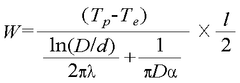Antifreeze in Eco-Smart Housing Design Frameworks
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Antifreeze in Eco-Housing: Background and Objectives
The use of antifreeze in eco-smart housing design frameworks represents a significant advancement in sustainable architecture and energy-efficient building technologies. This innovative approach aims to address the challenges of maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures in extreme climates while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Historically, antifreeze has been primarily associated with automotive applications, preventing engine coolant from freezing in cold temperatures. However, its potential in building design has gained attention in recent years as architects and engineers seek novel solutions for creating more sustainable and energy-efficient structures.
The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the growing awareness of climate change and the urgent need for reducing carbon emissions in the construction and housing sectors. As global temperatures continue to fluctuate, with more frequent extreme weather events, the demand for adaptive and resilient housing solutions has intensified.
In the context of eco-smart housing, antifreeze is being explored for its thermal properties and potential integration into various building systems. These applications range from enhanced insulation materials to innovative heating and cooling systems that leverage the unique characteristics of antifreeze compounds.
The primary objective of incorporating antifreeze in eco-smart housing design is to improve overall energy efficiency and thermal performance. By utilizing antifreeze-based solutions, designers aim to create buildings that can maintain stable indoor temperatures with minimal reliance on traditional heating and cooling systems, thereby reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
Another key goal is to enhance the adaptability of housing structures to diverse climate conditions. Antifreeze technologies offer the potential for buildings to respond more effectively to temperature fluctuations, providing comfort in both extremely cold and hot environments without compromising on sustainability principles.
Furthermore, research in this field seeks to develop cost-effective and environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations specifically tailored for building applications. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives and recyclable compounds that align with the broader objectives of eco-smart housing design.
As the construction industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the integration of antifreeze in eco-smart housing represents a promising avenue for innovation. This research not only aims to improve the performance of individual buildings but also contributes to the larger goal of creating more resilient and sustainable urban environments in the face of climate change.
Historically, antifreeze has been primarily associated with automotive applications, preventing engine coolant from freezing in cold temperatures. However, its potential in building design has gained attention in recent years as architects and engineers seek novel solutions for creating more sustainable and energy-efficient structures.
The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the growing awareness of climate change and the urgent need for reducing carbon emissions in the construction and housing sectors. As global temperatures continue to fluctuate, with more frequent extreme weather events, the demand for adaptive and resilient housing solutions has intensified.
In the context of eco-smart housing, antifreeze is being explored for its thermal properties and potential integration into various building systems. These applications range from enhanced insulation materials to innovative heating and cooling systems that leverage the unique characteristics of antifreeze compounds.
The primary objective of incorporating antifreeze in eco-smart housing design is to improve overall energy efficiency and thermal performance. By utilizing antifreeze-based solutions, designers aim to create buildings that can maintain stable indoor temperatures with minimal reliance on traditional heating and cooling systems, thereby reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
Another key goal is to enhance the adaptability of housing structures to diverse climate conditions. Antifreeze technologies offer the potential for buildings to respond more effectively to temperature fluctuations, providing comfort in both extremely cold and hot environments without compromising on sustainability principles.
Furthermore, research in this field seeks to develop cost-effective and environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations specifically tailored for building applications. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives and recyclable compounds that align with the broader objectives of eco-smart housing design.
As the construction industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the integration of antifreeze in eco-smart housing represents a promising avenue for innovation. This research not only aims to improve the performance of individual buildings but also contributes to the larger goal of creating more resilient and sustainable urban environments in the face of climate change.
Market Analysis for Eco-Smart Housing Solutions
The eco-smart housing market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental awareness, government regulations, and consumer demand for sustainable living solutions. This market segment encompasses a wide range of technologies and design principles aimed at reducing energy consumption, minimizing environmental impact, and enhancing overall living comfort.
The global eco-smart housing market was valued at approximately $79 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $132 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising energy costs, stringent building codes, and growing consumer preference for environmentally friendly homes.
