Nanocellulose Reinforcement For Concrete And Cementitious Composites
SEP 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nanocellulose in Concrete: Background and Objectives
Concrete, the most widely used construction material globally, has undergone significant technological advancements over the centuries. Traditional concrete, while robust, exhibits inherent limitations including brittleness, susceptibility to cracking, and environmental concerns related to its carbon footprint. The evolution of concrete technology has seen various reinforcement methods, from steel rebars to synthetic fibers, each addressing specific performance aspects.
Nanocellulose represents a revolutionary frontier in concrete reinforcement technology. Derived from plant cellulose fibers through mechanical or chemical processes, nanocellulose materials possess exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, modulus of elasticity, and remarkable surface area-to-volume ratio. These characteristics make nanocellulose particularly promising for enhancing concrete performance at the nanoscale level.
The historical trajectory of nanocellulose research began in the early 2000s, with pioneering studies exploring its potential in various applications. However, its specific application in cementitious composites gained momentum only in the last decade, marking a significant shift toward sustainable construction materials. This technological progression aligns with global sustainability initiatives and the construction industry's increasing focus on reducing environmental impact.
The primary objective of nanocellulose reinforcement in concrete is multifaceted. First, it aims to enhance mechanical properties, particularly tensile strength and flexural capacity, addressing concrete's inherent brittleness. Second, it seeks to improve durability by reducing crack propagation and enhancing resistance to environmental degradation. Third, it targets sustainability goals by potentially reducing cement content while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
Current research trends indicate growing interest in various nanocellulose forms, including cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC), each offering unique reinforcement mechanisms. The integration of these materials into concrete represents a convergence of nanotechnology, materials science, and civil engineering disciplines.
The technological objectives extend beyond mere performance enhancement to include practical considerations such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing concrete production methods. Additionally, researchers aim to understand the fundamental interaction mechanisms between nanocellulose and cement matrices, which remain partially elucidated.
As global construction demands continue to rise, coupled with increasing environmental regulations, nanocellulose reinforcement presents a promising pathway toward next-generation concrete materials that balance performance requirements with sustainability imperatives. This technological direction aligns with broader industry trends toward bio-based materials and circular economy principles in construction.
Nanocellulose represents a revolutionary frontier in concrete reinforcement technology. Derived from plant cellulose fibers through mechanical or chemical processes, nanocellulose materials possess exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength, modulus of elasticity, and remarkable surface area-to-volume ratio. These characteristics make nanocellulose particularly promising for enhancing concrete performance at the nanoscale level.
The historical trajectory of nanocellulose research began in the early 2000s, with pioneering studies exploring its potential in various applications. However, its specific application in cementitious composites gained momentum only in the last decade, marking a significant shift toward sustainable construction materials. This technological progression aligns with global sustainability initiatives and the construction industry's increasing focus on reducing environmental impact.
The primary objective of nanocellulose reinforcement in concrete is multifaceted. First, it aims to enhance mechanical properties, particularly tensile strength and flexural capacity, addressing concrete's inherent brittleness. Second, it seeks to improve durability by reducing crack propagation and enhancing resistance to environmental degradation. Third, it targets sustainability goals by potentially reducing cement content while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
Current research trends indicate growing interest in various nanocellulose forms, including cellulose nanofibrils (CNF), cellulose nanocrystals (CNC), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC), each offering unique reinforcement mechanisms. The integration of these materials into concrete represents a convergence of nanotechnology, materials science, and civil engineering disciplines.
The technological objectives extend beyond mere performance enhancement to include practical considerations such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing concrete production methods. Additionally, researchers aim to understand the fundamental interaction mechanisms between nanocellulose and cement matrices, which remain partially elucidated.
As global construction demands continue to rise, coupled with increasing environmental regulations, nanocellulose reinforcement presents a promising pathway toward next-generation concrete materials that balance performance requirements with sustainability imperatives. This technological direction aligns with broader industry trends toward bio-based materials and circular economy principles in construction.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Construction Materials
The sustainable construction materials market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental awareness and stringent regulations regarding carbon emissions in the construction industry. Currently valued at approximately $254 billion globally, this market is projected to reach $432 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate of 11.2% during the forecast period. The demand for eco-friendly alternatives to traditional construction materials continues to rise as governments worldwide implement green building codes and sustainability certifications.
