PMMA's Impact on the Evolution of Optical Devices
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMMA in Optical Devices: Background and Objectives
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, has played a pivotal role in the evolution of optical devices since its introduction in the 1930s. This versatile thermoplastic material has become a cornerstone in the development of various optical components due to its exceptional optical properties, including high transparency, low dispersion, and excellent light transmission capabilities.
The journey of PMMA in optical devices began with its use in simple applications such as lenses and light guides. Over time, its potential in more complex optical systems became apparent, leading to its widespread adoption in fields ranging from consumer electronics to advanced scientific instruments. The material's unique combination of optical clarity, durability, and ease of processing has made it an ideal choice for manufacturers seeking to innovate in the optical device market.
As the demand for more sophisticated optical devices grew, so did the need for materials that could meet increasingly stringent performance requirements. PMMA's ability to be modified and enhanced through various manufacturing processes has allowed it to keep pace with these evolving demands. Researchers and engineers have continually pushed the boundaries of what is possible with PMMA, developing new formulations and processing techniques to improve its optical and mechanical properties.
The objectives of utilizing PMMA in optical devices have expanded significantly since its initial applications. Today, the material is integral to achieving higher resolution in imaging systems, improved light transmission in fiber optics, and enhanced durability in outdoor optical installations. Additionally, PMMA's role in miniaturization efforts has been crucial, enabling the development of compact optical components for smartphones, wearable devices, and other portable technologies.
Looking ahead, the future of PMMA in optical devices is closely tied to emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and advanced sensing systems. These fields require optical materials that can deliver exceptional performance while meeting strict weight and size constraints. As such, ongoing research is focused on further refining PMMA's properties to meet these challenges, including efforts to increase its refractive index, improve its resistance to environmental factors, and enhance its compatibility with other materials used in optical systems.
The evolution of PMMA's use in optical devices reflects broader trends in materials science and engineering, where the continuous improvement of existing materials is as important as the discovery of new ones. By understanding the historical context and future potential of PMMA in optical applications, researchers and industry professionals can better appreciate the material's significance and continue to innovate in ways that push the boundaries of optical technology.
The journey of PMMA in optical devices began with its use in simple applications such as lenses and light guides. Over time, its potential in more complex optical systems became apparent, leading to its widespread adoption in fields ranging from consumer electronics to advanced scientific instruments. The material's unique combination of optical clarity, durability, and ease of processing has made it an ideal choice for manufacturers seeking to innovate in the optical device market.
As the demand for more sophisticated optical devices grew, so did the need for materials that could meet increasingly stringent performance requirements. PMMA's ability to be modified and enhanced through various manufacturing processes has allowed it to keep pace with these evolving demands. Researchers and engineers have continually pushed the boundaries of what is possible with PMMA, developing new formulations and processing techniques to improve its optical and mechanical properties.
The objectives of utilizing PMMA in optical devices have expanded significantly since its initial applications. Today, the material is integral to achieving higher resolution in imaging systems, improved light transmission in fiber optics, and enhanced durability in outdoor optical installations. Additionally, PMMA's role in miniaturization efforts has been crucial, enabling the development of compact optical components for smartphones, wearable devices, and other portable technologies.
Looking ahead, the future of PMMA in optical devices is closely tied to emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and advanced sensing systems. These fields require optical materials that can deliver exceptional performance while meeting strict weight and size constraints. As such, ongoing research is focused on further refining PMMA's properties to meet these challenges, including efforts to increase its refractive index, improve its resistance to environmental factors, and enhance its compatibility with other materials used in optical systems.
The evolution of PMMA's use in optical devices reflects broader trends in materials science and engineering, where the continuous improvement of existing materials is as important as the discovery of new ones. By understanding the historical context and future potential of PMMA in optical applications, researchers and industry professionals can better appreciate the material's significance and continue to innovate in ways that push the boundaries of optical technology.
Market Analysis for PMMA-based Optical Solutions
The market for PMMA-based optical solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance optical devices across various industries. PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, has become a crucial material in the development of optical components due to its excellent optical properties, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness.