In the context of antifreeze usage in eco-smart housing design frameworks, the market analysis reveals a niche but rapidly expanding segment. Antifreeze solutions in eco-smart housing primarily focus on improving the efficiency of heating and cooling systems, particularly in regions with extreme temperature variations.
The demand for antifreeze-based solutions in eco-smart housing is driven by the need for more efficient and sustainable temperature regulation systems. Traditional heating and cooling methods often consume significant amounts of energy, contributing to higher carbon emissions and increased utility costs. Antifreeze-based systems, when integrated into eco-smart housing designs, can offer improved thermal management, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced overall sustainability.
Key market trends in this sector include the development of bio-based antifreeze solutions, integration of smart control systems for optimized performance, and the adoption of closed-loop systems that minimize environmental impact. These innovations are attracting attention from both residential and commercial property developers seeking to differentiate their offerings in an increasingly competitive market.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for antifreeze applications in eco-smart housing, owing to their advanced building technologies and stringent energy efficiency regulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in this sector as urbanization accelerates and environmental concerns gain prominence.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established HVAC manufacturers, innovative startups, and sustainability-focused construction companies. Collaborations between technology providers and building developers are becoming more common, driving the integration of antifreeze-based solutions into comprehensive eco-smart housing frameworks.
Consumer awareness and education remain critical factors influencing market growth. As homeowners and businesses become more informed about the long-term benefits of eco-smart housing solutions, including those utilizing antifreeze technologies, the demand for such systems is expected to increase substantially in the coming years.
The global eco-smart housing market was valued at approximately $79 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $132 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising energy costs, stringent building codes, and growing consumer preference for environmentally friendly homes.
In the context of antifreeze usage in eco-smart housing design frameworks, the market analysis reveals a niche but rapidly expanding segment. Antifreeze solutions in eco-smart housing primarily focus on improving the efficiency of heating and cooling systems, particularly in regions with extreme temperature variations.
The demand for antifreeze-based solutions in eco-smart housing is driven by the need for more efficient and sustainable temperature regulation systems. Traditional heating and cooling methods often consume significant amounts of energy, contributing to higher carbon emissions and increased utility costs. Antifreeze-based systems, when integrated into eco-smart housing designs, can offer improved thermal management, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced overall sustainability.
Key market trends in this sector include the development of bio-based antifreeze solutions, integration of smart control systems for optimized performance, and the adoption of closed-loop systems that minimize environmental impact. These innovations are attracting attention from both residential and commercial property developers seeking to differentiate their offerings in an increasingly competitive market.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for antifreeze applications in eco-smart housing, owing to their advanced building technologies and stringent energy efficiency regulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in this sector as urbanization accelerates and environmental concerns gain prominence.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established HVAC manufacturers, innovative startups, and sustainability-focused construction companies. Collaborations between technology providers and building developers are becoming more common, driving the integration of antifreeze-based solutions into comprehensive eco-smart housing frameworks.
Consumer awareness and education remain critical factors influencing market growth. As homeowners and businesses become more informed about the long-term benefits of eco-smart housing solutions, including those utilizing antifreeze technologies, the demand for such systems is expected to increase substantially in the coming years.
Current Antifreeze Technologies in Sustainable Architecture
Current antifreeze technologies in sustainable architecture have evolved significantly to address the challenges of eco-smart housing design. Traditional antifreeze solutions, primarily used in HVAC systems, have been adapted and improved to align with sustainability goals. One of the most prominent advancements is the development of environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations. These new solutions utilize biodegradable compounds and non-toxic ingredients, reducing the environmental impact associated with conventional ethylene glycol-based products.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards propylene glycol-based antifreeze solutions in sustainable building designs. Propylene glycol is less toxic and more biodegradable than ethylene glycol, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious architects and engineers. These solutions offer comparable performance in terms of freeze protection and heat transfer efficiency while minimizing potential harm to the environment and human health.