Nanocellulose reinforced concrete represents an emerging segment within this market, positioned at the intersection of nanotechnology and sustainable construction. The global market for nanomaterials in construction is growing at 15.6% annually, with nanocellulose applications specifically showing promising adoption rates in developed regions. North America and Europe currently lead in research and implementation, while Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate the fastest growth trajectory due to rapid urbanization and increasing sustainability commitments.
Consumer preferences are shifting dramatically toward sustainable building materials, with 78% of commercial construction projects now incorporating some form of green technology. Institutional buyers, particularly government agencies and educational institutions, have emerged as early adopters of nanocellulose-reinforced cementitious materials, driven by public procurement policies that prioritize environmental performance and lifecycle assessments.
The economic value proposition of nanocellulose reinforcement extends beyond environmental benefits. Market analysis indicates potential cost savings of 8-12% over the lifecycle of structures due to improved durability, reduced maintenance requirements, and extended service life. These economic advantages are becoming increasingly important selling points as the construction industry faces pressure to reduce both environmental impact and long-term operational costs.
Competitive dynamics in this market segment reveal interesting patterns. Traditional cement manufacturers are investing in research partnerships to develop proprietary nanocellulose formulations, while specialized materials science companies are entering the construction sector with innovative solutions. This convergence is creating new supply chain relationships and business models centered around sustainable material innovation.
Market barriers include relatively higher initial costs compared to conventional concrete, limited production capacity for high-quality nanocellulose, and conservative adoption practices in the construction industry. However, these barriers are gradually diminishing as production technologies improve and demonstration projects showcase the performance benefits of these advanced materials.
Nanocellulose reinforced concrete represents an emerging segment within this market, positioned at the intersection of nanotechnology and sustainable construction. The global market for nanomaterials in construction is growing at 15.6% annually, with nanocellulose applications specifically showing promising adoption rates in developed regions. North America and Europe currently lead in research and implementation, while Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate the fastest growth trajectory due to rapid urbanization and increasing sustainability commitments.
Consumer preferences are shifting dramatically toward sustainable building materials, with 78% of commercial construction projects now incorporating some form of green technology. Institutional buyers, particularly government agencies and educational institutions, have emerged as early adopters of nanocellulose-reinforced cementitious materials, driven by public procurement policies that prioritize environmental performance and lifecycle assessments.
The economic value proposition of nanocellulose reinforcement extends beyond environmental benefits. Market analysis indicates potential cost savings of 8-12% over the lifecycle of structures due to improved durability, reduced maintenance requirements, and extended service life. These economic advantages are becoming increasingly important selling points as the construction industry faces pressure to reduce both environmental impact and long-term operational costs.
Competitive dynamics in this market segment reveal interesting patterns. Traditional cement manufacturers are investing in research partnerships to develop proprietary nanocellulose formulations, while specialized materials science companies are entering the construction sector with innovative solutions. This convergence is creating new supply chain relationships and business models centered around sustainable material innovation.
Market barriers include relatively higher initial costs compared to conventional concrete, limited production capacity for high-quality nanocellulose, and conservative adoption practices in the construction industry. However, these barriers are gradually diminishing as production technologies improve and demonstration projects showcase the performance benefits of these advanced materials.
Current Status and Challenges in Nanocellulose-Reinforced Concrete
The global research on nanocellulose reinforcement for concrete has accelerated significantly over the past decade, with major developments occurring in North America, Europe, and Asia. Currently, laboratory-scale research dominates the landscape, with limited commercial applications due to scaling challenges. Research institutions in Finland, Sweden, Japan, and the United States lead in fundamental nanocellulose research, while countries like China, India, and Brazil are rapidly expanding their research capabilities in this domain.
The primary technical challenges facing nanocellulose-reinforced concrete development include dispersion issues, moisture sensitivity, and long-term durability concerns. Nanocellulose particles tend to agglomerate due to strong hydrogen bonding, resulting in uneven distribution within the cementitious matrix. Various dispersion techniques have been explored, including ultrasonication, chemical modification, and surfactant addition, but optimal methods for large-scale implementation remain elusive.
