Dispersion Strategies For Homogeneous Nanocellulose Composite Materials
Nanocellulose Composite Background and Objectives
Nanocellulose has emerged as a revolutionary biomaterial over the past two decades, transitioning from laboratory curiosity to commercial reality. Derived from cellulose, the most abundant biopolymer on Earth, nanocellulose offers exceptional mechanical properties, biodegradability, and sustainability credentials that position it as a key material for future applications. The evolution of nanocellulose technology has progressed through several distinct phases, beginning with fundamental research in the 1980s and 1990s, followed by process optimization in the early 2000s, and now entering a commercialization phase with increasing industrial adoption.
The current technological trajectory indicates a growing focus on nanocellulose composite materials, which combine nanocellulose with various matrices to create high-performance sustainable materials. However, a persistent challenge in this field remains the effective dispersion of nanocellulose within composite matrices, particularly for homogeneous distribution that maximizes performance benefits.
Recent technological advancements have significantly improved production efficiency and quality consistency of nanocellulose, with breakthroughs in mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic extraction methods. These developments have reduced production costs from hundreds of dollars per kilogram to potentially under $10 per kilogram at industrial scale, making commercial applications increasingly viable.
The primary technical objective of this research is to develop and evaluate effective dispersion strategies that enable homogeneous distribution of nanocellulose within various matrix materials. This includes investigating surface modification techniques, processing methodologies, and compatibility enhancement approaches that overcome the inherent hydrophilicity of nanocellulose when incorporated into hydrophobic matrices.
Secondary objectives include quantifying the relationship between dispersion quality and resulting composite properties, establishing standardized protocols for dispersion assessment, and identifying scalable techniques suitable for industrial implementation. The research aims to bridge the gap between laboratory-scale success and commercial viability in nanocellulose composite manufacturing.
The technological evolution in this field is trending toward more sophisticated hybrid approaches that combine multiple dispersion strategies, alongside the development of specialized equipment designed specifically for nanocellulose processing. Emerging research also indicates potential breakthroughs in stimuli-responsive dispersion systems that could enable "on-demand" control of nanocellulose distribution within composites.
Understanding and overcoming dispersion challenges represents a critical milestone in the broader nanocellulose technology roadmap, potentially unlocking applications across industries including packaging, automotive, construction, electronics, and biomedical fields where high-performance sustainable materials are increasingly demanded.
Market Analysis for Nanocellulose Composite Applications
The global nanocellulose composite materials market has been experiencing significant growth, with a market value estimated to reach $700 million by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 18.5% from 2020. This remarkable expansion is primarily driven by increasing environmental concerns and the growing demand for sustainable alternatives to petroleum-based products across various industries.
The packaging industry represents the largest application segment for nanocellulose composites, accounting for approximately 35% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the exceptional barrier properties, biodegradability, and mechanical strength that homogeneously dispersed nanocellulose provides to packaging materials. Major food and beverage companies are actively incorporating these materials into their sustainable packaging initiatives to reduce plastic waste.
Automotive applications constitute the fastest-growing segment, with a projected growth rate of 22% annually through 2025. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing nanocellulose composites to develop lightweight components that enhance fuel efficiency while maintaining structural integrity. The homogeneous dispersion of nanocellulose in polymer matrices has proven critical for achieving the desired mechanical properties in these applications.
The construction sector has also emerged as a significant market for nanocellulose composites, particularly in insulation materials, cement reinforcement, and architectural panels. The market share in this segment has grown from 12% in 2018 to 18% in 2022, reflecting the increasing adoption of sustainable building materials with enhanced performance characteristics.
Regionally, North America and Europe currently dominate the market, collectively accounting for over 60% of global consumption. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, along with increasing government initiatives promoting sustainable materials.
Consumer preferences are shifting dramatically toward eco-friendly products, with surveys indicating that 73% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for sustainable materials. This trend has prompted major brands across industries to incorporate nanocellulose composites into their product development strategies, further stimulating market growth.
The economic viability of nanocellulose composites has improved significantly due to advancements in dispersion technologies, which have reduced production costs by approximately 30% over the past five years. This cost reduction has expanded the potential application scope beyond high-value products to more mainstream consumer goods, thereby enlarging the addressable market.