In the consumer electronics sector, PMMA-based optical solutions have found widespread application in smartphone displays, tablets, and wearable devices. The growing trend of miniaturization and improved display quality has led to a surge in demand for PMMA-based lenses and light guides. This segment is expected to continue its robust growth as consumers seek devices with enhanced visual experiences.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a key market for PMMA-based optical solutions. With the increasing adoption of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and the development of autonomous vehicles, there is a rising need for high-quality optical components. PMMA-based lenses and light guides are being utilized in headlights, taillights, and various sensors, contributing to improved safety and aesthetics in modern vehicles.
In the healthcare sector, PMMA-based optical solutions have gained traction in medical imaging devices, diagnostic equipment, and surgical instruments. The material's biocompatibility and optical clarity make it ideal for applications such as endoscopes, microscopes, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems. As healthcare technologies continue to advance, the demand for PMMA-based optical components in this sector is projected to grow steadily.
The telecommunications industry represents another significant market for PMMA-based optical solutions. With the ongoing expansion of fiber-optic networks and the rollout of 5G technology, there is an increasing need for optical components that can support high-speed data transmission. PMMA-based optical fibers and connectors are being utilized in various network infrastructure applications, contributing to improved connectivity and bandwidth.
Market analysts predict that the global PMMA-based optical solutions market will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the material's versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to meet the evolving requirements of various industries. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts are expected to further enhance the performance and applications of PMMA-based optical components, opening up new market opportunities.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in product development, the recyclability of PMMA is likely to drive its adoption in optical applications. This eco-friendly aspect of PMMA aligns with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles and may provide a competitive advantage in certain market segments.
In the consumer electronics sector, PMMA-based optical solutions have found widespread application in smartphone displays, tablets, and wearable devices. The growing trend of miniaturization and improved display quality has led to a surge in demand for PMMA-based lenses and light guides. This segment is expected to continue its robust growth as consumers seek devices with enhanced visual experiences.
The automotive industry has also emerged as a key market for PMMA-based optical solutions. With the increasing adoption of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and the development of autonomous vehicles, there is a rising need for high-quality optical components. PMMA-based lenses and light guides are being utilized in headlights, taillights, and various sensors, contributing to improved safety and aesthetics in modern vehicles.
In the healthcare sector, PMMA-based optical solutions have gained traction in medical imaging devices, diagnostic equipment, and surgical instruments. The material's biocompatibility and optical clarity make it ideal for applications such as endoscopes, microscopes, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems. As healthcare technologies continue to advance, the demand for PMMA-based optical components in this sector is projected to grow steadily.
The telecommunications industry represents another significant market for PMMA-based optical solutions. With the ongoing expansion of fiber-optic networks and the rollout of 5G technology, there is an increasing need for optical components that can support high-speed data transmission. PMMA-based optical fibers and connectors are being utilized in various network infrastructure applications, contributing to improved connectivity and bandwidth.
Market analysts predict that the global PMMA-based optical solutions market will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the material's versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to meet the evolving requirements of various industries. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts are expected to further enhance the performance and applications of PMMA-based optical components, opening up new market opportunities.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in product development, the recyclability of PMMA is likely to drive its adoption in optical applications. This eco-friendly aspect of PMMA aligns with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles and may provide a competitive advantage in certain market segments.
Current PMMA Applications and Technical Challenges
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, has become a cornerstone material in the development and production of various optical devices. Its widespread adoption can be attributed to its unique combination of properties, including excellent optical clarity, light transmission, and durability. In the field of optical devices, PMMA is extensively used in the manufacturing of lenses, optical fibers, light guides, and display screens.
One of the primary applications of PMMA in optical devices is in the production of high-quality lenses. Its optical properties, such as high refractive index and low dispersion, make it an ideal material for creating precision lenses used in cameras, projectors, and other imaging systems. PMMA lenses offer advantages over glass in terms of weight reduction and impact resistance, making them particularly suitable for portable devices and outdoor applications.
In the realm of light transmission, PMMA optical fibers have gained significant traction. These fibers are used in short-distance data communication, medical endoscopy, and decorative lighting. PMMA fibers offer advantages in terms of flexibility and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional glass fibers, although they typically have higher attenuation rates over long distances.