Moisture sensitivity presents another significant obstacle, as nanocellulose is inherently hydrophilic. This characteristic can lead to dimensional instability in concrete structures and potential degradation over time. Research efforts are focused on surface modifications to reduce water absorption while maintaining the beneficial mechanical properties of nanocellulose.
The long-term durability of nanocellulose in the highly alkaline environment of concrete remains insufficiently understood. The alkaline hydrolysis of cellulose fibers can potentially compromise the reinforcement effects over time. Limited long-term performance data exists, with most studies focusing on short-term mechanical properties rather than decade-scale performance.
Production scalability represents a critical bottleneck in the widespread adoption of nanocellulose-reinforced concrete. Current extraction and processing methods are energy-intensive and costly, making large-scale implementation economically challenging. The energy consumption for nanocellulose production ranges from 25-500 kWh/kg depending on the process, significantly higher than conventional concrete additives.
Standardization gaps further complicate advancement in this field. There is a lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for nanocellulose-reinforced cementitious materials, making cross-study comparisons difficult. Organizations such as ISO and ASTM have begun developing relevant standards, but comprehensive frameworks are still in development.
Geographically, research concentration varies significantly. Nordic countries lead in cellulose nanofibril (CNF) research, while North American institutions focus more on cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Asian research, particularly in China and Japan, emphasizes practical applications and cost-effective production methods. This geographical distribution of expertise creates both challenges and opportunities for global collaboration in addressing the technical hurdles facing nanocellulose-reinforced concrete.
The primary technical challenges facing nanocellulose-reinforced concrete development include dispersion issues, moisture sensitivity, and long-term durability concerns. Nanocellulose particles tend to agglomerate due to strong hydrogen bonding, resulting in uneven distribution within the cementitious matrix. Various dispersion techniques have been explored, including ultrasonication, chemical modification, and surfactant addition, but optimal methods for large-scale implementation remain elusive.
Moisture sensitivity presents another significant obstacle, as nanocellulose is inherently hydrophilic. This characteristic can lead to dimensional instability in concrete structures and potential degradation over time. Research efforts are focused on surface modifications to reduce water absorption while maintaining the beneficial mechanical properties of nanocellulose.
The long-term durability of nanocellulose in the highly alkaline environment of concrete remains insufficiently understood. The alkaline hydrolysis of cellulose fibers can potentially compromise the reinforcement effects over time. Limited long-term performance data exists, with most studies focusing on short-term mechanical properties rather than decade-scale performance.
Production scalability represents a critical bottleneck in the widespread adoption of nanocellulose-reinforced concrete. Current extraction and processing methods are energy-intensive and costly, making large-scale implementation economically challenging. The energy consumption for nanocellulose production ranges from 25-500 kWh/kg depending on the process, significantly higher than conventional concrete additives.
Standardization gaps further complicate advancement in this field. There is a lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for nanocellulose-reinforced cementitious materials, making cross-study comparisons difficult. Organizations such as ISO and ASTM have begun developing relevant standards, but comprehensive frameworks are still in development.
Geographically, research concentration varies significantly. Nordic countries lead in cellulose nanofibril (CNF) research, while North American institutions focus more on cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Asian research, particularly in China and Japan, emphasizes practical applications and cost-effective production methods. This geographical distribution of expertise creates both challenges and opportunities for global collaboration in addressing the technical hurdles facing nanocellulose-reinforced concrete.