Current Dispersion Challenges and Technical Barriers
Despite the promising properties of nanocellulose as a reinforcement material in composites, achieving homogeneous dispersion remains one of the most significant technical challenges in the field. The hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose creates inherent incompatibility with hydrophobic polymer matrices, resulting in agglomeration and poor interfacial adhesion. This fundamental mismatch in surface chemistry leads to phase separation during processing, significantly diminishing the mechanical and functional properties of the resulting composites.
Current dispersion methods often rely on mechanical approaches such as ultrasonication, high-pressure homogenization, and high-shear mixing. While these techniques can temporarily separate nanocellulose fibrils, they frequently fail to maintain stable dispersions during subsequent processing steps. Additionally, excessive mechanical treatment can damage the nanocellulose structure, reducing its aspect ratio and reinforcement capability.
Solvent-based dispersion strategies present another set of challenges. Organic solvents that effectively disperse nanocellulose often pose environmental and health concerns, contradicting the sustainable nature of nanocellulose itself. Water-based systems, while environmentally friendly, introduce processing complications including extended drying times and potential void formation during solvent evaporation.
Surface modification techniques, such as chemical functionalization and grafting, have shown promise in improving compatibility. However, these approaches face scalability issues, with laboratory-scale successes often failing to translate to industrial production. The cost-effectiveness of such modifications remains questionable, as complex chemical treatments significantly increase production costs while potentially altering the intrinsic properties of nanocellulose.
Processing parameters present additional barriers to homogeneous dispersion. Temperature sensitivity of nanocellulose limits processing windows, as degradation can occur at temperatures required for effective polymer processing. Viscosity increases dramatically with nanocellulose loading, creating processing difficulties in conventional equipment and limiting the maximum achievable reinforcement content.
Quality control and characterization of dispersion quality represent another significant challenge. Current analytical methods lack standardization, making it difficult to quantitatively assess and compare dispersion effectiveness across different studies and production batches. This hampers systematic improvement of dispersion strategies and slows industrial adoption.
The economic viability of current dispersion technologies presents perhaps the most significant barrier to widespread commercial implementation. Many effective laboratory techniques require specialized equipment, extended processing times, or expensive chemical treatments that are prohibitive at industrial scales. Bridging this gap between laboratory success and commercial feasibility remains a critical challenge for the field.
Current Dispersion Methodologies and Techniques
01 Nanocellulose dispersion methods for composite materials
Various methods are employed to achieve stable dispersions of nanocellulose in composite materials. These include mechanical processes such as ultrasonication, high-pressure homogenization, and high-shear mixing. Chemical modifications of the nanocellulose surface can also improve dispersion by reducing hydrogen bonding between fibrils. Surfactants and dispersing agents are often incorporated to prevent aggregation and ensure uniform distribution throughout the matrix material.- Nanocellulose dispersion methods for composite materials: Various methods are employed to achieve stable dispersions of nanocellulose in composite materials. These include mechanical processes such as high-shear mixing, ultrasonication, and homogenization techniques that help break down nanocellulose aggregates. Chemical modifications of the nanocellulose surface can also improve dispersion by enhancing compatibility with different matrix materials. These dispersion methods are critical for ensuring uniform distribution of nanocellulose throughout the composite matrix, which directly impacts the mechanical and functional properties of the final material.
- Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved dispersion: Surface modification techniques are applied to nanocellulose to improve its dispersion in various matrices, particularly in hydrophobic polymer systems. These modifications include grafting hydrophobic groups, silylation, acetylation, and other chemical treatments that alter the surface chemistry of nanocellulose. By reducing the hydrophilicity of nanocellulose and increasing its compatibility with polymer matrices, these modifications prevent aggregation and enable more uniform dispersion, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and performance of the composite materials.
- Nanocellulose-polymer composite formulations: Specific formulations have been developed for incorporating nanocellulose into polymer matrices to create high-performance composite materials. These formulations typically include dispersing agents, compatibilizers, and processing aids that facilitate the integration of nanocellulose into polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl alcohol, and biodegradable polymers. The optimal ratio of nanocellulose to polymer matrix is crucial for achieving desired mechanical properties, while maintaining processability. These composites exhibit enhanced strength, stiffness, barrier properties, and in some cases, biodegradability.