Another innovative approach in current antifreeze technologies is the integration of phase change materials (PCMs) into building envelopes. PCMs can absorb and release thermal energy during phase transitions, effectively regulating indoor temperatures and reducing the load on HVAC systems. This technology has been successfully incorporated into wall panels, ceiling tiles, and even window glazing, providing passive temperature control and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Nanotechnology has also played a crucial role in advancing antifreeze solutions for sustainable architecture. Nano-enhanced antifreeze fluids demonstrate improved thermal conductivity and heat transfer properties, allowing for more efficient operation of heating and cooling systems. These nanofluid formulations often require smaller volumes of antifreeze, further reducing the environmental footprint of building operations.
In the realm of geothermal heating and cooling systems, which are increasingly popular in eco-smart housing, specialized antifreeze solutions have been developed. These formulations are designed to withstand the unique conditions of underground heat exchangers, offering long-term stability and corrosion resistance while maintaining eco-friendly characteristics.
Smart antifreeze systems have emerged as a cutting-edge solution in sustainable architecture. These systems utilize sensors and automated controls to optimize antifreeze circulation and concentration based on real-time weather conditions and building requirements. By dynamically adjusting antifreeze properties, these intelligent systems maximize energy efficiency and minimize waste, aligning perfectly with the principles of eco-smart housing design.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards propylene glycol-based antifreeze solutions in sustainable building designs. Propylene glycol is less toxic and more biodegradable than ethylene glycol, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious architects and engineers. These solutions offer comparable performance in terms of freeze protection and heat transfer efficiency while minimizing potential harm to the environment and human health.
Another innovative approach in current antifreeze technologies is the integration of phase change materials (PCMs) into building envelopes. PCMs can absorb and release thermal energy during phase transitions, effectively regulating indoor temperatures and reducing the load on HVAC systems. This technology has been successfully incorporated into wall panels, ceiling tiles, and even window glazing, providing passive temperature control and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Nanotechnology has also played a crucial role in advancing antifreeze solutions for sustainable architecture. Nano-enhanced antifreeze fluids demonstrate improved thermal conductivity and heat transfer properties, allowing for more efficient operation of heating and cooling systems. These nanofluid formulations often require smaller volumes of antifreeze, further reducing the environmental footprint of building operations.
In the realm of geothermal heating and cooling systems, which are increasingly popular in eco-smart housing, specialized antifreeze solutions have been developed. These formulations are designed to withstand the unique conditions of underground heat exchangers, offering long-term stability and corrosion resistance while maintaining eco-friendly characteristics.
Smart antifreeze systems have emerged as a cutting-edge solution in sustainable architecture. These systems utilize sensors and automated controls to optimize antifreeze circulation and concentration based on real-time weather conditions and building requirements. By dynamically adjusting antifreeze properties, these intelligent systems maximize energy efficiency and minimize waste, aligning perfectly with the principles of eco-smart housing design.
Existing Antifreeze Integration Methods for Eco-Housing
01 Composition of antifreeze solutions
Antifreeze solutions are typically composed of a mixture of water and organic compounds such as glycols or alcohols. These compositions are designed to lower the freezing point and raise the boiling point of the solution, improving thermal performance in extreme temperatures. Additives may be included to enhance corrosion protection and heat transfer properties.- Composition of antifreeze solutions: Antifreeze solutions are typically composed of a mixture of water and organic compounds such as glycols or alcohols. These compositions are designed to lower the freezing point of the solution and improve its thermal performance. The specific ratios and additives used can significantly affect the overall thermal properties of the antifreeze.
- Nanoparticle-enhanced antifreeze formulations: The incorporation of nanoparticles into antifreeze solutions can enhance their thermal performance. These nanoparticles, such as metal oxides or carbon-based materials, can improve heat transfer properties and increase the overall efficiency of the antifreeze. The size, concentration, and type of nanoparticles used play crucial roles in determining the thermal characteristics of the resulting formulation.
- Heat transfer systems utilizing antifreeze: Antifreeze solutions are commonly used in heat transfer systems to improve thermal performance. These systems can include automotive cooling systems, HVAC applications, and industrial processes. The design of such systems, including factors like flow rates, heat exchanger configurations, and antifreeze concentration, can significantly impact the overall thermal efficiency.
- Additives for enhancing antifreeze thermal properties: Various additives can be incorporated into antifreeze formulations to enhance their thermal properties. These may include corrosion inhibitors, anti-foaming agents, and thermal conductivity enhancers. The selection and concentration of these additives can significantly affect the overall thermal performance of the antifreeze solution.