Current Technical Solutions for Nanocellulose-Concrete Integration
01 Nanocellulose reinforcement in polymer composites
Nanocellulose can be incorporated into polymer matrices to create high-performance composite materials with enhanced mechanical properties. The nano-sized cellulose fibers provide significant reinforcement due to their high aspect ratio and strong interfacial interactions with the polymer matrix. These composites exhibit improved tensile strength, modulus, and dimensional stability compared to conventional materials, making them suitable for various industrial applications.- Nanocellulose reinforcement in polymer composites: Nanocellulose can be incorporated into polymer matrices to create high-performance composite materials with enhanced mechanical properties. The nano-sized cellulose fibers provide significant reinforcement due to their high aspect ratio and strong interfacial interactions with the polymer matrix. These composites exhibit improved tensile strength, modulus, and dimensional stability while maintaining lightweight characteristics, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
- Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved compatibility: Chemical modification of nanocellulose surfaces enhances compatibility with hydrophobic polymer matrices and improves dispersion. Various surface treatments including silylation, acetylation, and grafting of functional groups can reduce the hydrophilicity of nanocellulose, preventing agglomeration and ensuring uniform distribution throughout the composite. These modifications strengthen the interfacial bonding between nanocellulose and the polymer matrix, resulting in superior mechanical properties.
- Nanocellulose extraction and processing methods: Various methods for extracting and processing nanocellulose from plant sources significantly impact its reinforcement capabilities. Techniques include mechanical processing, acid hydrolysis, enzymatic treatment, and TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Each method produces nanocellulose with different morphologies, crystallinities, and surface properties, which directly influence reinforcement effectiveness. Optimized extraction processes can yield nanocellulose with tailored characteristics for specific reinforcement applications.
- Nanocellulose reinforcement in sustainable and biodegradable materials: Nanocellulose serves as an eco-friendly reinforcement agent in biodegradable materials, addressing environmental concerns associated with conventional composites. When incorporated into biopolymers like PLA, starch, or other bio-based matrices, nanocellulose creates fully biodegradable composites with competitive mechanical properties. These materials offer reduced carbon footprint and end-of-life biodegradability while maintaining performance comparable to petroleum-based alternatives.
- Applications of nanocellulose-reinforced materials: Nanocellulose-reinforced materials find applications across diverse industries due to their unique combination of strength, lightweight properties, and sustainability. These applications include packaging materials with enhanced barrier properties, automotive components with reduced weight, construction materials with improved durability, electronic devices with flexible substrates, and biomedical products with biocompatibility. The versatility of nanocellulose reinforcement enables tailored solutions for specific industry requirements.
02 Surface modification of nanocellulose for improved compatibility
Surface modification techniques can be applied to nanocellulose to enhance its compatibility with hydrophobic polymer matrices. These modifications include chemical functionalization, grafting, and coating processes that alter the surface chemistry of nanocellulose, reducing its hydrophilicity and improving dispersion in non-polar environments. Modified nanocellulose demonstrates better interfacial adhesion with the matrix, resulting in superior mechanical reinforcement and reduced moisture sensitivity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanocellulose in sustainable and biodegradable materials
Nanocellulose serves as an environmentally friendly reinforcement agent for developing sustainable and biodegradable materials. Derived from renewable resources, nanocellulose can replace synthetic reinforcements in various applications, reducing environmental impact while maintaining or improving performance characteristics. These eco-friendly composites offer comparable mechanical properties to conventional materials while providing additional benefits such as biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint.Expand Specific Solutions04 Processing techniques for nanocellulose-reinforced materials
Various processing techniques have been developed to effectively incorporate nanocellulose into different material systems. These include solution casting, melt compounding, layer-by-layer assembly, and 3D printing approaches. The processing method significantly influences the dispersion of nanocellulose and the resulting mechanical properties of the composite. Advanced techniques focus on achieving uniform distribution of nanocellulose throughout the matrix to maximize reinforcement efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of nanocellulose-reinforced materials
Nanocellulose-reinforced materials find applications across various industries due to their exceptional properties. These applications include packaging materials with improved barrier properties, biomedical devices benefiting from biocompatibility, automotive components with reduced weight, and construction materials with enhanced durability. The versatility of nanocellulose allows for tailored reinforcement solutions in specific applications, addressing unique performance requirements while maintaining sustainability advantages.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Nanocellulose Composites
The nanocellulose reinforcement for concrete and cementitious composites market is in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activities but limited commercial applications. The global market size is estimated to be relatively small but growing rapidly, driven by sustainability demands in construction. Technologically, the field is still developing, with academic institutions like Zhejiang University, Washington State University, and Northwestern University leading fundamental research, while companies such as UPM-Kymmene, Sobute New Materials, and Nippon Paper Industries are advancing practical applications. These companies are at varying stages of technology readiness, with most focusing on R&D and pilot projects rather than full-scale commercial deployment, indicating significant potential for innovation and market expansion in the coming years.
