulose processing has also decreased by 40% over the past decade through process optimization and technological improvements.
End-of-life considerations strongly favor nanocellulose composites, as they demonstrate superior biodegradability compared to conventional thermal management materials. While pure nanocellulose is fully biodegradable, composite formulations containing synthetic polymers or metallic particles present mixed biodegradability profiles. Recent research has focused on developing fully biodegradable composite formulations that maintain thermal performance while ensuring complete environmental decomposition.
The sustainability assessment of nanocellulose heat spreaders extends beyond production and disposal to include performance efficiency. These materials enable more efficient thermal management in electronic devices, potentially extending product lifespans by 30-40% through better heat dissipation. This indirect environmental benefit reduces electronic waste generation and associated resource consumption for replacement devices.
Supply chain considerations reveal that nanocellulose production can be localized near forestry operations or agricultural centers, reducing transportation emissions compared to globally distributed metal mining and processing. Additionally, nanocellulose production creates opportunities for valorization of agricultural and forestry waste streams, transforming what would be waste material into high-value thermal management products.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly favor sustainable materials like nanocellulose, with several jurisdictions implementing policies that incentivize bio-based alternatives to traditional thermal management materials. These policies include carbon taxation systems, extended producer responsibility regulations, and green procurement initiatives that collectively strengthen the market position of nanocellulose-based thermal solutions.
Water consumption during nanocellulose production remains a concern, as the extraction and purification processes are water-intensive. However, closed-loop water recycling systems have been implemented in modern production facilities, reducing freshwater requirements by approximately 80%. Energy consumption during nanocellulose processing has also decreased by 40% over the past decade through process optimization and technological improvements.
End-of-life considerations strongly favor nanocellulose composites, as they demonstrate superior biodegradability compared to conventional thermal management materials. While pure nanocellulose is fully biodegradable, composite formulations containing synthetic polymers or metallic particles present mixed biodegradability profiles. Recent research has focused on developing fully biodegradable composite formulations that maintain thermal performance while ensuring complete environmental decomposition.
The sustainability assessment of nanocellulose heat spreaders extends beyond production and disposal to include performance efficiency. These materials enable more efficient thermal management in electronic devices, potentially extending product lifespans by 30-40% through better heat dissipation. This indirect environmental benefit reduces electronic waste generation and associated resource consumption for replacement devices.
Supply chain considerations reveal that nanocellulose production can be localized near forestry operations or agricultural centers, reducing transportation emissions compared to globally distributed metal mining and processing. Additionally, nanocellulose production creates opportunities for valorization of agricultural and forestry waste streams, transforming what would be waste material into high-value thermal management products.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly favor sustainable materials like nanocellulose, with several jurisdictions implementing policies that incentivize bio-based alternatives to traditional thermal management materials. These policies include carbon taxation systems, extended producer responsibility regulations, and green procurement initiatives that collectively strengthen the market position of nanocellulose-based thermal solutions.
Manufacturing Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability of nanocellulose-based thermal management solutions presents both significant opportunities and challenges for commercial implementation. Current manufacturing processes for nanocellulose heat spreader composites primarily operate at laboratory or pilot scales, with limited examples of full industrial production. The transition to mass production requires substantial investment in specialized equipment and process optimization to maintain the unique thermal properties observed in smaller-scale production.
Production methods for nanocellulose extraction, including mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic approaches, demonstrate varying degrees of scalability. Mechanical processes offer higher throughput but often result in lower quality nanocellulose with reduced aspect ratios, potentially compromising thermal conductivity. Chemical methods produce higher quality materials but generate chemical waste streams that require additional processing, increasing production costs.
Cost analysis reveals that raw material expenses currently constitute 40-55% of total production costs, with nanocellulose extraction representing the most significant component. Energy consumption during processing accounts for approximately 20-30% of costs, particularly in mechanical fibrillation and drying operations. The remaining expenses are distributed across labor, quality control, and facility overhead.
Economies of scale could potentially reduce production costs by 30-40% when moving from pilot to industrial scale. However, this requires initial capital investments estimated at $5-15 million for a medium-scale production facility. The current price point for nanocellulose-based thermal management materials ranges from $80-200/kg, significantly higher than conventional alternatives like aluminum ($3-5/kg) or copper ($6-10/kg).
Several technological innovations show promise for improving manufacturing scalability. Continuous processing systems for nanocellulose production could increase throughput by 3-5 times compared to batch processes. Advanced drying technologies, including spray drying and supercritical CO2 drying, may reduce energy consumption by up to 40% while preserving the nanostructure critical for thermal performance.
Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, composite manufacturers, and end-users are emerging as a viable approach to distribute development costs and accelerate commercialization. These collaborative models have successfully reduced time-to-market in similar advanced materials sectors and could be particularly effective for nanocellulose thermal management solutions.
For widespread adoption, production costs must decrease to approximately $20-30/kg, requiring both process optimization and increased production volumes. This price threshold would position nanocellulose composites as competitive alternatives in premium thermal management applications where performance advantages justify moderate cost premiums.
Production methods for nanocellulose extraction, including mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic approaches, demonstrate varying degrees of scalability. Mechanical processes offer higher throughput but often result in lower quality nanocellulose with reduced aspect ratios, potentially compromising thermal conductivity. Chemical methods produce higher quality materials but generate chemical waste streams that require additional processing, increasing production costs.
Cost analysis reveals that raw material expenses currently constitute 40-55% of total production costs, with nanocellulose extraction representing the most significant component. Energy consumption during processing accounts for approximately 20-30% of costs, particularly in mechanical fibrillation and drying operations. The remaining expenses are distributed across labor, quality control, and facility overhead.
Economies of scale could potentially reduce production costs by 30-40% when moving from pilot to industrial scale. However, this requires initial capital investments estimated at $5-15 million for a medium-scale production facility. The current price point for nanocellulose-based thermal management materials ranges from $80-200/kg, significantly higher than conventional alternatives like aluminum ($3-5/kg) or copper ($6-10/kg).
Several technological innovations show promise for improving manufacturing scalability. Continuous processing systems for nanocellulose production could increase throughput by 3-5 times compared to batch processes. Advanced drying technologies, including spray drying and supercritical CO2 drying, may reduce energy consumption by up to 40% while preserving the nanostructure critical for thermal performance.
Strategic partnerships between material suppliers, composite manufacturers, and end-users are emerging as a viable approach to distribute development costs and accelerate commercialization. These collaborative models have successfully reduced time-to-market in similar advanced materials sectors and could be particularly effective for nanocellulose thermal management solutions.
For widespread adoption, production costs must decrease to approximately $20-30/kg, requiring both process optimization and increased production volumes. This price threshold would position nanocellulose composites as competitive alternatives in premium thermal management applications where performance advantages justify moderate cost premiums.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!