- Testing and evaluation of antifreeze thermal performance: Accurate testing and evaluation methods are crucial for assessing the thermal performance of antifreeze solutions. These may include laboratory tests for freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, and heat transfer efficiency. Advanced techniques such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations can also be employed to predict and optimize the thermal behavior of antifreeze in various applications.
02 Nanoparticle-enhanced antifreeze formulations
Incorporating nanoparticles into antifreeze formulations can significantly improve thermal conductivity and heat transfer efficiency. These nanoparticles, often made of materials like metal oxides or carbon-based structures, increase the surface area for heat exchange and can lead to better overall thermal performance of the antifreeze solution.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polymer-based antifreeze additives
Certain polymers can be added to antifreeze solutions to enhance their thermal performance. These polymers may improve viscosity index, reduce pumping power requirements, and provide better heat transfer characteristics. Some polymer additives also offer additional benefits such as scale inhibition and corrosion protection.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bio-based antifreeze formulations
Environmentally friendly antifreeze solutions derived from renewable resources are being developed to improve sustainability. These bio-based formulations often utilize plant-derived glycols or other natural compounds that offer comparable thermal performance to traditional petroleum-based antifreeze while reducing environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions05 Antifreeze systems with enhanced heat exchange
Advanced antifreeze systems incorporate design elements to maximize heat exchange efficiency. These may include specialized heat exchangers, flow patterns, or surface treatments that work in conjunction with the antifreeze solution to optimize thermal performance in various applications, such as automotive cooling systems or industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Eco-Smart Housing and Antifreeze Industry
The research on antifreeze use in eco-smart housing design frameworks is in an emerging stage, with a growing market driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient buildings. The technology is moderately mature, with companies like Robert Bosch GmbH and Covestro Deutschland AG leading innovation in smart home systems and materials. China Construction Steel Structure Corp Ltd. and Sidco Homes, Inc. are advancing sustainable construction practices, while universities such as Arizona State University and Beijing Jiaotong University contribute to research and development. The competitive landscape is diverse, involving both established industry players and innovative startups, indicating a dynamic and evolving market with significant growth potential.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has developed innovative polyurethane-based phase change materials (PCMs) for use in eco-smart housing design. These PCMs can absorb, store, and release large amounts of latent heat during melting and freezing processes. When integrated into building materials, they act as a thermal buffer, reducing temperature fluctuations and improving energy efficiency[1]. The company's PCMs are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges, typically between 19°C and 25°C, making them ideal for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures[2]. Covestro's PCMs can be incorporated into various building components, such as walls, ceilings, and floors, providing a passive cooling and heating solution that reduces the need for traditional HVAC systems[3].
Strengths: Highly effective in temperature regulation, reducing energy consumption. Can be integrated into various building materials. Weaknesses: May require careful design integration and could increase initial construction costs.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell has developed smart home technologies that incorporate antifreeze principles in eco-smart housing design. Their Lyric™ Wi-Fi Water Leak and Freeze Detector uses advanced sensors to detect both moisture and temperature drops, alerting homeowners to potential freezing conditions before pipes burst[6]. This proactive approach helps prevent water damage and reduces energy waste. Additionally, Honeywell's T Series smart thermostats use machine learning algorithms to optimize heating and cooling schedules, incorporating weather forecasts to adjust settings in anticipation of freezing temperatures[7]. These systems can be integrated with Honeywell's whole-house humidification solutions, which help maintain optimal indoor humidity levels, preventing condensation and frost formation on windows and walls during cold weather[8].
Strengths: Integrates multiple smart home technologies for comprehensive freeze protection. User-friendly interfaces and remote monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Relies on consistent internet connectivity. May require professional installation for full system integration.
Innovative Antifreeze Solutions for Sustainable Buildings
Eco-friendly smart freeze prevention device
PatentWO2024167128A1
Innovation
- An eco-friendly smart freeze prevention device that uses real-time temperature information from adjacent temperature measuring units to control power supply to heaters, optimizing energy usage and preventing local freezing through wireless communication, thereby reducing energy consumption and construction complexities.