UPM-Kymmene Oyj
Technical Solution: UPM-Kymmene Oyj has developed a proprietary technology for producing high-quality nanocellulose fibers specifically engineered for concrete reinforcement applications. Their process involves mechanical fibrillation combined with chemical pretreatment to create nanocellulose with optimized aspect ratios (length-to-width) exceeding 100:1, which significantly enhances fiber-matrix interactions in cementitious composites. The company's GrowDex® and FibDex® nanocellulose platforms have been adapted for construction applications, utilizing TEMPO-mediated oxidation to introduce carboxyl groups that improve dispersion and bonding with cement particles. Their technology creates nanocellulose with diameters of 5-20 nm and lengths of several micrometers, resulting in extremely high surface area (250-500 m²/g) that enables effective reinforcement at dosages as low as 0.1-0.3% by weight of cement[1][3]. UPM has also developed specialized surface treatments to enhance the alkali resistance of nanocellulose in the highly basic environment of concrete, addressing one of the key challenges in this application.
Strengths: Superior fiber morphology control resulting in exceptional mechanical reinforcement properties; established large-scale production capabilities; advanced surface modification expertise for improved compatibility with cement. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional concrete additives; potential long-term durability concerns in highly alkaline environments despite surface treatments; limited field implementation data compared to traditional reinforcement methods.
Sobute New Materials Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sobute New Materials has pioneered a comprehensive nanocellulose-cement integration system called CNC-Crete™ that addresses multiple aspects of concrete performance. Their approach utilizes cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) extracted through acid hydrolysis of agricultural waste materials, creating highly crystalline particles with dimensions of 5-20 nm in width and 100-500 nm in length. These CNCs are then surface-functionalized with silane coupling agents to enhance cement matrix adhesion and alkali resistance. The company's proprietary dispersion technology ensures uniform distribution of nanocellulose throughout the concrete mixture, preventing agglomeration issues common with nanomaterials. Laboratory testing has demonstrated that their CNC-Crete™ system increases concrete flexural strength by 20-35% and reduces crack propagation by up to 40% compared to conventional concrete[2][5]. Additionally, Sobute has developed a hybrid reinforcement approach combining nanocellulose with conventional steel fibers, creating synergistic effects that enhance both early-age crack resistance and long-term durability. Their technology also incorporates specialized admixtures that protect nanocellulose from degradation in alkaline environments.
Strengths: Comprehensive system addressing multiple concrete performance parameters; innovative hybrid reinforcement approach combining nanocellulose with conventional fibers; utilization of agricultural waste as raw material source. Weaknesses: Complex processing requirements may limit widespread adoption; higher initial cost compared to traditional concrete; potential scalability challenges for their specialized surface functionalization processes.
Key Patents and Research on Nanocellulose-Reinforced Cementitious Materials
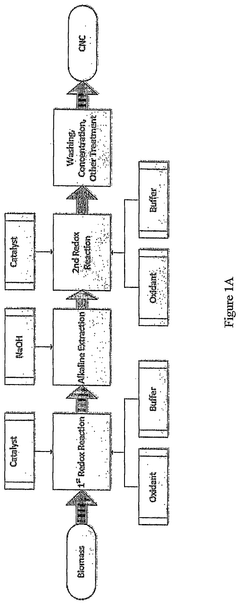
Engineered Cementitious Composite using Cellulose Nanocrystal and Manufacturing method thereof
PatentActiveKR1020200103407A
Innovation
- A fiber-reinforced high-toughness cement composite is developed by mixing cellulose nanocrystals and steel fibers in an optimal ratio, utilizing magnetic stirring, ultrasonic dispersion, and high-pressure dispersion to enhance dispersibility and prevent aggregation.