- Aqueous nanocellulose dispersions and stabilization: Aqueous dispersions of nanocellulose are fundamental to many processing methods for composite materials. These dispersions require specific stabilization approaches to prevent aggregation and sedimentation, including the use of surfactants, polyelectrolytes, and pH control. The concentration of nanocellulose in the aqueous medium affects viscosity and processing characteristics. Stable aqueous dispersions serve as precursors for films, coatings, and as reinforcing agents in water-based polymer systems, offering environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic reinforcements.
- Applications of nanocellulose composite dispersions: Nanocellulose composite dispersions find applications across multiple industries due to their unique properties. In packaging, they provide enhanced barrier properties and biodegradability. In construction materials, they improve mechanical strength and reduce weight. Medical applications utilize their biocompatibility for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems. Electronic applications leverage their potential in flexible electronics and sensors. Additionally, these dispersions are used in coatings, adhesives, and as rheology modifiers in various industrial processes, demonstrating the versatility of nanocellulose as a sustainable reinforcement material.
02 Polymer-nanocellulose composite formulations
Polymer matrices can be enhanced with nanocellulose to create high-performance composite materials. The incorporation of nanocellulose into polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl alcohol, and biodegradable polymers improves mechanical properties, thermal stability, and barrier properties. Compatibilizers are often used to enhance the interfacial adhesion between the hydrophilic nanocellulose and hydrophobic polymer matrices, resulting in better dispersion and stronger composite materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Functionalization of nanocellulose for improved dispersion
Chemical modification of nanocellulose surfaces through functionalization techniques enhances dispersion in various matrices. Methods include acetylation, silylation, TEMPO-mediated oxidation, and grafting of polymers onto the nanocellulose surface. These modifications reduce the hydrophilicity of nanocellulose, minimize agglomeration, and improve compatibility with hydrophobic matrices. Functionalized nanocellulose shows better dispersion stability and stronger interfacial interactions with the matrix material.Expand Specific Solutions04 Aqueous and non-aqueous nanocellulose dispersions
Nanocellulose can be dispersed in both aqueous and non-aqueous media for different composite applications. Aqueous dispersions utilize the natural hydrophilicity of nanocellulose and often incorporate additives to prevent aggregation during drying. Non-aqueous dispersions require surface modification or solvent exchange techniques to overcome the inherent hydrophilicity of nanocellulose. Solvent selection plays a crucial role in achieving stable dispersions, with polar organic solvents often serving as intermediaries for transitioning to non-polar systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications of nanocellulose composite dispersions
Nanocellulose composite dispersions find applications across various industries. In packaging, they provide enhanced barrier properties and mechanical strength. In construction materials, they improve durability and reduce weight. Medical applications utilize their biocompatibility for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems. Electronic applications leverage their potential in flexible electronics and sensors. The automotive and aerospace industries benefit from lightweight yet strong composite materials. Processing techniques have been developed to scale up production while maintaining dispersion quality for industrial implementation.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Nanocellulose Field
The nanocellulose composite materials market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across various industries due to superior mechanical properties and sustainability benefits. The global market size is estimated to reach $700 million by 2025, growing at a CAGR of approximately 18%. From a technological maturity perspective, dispersion strategies remain a critical challenge. Leading players like Nippon Paper Industries and Asahi Kasei have developed proprietary dispersion technologies for industrial applications, while research institutions such as VTT and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft are advancing fundamental science. Companies including FiberLean Technologies, LG Chem, and Betulium Oy are commercializing innovative approaches to overcome aggregation issues. The competitive landscape features both established chemical corporations and specialized startups focusing on specific dispersion methodologies for homogeneous nanocellulose integration.
Granbio Intellectual Property Holdings LLC
Nippon Paper Industries Co., Ltd.
Key Patents and Scientific Advances in Homogeneous Dispersion
- The development of nanocellulose-dispersion concentrates and masterbatches using dispersion/drying agents such as waxes, polyolefins, and starches, which prevent irreversible agglomeration and facilitate the incorporation of nanocellulose into polymer systems, allowing for the creation of stable, dry forms suitable for thermoplastic processing.