The display industry has also benefited greatly from PMMA's properties. It is commonly used in the production of light guide plates for LCD displays, enhancing brightness and uniformity of illumination. Additionally, PMMA is utilized in the manufacturing of diffusers and prisms for LED lighting systems, contributing to improved light distribution and energy efficiency.
Despite its widespread use, PMMA faces several technical challenges in optical device applications. One significant issue is its relatively low heat resistance compared to glass. This limitation can lead to deformation or degradation of optical components in high-temperature environments, restricting its use in certain applications.
Another challenge is PMMA's susceptibility to scratching and abrasion. While it offers good impact resistance, its surface hardness is lower than that of glass, potentially affecting the longevity and optical performance of devices exposed to harsh conditions or frequent handling.
The material's hygroscopic nature presents additional complications. PMMA can absorb moisture from the environment, leading to dimensional changes and potential degradation of optical properties over time. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration in design and packaging of PMMA-based optical components, especially for applications in humid environments.
Addressing these challenges has become a focus of ongoing research and development efforts. Scientists and engineers are exploring various approaches, including the development of hybrid materials, surface treatments, and advanced manufacturing techniques to enhance PMMA's performance in optical applications. These efforts aim to expand the material's applicability while maintaining its advantageous properties, driving further innovation in the field of optical devices.
One of the primary applications of PMMA in optical devices is in the production of high-quality lenses. Its optical properties, such as high refractive index and low dispersion, make it an ideal material for creating precision lenses used in cameras, projectors, and other imaging systems. PMMA lenses offer advantages over glass in terms of weight reduction and impact resistance, making them particularly suitable for portable devices and outdoor applications.
In the realm of light transmission, PMMA optical fibers have gained significant traction. These fibers are used in short-distance data communication, medical endoscopy, and decorative lighting. PMMA fibers offer advantages in terms of flexibility and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional glass fibers, although they typically have higher attenuation rates over long distances.
The display industry has also benefited greatly from PMMA's properties. It is commonly used in the production of light guide plates for LCD displays, enhancing brightness and uniformity of illumination. Additionally, PMMA is utilized in the manufacturing of diffusers and prisms for LED lighting systems, contributing to improved light distribution and energy efficiency.
Despite its widespread use, PMMA faces several technical challenges in optical device applications. One significant issue is its relatively low heat resistance compared to glass. This limitation can lead to deformation or degradation of optical components in high-temperature environments, restricting its use in certain applications.
Another challenge is PMMA's susceptibility to scratching and abrasion. While it offers good impact resistance, its surface hardness is lower than that of glass, potentially affecting the longevity and optical performance of devices exposed to harsh conditions or frequent handling.
The material's hygroscopic nature presents additional complications. PMMA can absorb moisture from the environment, leading to dimensional changes and potential degradation of optical properties over time. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration in design and packaging of PMMA-based optical components, especially for applications in humid environments.
Addressing these challenges has become a focus of ongoing research and development efforts. Scientists and engineers are exploring various approaches, including the development of hybrid materials, surface treatments, and advanced manufacturing techniques to enhance PMMA's performance in optical applications. These efforts aim to expand the material's applicability while maintaining its advantageous properties, driving further innovation in the field of optical devices.
Current PMMA Optical Device Solutions
01 Impact resistance improvement of PMMA
Various methods are employed to enhance the impact resistance of PMMA, including the incorporation of impact modifiers, core-shell particles, and elastomeric components. These additives can significantly improve the toughness and durability of PMMA-based materials, making them suitable for applications requiring high impact strength.- Impact resistance improvement of PMMA: Various methods are employed to enhance the impact resistance of PMMA, including the incorporation of impact modifiers, core-shell particles, and elastomeric components. These additives can significantly improve the toughness and durability of PMMA-based materials, making them suitable for applications requiring high impact strength.
- PMMA composite materials: PMMA is often combined with other materials to create composite structures with enhanced properties. These composites may include reinforcing fibers, nanoparticles, or other polymers, resulting in materials with improved mechanical strength, thermal stability, and impact resistance compared to pure PMMA.