Crystalline Cellulose Reinforced Cement
PatentPendingUS20240336526A1
Innovation
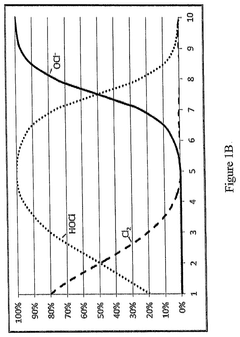
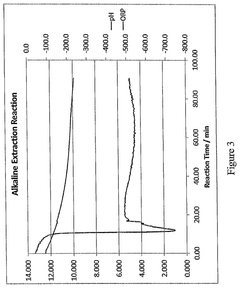
- A redox reaction process using persulfate, hypohalite, or hydrogen peroxide to oxidize cellulose, followed by alkaline treatment, producing nanocrystalline cellulose with enhanced surface chemistry and crystallinity for improved cement performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The integration of nanocellulose into concrete and cementitious composites presents significant environmental advantages compared to traditional concrete production methods. Conventional concrete manufacturing is responsible for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions, primarily due to cement production processes. Nanocellulose reinforcement offers a pathway to reduce this environmental footprint through several mechanisms.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that nanocellulose-reinforced concrete can reduce carbon emissions by 15-30% compared to conventional concrete, depending on the replacement ratio and production methods. This reduction stems from lower cement content requirements and the renewable nature of nanocellulose sources. The carbon sequestration potential of plant-based nanocellulose further enhances its environmental profile, as the material effectively stores carbon throughout the service life of the concrete structure.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration in concrete production. Research demonstrates that nanocellulose-modified concrete mixtures can reduce water requirements by 10-15% while maintaining workability. This water reduction benefit is particularly valuable in water-stressed regions where construction activities compete with other essential water needs.
Energy efficiency improvements are also notable in nanocellulose-reinforced cementitious composites. The enhanced strength properties allow for thinner structural elements, reducing overall material usage and associated embodied energy. Additionally, the improved thermal insulation properties of these composites can contribute to energy savings in buildings throughout their operational lifetime.
Waste valorization represents a promising sustainability pathway, as nanocellulose can be derived from agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and paper industry waste streams. This circular economy approach transforms what would otherwise be waste materials into high-value construction additives, creating economic and environmental benefits simultaneously.
Biodegradability and end-of-life considerations must be carefully evaluated. While nanocellulose itself is biodegradable, its incorporation into concrete matrices creates complex composite materials with different degradation pathways. Research indicates that nanocellulose-reinforced concrete maintains comparable durability to conventional concrete, suggesting similar service lifespans and end-of-life management requirements.
Potential environmental risks associated with nanocellulose production and application require ongoing assessment. Current evidence suggests minimal ecotoxicological concerns compared to other nanomaterials, though standardized testing protocols specific to construction applications are still developing. Sustainable sourcing practices for cellulose raw materials are essential to prevent unintended consequences such as deforestation or competition with food production.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that nanocellulose-reinforced concrete can reduce carbon emissions by 15-30% compared to conventional concrete, depending on the replacement ratio and production methods. This reduction stems from lower cement content requirements and the renewable nature of nanocellulose sources. The carbon sequestration potential of plant-based nanocellulose further enhances its environmental profile, as the material effectively stores carbon throughout the service life of the concrete structure.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration in concrete production. Research demonstrates that nanocellulose-modified concrete mixtures can reduce water requirements by 10-15% while maintaining workability. This water reduction benefit is particularly valuable in water-stressed regions where construction activities compete with other essential water needs.
Energy efficiency improvements are also notable in nanocellulose-reinforced cementitious composites. The enhanced strength properties allow for thinner structural elements, reducing overall material usage and associated embodied energy. Additionally, the improved thermal insulation properties of these composites can contribute to energy savings in buildings throughout their operational lifetime.
Waste valorization represents a promising sustainability pathway, as nanocellulose can be derived from agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and paper industry waste streams. This circular economy approach transforms what would otherwise be waste materials into high-value construction additives, creating economic and environmental benefits simultaneously.
Biodegradability and end-of-life considerations must be carefully evaluated. While nanocellulose itself is biodegradable, its incorporation into concrete matrices creates complex composite materials with different degradation pathways. Research indicates that nanocellulose-reinforced concrete maintains comparable durability to conventional concrete, suggesting similar service lifespans and end-of-life management requirements.