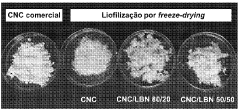
- A process involving the preparation of an aqueous suspension of nanocellulose with a polymer dispersible in aqueous media, followed by freezing, drying, and micronization, specifically using freeze-drying to prevent agglomeration and enhance dispersion, resulting in functionalized nanomaterials that can be homogeneously distributed in polymeric matrices.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact Assessment
The sustainability profile of nanocellulose composite materials represents a significant advantage in today's environmentally conscious manufacturing landscape. Derived from renewable biomass sources, nanocellulose offers a substantially lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based alternatives. Life cycle assessments indicate that nanocellulose production can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 35-55% when substituted for conventional composite reinforcement materials, depending on the specific manufacturing processes employed.
The environmental impact of dispersion strategies must be carefully evaluated as they directly influence the overall sustainability of the final composite. Chemical dispersion methods utilizing harsh solvents or surface modification agents may introduce toxicity concerns and reduce the biodegradability advantages inherent to nanocellulose. Water-based dispersion techniques generally present the most environmentally favorable profile, though they often require additional energy for subsequent drying processes.
Energy consumption during homogenization and dispersion represents a critical environmental consideration. High-pressure homogenization and ultrasonication methods, while effective for achieving uniform dispersion, can be energy-intensive. Recent innovations in low-energy mechanical dispersion techniques have demonstrated promising results, reducing energy requirements by up to 40% compared to conventional methods while maintaining dispersion quality.
End-of-life considerations for nanocellulose composites vary significantly based on the dispersion strategy employed. Composites utilizing biodegradable dispersants maintain compostability, while those incorporating synthetic polymers or chemical crosslinking agents may compromise this advantage. Research indicates that optimized dispersion strategies can preserve up to 85% of the inherent biodegradability of nanocellulose in the final composite material.
Water usage presents another important environmental metric. Traditional dispersion methods may require 15-20 liters of water per kilogram of nanocellulose processed. Closed-loop systems and water recycling technologies have demonstrated potential to reduce this consumption by 60-70%, significantly improving the sustainability profile of dispersion processes.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize the importance of environmental impact assessment for nanomaterials. The EU's REACH regulations and similar frameworks globally are evolving to address nanomaterial-specific concerns. Manufacturers implementing nanocellulose dispersion strategies must consider these regulatory requirements, particularly regarding potential nanoparticle release during processing and product lifecycle. Proactive adoption of green chemistry principles in dispersion strategy development can mitigate regulatory risks while enhancing market positioning.
Scale-up Considerations for Industrial Implementation
Scaling up nanocellulose dispersion strategies from laboratory to industrial scale presents significant challenges that require careful consideration of multiple factors. The transition demands substantial modifications to equipment, processes, and quality control systems to maintain the homogeneity achieved in smaller batches.
Industrial implementation necessitates specialized high-shear mixing equipment capable of handling large volumes while providing sufficient energy for nanocellulose dispersion. Continuous flow systems with inline homogenizers or high-pressure homogenization units represent viable options for large-scale production, though capital investment requirements are substantial. These systems must be designed to prevent agglomeration during processing and maintain consistent dispersion quality.
Process parameters require significant adjustment during scale-up. Mixing times, energy inputs, and temperature controls must be recalibrated to accommodate larger batch sizes. The rheological behavior of nanocellulose suspensions changes dramatically with concentration and scale, necessitating adaptive processing approaches. Maintaining consistent shear forces throughout larger volumes presents particular challenges that may require multi-stage mixing strategies.
Energy efficiency becomes increasingly critical at industrial scale. The high energy consumption associated with nanocellulose dispersion can significantly impact production costs. Implementation of energy recovery systems and process optimization can help mitigate these costs. Additionally, continuous monitoring systems must be integrated to ensure dispersion quality remains consistent throughout extended production runs.
Raw material handling represents another scale-up challenge. Industrial implementation requires consistent nanocellulose feedstock quality and moisture content. Variations in these parameters can dramatically affect dispersion outcomes. Developing robust supplier qualification programs and implementing rigorous incoming material testing protocols becomes essential for maintaining product consistency.
Quality control systems must evolve from laboratory-scale analytical methods to rapid, inline monitoring techniques suitable for production environments. Technologies such as online rheology measurements, particle size analysis, and optical monitoring can provide real-time feedback on dispersion quality. These systems should be integrated with automated process control to enable dynamic adjustments during production.
Regulatory considerations also impact scale-up strategies. Ensuring compliance with relevant standards while maintaining economic viability requires careful balance. Documentation systems must be established to demonstrate consistent product quality and traceability throughout the production process.