- Surface modification of PMMA: Surface treatments and modifications are applied to PMMA to improve its impact resistance and other properties. These techniques may include plasma treatment, chemical grafting, or the application of protective coatings, which can enhance the material's durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- PMMA blends and alloys: Blending PMMA with other polymers or creating polymer alloys can result in materials with improved impact resistance. These blends often combine the desirable properties of PMMA, such as optical clarity, with the toughness of other polymers, leading to materials suitable for high-impact applications.
- Processing techniques for impact-resistant PMMA: Specialized processing techniques are developed to produce PMMA with enhanced impact resistance. These may include specific extrusion or molding processes, heat treatments, or the use of additives during manufacturing. Such techniques aim to optimize the material's structure and properties for improved impact performance.
02 PMMA composites for specific applications
PMMA is often combined with other materials to create composites tailored for specific applications. These composites may include reinforcing fibers, nanoparticles, or other polymers to enhance properties such as strength, thermal stability, or optical characteristics, while maintaining the desirable features of PMMA.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification of PMMA
Surface treatments and modifications are applied to PMMA to improve its properties, such as scratch resistance, adhesion, or compatibility with other materials. These modifications can include plasma treatment, chemical etching, or the application of functional coatings, enhancing the material's performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 PMMA blends and alloys
PMMA is blended or alloyed with other polymers to create materials with enhanced properties. These blends can combine the transparency and weatherability of PMMA with the impact resistance or other desirable characteristics of the partner polymer, resulting in materials suitable for a wide range of applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing techniques for PMMA
Various processing techniques are developed and optimized for PMMA to improve its properties and performance. These may include specialized extrusion or molding processes, heat treatments, or the use of additives during processing to enhance the material's impact resistance, optical clarity, or other desired characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PMMA Optical Industry
The PMMA optical devices market is in a mature growth phase, with a significant global market size driven by increasing demand for high-performance optical components. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with established players like DuPont de Nemours, Canon, and Carl Zeiss SMT leading innovation. These companies, along with emerging players such as Kingfa Sci. & Tech. and Xinlun New Materials, are focusing on advanced PMMA formulations and manufacturing processes to enhance optical performance and durability. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized materials companies, with ongoing research collaborations between industry and academic institutions like MIT and Nankai University driving further advancements in PMMA-based optical technologies.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has developed advanced PMMA formulations with enhanced optical properties for use in various optical devices. Their PMMA-based materials feature improved light transmission, reduced haze, and increased durability. DuPont's research focuses on incorporating nanoparticles and specialty additives to enhance PMMA's performance in optical applications. They have successfully created PMMA grades with higher refractive indices and lower birefringence, making them suitable for high-precision optical components[1][3]. DuPont has also developed PMMA-based optical fibers with reduced attenuation and improved flexibility, enabling their use in telecommunications and medical imaging devices[2].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, wide range of PMMA formulations for different optical applications, and strong market presence. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to standard PMMA, and potential limitations in extreme environmental conditions.
Canon, Inc.
Technical Solution: Canon has leveraged PMMA in the development of advanced optical devices, particularly in camera lenses and imaging systems. They have engineered PMMA-based lens elements with aspherical surfaces, reducing chromatic aberration and improving overall image quality. Canon's research has focused on optimizing PMMA's optical properties through precision molding techniques and surface treatments. They have developed proprietary PMMA formulations with enhanced UV resistance and thermal stability, extending the lifespan of optical components in their products[4]. Canon has also explored the use of PMMA in diffractive optical elements, enabling more compact and lightweight lens designs for both consumer and professional camera systems[5].
Strengths: Expertise in precision optics, integration of PMMA in high-performance imaging systems, and strong brand recognition. Weaknesses: Limited to specific applications within the imaging industry, and potential higher costs compared to traditional glass optics.