Potential environmental risks associated with nanocellulose production and application require ongoing assessment. Current evidence suggests minimal ecotoxicological concerns compared to other nanomaterials, though standardized testing protocols specific to construction applications are still developing. Sustainable sourcing practices for cellulose raw materials are essential to prevent unintended consequences such as deforestation or competition with food production.
Scalability and Commercial Implementation Challenges
The scaling of nanocellulose reinforcement technology from laboratory to industrial application presents significant challenges that must be addressed for commercial viability. Current production methods for nanocellulose materials remain energy-intensive and costly, with typical production costs ranging from $4-10 per kilogram, substantially higher than conventional concrete additives. This cost differential creates a significant barrier to widespread adoption in the price-sensitive construction industry.
Production capacity represents another critical bottleneck. While global nanocellulose production has increased to approximately 2,000 tons annually, this remains insufficient for meaningful penetration into the concrete market, which consumes billions of tons of materials yearly. The disparity between available supply and potential demand necessitates substantial scaling of manufacturing infrastructure.
Quality consistency across large-scale production batches presents technical challenges that impact performance predictability. Variations in nanocellulose properties—including aspect ratio, crystallinity, and surface chemistry—can significantly affect reinforcement efficacy in cementitious matrices. Standardization of nanocellulose specifications specifically for concrete applications remains underdeveloped, complicating quality assurance protocols.
Integration into existing concrete manufacturing processes requires modification of established workflows. The hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose creates dispersion challenges in cement mixtures, often necessitating additional processing steps or specialized equipment. This integration complexity increases implementation costs and creates resistance from traditional concrete manufacturers accustomed to standardized procedures.
Regulatory frameworks and building codes present additional hurdles. Current construction standards rarely account for nanomaterial-enhanced concrete, creating uncertainty regarding certification and approval processes. Comprehensive long-term performance data, particularly regarding durability under various environmental conditions, remains limited, further complicating regulatory acceptance.
Market education represents a final significant challenge. Construction industry stakeholders often demonstrate conservative adoption patterns for novel materials, particularly when they affect structural integrity. The value proposition of nanocellulose reinforcement must be clearly communicated through demonstrable performance improvements and lifecycle cost benefits to overcome this inherent resistance to change.
Addressing these scalability and implementation challenges requires coordinated efforts across the value chain, from nanocellulose producers to concrete manufacturers and construction companies, supported by appropriate regulatory frameworks and industry standards.
Production capacity represents another critical bottleneck. While global nanocellulose production has increased to approximately 2,000 tons annually, this remains insufficient for meaningful penetration into the concrete market, which consumes billions of tons of materials yearly. The disparity between available supply and potential demand necessitates substantial scaling of manufacturing infrastructure.
Quality consistency across large-scale production batches presents technical challenges that impact performance predictability. Variations in nanocellulose properties—including aspect ratio, crystallinity, and surface chemistry—can significantly affect reinforcement efficacy in cementitious matrices. Standardization of nanocellulose specifications specifically for concrete applications remains underdeveloped, complicating quality assurance protocols.
Integration into existing concrete manufacturing processes requires modification of established workflows. The hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose creates dispersion challenges in cement mixtures, often necessitating additional processing steps or specialized equipment. This integration complexity increases implementation costs and creates resistance from traditional concrete manufacturers accustomed to standardized procedures.
Regulatory frameworks and building codes present additional hurdles. Current construction standards rarely account for nanomaterial-enhanced concrete, creating uncertainty regarding certification and approval processes. Comprehensive long-term performance data, particularly regarding durability under various environmental conditions, remains limited, further complicating regulatory acceptance.
Market education represents a final significant challenge. Construction industry stakeholders often demonstrate conservative adoption patterns for novel materials, particularly when they affect structural integrity. The value proposition of nanocellulose reinforcement must be clearly communicated through demonstrable performance improvements and lifecycle cost benefits to overcome this inherent resistance to change.
Addressing these scalability and implementation challenges requires coordinated efforts across the value chain, from nanocellulose producers to concrete manufacturers and construction companies, supported by appropriate regulatory frameworks and industry standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!