Eco smart panels for energy savings
PatentInactiveUS20190249904A1
Innovation
- The eco-smart panel, which incorporates layered materials including solar thermal panels, phase change materials, and electromagnetic shielding, is designed to reduce energy consumption by harnessing renewable energy, improving insulation, and providing active heating and cooling without fossil fuels, while also being adaptable for retrofitting existing buildings.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Antifreeze Use
The environmental impact assessment of antifreeze use in eco-smart housing design frameworks is a critical aspect of sustainable construction practices. Antifreeze compounds, primarily ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, are commonly used in heating and cooling systems to prevent freezing and improve energy efficiency. However, their potential environmental consequences must be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary concerns is the toxicity of antifreeze chemicals to flora and fauna. Ethylene glycol, in particular, poses a significant risk to wildlife and domestic animals if ingested. Leaks or improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems. Propylene glycol, while less toxic, still requires proper handling and disposal to minimize environmental impact.
The production and transportation of antifreeze also contribute to the overall carbon footprint of eco-smart housing. Manufacturing processes often involve energy-intensive operations and the use of petrochemicals, which can result in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the transportation of antifreeze to construction sites adds to the carbon footprint, especially when long distances are involved.
Proper disposal of antifreeze is another crucial environmental consideration. Improper disposal can lead to groundwater contamination and harm aquatic life. Many regions have specific regulations for antifreeze disposal, requiring specialized recycling or treatment facilities to mitigate environmental risks.
On the positive side, the use of antifreeze in eco-smart housing can contribute to improved energy efficiency. By allowing heating and cooling systems to operate more effectively in extreme temperatures, antifreeze can reduce overall energy consumption and associated emissions. This long-term benefit must be weighed against the potential environmental risks.
The lifecycle assessment of antifreeze use in eco-smart housing should also consider the potential for leaks and system failures. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to prevent unintended releases into the environment. The durability and lifespan of antifreeze-containing systems also impact the frequency of replacement and disposal, affecting the overall environmental footprint.
Alternatives to traditional antifreeze compounds are being explored in the context of eco-smart housing. These include bio-based antifreeze solutions derived from renewable resources, which may offer reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability. However, their effectiveness, cost, and long-term environmental impact require further research and assessment.
In conclusion, while antifreeze plays a vital role in eco-smart housing design frameworks, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of energy efficiency with the potential risks of toxicity and contamination is crucial. Ongoing research into safer alternatives and improved disposal methods will be key to minimizing the environmental footprint of antifreeze use in sustainable housing solutions.
One of the primary concerns is the toxicity of antifreeze chemicals to flora and fauna. Ethylene glycol, in particular, poses a significant risk to wildlife and domestic animals if ingested. Leaks or improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, affecting local ecosystems. Propylene glycol, while less toxic, still requires proper handling and disposal to minimize environmental impact.
The production and transportation of antifreeze also contribute to the overall carbon footprint of eco-smart housing. Manufacturing processes often involve energy-intensive operations and the use of petrochemicals, which can result in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the transportation of antifreeze to construction sites adds to the carbon footprint, especially when long distances are involved.
Proper disposal of antifreeze is another crucial environmental consideration. Improper disposal can lead to groundwater contamination and harm aquatic life. Many regions have specific regulations for antifreeze disposal, requiring specialized recycling or treatment facilities to mitigate environmental risks.
On the positive side, the use of antifreeze in eco-smart housing can contribute to improved energy efficiency. By allowing heating and cooling systems to operate more effectively in extreme temperatures, antifreeze can reduce overall energy consumption and associated emissions. This long-term benefit must be weighed against the potential environmental risks.
The lifecycle assessment of antifreeze use in eco-smart housing should also consider the potential for leaks and system failures. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to prevent unintended releases into the environment. The durability and lifespan of antifreeze-containing systems also impact the frequency of replacement and disposal, affecting the overall environmental footprint.