Core PMMA Optical Innovations
Printable films
PatentWO2022108678A1
Innovation
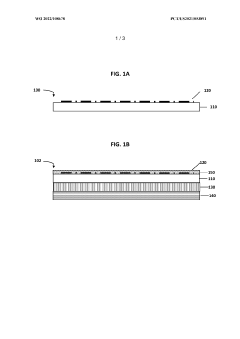
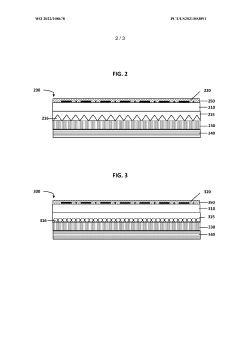
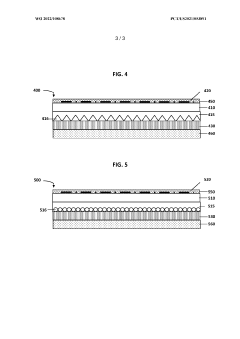
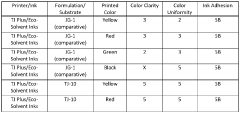
- A composition comprising PMMA and an acrylic copolymer with hard and soft segments, where the soft segments have a glass transition temperature less than 50°C, is used to enhance the print quality by improving ink adhesion and clarity, including the use of a pressure-sensitive adhesive and retroreflective elements in multilayer systems.
Environmental Impact of PMMA in Optics
The environmental impact of PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) in optics is a crucial consideration as the material continues to play a significant role in the evolution of optical devices. PMMA, also known as acrylic or plexiglass, has become a popular choice for various optical applications due to its excellent optical properties and versatility. However, its widespread use has raised concerns about its environmental footprint throughout its lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental advantages of PMMA in optics is its potential for recycling. Unlike some other optical materials, PMMA can be effectively recycled without significant loss of quality. This characteristic allows for the reduction of waste and the conservation of resources in the production of optical devices. However, the recycling process itself requires energy and may produce emissions, which must be carefully managed to minimize environmental impact.
The production of PMMA involves the use of petrochemical resources, which raises concerns about its sustainability. The manufacturing process can be energy-intensive and may result in the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled. As the demand for optical devices increases, the environmental burden of PMMA production could become more significant, necessitating the development of more sustainable manufacturing methods.
In terms of durability, PMMA offers advantages that can indirectly benefit the environment. Its resistance to weathering and UV radiation means that optical devices made with PMMA often have longer lifespans than those made with less durable materials. This longevity can reduce the frequency of replacement and, consequently, the overall environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of optical devices.
However, the disposal of PMMA-based optical devices at the end of their life cycle presents environmental challenges. While recyclable, not all PMMA products are recycled in practice due to various factors such as contamination or lack of appropriate recycling facilities. Improper disposal can lead to PMMA contributing to plastic pollution, particularly in marine environments where it may persist for many years.
The use of PMMA in optical devices also has implications for energy efficiency. Its excellent light transmission properties can contribute to the development of more energy-efficient lighting and display technologies. This indirect environmental benefit must be weighed against the material's production and end-of-life impacts when assessing its overall environmental footprint in the optics industry.
As the optical industry continues to evolve, there is growing research into bio-based alternatives to PMMA that could offer similar optical properties with reduced environmental impact. These developments, along with improvements in recycling technologies and manufacturing processes, may help to mitigate the environmental concerns associated with PMMA use in optical applications.
One of the primary environmental advantages of PMMA in optics is its potential for recycling. Unlike some other optical materials, PMMA can be effectively recycled without significant loss of quality. This characteristic allows for the reduction of waste and the conservation of resources in the production of optical devices. However, the recycling process itself requires energy and may produce emissions, which must be carefully managed to minimize environmental impact.
The production of PMMA involves the use of petrochemical resources, which raises concerns about its sustainability. The manufacturing process can be energy-intensive and may result in the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) if not properly controlled. As the demand for optical devices increases, the environmental burden of PMMA production could become more significant, necessitating the development of more sustainable manufacturing methods.
In terms of durability, PMMA offers advantages that can indirectly benefit the environment. Its resistance to weathering and UV radiation means that optical devices made with PMMA often have longer lifespans than those made with less durable materials. This longevity can reduce the frequency of replacement and, consequently, the overall environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of optical devices.
However, the disposal of PMMA-based optical devices at the end of their life cycle presents environmental challenges. While recyclable, not all PMMA products are recycled in practice due to various factors such as contamination or lack of appropriate recycling facilities. Improper disposal can lead to PMMA contributing to plastic pollution, particularly in marine environments where it may persist for many years.
The use of PMMA in optical devices also has implications for energy efficiency. Its excellent light transmission properties can contribute to the development of more energy-efficient lighting and display technologies. This indirect environmental benefit must be weighed against the material's production and end-of-life impacts when assessing its overall environmental footprint in the optics industry.