Alternatives to traditional antifreeze compounds are being explored in the context of eco-smart housing. These include bio-based antifreeze solutions derived from renewable resources, which may offer reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability. However, their effectiveness, cost, and long-term environmental impact require further research and assessment.
In conclusion, while antifreeze plays a vital role in eco-smart housing design frameworks, its environmental impact must be carefully managed. Balancing the benefits of energy efficiency with the potential risks of toxicity and contamination is crucial. Ongoing research into safer alternatives and improved disposal methods will be key to minimizing the environmental footprint of antifreeze use in sustainable housing solutions.
Regulatory Framework for Antifreeze in Green Buildings
The regulatory framework for antifreeze in green buildings is a critical aspect of eco-smart housing design. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in construction, governments and industry bodies have developed comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safe and environmentally responsible use of antifreeze compounds in building systems.
At the federal level, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established regulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) that govern the manufacture, use, and disposal of antifreeze chemicals. These regulations require manufacturers to report new chemical substances and provide safety data, ensuring that only approved antifreeze compounds are used in green building applications.
State-level regulations often complement federal guidelines, with some states imposing stricter requirements. For instance, California's Proposition 65 mandates clear labeling of products containing chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm, which includes certain antifreeze compounds. This has led to the development of more environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations for use in green buildings.
The International Green Construction Code (IgCC) provides a model code for sustainable construction practices, including guidelines for the use of antifreeze in building systems. It emphasizes the importance of using non-toxic, biodegradable antifreeze solutions in closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact in case of leaks or during disposal.
Industry standards, such as those set by ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers), provide specific technical guidelines for the selection and use of antifreeze in HVAC systems. These standards emphasize the importance of using propylene glycol-based antifreeze in green buildings due to its lower toxicity compared to ethylene glycol-based alternatives.
The U.S. Green Building Council's LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification program includes criteria related to the use of antifreeze in building systems. To achieve LEED certification, projects must demonstrate the use of environmentally preferable antifreeze solutions and implement proper management practices to prevent environmental contamination.
Building codes in many jurisdictions now incorporate specific requirements for antifreeze use in fire sprinkler systems, balancing fire safety with environmental concerns. These codes often mandate the use of listed antifreeze solutions that meet strict safety and environmental standards.
As the green building industry evolves, regulatory frameworks continue to adapt. Recent trends include the development of performance-based standards that focus on the overall environmental impact of antifreeze use rather than prescriptive requirements. This approach allows for greater innovation in antifreeze formulations and application methods while maintaining high environmental standards.
At the federal level, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established regulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) that govern the manufacture, use, and disposal of antifreeze chemicals. These regulations require manufacturers to report new chemical substances and provide safety data, ensuring that only approved antifreeze compounds are used in green building applications.
State-level regulations often complement federal guidelines, with some states imposing stricter requirements. For instance, California's Proposition 65 mandates clear labeling of products containing chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm, which includes certain antifreeze compounds. This has led to the development of more environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations for use in green buildings.
The International Green Construction Code (IgCC) provides a model code for sustainable construction practices, including guidelines for the use of antifreeze in building systems. It emphasizes the importance of using non-toxic, biodegradable antifreeze solutions in closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact in case of leaks or during disposal.
Industry standards, such as those set by ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers), provide specific technical guidelines for the selection and use of antifreeze in HVAC systems. These standards emphasize the importance of using propylene glycol-based antifreeze in green buildings due to its lower toxicity compared to ethylene glycol-based alternatives.
The U.S. Green Building Council's LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification program includes criteria related to the use of antifreeze in building systems. To achieve LEED certification, projects must demonstrate the use of environmentally preferable antifreeze solutions and implement proper management practices to prevent environmental contamination.
Building codes in many jurisdictions now incorporate specific requirements for antifreeze use in fire sprinkler systems, balancing fire safety with environmental concerns. These codes often mandate the use of listed antifreeze solutions that meet strict safety and environmental standards.
As the green building industry evolves, regulatory frameworks continue to adapt. Recent trends include the development of performance-based standards that focus on the overall environmental impact of antifreeze use rather than prescriptive requirements. This approach allows for greater innovation in antifreeze formulations and application methods while maintaining high environmental standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!