As the optical industry continues to evolve, there is growing research into bio-based alternatives to PMMA that could offer similar optical properties with reduced environmental impact. These developments, along with improvements in recycling technologies and manufacturing processes, may help to mitigate the environmental concerns associated with PMMA use in optical applications.
PMMA Optical Device Manufacturing Processes
PMMA optical device manufacturing processes have evolved significantly over the years, driven by the unique properties of this versatile material. The process typically begins with the production of high-quality PMMA sheets or rods, which are then subjected to various shaping and finishing techniques to create optical components.
Injection molding is a widely used method for mass-producing PMMA optical devices. This process involves heating PMMA pellets until they melt, then injecting the molten material into precision-engineered molds. The molds are designed to create complex shapes with high accuracy, making this method ideal for producing lenses, light guides, and other optical components in large quantities. The cooling and solidification process is carefully controlled to minimize internal stresses and ensure optical clarity.
For more specialized applications, precision machining techniques are employed. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling and turning are used to shape PMMA blocks or rods into precise optical components. These processes allow for the creation of custom shapes and surface profiles with tight tolerances. Diamond turning, in particular, is utilized for producing high-precision aspheric lenses and mirrors, achieving surface roughness levels as low as a few nanometers.
Casting is another important manufacturing process for PMMA optical devices. This method is particularly useful for creating large optical elements or those with complex geometries. Liquid PMMA monomer is carefully poured into molds and then polymerized under controlled conditions. This process allows for the production of optical components with excellent homogeneity and low internal stress.
Surface treatments play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of PMMA optical devices. Polishing techniques, such as magnetorheological finishing, are used to achieve ultra-smooth surfaces with sub-nanometer roughness. Anti-reflective coatings are often applied to reduce glare and improve light transmission. Additionally, hard coatings can be used to increase scratch resistance and durability of PMMA optical components.
Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, are increasingly being explored for PMMA optical device production. While still in the early stages, these additive manufacturing methods offer the potential for rapid prototyping and the creation of complex optical structures that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods.
Quality control is a critical aspect of PMMA optical device manufacturing. Sophisticated metrology tools, including interferometers and profilometers, are used to verify the optical and geometric properties of the finished components. Environmental testing is also conducted to ensure the stability and performance of PMMA optical devices under various conditions of temperature, humidity, and UV exposure.
Injection molding is a widely used method for mass-producing PMMA optical devices. This process involves heating PMMA pellets until they melt, then injecting the molten material into precision-engineered molds. The molds are designed to create complex shapes with high accuracy, making this method ideal for producing lenses, light guides, and other optical components in large quantities. The cooling and solidification process is carefully controlled to minimize internal stresses and ensure optical clarity.
For more specialized applications, precision machining techniques are employed. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling and turning are used to shape PMMA blocks or rods into precise optical components. These processes allow for the creation of custom shapes and surface profiles with tight tolerances. Diamond turning, in particular, is utilized for producing high-precision aspheric lenses and mirrors, achieving surface roughness levels as low as a few nanometers.
Casting is another important manufacturing process for PMMA optical devices. This method is particularly useful for creating large optical elements or those with complex geometries. Liquid PMMA monomer is carefully poured into molds and then polymerized under controlled conditions. This process allows for the production of optical components with excellent homogeneity and low internal stress.
Surface treatments play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of PMMA optical devices. Polishing techniques, such as magnetorheological finishing, are used to achieve ultra-smooth surfaces with sub-nanometer roughness. Anti-reflective coatings are often applied to reduce glare and improve light transmission. Additionally, hard coatings can be used to increase scratch resistance and durability of PMMA optical components.
Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, are increasingly being explored for PMMA optical device production. While still in the early stages, these additive manufacturing methods offer the potential for rapid prototyping and the creation of complex optical structures that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional methods.
Quality control is a critical aspect of PMMA optical device manufacturing. Sophisticated metrology tools, including interferometers and profilometers, are used to verify the optical and geometric properties of the finished components. Environmental testing is also conducted to ensure the stability and performance of PMMA optical devices under various conditions of temperature, humidity, and UV exposure.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!